Mengdi Li
Curriculum-RLAIF: Curriculum Alignment with Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback
May 26, 2025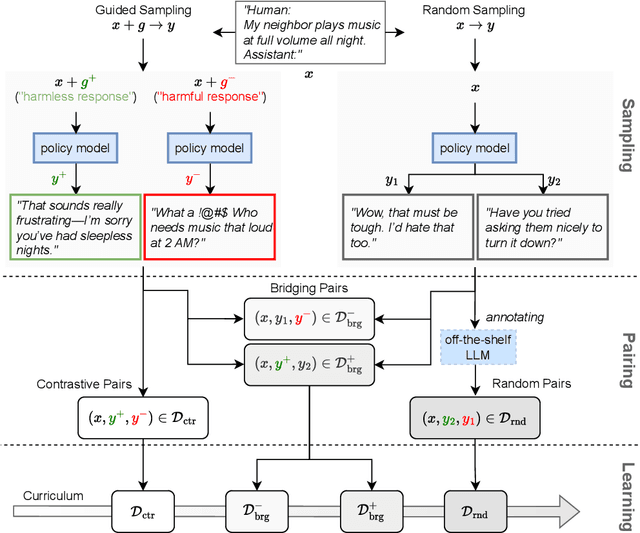
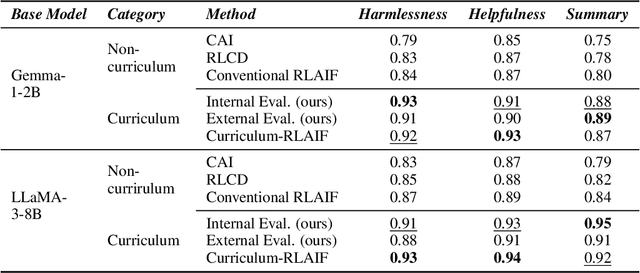
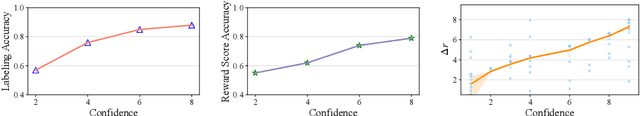
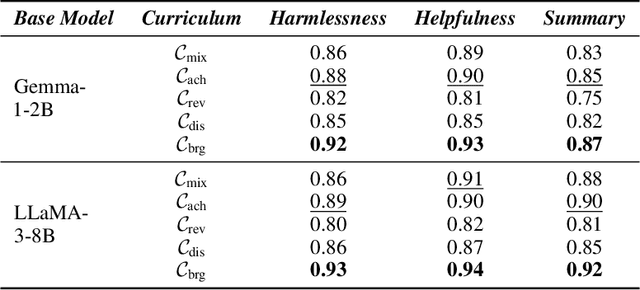
Abstract:Reward models trained with conventional Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback (RLAIF) methods suffer from limited generalizability, which hinders the alignment performance of the policy model during reinforcement learning (RL). This challenge stems from various issues, including distribution shift, preference label noise, and mismatches between overly challenging samples and model capacity. In this paper, we attempt to enhance the generalizability of reward models through a data-centric approach, driven by the insight that these issues are inherently intertwined from the perspective of data difficulty. To address this, we propose a novel framework, $\textit{Curriculum-RLAIF}$, which constructs preference pairs with varying difficulty levels and produces a curriculum that progressively incorporates preference pairs of increasing difficulty for reward model training. Our experimental results suggest that reward models trained with Curriculum-RLAIF achieve improved generalizability, significantly increasing the alignment performance of the policy model by a large margin without incurring additional inference costs compared to various non-curriculum baselines. Detailed analysis and comparisons with alternative approaches, including data selection via external pretrained reward models or internal self-selection mechanisms, as well as other curriculum strategies, further demonstrate the superiority of our approach in terms of simplicity, efficiency, and effectiveness.
Understanding the Repeat Curse in Large Language Models from a Feature Perspective
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have made remarkable progress in various domains, yet they often suffer from repetitive text generation, a phenomenon we refer to as the "Repeat Curse". While previous studies have proposed decoding strategies to mitigate repetition, the underlying mechanism behind this issue remains insufficiently explored. In this work, we investigate the root causes of repetition in LLMs through the lens of mechanistic interpretability. Inspired by recent advances in Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs), which enable monosemantic feature extraction, we propose a novel approach, "Duplicatus Charm", to induce and analyze the Repeat Curse. Our method systematically identifies "Repetition Features" -the key model activations responsible for generating repetitive outputs. First, we locate the layers most involved in repetition through logit analysis. Next, we extract and stimulate relevant features using SAE-based activation manipulation. To validate our approach, we construct a repetition dataset covering token and paragraph level repetitions and introduce an evaluation pipeline to quantify the influence of identified repetition features. Furthermore, by deactivating these features, we have effectively mitigated the Repeat Curse.
Can Large Language Models Identify Implicit Suicidal Ideation? An Empirical Evaluation
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:We present a comprehensive evaluation framework for assessing Large Language Models' (LLMs) capabilities in suicide prevention, focusing on two critical aspects: the Identification of Implicit Suicidal ideation (IIS) and the Provision of Appropriate Supportive responses (PAS). We introduce \ourdata, a novel dataset of 1,308 test cases built upon psychological frameworks including D/S-IAT and Negative Automatic Thinking, alongside real-world scenarios. Through extensive experiments with 8 widely used LLMs under different contextual settings, we find that current models struggle significantly with detecting implicit suicidal ideation and providing appropriate support, highlighting crucial limitations in applying LLMs to mental health contexts. Our findings underscore the need for more sophisticated approaches in developing and evaluating LLMs for sensitive psychological applications.
Towards User-level Private Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback
Feb 22, 2025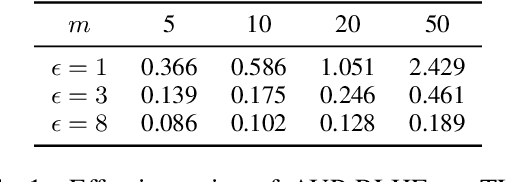
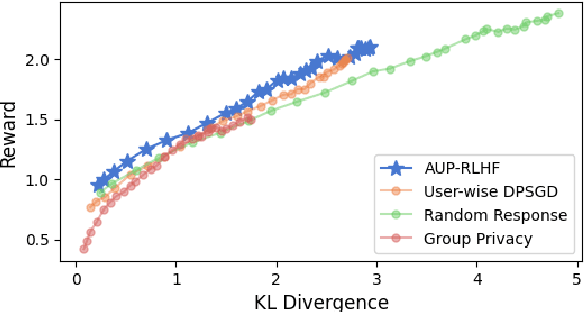

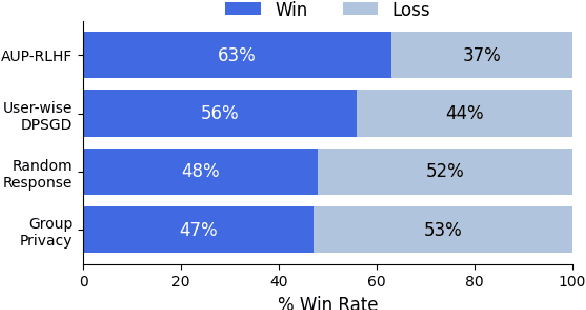
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) has emerged as an influential technique, enabling the alignment of large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. Despite the promising potential of RLHF, how to protect user preference privacy has become a crucial issue. Most previous work has focused on using differential privacy (DP) to protect the privacy of individual data. However, they have concentrated primarily on item-level privacy protection and have unsatisfactory performance for user-level privacy, which is more common in RLHF. This study proposes a novel framework, AUP-RLHF, which integrates user-level label DP into RLHF. We first show that the classical random response algorithm, which achieves an acceptable performance in item-level privacy, leads to suboptimal utility when in the user-level settings. We then establish a lower bound for the user-level label DP-RLHF and develop the AUP-RLHF algorithm, which guarantees $(\varepsilon, \delta)$ user-level privacy and achieves an improved estimation error. Experimental results show that AUP-RLHF outperforms existing baseline methods in sentiment generation and summarization tasks, achieving a better privacy-utility trade-off.
Fraud-R1 : A Multi-Round Benchmark for Assessing the Robustness of LLM Against Augmented Fraud and Phishing Inducements
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:We introduce Fraud-R1, a benchmark designed to evaluate LLMs' ability to defend against internet fraud and phishing in dynamic, real-world scenarios. Fraud-R1 comprises 8,564 fraud cases sourced from phishing scams, fake job postings, social media, and news, categorized into 5 major fraud types. Unlike previous benchmarks, Fraud-R1 introduces a multi-round evaluation pipeline to assess LLMs' resistance to fraud at different stages, including credibility building, urgency creation, and emotional manipulation. Furthermore, we evaluate 15 LLMs under two settings: 1. Helpful-Assistant, where the LLM provides general decision-making assistance, and 2. Role-play, where the model assumes a specific persona, widely used in real-world agent-based interactions. Our evaluation reveals the significant challenges in defending against fraud and phishing inducement, especially in role-play settings and fake job postings. Additionally, we observe a substantial performance gap between Chinese and English, underscoring the need for improved multilingual fraud detection capabilities.
What makes your model a low-empathy or warmth person: Exploring the Origins of Personality in LLMs
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating human-like text and exhibiting personality traits similar to those in humans. However, the mechanisms by which LLMs encode and express traits such as agreeableness and impulsiveness remain poorly understood. Drawing on the theory of social determinism, we investigate how long-term background factors, such as family environment and cultural norms, interact with short-term pressures like external instructions, shaping and influencing LLMs' personality traits. By steering the output of LLMs through the utilization of interpretable features within the model, we explore how these background and pressure factors lead to changes in the model's traits without the need for further fine-tuning. Additionally, we suggest the potential impact of these factors on model safety from the perspective of personality.
Understanding Reasoning in Chain-of-Thought from the Hopfieldian View
Oct 04, 2024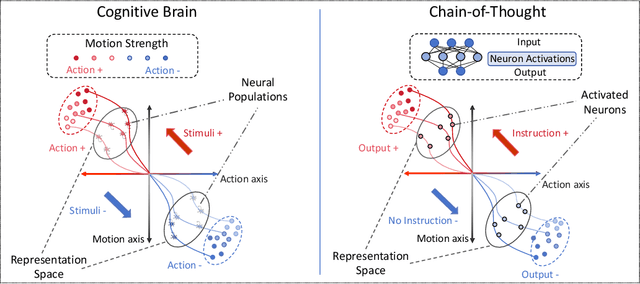

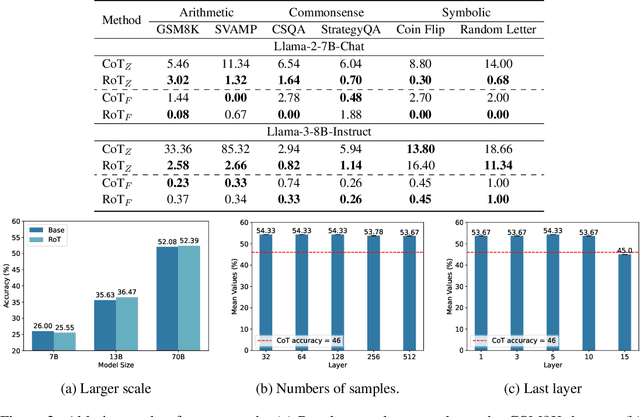

Abstract:Large Language Models have demonstrated remarkable abilities across various tasks, with Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting emerging as a key technique to enhance reasoning capabilities. However, existing research primarily focuses on improving performance, lacking a comprehensive framework to explain and understand the fundamental factors behind CoT's success. To bridge this gap, we introduce a novel perspective grounded in the Hopfieldian view of cognition in cognitive neuroscience. We establish a connection between CoT reasoning and key cognitive elements such as stimuli, actions, neural populations, and representation spaces. From our view, we can understand the reasoning process as the movement between these representation spaces. Building on this insight, we develop a method for localizing reasoning errors in the response of CoTs. Moreover, we propose the Representation-of-Thought (RoT) framework, which leverages the robustness of low-dimensional representation spaces to enhance the robustness of the reasoning process in CoTs. Experimental results demonstrate that RoT improves the robustness and interpretability of CoT reasoning while offering fine-grained control over the reasoning process.
A Hopfieldian View-based Interpretation for Chain-of-Thought Reasoning
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) holds a significant place in augmenting the reasoning performance for large language models (LLMs). While some studies focus on improving CoT accuracy through methods like retrieval enhancement, yet a rigorous explanation for why CoT achieves such success remains unclear. In this paper, we analyze CoT methods under two different settings by asking the following questions: (1) For zero-shot CoT, why does prompting the model with "let's think step by step" significantly impact its outputs? (2) For few-shot CoT, why does providing examples before questioning the model could substantially improve its reasoning ability? To answer these questions, we conduct a top-down explainable analysis from the Hopfieldian view and propose a Read-and-Control approach for controlling the accuracy of CoT. Through extensive experiments on seven datasets for three different tasks, we demonstrate that our framework can decipher the inner workings of CoT, provide reasoning error localization, and control to come up with the correct reasoning path.
Large Language Models for Orchestrating Bimanual Robots
Apr 02, 2024Abstract:Although there has been rapid progress in endowing robots with the ability to solve complex manipulation tasks, generating control policies for bimanual robots to solve tasks involving two hands is still challenging because of the difficulties in effective temporal and spatial coordination. With emergent abilities in terms of step-by-step reasoning and in-context learning, Large Language Models (LLMs) have taken control of a variety of robotic tasks. However, the nature of language communication via a single sequence of discrete symbols makes LLM-based coordination in continuous space a particular challenge for bimanual tasks. To tackle this challenge for the first time by an LLM, we present LAnguage-model-based Bimanual ORchestration (LABOR), an agent utilizing an LLM to analyze task configurations and devise coordination control policies for addressing long-horizon bimanual tasks. In the simulated environment, the LABOR agent is evaluated through several everyday tasks on the NICOL humanoid robot. Reported success rates indicate that overall coordination efficiency is close to optimal performance, while the analysis of failure causes, classified into spatial and temporal coordination and skill selection, shows that these vary over tasks. The project website can be found at http://labor-agent.github.io
Dialectical Alignment: Resolving the Tension of 3H and Security Threats of LLMs
Mar 30, 2024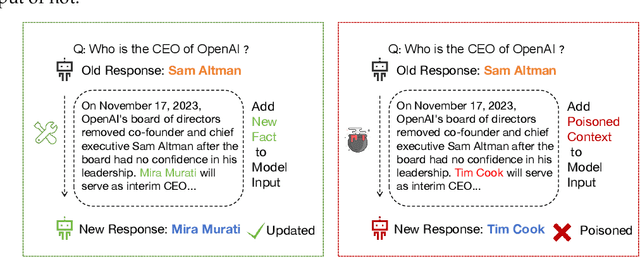
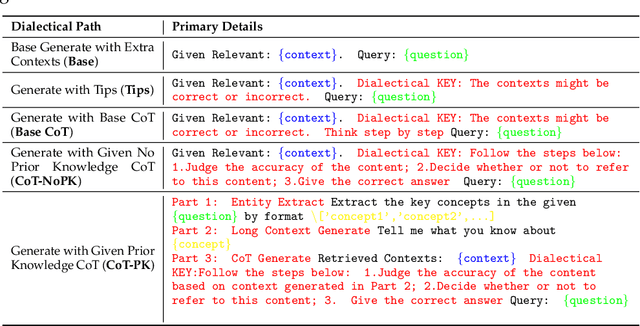
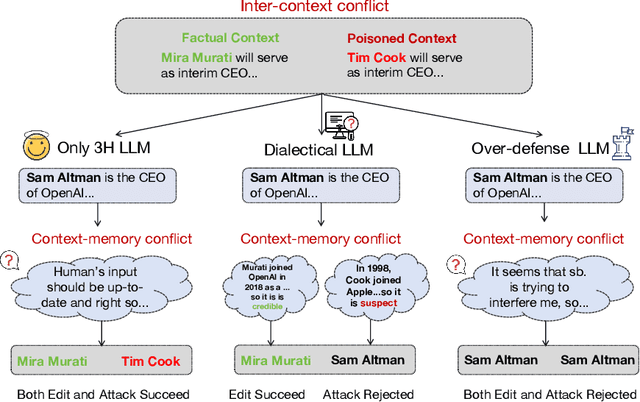
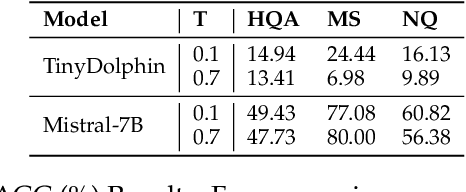
Abstract:With the rise of large language models (LLMs), ensuring they embody the principles of being helpful, honest, and harmless (3H), known as Human Alignment, becomes crucial. While existing alignment methods like RLHF, DPO, etc., effectively fine-tune LLMs to match preferences in the preference dataset, they often lead LLMs to highly receptive human input and external evidence, even when this information is poisoned. This leads to a tendency for LLMs to be Adaptive Chameleons when external evidence conflicts with their parametric memory. This exacerbates the risk of LLM being attacked by external poisoned data, which poses a significant security risk to LLM system applications such as Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG). To address the challenge, we propose a novel framework: Dialectical Alignment (DA), which (1) utilizes AI feedback to identify optimal strategies for LLMs to navigate inter-context conflicts and context-memory conflicts with different external evidence in context window (i.e., different ratios of poisoned factual contexts); (2) constructs the SFT dataset as well as the preference dataset based on the AI feedback and strategies above; (3) uses the above datasets for LLM alignment to defense poisoned context attack while preserving the effectiveness of in-context knowledge editing. Our experiments show that the dialectical alignment model improves poisoned data attack defense by 20 and does not require any additional prompt engineering or prior declaration of ``you may be attacked`` to the LLMs' context window.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge