Peng Sun
Tsinghua University
BoRP: Bootstrapped Regression Probing for Scalable and Human-Aligned LLM Evaluation
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Accurate evaluation of user satisfaction is critical for iterative development of conversational AI. However, for open-ended assistants, traditional A/B testing lacks reliable metrics: explicit feedback is sparse, while implicit metrics are ambiguous. To bridge this gap, we introduce BoRP (Bootstrapped Regression Probing), a scalable framework for high-fidelity satisfaction evaluation. Unlike generative approaches, BoRP leverages the geometric properties of LLM latent space. It employs a polarization-index-based bootstrapping mechanism to automate rubric generation and utilizes Partial Least Squares (PLS) to map hidden states to continuous scores. Experiments on industrial datasets show that BoRP (Qwen3-8B/14B) significantly outperforms generative baselines (even Qwen3-Max) in alignment with human judgments. Furthermore, BoRP reduces inference costs by orders of magnitude, enabling full-scale monitoring and highly sensitive A/B testing via CUPED.
DecisionLLM: Large Language Models for Long Sequence Decision Exploration
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Long-sequence decision-making, which is usually addressed through reinforcement learning (RL), is a critical component for optimizing strategic operations in dynamic environments, such as real-time bidding in computational advertising. The Decision Transformer (DT) introduced a powerful paradigm by framing RL as an autoregressive sequence modeling problem. Concurrently, Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable success in complex reasoning and planning tasks. This inspires us whether LLMs, which share the same Transformer foundation, but operate at a much larger scale, can unlock new levels of performance in long-horizon sequential decision-making problem. This work investigates the application of LLMs to offline decision making tasks. A fundamental challenge in this domain is the LLMs' inherent inability to interpret continuous values, as they lack a native understanding of numerical magnitude and order when values are represented as text strings. To address this, we propose treating trajectories as a distinct modality. By learning to align trajectory data with natural language task descriptions, our model can autoregressively predict future decisions within a cohesive framework we term DecisionLLM. We establish a set of scaling laws governing this paradigm, demonstrating that performance hinges on three factors: model scale, data volume, and data quality. In offline experimental benchmarks and bidding scenarios, DecisionLLM achieves strong performance. Specifically, DecisionLLM-3B outperforms the traditional Decision Transformer (DT) by 69.4 on Maze2D umaze-v1 and by 0.085 on AuctionNet. It extends the AIGB paradigm and points to promising directions for future exploration in online bidding.
Stephanie2: Thinking, Waiting, and Making Decisions Like Humans in Step-by-Step AI Social Chat
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Instant-messaging human social chat typically progresses through a sequence of short messages. Existing step-by-step AI chatting systems typically split a one-shot generation into multiple messages and send them sequentially, but they lack an active waiting mechanism and exhibit unnatural message pacing. In order to address these issues, we propose Stephanie2, a novel next-generation step-wise decision-making dialogue agent. With active waiting and message-pace adaptation, Stephanie2 explicitly decides at each step whether to send or wait, and models latency as the sum of thinking time and typing time to achieve more natural pacing. We further introduce a time-window-based dual-agent dialogue system to generate pseudo dialogue histories for human and automatic evaluations. Experiments show that Stephanie2 clearly outperforms Stephanie1 on metrics such as naturalness and engagement, and achieves a higher pass rate on human evaluation with the role identification Turing test.
TAP-ViTs: Task-Adaptive Pruning for On-Device Deployment of Vision Transformers
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) have demonstrated strong performance across a wide range of vision tasks, yet their substantial computational and memory demands hinder efficient deployment on resource-constrained mobile and edge devices. Pruning has emerged as a promising direction for reducing ViT complexity. However, existing approaches either (i) produce a single pruned model shared across all devices, ignoring device heterogeneity, or (ii) rely on fine-tuning with device-local data, which is often infeasible due to limited on-device resources and strict privacy constraints. As a result, current methods fall short of enabling task-customized ViT pruning in privacy-preserving mobile computing settings. This paper introduces TAP-ViTs, a novel task-adaptive pruning framework that generates device-specific pruned ViT models without requiring access to any raw local data. Specifically, to infer device-level task characteristics under privacy constraints, we propose a Gaussian Mixture Model (GMM)-based metric dataset construction mechanism. Each device fits a lightweight GMM to approximate its private data distribution and uploads only the GMM parameters. Using these parameters, the cloud selects distribution-consistent samples from public data to construct a task-representative metric dataset for each device. Based on this proxy dataset, we further develop a dual-granularity importance evaluation-based pruning strategy that jointly measures composite neuron importance and adaptive layer importance, enabling fine-grained, task-aware pruning tailored to each device's computational budget. Extensive experiments across multiple ViT backbones and datasets demonstrate that TAP-ViTs consistently outperforms state-of-the-art pruning methods under comparable compression ratios.
Optimizing Decoding Paths in Masked Diffusion Models by Quantifying Uncertainty
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Masked Diffusion Models (MDMs) offer flexible, non-autoregressive generation, but this freedom introduces a challenge: final output quality is highly sensitive to the decoding order. We are the first to formalize this issue, attributing the variability in output quality to the cumulative predictive uncertainty along a generative path. To quantify this uncertainty, we introduce Denoising Entropy, a computable metric that serves as an internal signal for evaluating generative process. Leveraging this metric, we propose two algorithms designed to optimize the decoding path: a post-hoc selection method and a real-time guidance strategy. Experiments demonstrate that our entropy-guided methods significantly improve generation quality, consistently boosting accuracy on challenging reasoning, planning, and code benchmarks. Our work establishes Denoising Entropy as a principled tool for understanding and controlling generation, effectively turning the uncertainty in MDMs from a liability into a key advantage for discovering high-quality solutions.
Learning to Wait: Synchronizing Agents with the Physical World
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Real-world agentic tasks, unlike synchronous Markov Decision Processes (MDPs), often involve non-blocking actions with variable latencies, creating a fundamental \textit{Temporal Gap} between action initiation and completion. Existing environment-side solutions, such as blocking wrappers or frequent polling, either limit scalability or dilute the agent's context window with redundant observations. In this work, we propose an \textbf{Agent-side Approach} that empowers Large Language Models (LLMs) to actively align their \textit{Cognitive Timeline} with the physical world. By extending the Code-as-Action paradigm to the temporal domain, agents utilize semantic priors and In-Context Learning (ICL) to predict precise waiting durations (\texttt{time.sleep(t)}), effectively synchronizing with asynchronous environment without exhaustive checking. Experiments in a simulated Kubernetes cluster demonstrate that agents can precisely calibrate their internal clocks to minimize both query overhead and execution latency, validating that temporal awareness is a learnable capability essential for autonomous evolution in open-ended environments.
Sigil: Server-Enforced Watermarking in U-Shaped Split Federated Learning via Gradient Injection
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:In decentralized machine learning paradigms such as Split Federated Learning (SFL) and its variant U-shaped SFL, the server's capabilities are severely restricted. Although this enhances client-side privacy, it also leaves the server highly vulnerable to model theft by malicious clients. Ensuring intellectual property protection for such capability-limited servers presents a dual challenge: watermarking schemes that depend on client cooperation are unreliable in adversarial settings, whereas traditional server-side watermarking schemes are technically infeasible because the server lacks access to critical elements such as model parameters or labels. To address this challenge, this paper proposes Sigil, a mandatory watermarking framework designed specifically for capability-limited servers. Sigil defines the watermark as a statistical constraint on the server-visible activation space and embeds the watermark into the client model via gradient injection, without requiring any knowledge of the data. Besides, we design an adaptive gradient clipping mechanism to ensure that our watermarking process remains both mandatory and stealthy, effectively countering existing gradient anomaly detection methods and a specifically designed adaptive subspace removal attack. Extensive experiments on multiple datasets and models demonstrate Sigil's fidelity, robustness, and stealthiness.
Robust Client-Server Watermarking for Split Federated Learning
Nov 17, 2025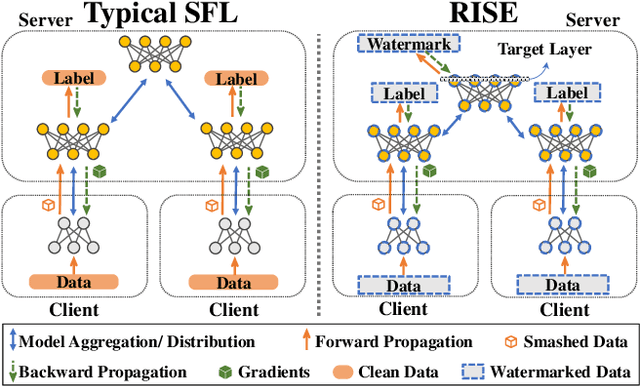
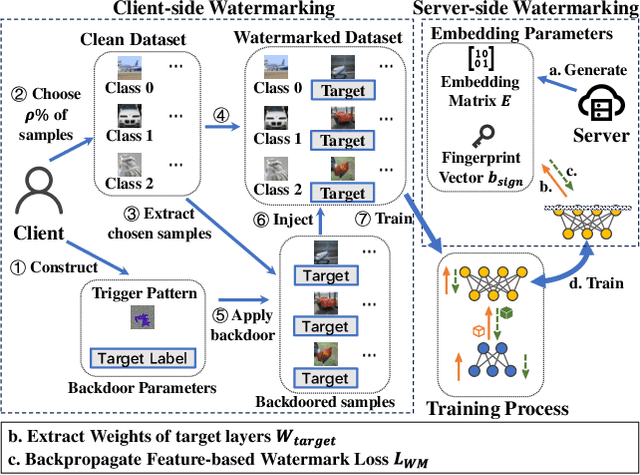
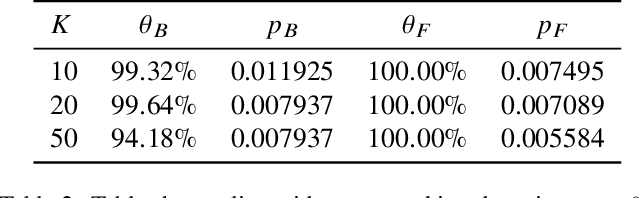
Abstract:Split Federated Learning (SFL) is renowned for its privacy-preserving nature and low computational overhead among decentralized machine learning paradigms. In this framework, clients employ lightweight models to process private data locally and transmit intermediate outputs to a powerful server for further computation. However, SFL is a double-edged sword: while it enables edge computing and enhances privacy, it also introduces intellectual property ambiguity as both clients and the server jointly contribute to training. Existing watermarking techniques fail to protect both sides since no single participant possesses the complete model. To address this, we propose RISE, a Robust model Intellectual property protection scheme using client-Server watermark Embedding for SFL. Specifically, RISE adopts an asymmetric client-server watermarking design: the server embeds feature-based watermarks through a loss regularization term, while clients embed backdoor-based watermarks by injecting predefined trigger samples into private datasets. This co-embedding strategy enables both clients and the server to verify model ownership. Experimental results on standard datasets and multiple network architectures show that RISE achieves over $95\%$ watermark detection rate ($p-value \lt 0.03$) across most settings. It exhibits no mutual interference between client- and server-side watermarks and remains robust against common removal attacks.
Event-CausNet: Unlocking Causal Knowledge from Text with Large Language Models for Reliable Spatio-Temporal Forecasting
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:While spatio-temporal Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) excel at modeling recurring traffic patterns, their reliability plummets during non-recurring events like accidents. This failure occurs because GNNs are fundamentally correlational models, learning historical patterns that are invalidated by the new causal factors introduced during disruptions. To address this, we propose Event-CausNet, a framework that uses a Large Language Model to quantify unstructured event reports, builds a causal knowledge base by estimating average treatment effects, and injects this knowledge into a dual-stream GNN-LSTM network using a novel causal attention mechanism to adjust and enhance the forecast. Experiments on a real-world dataset demonstrate that Event-CausNet achieves robust performance, reducing prediction error (MAE) by up to 35.87%, significantly outperforming state-of-the-art baselines. Our framework bridges the gap between correlational models and causal reasoning, providing a solution that is more accurate and transferable, while also offering crucial interpretability, providing a more reliable foundation for real-world traffic management during critical disruptions.
AIonopedia: an LLM agent orchestrating multimodal learning for ionic liquid discovery
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:The discovery of novel Ionic Liquids (ILs) is hindered by critical challenges in property prediction, including limited data, poor model accuracy, and fragmented workflows. Leveraging the power of Large Language Models (LLMs), we introduce AIonopedia, to the best of our knowledge, the first LLM agent for IL discovery. Powered by an LLM-augmented multimodal domain foundation model for ILs, AIonopedia enables accurate property predictions and incorporates a hierarchical search architecture for molecular screening and design. Trained and evaluated on a newly curated and comprehensive IL dataset, our model delivers superior performance. Complementing these results, evaluations on literature-reported systems indicate that the agent can perform effective IL modification. Moving beyond offline tests, the practical efficacy was further confirmed through real-world wet-lab validation, in which the agent demonstrated exceptional generalization capabilities on challenging out-of-distribution tasks, underscoring its ability to accelerate real-world IL discovery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge