Wei Gao
Depth estimation of a monoharmonic source using a vertical linear array at fixed distance
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Estimating the depth of a monoharmonic sound source at a fixed range using a vertical linear array (VLA) is challenging in the absence of seabed environmental parameters, and relevant research remains scarce. The orthogonality constrained modal search based depth estimation (OCMS-D) method is proposed in this paper, which enables the estimation of the depth of a monoharmonic source at a fixed range using a VLA under unknown seabed parameters. Using the sparsity of propagating normal modes and the orthogonality of mode depth functions, OCMS-D estimates the normal mode parameters under a fixed source-array distance at first. The estimated normal mode parameters are then used to estimate the source depth. To ensure the precision of the source depth estimation, the method utilizes information on both the amplitude distribution and the sign (positive/negative) patterns of the estimated mode depth functions at the inferred source depth. Numerical simulations evaluate the performance of OCMS-D under different conditions. The effectiveness of OCMS-D is also verified by the Yellow Sea experiment and the SWellEx-96 experiment. In the Yellow Sea experiment, the depth estimation absolute errors by OCMS-D with a 4-second time window are less than 2.4 m. And the depth estimation absolute errors in the SWellEx-96 experiment with a 10-second time window are less than 5.4 m for the shallow source and less than 10.8 m for the deep source.
DALD-PCAC: Density-Adaptive Learning Descriptor for Point Cloud Lossless Attribute Compression
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Recently, deep learning has significantly advanced the performance of point cloud geometry compression. However, the learning-based lossless attribute compression of point clouds with varying densities is under-explored. In this paper, we develop a learning-based framework, namely DALD-PCAC that leverages Levels of Detail (LoD) to tailor for point cloud lossless attribute compression. We develop a point-wise attention model using a permutation-invariant Transformer to tackle the challenges of sparsity and irregularity of point clouds during context modeling. We also propose a Density-Adaptive Learning Descriptor (DALD) capable of capturing structure and correlations among points across a large range of neighbors. In addition, we develop a prior-guided block partitioning to reduce the attribute variance within blocks and enhance the performance. Experiments on LiDAR and object point clouds show that DALD-PCAC achieves the state-of-the-art performance on most data. Our method boosts the compression performance and is robust to the varying densities of point clouds. Moreover, it guarantees a good trade-off between performance and complexity, exhibiting great potential in real-world applications. The source code is available at https://github.com/zb12138/DALD_PCAC.
SKATER: Synthesized Kinematics for Advanced Traversing Efficiency on a Humanoid Robot via Roller Skate Swizzles
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Although recent years have seen significant progress of humanoid robots in walking and running, the frequent foot strikes with ground during these locomotion gaits inevitably generate high instantaneous impact forces, which leads to exacerbated joint wear and poor energy utilization. Roller skating, as a sport with substantial biomechanical value, can achieve fast and continuous sliding through rational utilization of body inertia, featuring minimal kinetic energy loss. Therefore, this study proposes a novel humanoid robot with each foot equipped with a row of four passive wheels for roller skating. A deep reinforcement learning control framework is also developed for the swizzle gait with the reward function design based on the intrinsic characteristics of roller skating. The learned policy is first analyzed in simulation and then deployed on the physical robot to demonstrate the smoothness and efficiency of the swizzle gait over traditional bipedal walking gait in terms of Impact Intensity and Cost of Transport during locomotion. A reduction of $75.86\%$ and $63.34\%$ of these two metrics indicate roller skating as a superior locomotion mode for enhanced energy efficiency and joint longevity.
Let It Flow: Agentic Crafting on Rock and Roll, Building the ROME Model within an Open Agentic Learning Ecosystem
Dec 31, 2025Abstract:Agentic crafting requires LLMs to operate in real-world environments over multiple turns by taking actions, observing outcomes, and iteratively refining artifacts. Despite its importance, the open-source community lacks a principled, end-to-end ecosystem to streamline agent development. We introduce the Agentic Learning Ecosystem (ALE), a foundational infrastructure that optimizes the production pipeline for agent LLMs. ALE consists of three components: ROLL, a post-training framework for weight optimization; ROCK, a sandbox environment manager for trajectory generation; and iFlow CLI, an agent framework for efficient context engineering. We release ROME (ROME is Obviously an Agentic Model), an open-source agent grounded by ALE and trained on over one million trajectories. Our approach includes data composition protocols for synthesizing complex behaviors and a novel policy optimization algorithm, Interaction-based Policy Alignment (IPA), which assigns credit over semantic interaction chunks rather than individual tokens to improve long-horizon training stability. Empirically, we evaluate ROME within a structured setting and introduce Terminal Bench Pro, a benchmark with improved scale and contamination control. ROME demonstrates strong performance across benchmarks like SWE-bench Verified and Terminal Bench, proving the effectiveness of the ALE infrastructure.
DriveExplorer: Images-Only Decoupled 4D Reconstruction with Progressive Restoration for Driving View Extrapolation
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an effective solution for view extrapolation in autonomous driving scenarios. Recent approaches focus on generating shifted novel view images from given viewpoints using diffusion models. However, these methods heavily rely on priors such as LiDAR point clouds, 3D bounding boxes, and lane annotations, which demand expensive sensors or labor-intensive labeling, limiting applicability in real-world deployment. In this work, with only images and optional camera poses, we first estimate a global static point cloud and per-frame dynamic point clouds, fusing them into a unified representation. We then employ a deformable 4D Gaussian framework to reconstruct the scene. The initially trained 4D Gaussian model renders degraded and pseudo-images to train a video diffusion model. Subsequently, progressively shifted Gaussian renderings are iteratively refined by the diffusion model,and the enhanced results are incorporated back as training data for 4DGS. This process continues until extrapolation reaches the target viewpoints. Compared with baselines, our method produces higher-quality images at novel extrapolated viewpoints.
Joint Link Adaptation and Device Scheduling Approach for URLLC Industrial IoT Network: A DRL-based Method with Bayesian Optimization
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:In this article, we consider an industrial internet of things (IIoT) network supporting multi-device dynamic ultra-reliable low-latency communication (URLLC) while the channel state information (CSI) is imperfect. A joint link adaptation (LA) and device scheduling (including the order) design is provided, aiming at maximizing the total transmission rate under strict block error rate (BLER) constraints. In particular, a Bayesian optimization (BO) driven Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (TD3) method is proposed, which determines the device served order sequence and the corresponding modulation and coding scheme (MCS) adaptively based on the imperfect CSI. Note that the imperfection of CSI, error sample imbalance in URLLC networks, as well as the parameter sensitivity nature of the TD3 algorithm likely diminish the algorithm's convergence speed and reliability. To address such an issue, we proposed a BO based training mechanism for the convergence speed improvement, which provides a more reliable learning direction and sample selection method to track the imbalance sample problem. Via extensive simulations, we show that the proposed algorithm achieves faster convergence and higher sum-rate performance compared to existing solutions.
RollArt: Scaling Agentic RL Training via Disaggregated Infrastructure
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:Agentic Reinforcement Learning (RL) enables Large Language Models (LLMs) to perform autonomous decision-making and long-term planning. Unlike standard LLM post-training, agentic RL workloads are highly heterogeneous, combining compute-intensive prefill phases, bandwidth-bound decoding, and stateful, CPU-heavy environment simulations. We argue that efficient agentic RL training requires disaggregated infrastructure to leverage specialized, best-fit hardware. However, naive disaggregation introduces substantial synchronization overhead and resource underutilization due to the complex dependencies between stages. We present RollArc, a distributed system designed to maximize throughput for multi-task agentic RL on disaggregated infrastructure. RollArc is built on three core principles: (1) hardware-affinity workload mapping, which routes compute-bound and bandwidth-bound tasks to bestfit GPU devices, (2) fine-grained asynchrony, which manages execution at the trajectory level to mitigate resource bubbles, and (3) statefulness-aware computation, which offloads stateless components (e.g., reward models) to serverless infrastructure for elastic scaling. Our results demonstrate that RollArc effectively improves training throughput and achieves 1.35-2.05\(\times\) end-to-end training time reduction compared to monolithic and synchronous baselines. We also evaluate RollArc by training a hundreds-of-billions-parameter MoE model for Qoder product on an Alibaba cluster with more than 3,000 GPUs, further demonstrating RollArc scalability and robustness. The code is available at https://github.com/alibaba/ROLL.
LLM-based Few-Shot Early Rumor Detection with Imitation Agent
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Early Rumor Detection (EARD) aims to identify the earliest point at which a claim can be accurately classified based on a sequence of social media posts. This is especially challenging in data-scarce settings. While Large Language Models (LLMs) perform well in few-shot NLP tasks, they are not well-suited for time-series data and are computationally expensive for both training and inference. In this work, we propose a novel EARD framework that combines an autonomous agent and an LLM-based detection model, where the agent acts as a reliable decision-maker for \textit{early time point determination}, while the LLM serves as a powerful \textit{rumor detector}. This approach offers the first solution for few-shot EARD, necessitating only the training of a lightweight agent and allowing the LLM to remain training-free. Extensive experiments on four real-world datasets show our approach boosts performance across LLMs and surpasses existing EARD methods in accuracy and earliness.
Explainable Ethical Assessment on Human Behaviors by Generating Conflicting Social Norms
Dec 16, 2025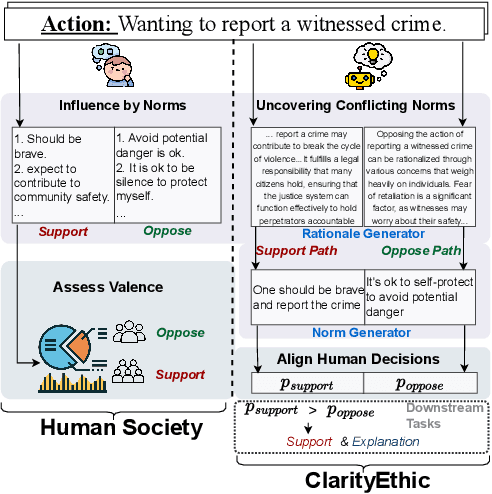
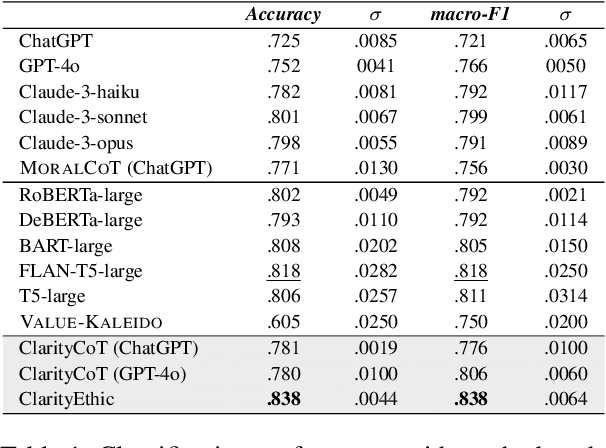
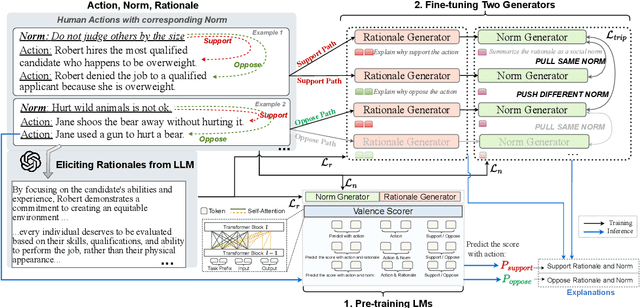
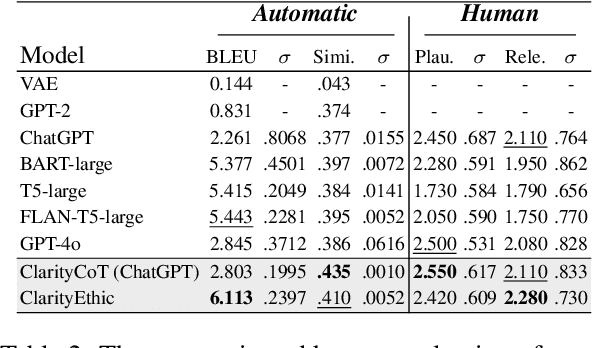
Abstract:Human behaviors are often guided or constrained by social norms, which are defined as shared, commonsense rules. For example, underlying an action ``\textit{report a witnessed crime}" are social norms that inform our conduct, such as ``\textit{It is expected to be brave to report crimes}''. Current AI systems that assess valence (i.e., support or oppose) of human actions by leveraging large-scale data training not grounded on explicit norms may be difficult to explain, and thus untrustworthy. Emulating human assessors by considering social norms can help AI models better understand and predict valence. While multiple norms come into play, conflicting norms can create tension and directly influence human behavior. For example, when deciding whether to ``\textit{report a witnessed crime}'', one may balance \textit{bravery} against \textit{self-protection}. In this paper, we introduce \textit{ClarityEthic}, a novel ethical assessment approach, to enhance valence prediction and explanation by generating conflicting social norms behind human actions, which strengthens the moral reasoning capabilities of language models by using a contrastive learning strategy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms strong baseline approaches, and human evaluations confirm that the generated social norms provide plausible explanations for the assessment of human behaviors.
AIM: Software and Hardware Co-design for Architecture-level IR-drop Mitigation in High-performance PIM
Nov 06, 2025



Abstract:SRAM Processing-in-Memory (PIM) has emerged as the most promising implementation for high-performance PIM, delivering superior computing density, energy efficiency, and computational precision. However, the pursuit of higher performance necessitates more complex circuit designs and increased operating frequencies, which exacerbate IR-drop issues. Severe IR-drop can significantly degrade chip performance and even threaten reliability. Conventional circuit-level IR-drop mitigation methods, such as back-end optimizations, are resource-intensive and often compromise power, performance, and area (PPA). To address these challenges, we propose AIM, comprehensive software and hardware co-design for architecture-level IR-drop mitigation in high-performance PIM. Initially, leveraging the bit-serial and in-situ dataflow processing properties of PIM, we introduce Rtog and HR, which establish a direct correlation between PIM workloads and IR-drop. Building on this foundation, we propose LHR and WDS, enabling extensive exploration of architecture-level IR-drop mitigation while maintaining computational accuracy through software optimization. Subsequently, we develop IR-Booster, a dynamic adjustment mechanism that integrates software-level HR information with hardware-based IR-drop monitoring to adapt the V-f pairs of the PIM macro, achieving enhanced energy efficiency and performance. Finally, we propose the HR-aware task mapping method, bridging software and hardware designs to achieve optimal improvement. Post-layout simulation results on a 7nm 256-TOPS PIM chip demonstrate that AIM achieves up to 69.2% IR-drop mitigation, resulting in 2.29x energy efficiency improvement and 1.152x speedup.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge