Jianhua Xu
AI Business, Alibaba Group
InceptionMamba: An Efficient Hybrid Network with Large Band Convolution and Bottleneck Mamba
Jun 12, 2025Abstract:Within the family of convolutional neural networks, InceptionNeXt has shown excellent competitiveness in image classification and a number of downstream tasks. Built on parallel one-dimensional strip convolutions, however, it suffers from limited ability of capturing spatial dependencies along different dimensions and fails to fully explore spatial modeling in local neighborhood. Besides, inherent locality constraints of convolution operations are detrimental to effective global context modeling. To overcome these limitations, we propose a novel backbone architecture termed InceptionMamba in this study. More specifically, the traditional one-dimensional strip convolutions are replaced by orthogonal band convolutions in our InceptionMamba to achieve cohesive spatial modeling. Furthermore, global contextual modeling can be achieved via a bottleneck Mamba module, facilitating enhanced cross-channel information fusion and enlarged receptive field. Extensive evaluations on classification and various downstream tasks demonstrate that the proposed InceptionMamba achieves state-of-the-art performance with superior parameter and computational efficiency. The source code will be available at https://github.com/Wake1021/InceptionMamba.
Progressive Class-level Distillation
May 30, 2025Abstract:In knowledge distillation (KD), logit distillation (LD) aims to transfer class-level knowledge from a more powerful teacher network to a small student model via accurate teacher-student alignment at the logits level. Since high-confidence object classes usually dominate the distillation process, low-probability classes which also contain discriminating information are downplayed in conventional methods, leading to insufficient knowledge transfer. To address this issue, we propose a simple yet effective LD method termed Progressive Class-level Distillation (PCD). In contrast to existing methods which perform all-class ensemble distillation, our PCD approach performs stage-wise distillation for step-by-step knowledge transfer. More specifically, we perform ranking on teacher-student logits difference for identifying distillation priority from scratch, and subsequently divide the entire LD process into multiple stages. Next, bidirectional stage-wise distillation incorporating fine-to-coarse progressive learning and reverse coarse-to-fine refinement is conducted, allowing comprehensive knowledge transfer via sufficient logits alignment within separate class groups in different distillation stages. Extension experiments on public benchmarking datasets demonstrate the superiority of our method compared to state-of-the-arts for both classification and detection tasks.
Understanding the Repeat Curse in Large Language Models from a Feature Perspective
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have made remarkable progress in various domains, yet they often suffer from repetitive text generation, a phenomenon we refer to as the "Repeat Curse". While previous studies have proposed decoding strategies to mitigate repetition, the underlying mechanism behind this issue remains insufficiently explored. In this work, we investigate the root causes of repetition in LLMs through the lens of mechanistic interpretability. Inspired by recent advances in Sparse Autoencoders (SAEs), which enable monosemantic feature extraction, we propose a novel approach, "Duplicatus Charm", to induce and analyze the Repeat Curse. Our method systematically identifies "Repetition Features" -the key model activations responsible for generating repetitive outputs. First, we locate the layers most involved in repetition through logit analysis. Next, we extract and stimulate relevant features using SAE-based activation manipulation. To validate our approach, we construct a repetition dataset covering token and paragraph level repetitions and introduce an evaluation pipeline to quantify the influence of identified repetition features. Furthermore, by deactivating these features, we have effectively mitigated the Repeat Curse.
DualToken: Towards Unifying Visual Understanding and Generation with Dual Visual Vocabularies
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:The differing representation spaces required for visual understanding and generation pose a challenge in unifying them within the autoregressive paradigm of large language models. A vision tokenizer trained for reconstruction excels at capturing low-level perceptual details, making it well-suited for visual generation but lacking high-level semantic representations for understanding tasks. Conversely, a vision encoder trained via contrastive learning aligns well with language but struggles to decode back into the pixel space for generation tasks. To bridge this gap, we propose DualToken, a method that unifies representations for both understanding and generation within a single tokenizer. However, directly integrating reconstruction and semantic objectives in a single tokenizer creates conflicts, leading to degraded performance in both reconstruction quality and semantic performance. Instead of forcing a single codebook to handle both semantic and perceptual information, DualToken disentangles them by introducing separate codebooks for high and low-level features, effectively transforming their inherent conflict into a synergistic relationship. As a result, DualToken achieves state-of-the-art performance in both reconstruction and semantic tasks while demonstrating remarkable effectiveness in downstream MLLM understanding and generation tasks. Notably, we also show that DualToken, as a unified tokenizer, surpasses the naive combination of two distinct types vision encoders, providing superior performance within a unified MLLM.
Baichuan-Audio: A Unified Framework for End-to-End Speech Interaction
Feb 24, 2025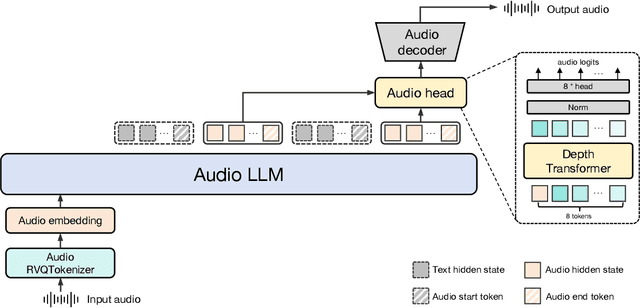
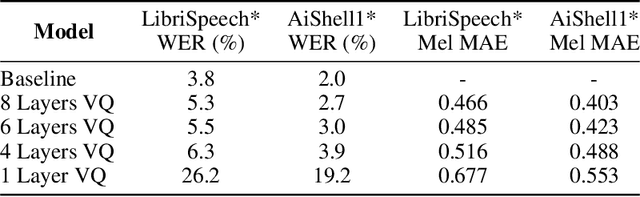
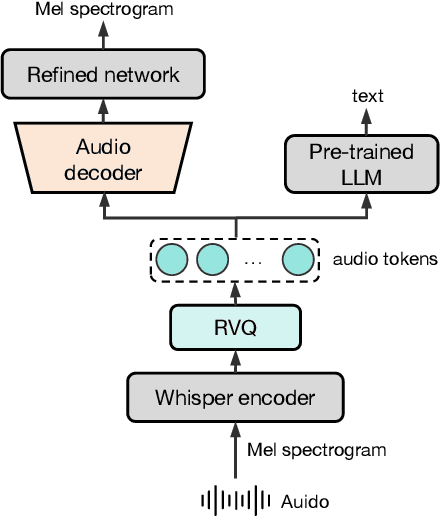
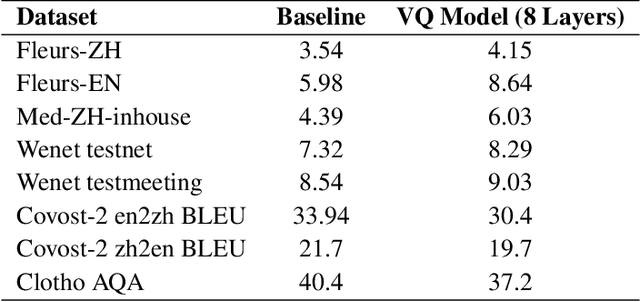
Abstract:We introduce Baichuan-Audio, an end-to-end audio large language model that seamlessly integrates audio understanding and generation. It features a text-guided aligned speech generation mechanism, enabling real-time speech interaction with both comprehension and generation capabilities. Baichuan-Audio leverages a pre-trained ASR model, followed by multi-codebook discretization of speech at a frame rate of 12.5 Hz. This multi-codebook setup ensures that speech tokens retain both semantic and acoustic information. To further enhance modeling, an independent audio head is employed to process audio tokens, effectively capturing their unique characteristics. To mitigate the loss of intelligence during pre-training and preserve the original capabilities of the LLM, we propose a two-stage pre-training strategy that maintains language understanding while enhancing audio modeling. Following alignment, the model excels in real-time speech-based conversation and exhibits outstanding question-answering capabilities, demonstrating its versatility and efficiency. The proposed model demonstrates superior performance in real-time spoken dialogue and exhibits strong question-answering abilities. Our code, model and training data are available at https://github.com/baichuan-inc/Baichuan-Audio
Baichuan-Omni-1.5 Technical Report
Jan 26, 2025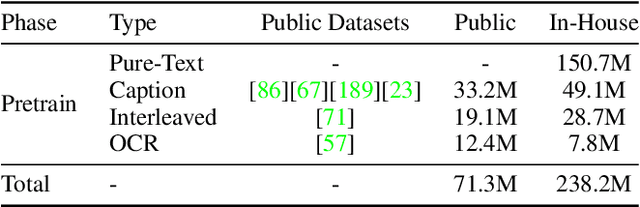
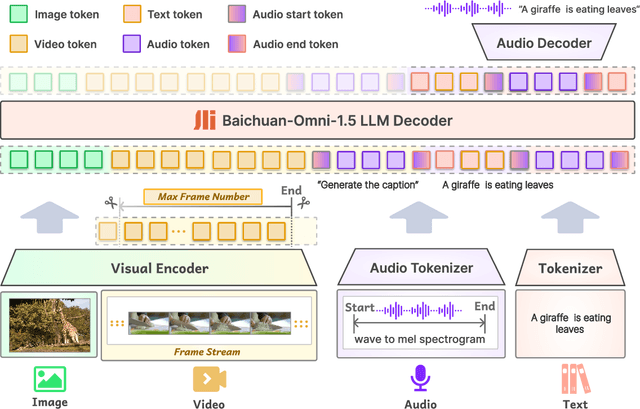
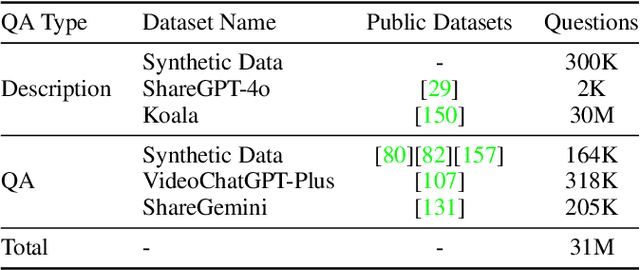
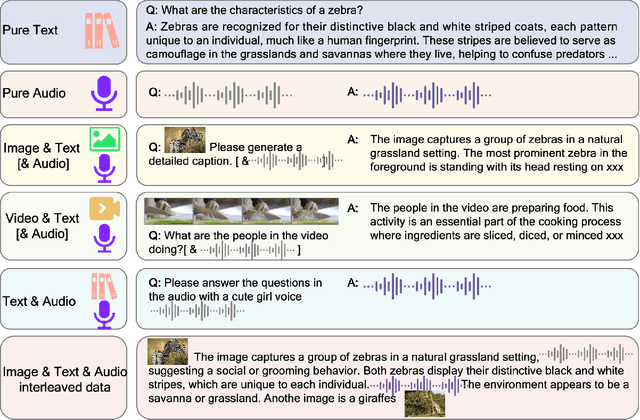
Abstract:We introduce Baichuan-Omni-1.5, an omni-modal model that not only has omni-modal understanding capabilities but also provides end-to-end audio generation capabilities. To achieve fluent and high-quality interaction across modalities without compromising the capabilities of any modality, we prioritized optimizing three key aspects. First, we establish a comprehensive data cleaning and synthesis pipeline for multimodal data, obtaining about 500B high-quality data (text, audio, and vision). Second, an audio-tokenizer (Baichuan-Audio-Tokenizer) has been designed to capture both semantic and acoustic information from audio, enabling seamless integration and enhanced compatibility with MLLM. Lastly, we designed a multi-stage training strategy that progressively integrates multimodal alignment and multitask fine-tuning, ensuring effective synergy across all modalities. Baichuan-Omni-1.5 leads contemporary models (including GPT4o-mini and MiniCPM-o 2.6) in terms of comprehensive omni-modal capabilities. Notably, it achieves results comparable to leading models such as Qwen2-VL-72B across various multimodal medical benchmarks.
Ocean-OCR: Towards General OCR Application via a Vision-Language Model
Jan 26, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown impressive capabilities across various domains, excelling in processing and understanding information from multiple modalities. Despite the rapid progress made previously, insufficient OCR ability hinders MLLMs from excelling in text-related tasks. In this paper, we present \textbf{Ocean-OCR}, a 3B MLLM with state-of-the-art performance on various OCR scenarios and comparable understanding ability on general tasks. We employ Native Resolution ViT to enable variable resolution input and utilize a substantial collection of high-quality OCR datasets to enhance the model performance. We demonstrate the superiority of Ocean-OCR through comprehensive experiments on open-source OCR benchmarks and across various OCR scenarios. These scenarios encompass document understanding, scene text recognition, and handwritten recognition, highlighting the robust OCR capabilities of Ocean-OCR. Note that Ocean-OCR is the first MLLM to outperform professional OCR models such as TextIn and PaddleOCR.
Baichuan Alignment Technical Report
Oct 19, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Baichuan Alignment, a detailed analysis of the alignment techniques employed in the Baichuan series of models. This represents the industry's first comprehensive account of alignment methodologies, offering valuable insights for advancing AI research. We investigate the critical components that enhance model performance during the alignment process, including optimization methods, data strategies, capability enhancements, and evaluation processes. The process spans three key stages: Prompt Augmentation System (PAS), Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), and Preference Alignment. The problems encountered, the solutions applied, and the improvements made are thoroughly recorded. Through comparisons across well-established benchmarks, we highlight the technological advancements enabled by Baichuan Alignment. Baichuan-Instruct is an internal model, while Qwen2-Nova-72B and Llama3-PBM-Nova-70B are instruct versions of the Qwen2-72B and Llama-3-70B base models, optimized through Baichuan Alignment. Baichuan-Instruct demonstrates significant improvements in core capabilities, with user experience gains ranging from 17% to 28%, and performs exceptionally well on specialized benchmarks. In open-source benchmark evaluations, both Qwen2-Nova-72B and Llama3-PBM-Nova-70B consistently outperform their respective official instruct versions across nearly all datasets. This report aims to clarify the key technologies behind the alignment process, fostering a deeper understanding within the community. Llama3-PBM-Nova-70B model is available at https://huggingface.co/PKU-Baichuan-MLSystemLab/Llama3-PBM-Nova-70B.
Baichuan-Omni Technical Report
Oct 11, 2024



Abstract:The salient multimodal capabilities and interactive experience of GPT-4o highlight its critical role in practical applications, yet it lacks a high-performing open-source counterpart. In this paper, we introduce Baichuan-Omni, the first open-source 7B Multimodal Large Language Model (MLLM) adept at concurrently processing and analyzing modalities of image, video, audio, and text, while delivering an advanced multimodal interactive experience and strong performance. We propose an effective multimodal training schema starting with 7B model and proceeding through two stages of multimodal alignment and multitask fine-tuning across audio, image, video, and text modal. This approach equips the language model with the ability to handle visual and audio data effectively. Demonstrating strong performance across various omni-modal and multimodal benchmarks, we aim for this contribution to serve as a competitive baseline for the open-source community in advancing multimodal understanding and real-time interaction.
BaichuanSEED: Sharing the Potential of ExtensivE Data Collection and Deduplication by Introducing a Competitive Large Language Model Baseline
Aug 27, 2024
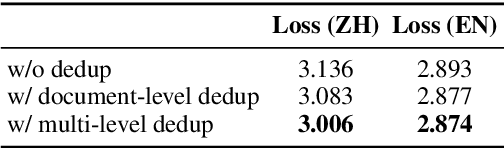

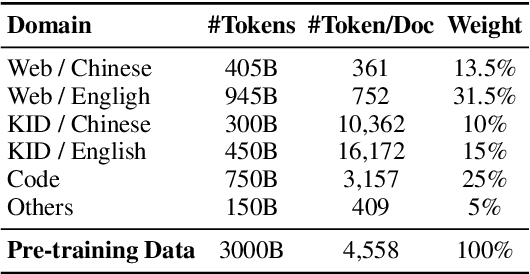
Abstract:The general capabilities of Large Language Models (LLM) highly rely on the composition and selection on extensive pretraining datasets, treated as commercial secrets by several institutions. To mitigate this issue, we open-source the details of a universally applicable data processing pipeline and validate its effectiveness and potential by introducing a competitive LLM baseline. Specifically, the data processing pipeline consists of broad collection to scale up and reweighting to improve quality. We then pretrain a 7B model BaichuanSEED with 3T tokens processed by our pipeline without any deliberate downstream task-related optimization, followed by an easy but effective supervised fine-tuning stage. BaichuanSEED demonstrates consistency and predictability throughout training and achieves comparable performance on comprehensive benchmarks with several commercial advanced large language models, such as Qwen1.5 and Llama3. We also conduct several heuristic experiments to discuss the potential for further optimization of downstream tasks, such as mathematics and coding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge