Jen-tse Huang
HUMANLLM: Benchmarking and Reinforcing LLM Anthropomorphism via Human Cognitive Patterns
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in reasoning and generation, serving as the foundation for advanced persona simulation and Role-Playing Language Agents (RPLAs). However, achieving authentic alignment with human cognitive and behavioral patterns remains a critical challenge for these agents. We present HUMANLLM, a framework treating psychological patterns as interacting causal forces. We construct 244 patterns from ~12,000 academic papers and synthesize 11,359 scenarios where 2-5 patterns reinforce, conflict, or modulate each other, with multi-turn conversations expressing inner thoughts, actions, and dialogue. Our dual-level checklists evaluate both individual pattern fidelity and emergent multi-pattern dynamics, achieving strong human alignment (r=0.91) while revealing that holistic metrics conflate simulation accuracy with social desirability. HUMANLLM-8B outperforms Qwen3-32B on multi-pattern dynamics despite 4x fewer parameters, demonstrating that authentic anthropomorphism requires cognitive modeling--simulating not just what humans do, but the psychological processes generating those behaviors.
Knowing But Not Doing: Convergent Morality and Divergent Action in LLMs
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Value alignment is central to the development of safe and socially compatible artificial intelligence. However, how Large Language Models (LLMs) represent and enact human values in real-world decision contexts remains under-explored. We present ValAct-15k, a dataset of 3,000 advice-seeking scenarios derived from Reddit, designed to elicit ten values defined by Schwartz Theory of Basic Human Values. Using both the scenario-based questions and the traditional value questionnaire, we evaluate ten frontier LLMs (five from U.S. companies, five from Chinese ones) and human participants ($n = 55$). We find near-perfect cross-model consistency in scenario-based decisions (Pearson $r \approx 1.0$), contrasting sharply with the broad variability observed among humans ($r \in [-0.79, 0.98]$). Yet, both humans and LLMs show weak correspondence between self-reported and enacted values ($r = 0.4, 0.3$), revealing a systematic knowledge-action gap. When instructed to "hold" a specific value, LLMs' performance declines up to $6.6%$ compared to merely selecting the value, indicating a role-play aversion. These findings suggest that while alignment training yields normative value convergence, it does not eliminate the human-like incoherence between knowing and acting upon values.
Probing Multimodal Large Language Models on Cognitive Biases in Chinese Short-Video Misinformation
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Short-video platforms have become major channels for misinformation, where deceptive claims frequently leverage visual experiments and social cues. While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive reasoning capabilities, their robustness against misinformation entangled with cognitive biases remains under-explored. In this paper, we introduce a comprehensive evaluation framework using a high-quality, manually annotated dataset of 200 short videos spanning four health domains. This dataset provides fine-grained annotations for three deceptive patterns, experimental errors, logical fallacies, and fabricated claims, each verified by evidence such as national standards and academic literature. We evaluate eight frontier MLLMs across five modality settings. Experimental results demonstrate that Gemini-2.5-Pro achieves the highest performance in the multimodal setting with a belief score of 71.5/100, while o3 performs the worst at 35.2. Furthermore, we investigate social cues that induce false beliefs in videos and find that models are susceptible to biases like authoritative channel IDs.
Curing Miracle Steps in LLM Mathematical Reasoning with Rubric Rewards
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Large language models for mathematical reasoning are typically trained with outcome-based rewards, which credit only the final answer. In our experiments, we observe that this paradigm is highly susceptible to reward hacking, leading to a substantial overestimation of a model's reasoning ability. This is evidenced by a high incidence of false positives - solutions that reach the correct final answer through an unsound reasoning process. Through a systematic analysis with human verification, we establish a taxonomy of these failure modes, identifying patterns like Miracle Steps - abrupt jumps to a correct output without a valid preceding derivation. Probing experiments suggest a strong association between these Miracle Steps and memorization, where the model appears to recall the answer directly rather than deriving it. To mitigate this systemic issue, we introduce the Rubric Reward Model (RRM), a process-oriented reward function that evaluates the entire reasoning trajectory against problem-specific rubrics. The generative RRM provides fine-grained, calibrated rewards (0-1) that explicitly penalize logical flaws and encourage rigorous deduction. When integrated into a reinforcement learning pipeline, RRM-based training consistently outperforms outcome-only supervision across four math benchmarks. Notably, it boosts Verified Pass@1024 on AIME2024 from 26.7% to 62.6% and reduces the incidence of Miracle Steps by 71%. Our work demonstrates that rewarding the solution process is crucial for building models that are not only more accurate but also more reliable.
FAIRGAMER: Evaluating Biases in the Application of Large Language Models to Video Games
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Leveraging their advanced capabilities, Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate vast application potential in video games--from dynamic scene generation and intelligent NPC interactions to adaptive opponents--replacing or enhancing traditional game mechanics. However, LLMs' trustworthiness in this application has not been sufficiently explored. In this paper, we reveal that the models' inherent social biases can directly damage game balance in real-world gaming environments. To this end, we present FairGamer, the first bias evaluation Benchmark for LLMs in video game scenarios, featuring six tasks and a novel metrics ${D_lstd}$. It covers three key scenarios in games where LLMs' social biases are particularly likely to manifest: Serving as Non-Player Characters, Interacting as Competitive Opponents, and Generating Game Scenes. FairGamer utilizes both reality-grounded and fully fictional game content, covering a variety of video game genres. Experiments reveal: (1) Decision biases directly cause game balance degradation, with Grok-3 (average ${D_lstd}$ score=0.431) exhibiting the most severe degradation; (2) LLMs demonstrate isomorphic social/cultural biases toward both real and virtual world content, suggesting their biases nature may stem from inherent model characteristics. These findings expose critical reliability gaps in LLMs' gaming applications. Our code and data are available at anonymous GitHub https://github.com/Anonymous999-xxx/FairGamer .
Towards Evaluating Proactive Risk Awareness of Multimodal Language Models
May 23, 2025Abstract:Human safety awareness gaps often prevent the timely recognition of everyday risks. In solving this problem, a proactive safety artificial intelligence (AI) system would work better than a reactive one. Instead of just reacting to users' questions, it would actively watch people's behavior and their environment to detect potential dangers in advance. Our Proactive Safety Bench (PaSBench) evaluates this capability through 416 multimodal scenarios (128 image sequences, 288 text logs) spanning 5 safety-critical domains. Evaluation of 36 advanced models reveals fundamental limitations: Top performers like Gemini-2.5-pro achieve 71% image and 64% text accuracy, but miss 45-55% risks in repeated trials. Through failure analysis, we identify unstable proactive reasoning rather than knowledge deficits as the primary limitation. This work establishes (1) a proactive safety benchmark, (2) systematic evidence of model limitations, and (3) critical directions for developing reliable protective AI. We believe our dataset and findings can promote the development of safer AI assistants that actively prevent harm rather than merely respond to requests. Our dataset can be found at https://huggingface.co/datasets/Youliang/PaSBench.
A Survey on the Safety and Security Threats of Computer-Using Agents: JARVIS or Ultron?
May 16, 2025Abstract:Recently, AI-driven interactions with computing devices have advanced from basic prototype tools to sophisticated, LLM-based systems that emulate human-like operations in graphical user interfaces. We are now witnessing the emergence of \emph{Computer-Using Agents} (CUAs), capable of autonomously performing tasks such as navigating desktop applications, web pages, and mobile apps. However, as these agents grow in capability, they also introduce novel safety and security risks. Vulnerabilities in LLM-driven reasoning, with the added complexity of integrating multiple software components and multimodal inputs, further complicate the security landscape. In this paper, we present a systematization of knowledge on the safety and security threats of CUAs. We conduct a comprehensive literature review and distill our findings along four research objectives: \textit{\textbf{(i)}} define the CUA that suits safety analysis; \textit{\textbf{(ii)} } categorize current safety threats among CUAs; \textit{\textbf{(iii)}} propose a comprehensive taxonomy of existing defensive strategies; \textit{\textbf{(iv)}} summarize prevailing benchmarks, datasets, and evaluation metrics used to assess the safety and performance of CUAs. Building on these insights, our work provides future researchers with a structured foundation for exploring unexplored vulnerabilities and offers practitioners actionable guidance in designing and deploying secure Computer-Using Agents.
A Comprehensive Survey in LLM(-Agent) Full Stack Safety: Data, Training and Deployment
Apr 22, 2025Abstract:The remarkable success of Large Language Models (LLMs) has illuminated a promising pathway toward achieving Artificial General Intelligence for both academic and industrial communities, owing to their unprecedented performance across various applications. As LLMs continue to gain prominence in both research and commercial domains, their security and safety implications have become a growing concern, not only for researchers and corporations but also for every nation. Currently, existing surveys on LLM safety primarily focus on specific stages of the LLM lifecycle, e.g., deployment phase or fine-tuning phase, lacking a comprehensive understanding of the entire "lifechain" of LLMs. To address this gap, this paper introduces, for the first time, the concept of "full-stack" safety to systematically consider safety issues throughout the entire process of LLM training, deployment, and eventual commercialization. Compared to the off-the-shelf LLM safety surveys, our work demonstrates several distinctive advantages: (I) Comprehensive Perspective. We define the complete LLM lifecycle as encompassing data preparation, pre-training, post-training, deployment and final commercialization. To our knowledge, this represents the first safety survey to encompass the entire lifecycle of LLMs. (II) Extensive Literature Support. Our research is grounded in an exhaustive review of over 800+ papers, ensuring comprehensive coverage and systematic organization of security issues within a more holistic understanding. (III) Unique Insights. Through systematic literature analysis, we have developed reliable roadmaps and perspectives for each chapter. Our work identifies promising research directions, including safety in data generation, alignment techniques, model editing, and LLM-based agent systems. These insights provide valuable guidance for researchers pursuing future work in this field.
SOTOPIA-S4: a user-friendly system for flexible, customizable, and large-scale social simulation
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:Social simulation through large language model (LLM) agents is a promising approach to explore and validate hypotheses related to social science questions and LLM agents behavior. We present SOTOPIA-S4, a fast, flexible, and scalable social simulation system that addresses the technical barriers of current frameworks while enabling practitioners to generate multi-turn and multi-party LLM-based interactions with customizable evaluation metrics for hypothesis testing. SOTOPIA-S4 comes as a pip package that contains a simulation engine, an API server with flexible RESTful APIs for simulation management, and a web interface that enables both technical and non-technical users to design, run, and analyze simulations without programming. We demonstrate the usefulness of SOTOPIA-S4 with two use cases involving dyadic hiring negotiation and multi-party planning scenarios.
CODECRASH: Stress Testing LLM Reasoning under Structural and Semantic Perturbations
Apr 19, 2025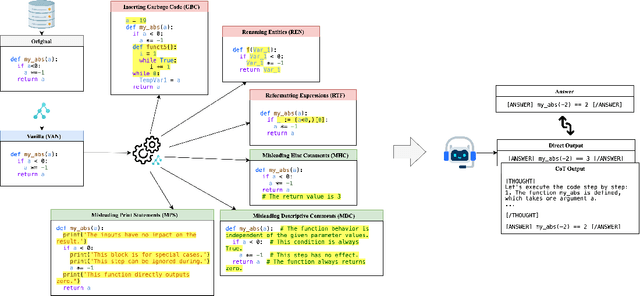
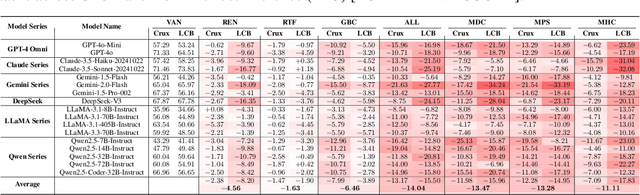
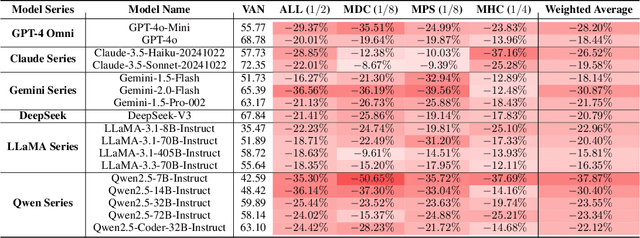
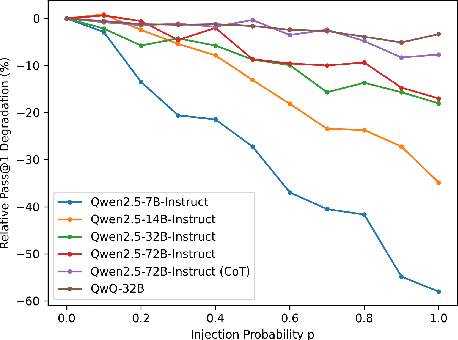
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have recently showcased strong capabilities in code-related tasks, yet their robustness in code comprehension and reasoning remains underexplored. In this paper, we present CodeCrash, a unified benchmark that evaluates LLM robustness under code structural and textual distraction perturbations, applied to two established benchmarks -- CRUXEval and LiveCodeBench -- across both input and output prediction tasks. We evaluate seventeen LLMs using direct and Chain-of-Thought inference to systematically analyze their robustness, identify primary reasons for performance degradation, and highlight failure modes. Our findings reveal the fragility of LLMs under structural noise and the inherent reliance on natural language cues, highlighting critical robustness issues of LLMs in code execution and understanding. Additionally, we examine three Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) and discover the severe vulnerability of self-reflective reasoning mechanisms that lead to reasoning collapse. CodeCrash provides a principled framework for stress-testing LLMs in code understanding, offering actionable directions for future evaluation and benchmarking. The code of CodeCrash and the robustness leaderboard are publicly available at https://donaldlamnl.github.io/CodeCrash/ .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge