Gengru Chen
ShopSimulator: Evaluating and Exploring RL-Driven LLM Agent for Shopping Assistants
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Large language model (LLM)-based agents are increasingly deployed in e-commerce shopping. To perform thorough, user-tailored product searches, agents should interpret personal preferences, engage in multi-turn dialogues, and ultimately retrieve and discriminate among highly similar products. However, existing research has yet to provide a unified simulation environment that consistently captures all of these aspects, and always focuses solely on evaluation benchmarks without training support. In this paper, we introduce ShopSimulator, a large-scale and challenging Chinese shopping environment. Leveraging ShopSimulator, we evaluate LLMs across diverse scenarios, finding that even the best-performing models achieve less than 40% full-success rate. Error analysis reveals that agents struggle with deep search and product selection in long trajectories, fail to balance the use of personalization cues, and to effectively engage with users. Further training exploration provides practical guidance for overcoming these weaknesses, with the combination of supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement learning (RL) yielding significant performance improvements. Code and data will be released at https://github.com/ShopAgent-Team/ShopSimulator.
Reinforcement Learning Optimization for Large-Scale Learning: An Efficient and User-Friendly Scaling Library
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:We introduce ROLL, an efficient, scalable, and user-friendly library designed for Reinforcement Learning Optimization for Large-scale Learning. ROLL caters to three primary user groups: tech pioneers aiming for cost-effective, fault-tolerant large-scale training, developers requiring flexible control over training workflows, and researchers seeking agile experimentation. ROLL is built upon several key modules to serve these user groups effectively. First, a single-controller architecture combined with an abstraction of the parallel worker simplifies the development of the training pipeline. Second, the parallel strategy and data transfer modules enable efficient and scalable training. Third, the rollout scheduler offers fine-grained management of each sample's lifecycle during the rollout stage. Fourth, the environment worker and reward worker support rapid and flexible experimentation with agentic RL algorithms and reward designs. Finally, AutoDeviceMapping allows users to assign resources to different models flexibly across various stages.
Adaptive Dense Reward: Understanding the Gap Between Action and Reward Space in Alignment
Oct 23, 2024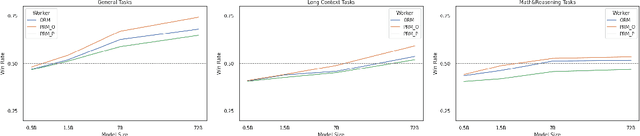
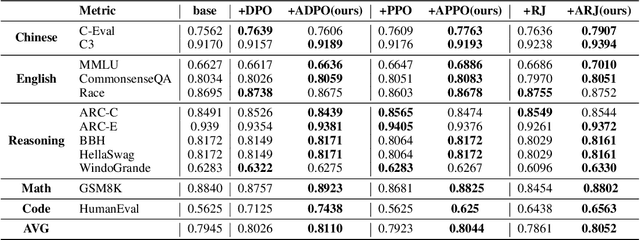
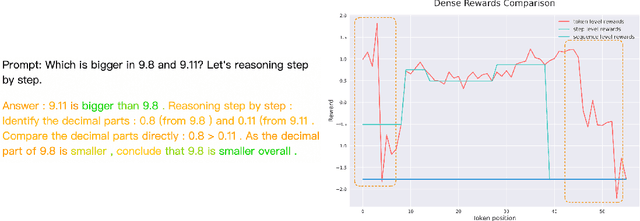
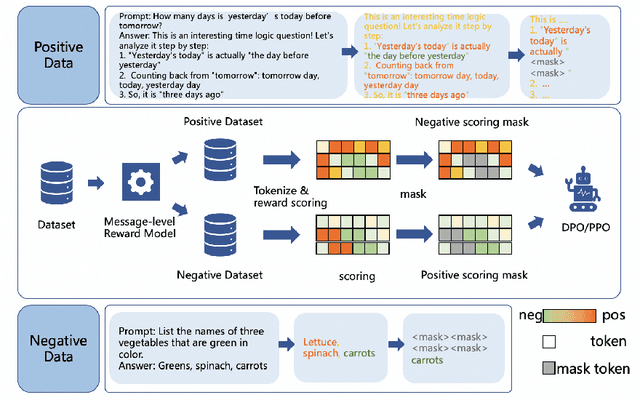
Abstract:Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) has proven highly effective in aligning Large Language Models (LLMs) with human preferences. However, the original RLHF typically optimizes under an overall reward, which can lead to a suboptimal learning process. This limitation stems from RLHF's lack of awareness regarding which specific tokens should be reinforced or suppressed. Moreover, conflicts in supervision can arise, for instance, when a chosen response includes erroneous tokens, while a rejected response contains accurate elements. To rectify these shortcomings, increasing dense reward methods, such as step-wise and token-wise RLHF, have been proposed. However, these existing methods are limited to specific tasks (like mathematics). In this paper, we propose the ``Adaptive Message-wise RLHF'' method, which robustly applies to various tasks. By defining pivot tokens as key indicators, our approach adaptively identifies essential information and converts sample-level supervision into fine-grained, subsequence-level supervision. This aligns the density of rewards and action spaces more closely with the information density of the input. Experiments demonstrate that our method can be integrated into various training methods, significantly mitigating hallucinations and catastrophic forgetting problems while outperforming other methods on multiple evaluation metrics. Our method improves the success rate on adversarial samples by 10\% compared to the sample-wise approach and achieves a 1.3\% improvement on evaluation benchmarks such as MMLU, GSM8K, and HumanEval et al.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge