Wei Song
Department of Radiology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, Beijing, China
UniReason 1.0: A Unified Reasoning Framework for World Knowledge Aligned Image Generation and Editing
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Unified multimodal models often struggle with complex synthesis tasks that demand deep reasoning, and typically treat text-to-image generation and image editing as isolated capabilities rather than interconnected reasoning steps. To address this, we propose UniReason, a unified framework that harmonizes these two tasks through a dual reasoning paradigm. We formulate generation as world knowledge-enhanced planning to inject implicit constraints, and leverage editing capabilities for fine-grained visual refinement to further correct visual errors via self-reflection. This approach unifies generation and editing within a shared representation, mirroring the human cognitive process of planning followed by refinement. We support this framework by systematically constructing a large-scale reasoning-centric dataset (~300k samples) covering five major knowledge domains (e.g., cultural commonsense, physics, etc.) for planning, alongside an agent-generated corpus for visual self-correction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniReason achieves advanced performance on reasoning-intensive benchmarks such as WISE, KrisBench and UniREditBench, while maintaining superior general synthesis capabilities.
FAIRT2V: Training-Free Debiasing for Text-to-Video Diffusion Models
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Text-to-video (T2V) diffusion models have achieved rapid progress, yet their demographic biases, particularly gender bias, remain largely unexplored. We present FairT2V, a training-free debiasing framework for text-to-video generation that mitigates encoder-induced bias without finetuning. We first analyze demographic bias in T2V models and show that it primarily originates from pretrained text encoders, which encode implicit gender associations even for neutral prompts. We quantify this effect with a gender-leaning score that correlates with bias in generated videos. Based on this insight, FairT2V mitigates demographic bias by neutralizing prompt embeddings via anchor-based spherical geodesic transformations while preserving semantics. To maintain temporal coherence, we apply debiasing only during early identity-forming steps through a dynamic denoising schedule. We further propose a video-level fairness evaluation protocol combining VideoLLM-based reasoning with human verification. Experiments on the modern T2V model Open-Sora show that FairT2V substantially reduces demographic bias across occupations with minimal impact on video quality.
DeMark: A Query-Free Black-Box Attack on Deepfake Watermarking Defenses
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:The rapid proliferation of realistic deepfakes has raised urgent concerns over their misuse, motivating the use of defensive watermarks in synthetic images for reliable detection and provenance tracking. However, this defense paradigm assumes such watermarks are inherently resistant to removal. We challenge this assumption with DeMark, a query-free black-box attack framework that targets defensive image watermarking schemes for deepfakes. DeMark exploits latent-space vulnerabilities in encoder-decoder watermarking models through a compressive sensing based sparsification process, suppressing watermark signals while preserving perceptual and structural realism appropriate for deepfakes. Across eight state-of-the-art watermarking schemes, DeMark reduces watermark detection accuracy from 100% to 32.9% on average while maintaining natural visual quality, outperforming existing attacks. We further evaluate three defense strategies, including image super resolution, sparse watermarking, and adversarial training, and find them largely ineffective. These results demonstrate that current encoder decoder watermarking schemes remain vulnerable to latent-space manipulations, underscoring the need for more robust watermarking methods to safeguard against deepfakes.
Robust CAPTCHA Using Audio Illusions in the Era of Large Language Models: from Evaluation to Advances
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:CAPTCHAs are widely used by websites to block bots and spam by presenting challenges that are easy for humans but difficult for automated programs to solve. To improve accessibility, audio CAPTCHAs are designed to complement visual ones. However, the robustness of audio CAPTCHAs against advanced Large Audio Language Models (LALMs) and Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models remains unclear. In this paper, we introduce AI-CAPTCHA, a unified framework that offers (i) an evaluation framework, ACEval, which includes advanced LALM- and ASR-based solvers, and (ii) a novel audio CAPTCHA approach, IllusionAudio, leveraging audio illusions. Through extensive evaluations of seven widely deployed audio CAPTCHAs, we show that most existing methods can be solved with high success rates by advanced LALMs and ASR models, exposing critical security weaknesses. To address these vulnerabilities, we design a new audio CAPTCHA approach, IllusionAudio, which exploits perceptual illusion cues rooted in human auditory mechanisms. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method defeats all tested LALM- and ASR-based attacks while achieving a 100% human pass rate, significantly outperforming existing audio CAPTCHA methods.
Knowledge Distillation for Temporal Knowledge Graph Reasoning with Large Language Models
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Reasoning over temporal knowledge graphs (TKGs) is fundamental to improving the efficiency and reliability of intelligent decision-making systems and has become a key technological foundation for future artificial intelligence applications. Despite recent progress, existing TKG reasoning models typically rely on large parameter sizes and intensive computation, leading to high hardware costs and energy consumption. These constraints hinder their deployment on resource-constrained, low-power, and distributed platforms that require real-time inference. Moreover, most existing model compression and distillation techniques are designed for static knowledge graphs and fail to adequately capture the temporal dependencies inherent in TKGs, often resulting in degraded reasoning performance. To address these challenges, we propose a distillation framework specifically tailored for temporal knowledge graph reasoning. Our approach leverages large language models as teacher models to guide the distillation process, enabling effective transfer of both structural and temporal reasoning capabilities to lightweight student models. By integrating large-scale public knowledge with task-specific temporal information, the proposed framework enhances the student model's ability to model temporal dynamics while maintaining a compact and efficient architecture. Extensive experiments on multiple publicly available benchmark datasets demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms strong baselines, achieving a favorable trade-off between reasoning accuracy, computational efficiency, and practical deployability.
A Structured Review of Underwater Object Detection Challenges and Solutions: From Traditional to Large Vision Language Models
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Underwater object detection (UOD) is vital to diverse marine applications, including oceanographic research, underwater robotics, and marine conservation. However, UOD faces numerous challenges that compromise its performance. Over the years, various methods have been proposed to address these issues, but they often fail to fully capture the complexities of underwater environments. This review systematically categorizes UOD challenges into five key areas: Image quality degradation, target-related issues, data-related challenges, computational and processing constraints, and limitations in detection methodologies. To address these challenges, we analyze the progression from traditional image processing and object detection techniques to modern approaches. Additionally, we explore the potential of large vision-language models (LVLMs) in UOD, leveraging their multi-modal capabilities demonstrated in other domains. We also present case studies, including synthetic dataset generation using DALL-E 3 and fine-tuning Florence-2 LVLM for UOD. This review identifies three key insights: (i) Current UOD methods are insufficient to fully address challenges like image degradation and small object detection in dynamic underwater environments. (ii) Synthetic data generation using LVLMs shows potential for augmenting datasets but requires further refinement to ensure realism and applicability. (iii) LVLMs hold significant promise for UOD, but their real-time application remains under-explored, requiring further research on optimization techniques.
Help or Hurdle? Rethinking Model Context Protocol-Augmented Large Language Models
Aug 18, 2025Abstract:The Model Context Protocol (MCP) enables large language models (LLMs) to access external resources on demand. While commonly assumed to enhance performance, how LLMs actually leverage this capability remains poorly understood. We introduce MCPGAUGE, the first comprehensive evaluation framework for probing LLM-MCP interactions along four key dimensions: proactivity (self-initiated tool use), compliance (adherence to tool-use instructions), effectiveness (task performance post-integration), and overhead (computational cost incurred). MCPGAUGE comprises a 160-prompt suite and 25 datasets spanning knowledge comprehension, general reasoning, and code generation. Our large-scale evaluation, spanning six commercial LLMs, 30 MCP tool suites, and both one- and two-turn interaction settings, comprises around 20,000 API calls and over USD 6,000 in computational cost. This comprehensive study reveals four key findings that challenge prevailing assumptions about the effectiveness of MCP integration. These insights highlight critical limitations in current AI-tool integration and position MCPGAUGE as a principled benchmark for advancing controllable, tool-augmented LLMs.
Autoregressive Semantic Visual Reconstruction Helps VLMs Understand Better
Jun 10, 2025
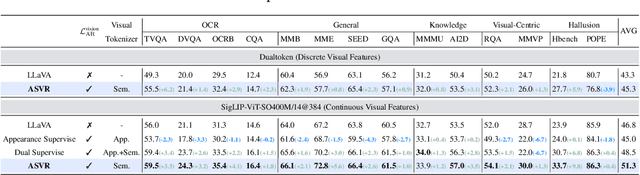
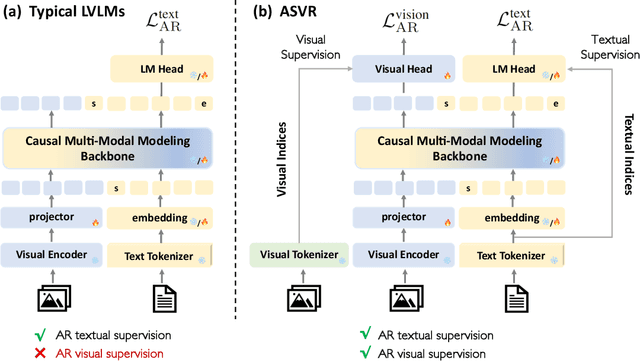
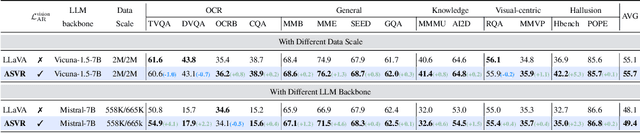
Abstract:Typical large vision-language models (LVLMs) apply autoregressive supervision solely to textual sequences, without fully incorporating the visual modality into the learning process. This results in three key limitations: (1) an inability to utilize images without accompanying captions, (2) the risk that captions omit critical visual details, and (3) the challenge that certain vision-centric content cannot be adequately conveyed through text. As a result, current LVLMs often prioritize vision-to-language alignment while potentially overlooking fine-grained visual information. While some prior works have explored autoregressive image generation, effectively leveraging autoregressive visual supervision to enhance image understanding remains an open challenge. In this paper, we introduce Autoregressive Semantic Visual Reconstruction (ASVR), which enables joint learning of visual and textual modalities within a unified autoregressive framework. We show that autoregressively reconstructing the raw visual appearance of images does not enhance and may even impair multimodal understanding. In contrast, autoregressively reconstructing the semantic representation of images consistently improves comprehension. Notably, we find that even when models are given continuous image features as input, they can effectively reconstruct discrete semantic tokens, resulting in stable and consistent improvements across a wide range of multimodal understanding benchmarks. Our approach delivers significant performance gains across varying data scales (556k-2M) and types of LLM bacbones. Specifically, ASVR improves LLaVA-1.5 by 5% in average scores across 14 multimodal benchmarks. The code is available at https://github.com/AlenjandroWang/ASVR.
Graph Foundation Models: A Comprehensive Survey
May 21, 2025Abstract:Graph-structured data pervades domains such as social networks, biological systems, knowledge graphs, and recommender systems. While foundation models have transformed natural language processing, vision, and multimodal learning through large-scale pretraining and generalization, extending these capabilities to graphs -- characterized by non-Euclidean structures and complex relational semantics -- poses unique challenges and opens new opportunities. To this end, Graph Foundation Models (GFMs) aim to bring scalable, general-purpose intelligence to structured data, enabling broad transfer across graph-centric tasks and domains. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of GFMs, unifying diverse efforts under a modular framework comprising three key components: backbone architectures, pretraining strategies, and adaptation mechanisms. We categorize GFMs by their generalization scope -- universal, task-specific, and domain-specific -- and review representative methods, key innovations, and theoretical insights within each category. Beyond methodology, we examine theoretical foundations including transferability and emergent capabilities, and highlight key challenges such as structural alignment, heterogeneity, scalability, and evaluation. Positioned at the intersection of graph learning and general-purpose AI, GFMs are poised to become foundational infrastructure for open-ended reasoning over structured data. This survey consolidates current progress and outlines future directions to guide research in this rapidly evolving field. Resources are available at https://github.com/Zehong-Wang/Awesome-Foundation-Models-on-Graphs.
EfficientLLM: Efficiency in Large Language Models
May 20, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have driven significant progress, yet their growing parameter counts and context windows incur prohibitive compute, energy, and monetary costs. We introduce EfficientLLM, a novel benchmark and the first comprehensive empirical study evaluating efficiency techniques for LLMs at scale. Conducted on a production-class cluster (48xGH200, 8xH200 GPUs), our study systematically explores three key axes: (1) architecture pretraining (efficient attention variants: MQA, GQA, MLA, NSA; sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE)), (2) fine-tuning (parameter-efficient methods: LoRA, RSLoRA, DoRA), and (3) inference (quantization methods: int4, float16). We define six fine-grained metrics (Memory Utilization, Compute Utilization, Latency, Throughput, Energy Consumption, Compression Rate) to capture hardware saturation, latency-throughput balance, and carbon cost. Evaluating over 100 model-technique pairs (0.5B-72B parameters), we derive three core insights: (i) Efficiency involves quantifiable trade-offs: no single method is universally optimal; e.g., MoE reduces FLOPs and improves accuracy but increases VRAM by 40%, while int4 quantization cuts memory/energy by up to 3.9x at a 3-5% accuracy drop. (ii) Optima are task- and scale-dependent: MQA offers optimal memory-latency trade-offs for constrained devices, MLA achieves lowest perplexity for quality-critical tasks, and RSLoRA surpasses LoRA efficiency only beyond 14B parameters. (iii) Techniques generalize across modalities: we extend evaluations to Large Vision Models (Stable Diffusion 3.5, Wan 2.1) and Vision-Language Models (Qwen2.5-VL), confirming effective transferability. By open-sourcing datasets, evaluation pipelines, and leaderboards, EfficientLLM provides essential guidance for researchers and engineers navigating the efficiency-performance landscape of next-generation foundation models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge