Shu Yang
Concept-Based Dictionary Learning for Inference-Time Safety in Vision Language Action Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Vision Language Action (VLA) models close the perception action loop by translating multimodal instructions into executable behaviors, but this very capability magnifies safety risks: jailbreaks that merely yield toxic text in LLMs can trigger unsafe physical actions in embodied systems. Existing defenses alignment, filtering, or prompt hardening intervene too late or at the wrong modality, leaving fused representations exploitable. We introduce a concept-based dictionary learning framework for inference-time safety control. By constructing sparse, interpretable dictionaries from hidden activations, our method identifies harmful concept directions and applies threshold-based interventions to suppress or block unsafe activations. Experiments on Libero-Harm, BadRobot, RoboPair, and IS-Bench show that our approach achieves state-of-the-art defense performance, cutting attack success rates by over 70\% while maintaining task success. Crucially, the framework is plug-in and model-agnostic, requiring no retraining and integrating seamlessly with diverse VLAs. To our knowledge, this is the first inference-time concept-based safety method for embodied systems, advancing both interpretability and safe deployment of VLA models.
Faithful-Patchscopes: Understanding and Mitigating Model Bias in Hidden Representations Explanation of Large Language Models
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong capabilities for hidden representation interpretation through Patchscopes, a framework that uses LLMs themselves to generate human-readable explanations by decoding from internal hidden representations. However, our work shows that LLMs tend to rely on inherent linguistic patterns, which can override contextual information encoded in the hidden representations during decoding. For example, even when a hidden representation encodes the contextual attribute "purple" for "broccoli", LLMs still generate "green" in their explanations, reflecting a strong prior association. This behavior reveals a systematic unfaithfulness in Patchscopes. To systematically study this issue, we first designed a dataset to evaluate the faithfulness of Patchscopes under biased cases, and our results show that there is an 18.84\% faithfulness decrease on average. We then propose Bias Alignment through Logit Recalibration (BALOR), which treats the output logits from an unpatched prompt as capturing model bias and contrasts them with logits obtained under patched contextual information. By recalibrating the logit distribution through this contrast, BALOR suppresses model bias and amplifies contextual information during generation. Experiments across multiple LLMs demonstrate that BALOR consistently outperforms existing baselines, achieving up to 33\% relative performance improvement.
Not All Code Is Equal: A Data-Centric Study of Code Complexity and LLM Reasoning
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) increasingly exhibit strong reasoning abilities, often attributed to their capacity to generate chain-of-thought-style intermediate reasoning. Recent work suggests that exposure to code can further enhance these skills, but existing studies largely treat code as a generic training signal, leaving open the question of which properties of code actually contribute to improved reasoning. To address this gap, we study the structural complexity of code, which captures control flow and compositional structure that may shape how models internalise multi-step reasoning during fine-tuning. We examine two complementary settings: solution-driven complexity, where complexity varies across multiple solutions to the same problem, and problem-driven complexity, where complexity reflects variation in the underlying tasks. Using cyclomatic complexity and logical lines of code to construct controlled fine-tuning datasets, we evaluate a range of open-weight LLMs on diverse reasoning benchmarks. Our findings show that although code can improve reasoning, structural properties strongly determine its usefulness. In 83% of experiments, restricting fine-tuning data to a specific structural complexity range outperforms training on structurally diverse code, pointing to a data-centric path for improving reasoning beyond scaling.
PocketGS: On-Device Training of 3D Gaussian Splatting for High Perceptual Modeling
Jan 24, 2026Abstract:Efficient and high-fidelity 3D scene modeling is a long-standing pursuit in computer graphics. While recent 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) methods achieve impressive real-time modeling performance, they rely on resource-unconstrained training assumptions that fail on mobile devices, which are limited by minute-scale training budgets and hardware-available peak-memory. We present PocketGS, a mobile scene modeling paradigm that enables on-device 3DGS training under these tightly coupled constraints while preserving high perceptual fidelity. Our method resolves the fundamental contradictions of standard 3DGS through three co-designed operators: G builds geometry-faithful point-cloud priors; I injects local surface statistics to seed anisotropic Gaussians, thereby reducing early conditioning gaps; and T unrolls alpha compositing with cached intermediates and index-mapped gradient scattering for stable mobile backpropagation. Collectively, these operators satisfy the competing requirements of training efficiency, memory compactness, and modeling fidelity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PocketGS is able to outperform the powerful mainstream workstation 3DGS baseline to deliver high-quality reconstructions, enabling a fully on-device, practical capture-to-rendering workflow.
AutoMonitor-Bench: Evaluating the Reliability of LLM-Based Misbehavior Monitor
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:We introduce AutoMonitor-Bench, the first benchmark designed to systematically evaluate the reliability of LLM-based misbehavior monitors across diverse tasks and failure modes. AutoMonitor-Bench consists of 3,010 carefully annotated test samples spanning question answering, code generation, and reasoning, with paired misbehavior and benign instances. We evaluate monitors using two complementary metrics: Miss Rate (MR) and False Alarm Rate (FAR), capturing failures to detect misbehavior and oversensitivity to benign behavior, respectively. Evaluating 12 proprietary and 10 open-source LLMs, we observe substantial variability in monitoring performance and a consistent trade-off between MR and FAR, revealing an inherent safety-utility tension. To further explore the limits of monitor reliability, we construct a large-scale training corpus of 153,581 samples and fine-tune Qwen3-4B-Instruction to investigate whether training on known, relatively easy-to-construct misbehavior datasets improves monitoring performance on unseen and more implicit misbehaviors. Our results highlight the challenges of reliable, scalable misbehavior monitoring and motivate future work on task-aware designing and training strategies for LLM-based monitors.
MambaMIL+: Modeling Long-Term Contextual Patterns for Gigapixel Whole Slide Image
Dec 19, 2025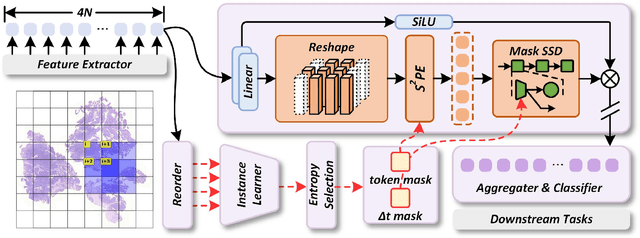
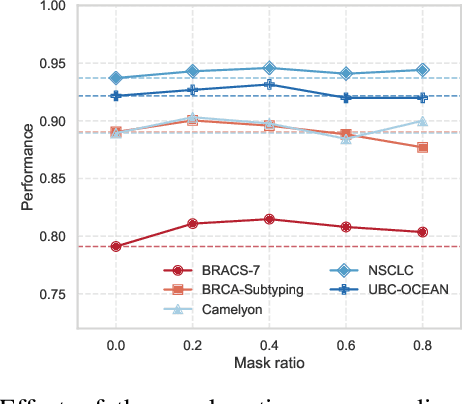
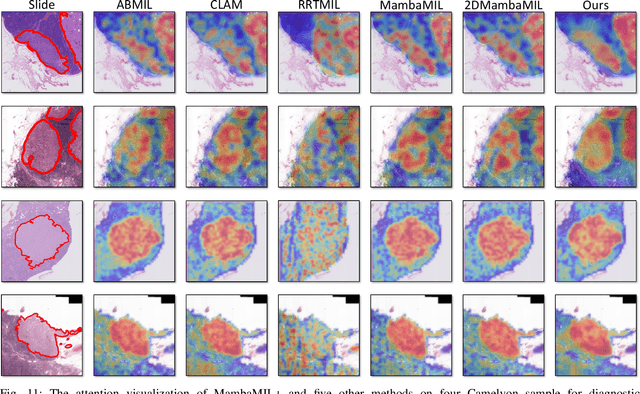
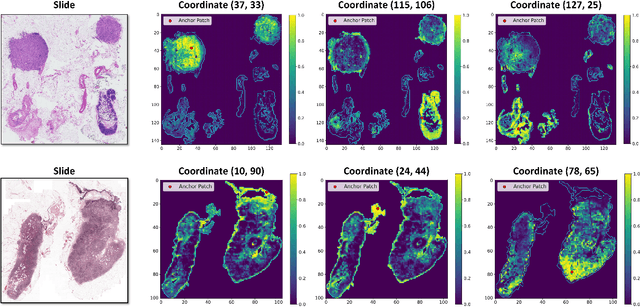
Abstract:Whole-slide images (WSIs) are an important data modality in computational pathology, yet their gigapixel resolution and lack of fine-grained annotations challenge conventional deep learning models. Multiple instance learning (MIL) offers a solution by treating each WSI as a bag of patch-level instances, but effectively modeling ultra-long sequences with rich spatial context remains difficult. Recently, Mamba has emerged as a promising alternative for long sequence learning, scaling linearly to thousands of tokens. However, despite its efficiency, it still suffers from limited spatial context modeling and memory decay, constraining its effectiveness to WSI analysis. To address these limitations, we propose MambaMIL+, a new MIL framework that explicitly integrates spatial context while maintaining long-range dependency modeling without memory forgetting. Specifically, MambaMIL+ introduces 1) overlapping scanning, which restructures the patch sequence to embed spatial continuity and instance correlations; 2) a selective stripe position encoder (S2PE) that encodes positional information while mitigating the biases of fixed scanning orders; and 3) a contextual token selection (CTS) mechanism, which leverages supervisory knowledge to dynamically enlarge the contextual memory for stable long-range modeling. Extensive experiments on 20 benchmarks across diagnostic classification, molecular prediction, and survival analysis demonstrate that MambaMIL+ consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance under three feature extractors (ResNet-50, PLIP, and CONCH), highlighting its effectiveness and robustness for large-scale computational pathology
Investigating CoT Monitorability in Large Reasoning Models
Nov 13, 2025



Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on complex tasks by engaging in extended reasoning before producing final answers. Beyond improving abilities, these detailed reasoning traces also create a new opportunity for AI safety, CoT Monitorability: monitoring potential model misbehavior, such as the use of shortcuts or sycophancy, through their chain-of-thought (CoT) during decision-making. However, two key fundamental challenges arise when attempting to build more effective monitors through CoT analysis. First, as prior research on CoT faithfulness has pointed out, models do not always truthfully represent their internal decision-making in the generated reasoning. Second, monitors themselves may be either overly sensitive or insufficiently sensitive, and can potentially be deceived by models' long, elaborate reasoning traces. In this paper, we present the first systematic investigation of the challenges and potential of CoT monitorability. Motivated by two fundamental challenges we mentioned before, we structure our study around two central perspectives: (i) verbalization: to what extent do LRMs faithfully verbalize the true factors guiding their decisions in the CoT, and (ii) monitor reliability: to what extent can misbehavior be reliably detected by a CoT-based monitor? Specifically, we provide empirical evidence and correlation analyses between verbalization quality, monitor reliability, and LLM performance across mathematical, scientific, and ethical domains. Then we further investigate how different CoT intervention methods, designed to improve reasoning efficiency or performance, will affect monitoring effectiveness. Finally, we propose MoME, a new paradigm in which LLMs monitor other models' misbehavior through their CoT and provide structured judgments along with supporting evidence.
MONICA: Real-Time Monitoring and Calibration of Chain-of-Thought Sycophancy in Large Reasoning Models
Nov 09, 2025Abstract:Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) suffer from sycophantic behavior, where models tend to agree with users' incorrect beliefs and follow misinformation rather than maintain independent reasoning. This behavior undermines model reliability and poses societal risks. Mitigating LRM sycophancy requires monitoring how this sycophancy emerges during the reasoning trajectory; however, current methods mainly focus on judging based on final answers and correcting them, without understanding how sycophancy develops during reasoning processes. To address this limitation, we propose MONICA, a novel Monitor-guided Calibration framework that monitors and mitigates sycophancy during model inference at the level of reasoning steps, without requiring the model to finish generating its complete answer. MONICA integrates a sycophantic monitor that provides real-time monitoring of sycophantic drift scores during response generation with a calibrator that dynamically suppresses sycophantic behavior when scores exceed predefined thresholds. Extensive experiments across 12 datasets and 3 LRMs demonstrate that our method effectively reduces sycophantic behavior in both intermediate reasoning steps and final answers, yielding robust performance improvements.
GenAR: Next-Scale Autoregressive Generation for Spatial Gene Expression Prediction
Oct 05, 2025



Abstract:Spatial Transcriptomics (ST) offers spatially resolved gene expression but remains costly. Predicting expression directly from widely available Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) stained images presents a cost-effective alternative. However, most computational approaches (i) predict each gene independently, overlooking co-expression structure, and (ii) cast the task as continuous regression despite expression being discrete counts. This mismatch can yield biologically implausible outputs and complicate downstream analyses. We introduce GenAR, a multi-scale autoregressive framework that refines predictions from coarse to fine. GenAR clusters genes into hierarchical groups to expose cross-gene dependencies, models expression as codebook-free discrete token generation to directly predict raw counts, and conditions decoding on fused histological and spatial embeddings. From an information-theoretic perspective, the discrete formulation avoids log-induced biases and the coarse-to-fine factorization aligns with a principled conditional decomposition. Extensive experimental results on four Spatial Transcriptomics datasets across different tissue types demonstrate that GenAR achieves state-of-the-art performance, offering potential implications for precision medicine and cost-effective molecular profiling. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/oyjr/genar.
Benchmarking and Mitigate Psychological Sycophancy in Medical Vision-Language Models
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Vision language models(VLMs) are increasingly integrated into clinical workflows, but they often exhibit sycophantic behavior prioritizing alignment with user phrasing social cues or perceived authority over evidence based reasoning. This study evaluate clinical sycophancy in medical visual question answering through a novel clinically grounded benchmark. We propose a medical sycophancy dataset construct from PathVQA, SLAKE, and VQA-RAD stratified by different type organ system and modality. Using psychologically motivated pressure templates including various sycophancy. In our adversarial experiments on various VLMs, we found that these models are generally vulnerable, exhibiting significant variations in the occurrence of adversarial responses, with weak correlations to the model accuracy or size. Imitation and expert provided corrections were found to be the most effective triggers, suggesting that the models possess a bias mechanism independent of visual evidence. To address this, we propose Visual Information Purification for Evidence based Response (VIPER) a lightweight mitigation strategy that filters non evidentiary content for example social pressures and then generates constrained evidence first answers. This framework reduces sycophancy by an average amount outperforming baselines while maintaining interpretability. Our benchmark analysis and mitigation framework lay the groundwork for robust deployment of medical VLMs in real world clinician interactions emphasizing the need for evidence anchored defenses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge