Yuchen Duan
InternVL3.5: Advancing Open-Source Multimodal Models in Versatility, Reasoning, and Efficiency
Aug 25, 2025



Abstract:We introduce InternVL 3.5, a new family of open-source multimodal models that significantly advances versatility, reasoning capability, and inference efficiency along the InternVL series. A key innovation is the Cascade Reinforcement Learning (Cascade RL) framework, which enhances reasoning through a two-stage process: offline RL for stable convergence and online RL for refined alignment. This coarse-to-fine training strategy leads to substantial improvements on downstream reasoning tasks, e.g., MMMU and MathVista. To optimize efficiency, we propose a Visual Resolution Router (ViR) that dynamically adjusts the resolution of visual tokens without compromising performance. Coupled with ViR, our Decoupled Vision-Language Deployment (DvD) strategy separates the vision encoder and language model across different GPUs, effectively balancing computational load. These contributions collectively enable InternVL3.5 to achieve up to a +16.0\% gain in overall reasoning performance and a 4.05$\times$ inference speedup compared to its predecessor, i.e., InternVL3. In addition, InternVL3.5 supports novel capabilities such as GUI interaction and embodied agency. Notably, our largest model, i.e., InternVL3.5-241B-A28B, attains state-of-the-art results among open-source MLLMs across general multimodal, reasoning, text, and agentic tasks -- narrowing the performance gap with leading commercial models like GPT-5. All models and code are publicly released.
InternVL3: Exploring Advanced Training and Test-Time Recipes for Open-Source Multimodal Models
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce InternVL3, a significant advancement in the InternVL series featuring a native multimodal pre-training paradigm. Rather than adapting a text-only large language model (LLM) into a multimodal large language model (MLLM) that supports visual inputs, InternVL3 jointly acquires multimodal and linguistic capabilities from both diverse multimodal data and pure-text corpora during a single pre-training stage. This unified training paradigm effectively addresses the complexities and alignment challenges commonly encountered in conventional post-hoc training pipelines for MLLMs. To further improve performance and scalability, InternVL3 incorporates variable visual position encoding (V2PE) to support extended multimodal contexts, employs advanced post-training techniques such as supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and mixed preference optimization (MPO), and adopts test-time scaling strategies alongside an optimized training infrastructure. Extensive empirical evaluations demonstrate that InternVL3 delivers superior performance across a wide range of multi-modal tasks. In particular, InternVL3-78B achieves a score of 72.2 on the MMMU benchmark, setting a new state-of-the-art among open-source MLLMs. Its capabilities remain highly competitive with leading proprietary models, including ChatGPT-4o, Claude 3.5 Sonnet, and Gemini 2.5 Pro, while also maintaining strong pure-language proficiency. In pursuit of open-science principles, we will publicly release both the training data and model weights to foster further research and development in next-generation MLLMs.
Needle In A Multimodal Haystack
Jun 11, 2024Abstract:With the rapid advancement of multimodal large language models (MLLMs), their evaluation has become increasingly comprehensive. However, understanding long multimodal content, as a foundational ability for real-world applications, remains underexplored. In this work, we present Needle In A Multimodal Haystack (MM-NIAH), the first benchmark specifically designed to systematically evaluate the capability of existing MLLMs to comprehend long multimodal documents. Our benchmark includes three types of evaluation tasks: multimodal retrieval, counting, and reasoning. In each task, the model is required to answer the questions according to different key information scattered throughout the given multimodal document. Evaluating the leading MLLMs on MM-NIAH, we observe that existing models still have significant room for improvement on these tasks, especially on vision-centric evaluation. We hope this work can provide a platform for further research on long multimodal document comprehension and contribute to the advancement of MLLMs. Code and benchmark are released at https://github.com/OpenGVLab/MM-NIAH.
Vision-RWKV: Efficient and Scalable Visual Perception with RWKV-Like Architectures
Mar 07, 2024Abstract:Transformers have revolutionized computer vision and natural language processing, but their high computational complexity limits their application in high-resolution image processing and long-context analysis. This paper introduces Vision-RWKV (VRWKV), a model adapted from the RWKV model used in the NLP field with necessary modifications for vision tasks. Similar to the Vision Transformer (ViT), our model is designed to efficiently handle sparse inputs and demonstrate robust global processing capabilities, while also scaling up effectively, accommodating both large-scale parameters and extensive datasets. Its distinctive advantage lies in its reduced spatial aggregation complexity, which renders it exceptionally adept at processing high-resolution images seamlessly, eliminating the necessity for windowing operations. Our evaluations demonstrate that VRWKV surpasses ViT's performance in image classification and has significantly faster speeds and lower memory usage processing high-resolution inputs. In dense prediction tasks, it outperforms window-based models, maintaining comparable speeds. These results highlight VRWKV's potential as a more efficient alternative for visual perception tasks. Code is released at \url{https://github.com/OpenGVLab/Vision-RWKV}.
Denoising Diffusion Semantic Segmentation with Mask Prior Modeling
Jun 22, 2023



Abstract:The evolution of semantic segmentation has long been dominated by learning more discriminative image representations for classifying each pixel. Despite the prominent advancements, the priors of segmentation masks themselves, e.g., geometric and semantic constraints, are still under-explored. In this paper, we propose to ameliorate the semantic segmentation quality of existing discriminative approaches with a mask prior modeled by a recently-developed denoising diffusion generative model. Beginning with a unified architecture that adapts diffusion models for mask prior modeling, we focus this work on a specific instantiation with discrete diffusion and identify a variety of key design choices for its successful application. Our exploratory analysis revealed several important findings, including: (1) a simple integration of diffusion models into semantic segmentation is not sufficient, and a poorly-designed diffusion process might lead to degradation in segmentation performance; (2) during the training, the object to which noise is added is more important than the type of noise; (3) during the inference, the strict diffusion denoising scheme may not be essential and can be relaxed to a simpler scheme that even works better. We evaluate the proposed prior modeling with several off-the-shelf segmentors, and our experimental results on ADE20K and Cityscapes demonstrate that our approach could achieve competitively quantitative performance and more appealing visual quality.
Vision Transformer Adapter for Dense Predictions
May 18, 2022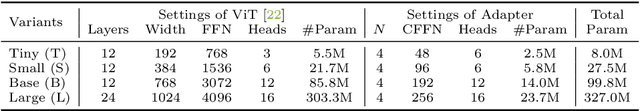
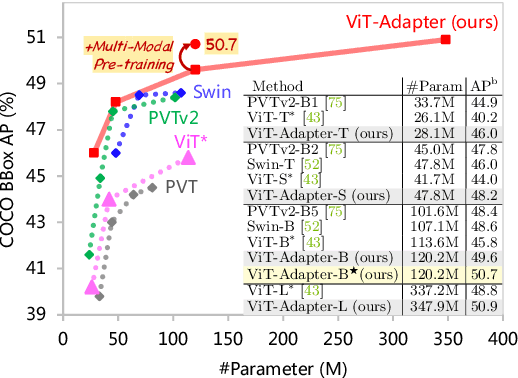
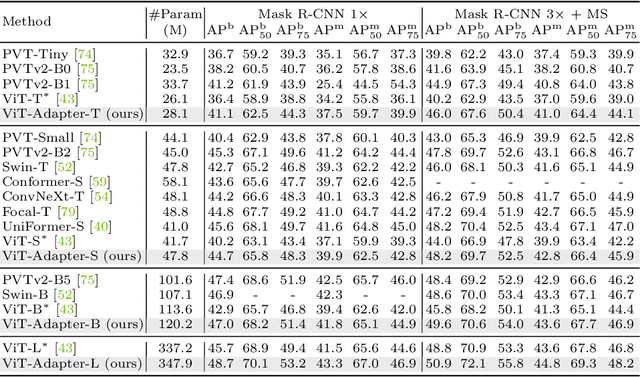
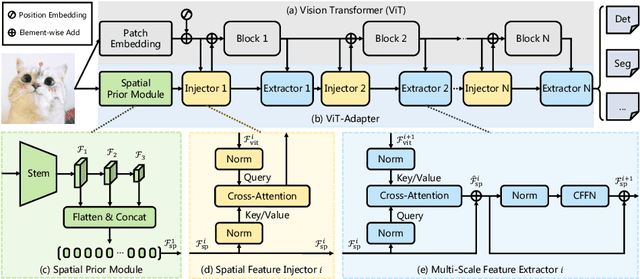
Abstract:This work investigates a simple yet powerful adapter for Vision Transformer (ViT). Unlike recent visual transformers that introduce vision-specific inductive biases into their architectures, ViT achieves inferior performance on dense prediction tasks due to lacking prior information of images. To solve this issue, we propose a Vision Transformer Adapter (ViT-Adapter), which can remedy the defects of ViT and achieve comparable performance to vision-specific models by introducing inductive biases via an additional architecture. Specifically, the backbone in our framework is a vanilla transformer that can be pre-trained with multi-modal data. When fine-tuning on downstream tasks, a modality-specific adapter is used to introduce the data and tasks' prior information into the model, making it suitable for these tasks. We verify the effectiveness of our ViT-Adapter on multiple downstream tasks, including object detection, instance segmentation, and semantic segmentation. Notably, when using HTC++, our ViT-Adapter-L yields 60.1 box AP and 52.1 mask AP on COCO test-dev, surpassing Swin-L by 1.4 box AP and 1.0 mask AP. For semantic segmentation, our ViT-Adapter-L establishes a new state-of-the-art of 60.5 mIoU on ADE20K val, 0.6 points higher than SwinV2-G. We hope that the proposed ViT-Adapter could serve as an alternative for vision-specific transformers and facilitate future research. The code and models will be released at https://github.com/czczup/ViT-Adapter.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge