Xiping Hu
Sparse Shortcuts: Facilitating Efficient Fusion in Multimodal Large Language Models
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:With the remarkable success of large language models (LLMs) in natural language understanding and generation, multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have rapidly advanced in their ability to process data across multiple modalities. While most existing efforts focus on scaling up language models or constructing higher-quality training data, limited attention has been paid to effectively integrating cross-modal knowledge into the language space. In vision-language models, for instance, aligning modalities using only high-level visual features often discards the rich semantic information present in mid- and low-level features, limiting the model's ability of cross-modality understanding. To address this issue, we propose SparseCut, a general cross-modal fusion architecture for MLLMs, introducing sparse shortcut connections between the cross-modal encoder and the LLM. These shortcut connections enable the efficient and hierarchical integration of visual features at multiple levels, facilitating richer semantic fusion without increasing computational overhead. We further introduce an efficient multi-grained feature fusion module, which performs the fusion of visual features before routing them through the shortcuts. This preserves the original language context and does not increase the overall input length, thereby avoiding an increase in computational complexity for the LLM. Experiments demonstrate that SparseCut significantly enhances the performance of MLLMs across various multimodal benchmarks with generality and scalability for different base LLMs.
Opening the Black Box: Preliminary Insights into Affective Modeling in Multimodal Foundation Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Understanding where and how emotions are represented in large-scale foundation models remains an open problem, particularly in multimodal affective settings. Despite the strong empirical performance of recent affective models, the internal architectural mechanisms that support affective understanding and generation are still poorly understood. In this work, we present a systematic mechanistic study of affective modeling in multimodal foundation models. Across multiple architectures, training strategies, and affective tasks, we analyze how emotion-oriented supervision reshapes internal model parameters. Our results consistently reveal a clear and robust pattern: affective adaptation does not primarily focus on the attention module, but instead localizes to the feed-forward gating projection (\texttt{gate\_proj}). Through controlled module transfer, targeted single-module adaptation, and destructive ablation, we further demonstrate that \texttt{gate\_proj} is sufficient, efficient, and necessary for affective understanding and generation. Notably, by tuning only approximately 24.5\% of the parameters tuned by AffectGPT, our approach achieves 96.6\% of its average performance across eight affective tasks, highlighting substantial parameter efficiency. Together, these findings provide empirical evidence that affective capabilities in foundation models are structurally mediated by feed-forward gating mechanisms and identify \texttt{gate\_proj} as a central architectural locus of affective modeling.
Revisiting Cross-Architecture Distillation: Adaptive Dual-Teacher Transfer for Lightweight Video Models
Nov 12, 2025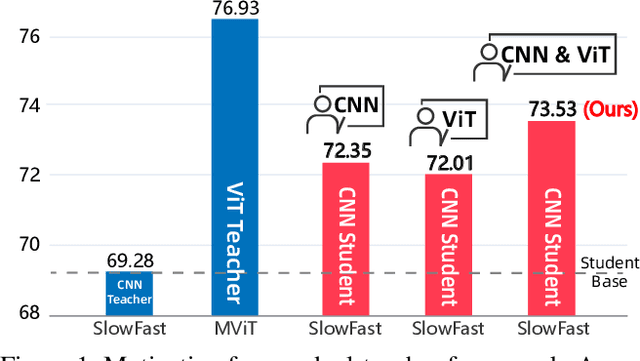
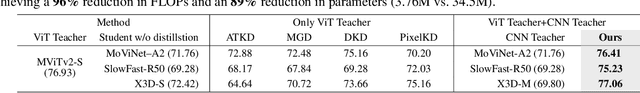
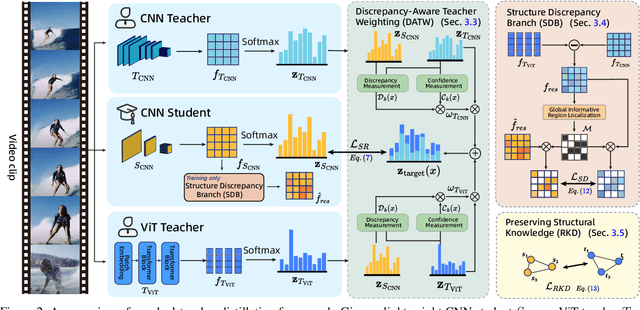
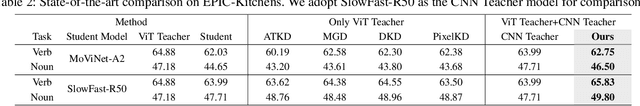
Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have achieved strong performance in video action recognition, but their high computational cost limits their practicality. Lightweight CNNs are more efficient but suffer from accuracy gaps. Cross-Architecture Knowledge Distillation (CAKD) addresses this by transferring knowledge from ViTs to CNNs, yet existing methods often struggle with architectural mismatch and overlook the value of stronger homogeneous CNN teachers. To tackle these challenges, we propose a Dual-Teacher Knowledge Distillation framework that leverages both a heterogeneous ViT teacher and a homogeneous CNN teacher to collaboratively guide a lightweight CNN student. We introduce two key components: (1) Discrepancy-Aware Teacher Weighting, which dynamically fuses the predictions from ViT and CNN teachers by assigning adaptive weights based on teacher confidence and prediction discrepancy with the student, enabling more informative and effective supervision; and (2) a Structure Discrepancy-Aware Distillation strategy, where the student learns the residual features between ViT and CNN teachers via a lightweight auxiliary branch, focusing on transferable architectural differences without mimicking all of ViT's high-dimensional patterns. Extensive experiments on benchmarks including HMDB51, EPIC-KITCHENS-100, and Kinetics-400 demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms state-of-the-art distillation approaches, achieving notable performance improvements with a maximum accuracy gain of 5.95% on HMDB51.
FedSM: Robust Semantics-Guided Feature Mixup for Bias Reduction in Federated Learning with Long-Tail Data
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative model training across decentralized clients without sharing private data. However, FL suffers from biased global models due to non-IID and long-tail data distributions. We propose \textbf{FedSM}, a novel client-centric framework that mitigates this bias through semantics-guided feature mixup and lightweight classifier retraining. FedSM uses a pretrained image-text-aligned model to compute category-level semantic relevance, guiding the category selection of local features to mix-up with global prototypes to generate class-consistent pseudo-features. These features correct classifier bias, especially when data are heavily skewed. To address the concern of potential domain shift between the pretrained model and the data, we propose probabilistic category selection, enhancing feature diversity to effectively mitigate biases. All computations are performed locally, requiring minimal server overhead. Extensive experiments on long-tail datasets with various imbalanced levels demonstrate that FedSM consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods in accuracy, with high robustness to domain shift and computational efficiency.
Emotion Recognition from Skeleton Data: A Comprehensive Survey
Jul 24, 2025Abstract:Emotion recognition through body movements has emerged as a compelling and privacy-preserving alternative to traditional methods that rely on facial expressions or physiological signals. Recent advancements in 3D skeleton acquisition technologies and pose estimation algorithms have significantly enhanced the feasibility of emotion recognition based on full-body motion. This survey provides a comprehensive and systematic review of skeleton-based emotion recognition techniques. First, we introduce psychological models of emotion and examine the relationship between bodily movements and emotional expression. Next, we summarize publicly available datasets, highlighting the differences in data acquisition methods and emotion labeling strategies. We then categorize existing methods into posture-based and gait-based approaches, analyzing them from both data-driven and technical perspectives. In particular, we propose a unified taxonomy that encompasses four primary technical paradigms: Traditional approaches, Feat2Net, FeatFusionNet, and End2EndNet. Representative works within each category are reviewed and compared, with benchmarking results across commonly used datasets. Finally, we explore the extended applications of emotion recognition in mental health assessment, such as detecting depression and autism, and discuss the open challenges and future research directions in this rapidly evolving field.
NLGCL: Naturally Existing Neighbor Layers Graph Contrastive Learning for Recommendation
Jul 10, 2025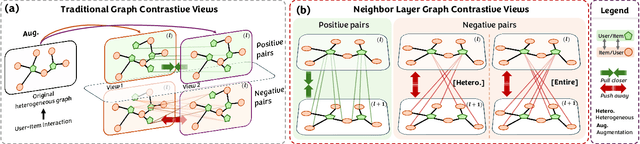
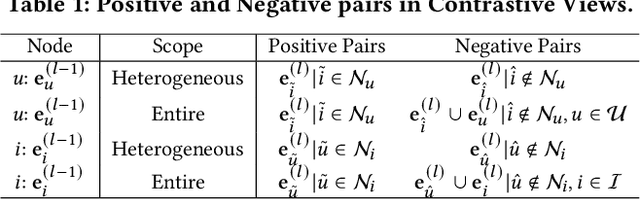
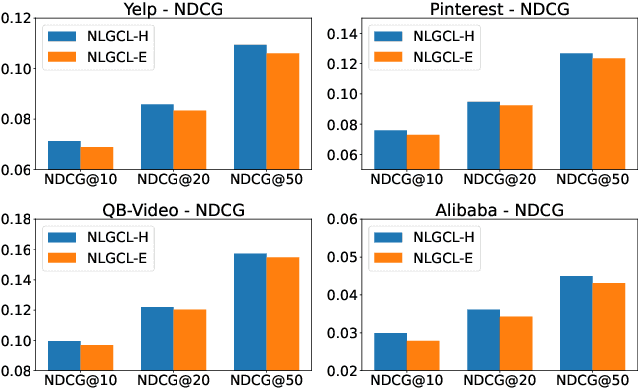
Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) are widely used in collaborative filtering to capture high-order user-item relationships. To address the data sparsity problem in recommendation systems, Graph Contrastive Learning (GCL) has emerged as a promising paradigm that maximizes mutual information between contrastive views. However, existing GCL methods rely on augmentation techniques that introduce semantically irrelevant noise and incur significant computational and storage costs, limiting effectiveness and efficiency. To overcome these challenges, we propose NLGCL, a novel contrastive learning framework that leverages naturally contrastive views between neighbor layers within GNNs. By treating each node and its neighbors in the next layer as positive pairs, and other nodes as negatives, NLGCL avoids augmentation-based noise while preserving semantic relevance. This paradigm eliminates costly view construction and storage, making it computationally efficient and practical for real-world scenarios. Extensive experiments on four public datasets demonstrate that NLGCL outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in effectiveness and efficiency.
Exploring Audio Cues for Enhanced Test-Time Video Model Adaptation
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Test-time adaptation (TTA) aims to boost the generalization capability of a trained model by conducting self-/unsupervised learning during the testing phase. While most existing TTA methods for video primarily utilize visual supervisory signals, they often overlook the potential contribution of inherent audio data. To address this gap, we propose a novel approach that incorporates audio information into video TTA. Our method capitalizes on the rich semantic content of audio to generate audio-assisted pseudo-labels, a new concept in the context of video TTA. Specifically, we propose an audio-to-video label mapping method by first employing pre-trained audio models to classify audio signals extracted from videos and then mapping the audio-based predictions to video label spaces through large language models, thereby establishing a connection between the audio categories and video labels. To effectively leverage the generated pseudo-labels, we present a flexible adaptation cycle that determines the optimal number of adaptation iterations for each sample, based on changes in loss and consistency across different views. This enables a customized adaptation process for each sample. Experimental results on two widely used datasets (UCF101-C and Kinetics-Sounds-C), as well as on two newly constructed audio-video TTA datasets (AVE-C and AVMIT-C) with various corruption types, demonstrate the superiority of our approach. Our method consistently improves adaptation performance across different video classification models and represents a significant step forward in integrating audio information into video TTA. Code: https://github.com/keikeiqi/Audio-Assisted-TTA.
Model Splitting Enhanced Communication-Efficient Federated Learning for CSI Feedback
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements have introduced federated machine learning-based channel state information (CSI) compression before the user equipments (UEs) upload the downlink CSI to the base transceiver station (BTS). However, most existing algorithms impose a high communication overhead due to frequent parameter exchanges between UEs and BTS. In this work, we propose a model splitting approach with a shared model at the BTS and multiple local models at the UEs to reduce communication overhead. Moreover, we implant a pipeline module at the BTS to reduce training time. By limiting exchanges of boundary parameters during forward and backward passes, our algorithm can significantly reduce the exchanged parameters over the benchmarks during federated CSI feedback training.
Edge-Cloud Collaborative Computing on Distributed Intelligence and Model Optimization: A Survey
May 03, 2025



Abstract:Edge-cloud collaborative computing (ECCC) has emerged as a pivotal paradigm for addressing the computational demands of modern intelligent applications, integrating cloud resources with edge devices to enable efficient, low-latency processing. Recent advancements in AI, particularly deep learning and large language models (LLMs), have dramatically enhanced the capabilities of these distributed systems, yet introduce significant challenges in model deployment and resource management. In this survey, we comprehensive examine the intersection of distributed intelligence and model optimization within edge-cloud environments, providing a structured tutorial on fundamental architectures, enabling technologies, and emerging applications. Additionally, we systematically analyze model optimization approaches, including compression, adaptation, and neural architecture search, alongside AI-driven resource management strategies that balance performance, energy efficiency, and latency requirements. We further explore critical aspects of privacy protection and security enhancement within ECCC systems and examines practical deployments through diverse applications, spanning autonomous driving, healthcare, and industrial automation. Performance analysis and benchmarking techniques are also thoroughly explored to establish evaluation standards for these complex systems. Furthermore, the review identifies critical research directions including LLMs deployment, 6G integration, neuromorphic computing, and quantum computing, offering a roadmap for addressing persistent challenges in heterogeneity management, real-time processing, and scalability. By bridging theoretical advancements and practical deployments, this survey offers researchers and practitioners a holistic perspective on leveraging AI to optimize distributed computing environments, fostering innovation in next-generation intelligent systems.
COHESION: Composite Graph Convolutional Network with Dual-Stage Fusion for Multimodal Recommendation
Apr 06, 2025



Abstract:Recent works in multimodal recommendations, which leverage diverse modal information to address data sparsity and enhance recommendation accuracy, have garnered considerable interest. Two key processes in multimodal recommendations are modality fusion and representation learning. Previous approaches in modality fusion often employ simplistic attentive or pre-defined strategies at early or late stages, failing to effectively handle irrelevant information among modalities. In representation learning, prior research has constructed heterogeneous and homogeneous graph structures encapsulating user-item, user-user, and item-item relationships to better capture user interests and item profiles. Modality fusion and representation learning were considered as two independent processes in previous work. In this paper, we reveal that these two processes are complementary and can support each other. Specifically, powerful representation learning enhances modality fusion, while effective fusion improves representation quality. Stemming from these two processes, we introduce a COmposite grapH convolutional nEtwork with dual-stage fuSION for the multimodal recommendation, named COHESION. Specifically, it introduces a dual-stage fusion strategy to reduce the impact of irrelevant information, refining all modalities using ID embedding in the early stage and fusing their representations at the late stage. It also proposes a composite graph convolutional network that utilizes user-item, user-user, and item-item graphs to extract heterogeneous and homogeneous latent relationships within users and items. Besides, it introduces a novel adaptive optimization to ensure balanced and reasonable representations across modalities. Extensive experiments on three widely used datasets demonstrate the significant superiority of COHESION over various competitive baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge