Sheng Guo
MobileViCLIP: An Efficient Video-Text Model for Mobile Devices
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Efficient lightweight neural networks are with increasing attention due to their faster reasoning speed and easier deployment on mobile devices. However, existing video pre-trained models still focus on the common ViT architecture with high latency, and few works attempt to build efficient architecture on mobile devices. This paper bridges this gap by introducing temporal structural reparameterization into an efficient image-text model and training it on a large-scale high-quality video-text dataset, resulting in an efficient video-text model that can run on mobile devices with strong zero-shot classification and retrieval capabilities, termed as MobileViCLIP. In particular, in terms of inference speed on mobile devices, our MobileViCLIP-Small is 55.4x times faster than InternVideo2-L14 and 6.7x faster than InternVideo2-S14. In terms of zero-shot retrieval performance, our MobileViCLIP-Small obtains similar performance as InternVideo2-L14 and obtains 6.9\% better than InternVideo2-S14 on MSR-VTT. The code is available at https://github.com/MCG-NJU/MobileViCLIP.
Reinforcement Learning Optimization for Large-Scale Learning: An Efficient and User-Friendly Scaling Library
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:We introduce ROLL, an efficient, scalable, and user-friendly library designed for Reinforcement Learning Optimization for Large-scale Learning. ROLL caters to three primary user groups: tech pioneers aiming for cost-effective, fault-tolerant large-scale training, developers requiring flexible control over training workflows, and researchers seeking agile experimentation. ROLL is built upon several key modules to serve these user groups effectively. First, a single-controller architecture combined with an abstraction of the parallel worker simplifies the development of the training pipeline. Second, the parallel strategy and data transfer modules enable efficient and scalable training. Third, the rollout scheduler offers fine-grained management of each sample's lifecycle during the rollout stage. Fourth, the environment worker and reward worker support rapid and flexible experimentation with agentic RL algorithms and reward designs. Finally, AutoDeviceMapping allows users to assign resources to different models flexibly across various stages.
LeTS: Learning to Think-and-Search via Process-and-Outcome Reward Hybridization
May 23, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in reasoning with the emergence of reasoning models like OpenAI-o1 and DeepSeek-R1. Recent research focuses on integrating reasoning capabilities into the realm of retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) via outcome-supervised reinforcement learning (RL) approaches, while the correctness of intermediate think-and-search steps is usually neglected. To address this issue, we design a process-level reward module to mitigate the unawareness of intermediate reasoning steps in outcome-level supervision without additional annotation. Grounded on this, we propose Learning to Think-and-Search (LeTS), a novel framework that hybridizes stepwise process reward and outcome-based reward to current RL methods for RAG. Extensive experiments demonstrate the generalization and inference efficiency of LeTS across various RAG benchmarks. In addition, these results reveal the potential of process- and outcome-level reward hybridization in boosting LLMs' reasoning ability via RL under other scenarios. The code will be released soon.
IMPACT: Behavioral Intention-aware Multimodal Trajectory Prediction with Adaptive Context Trimming
Apr 12, 2025Abstract:While most prior research has focused on improving the precision of multimodal trajectory predictions, the explicit modeling of multimodal behavioral intentions (e.g., yielding, overtaking) remains relatively underexplored. This paper proposes a unified framework that jointly predicts both behavioral intentions and trajectories to enhance prediction accuracy, interpretability, and efficiency. Specifically, we employ a shared context encoder for both intention and trajectory predictions, thereby reducing structural redundancy and information loss. Moreover, we address the lack of ground-truth behavioral intention labels in mainstream datasets (Waymo, Argoverse) by auto-labeling these datasets, thus advancing the community's efforts in this direction. We further introduce a vectorized occupancy prediction module that infers the probability of each map polyline being occupied by the target vehicle's future trajectory. By leveraging these intention and occupancy prediction priors, our method conducts dynamic, modality-dependent pruning of irrelevant agents and map polylines in the decoding stage, effectively reducing computational overhead and mitigating noise from non-critical elements. Our approach ranks first among LiDAR-free methods on the Waymo Motion Dataset and achieves first place on the Waymo Interactive Prediction Dataset. Remarkably, even without model ensembling, our single-model framework improves the soft mean average precision (softmAP) by 10 percent compared to the second-best method in the Waymo Interactive Prediction Leaderboard. Furthermore, the proposed framework has been successfully deployed on real vehicles, demonstrating its practical effectiveness in real-world applications.
A Large-Scale Study on Video Action Dataset Condensation
Dec 30, 2024Abstract:Dataset condensation has made significant progress in the image domain. Unlike images, videos possess an additional temporal dimension, which harbors considerable redundant information, making condensation even more crucial. However, video dataset condensation still remains an underexplored area. We aim to bridge this gap by providing a large-scale empirical study with systematic design and fair comparison. Specifically, our work delves into three key aspects to provide valuable empirical insights: (1) temporal processing of video data, (2) establishing a comprehensive evaluation protocol for video dataset condensation, and (3) adaptation of condensation methods to the space-time domain and fair comparisons among them. From this study, we derive several intriguing observations: (i) sample diversity appears to be more crucial than temporal diversity for video dataset condensation, (ii) simple slide-window sampling proves to be effective, and (iii) sample selection currently outperforms dataset distillation in most cases. Furthermore, we conduct experiments on three prominent action recognition datasets (HMDB51, UCF101 and Kinetics-400) and achieve state-of-the-art results on all of them. Our code is available at https://github.com/MCG-NJU/Video-DC.
FocusLLaVA: A Coarse-to-Fine Approach for Efficient and Effective Visual Token Compression
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances on Multi-modal Large Language Models have demonstrated that high-resolution image input is crucial for model capabilities, especially for fine-grained tasks. However, high-resolution images lead to a quadratic increase in the number of visual tokens input into LLMs, resulting in significant computational costs. Current work develop visual token compression methods to achieve efficiency improvements, often at the expense of performance. We argue that removing visual redundancy can simultaneously improve both efficiency and performance. We build a coarse-to-fine visual token compression method, with a vision-guided sampler for compressing redundant regions with low information density, and a text-guided sampler for selecting visual tokens that are strongly correlated with the user instructions.With these two modules, the proposed FocusLLaVA achieves improvements in both efficiency and performance. We validate the effectiveness of our approach on a wide range of evaluation datasets.
DexGrasp-Diffusion: Diffusion-based Unified Functional Grasp Synthesis Pipeline for Multi-Dexterous Robotic Hands
Jul 13, 2024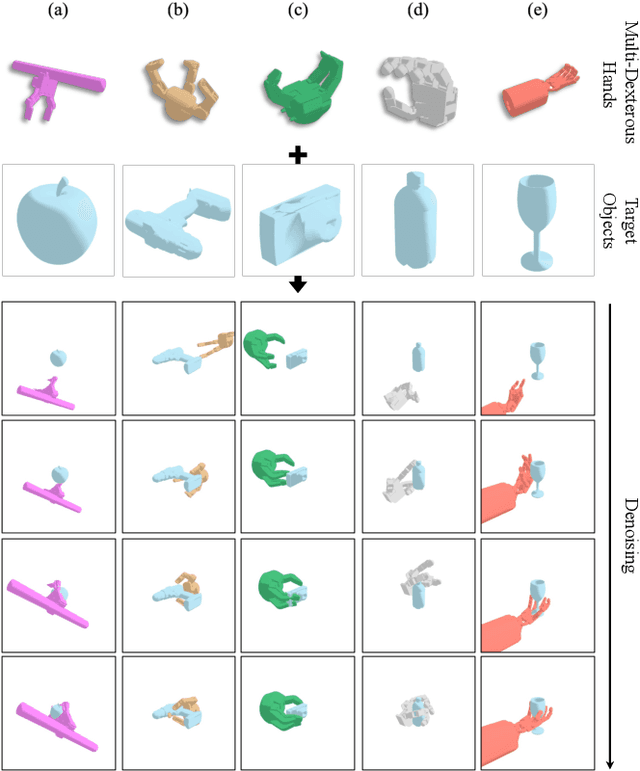
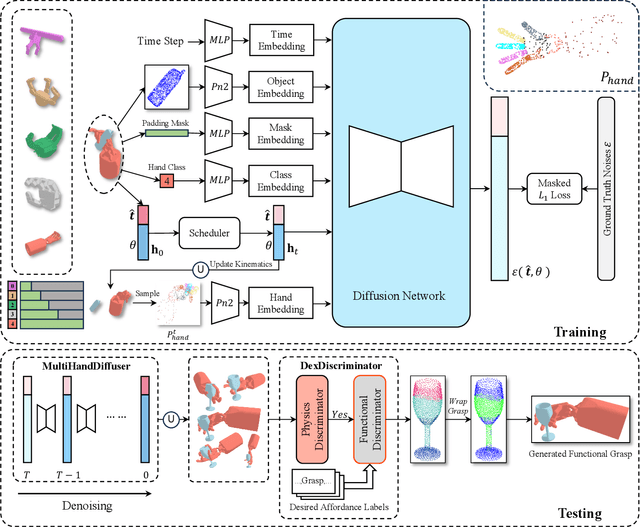

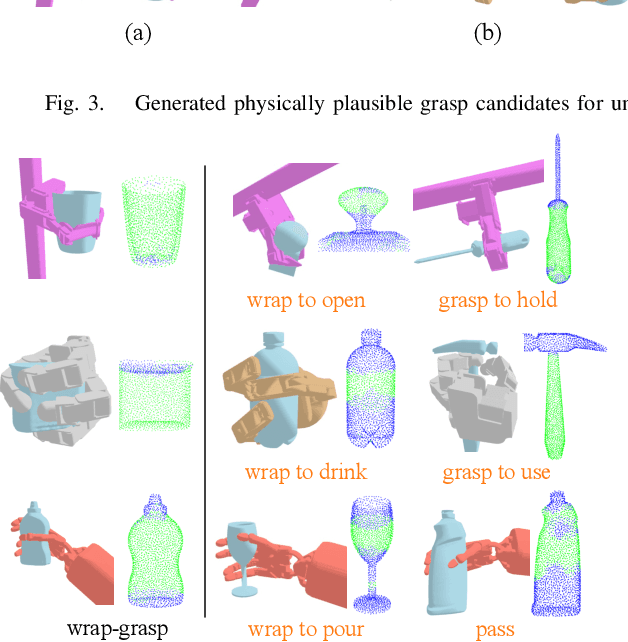
Abstract:The versatility and adaptability of human grasping catalyze advancing dexterous robotic manipulation. While significant strides have been made in dexterous grasp generation, current research endeavors pivot towards optimizing object manipulation while ensuring functional integrity, emphasizing the synthesis of functional grasps following desired affordance instructions. This paper addresses the challenge of synthesizing functional grasps tailored to diverse dexterous robotic hands by proposing DexGrasp-Diffusion, an end-to-end modularized diffusion-based pipeline. DexGrasp-Diffusion integrates MultiHandDiffuser, a novel unified data-driven diffusion model for multi-dexterous hands grasp estimation, with DexDiscriminator, which employs a Physics Discriminator and a Functional Discriminator with open-vocabulary setting to filter physically plausible functional grasps based on object affordances. The experimental evaluation conducted on the MultiDex dataset provides substantiating evidence supporting the superior performance of MultiHandDiffuser over the baseline model in terms of success rate, grasp diversity, and collision depth. Moreover, we demonstrate the capacity of DexGrasp-Diffusion to reliably generate functional grasps for household objects aligned with specific affordance instructions.
Edge Wasserstein Distance Loss for Oriented Object Detection
Dec 12, 2023Abstract:Regression loss design is an essential topic for oriented object detection. Due to the periodicity of the angle and the ambiguity of width and height definition, traditional L1-distance loss and its variants have been suffered from the metric discontinuity and the square-like problem. As a solution, the distribution based methods show significant advantages by representing oriented boxes as distributions. Differing from exploited the Gaussian distribution to get analytical form of distance measure, we propose a novel oriented regression loss, Wasserstein Distance(EWD) loss, to alleviate the square-like problem. Specifically, for the oriented box(OBox) representation, we choose a specially-designed distribution whose probability density function is only nonzero over the edges. On this basis, we develop Wasserstein distance as the measure. Besides, based on the edge representation of OBox, the EWD loss can be generalized to quadrilateral and polynomial regression scenarios. Experiments on multiple popular datasets and different detectors show the effectiveness of the proposed method.
StageInteractor: Query-based Object Detector with Cross-stage Interaction
Apr 11, 2023Abstract:Previous object detectors make predictions based on dense grid points or numerous preset anchors. Most of these detectors are trained with one-to-many label assignment strategies. On the contrary, recent query-based object detectors depend on a sparse set of learnable queries and a series of decoder layers. The one-to-one label assignment is independently applied on each layer for the deep supervision during training. Despite the great success of query-based object detection, however, this one-to-one label assignment strategy demands the detectors to have strong fine-grained discrimination and modeling capacity. To solve the above problems, in this paper, we propose a new query-based object detector with cross-stage interaction, coined as StageInteractor. During the forward propagation, we come up with an efficient way to improve this modeling ability by reusing dynamic operators with lightweight adapters. As for the label assignment, a cross-stage label assigner is applied subsequent to the one-to-one label assignment. With this assigner, the training target class labels are gathered across stages and then reallocated to proper predictions at each decoder layer. On MS COCO benchmark, our model improves the baseline by 2.2 AP, and achieves 44.8 AP with ResNet-50 as backbone, 100 queries and 12 training epochs. With longer training time and 300 queries, StageInteractor achieves 51.1 AP and 52.2 AP with ResNeXt-101-DCN and Swin-S, respectively.
PDPP:Projected Diffusion for Procedure Planning in Instructional Videos
Mar 26, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we study the problem of procedure planning in instructional videos, which aims to make goal-directed plans given the current visual observations in unstructured real-life videos. Previous works cast this problem as a sequence planning problem and leverage either heavy intermediate visual observations or natural language instructions as supervision, resulting in complex learning schemes and expensive annotation costs. In contrast, we treat this problem as a distribution fitting problem. In this sense, we model the whole intermediate action sequence distribution with a diffusion model (PDPP), and thus transform the planning problem to a sampling process from this distribution. In addition, we remove the expensive intermediate supervision, and simply use task labels from instructional videos as supervision instead. Our model is a U-Net based diffusion model, which directly samples action sequences from the learned distribution with the given start and end observations. Furthermore, we apply an efficient projection method to provide accurate conditional guides for our model during the learning and sampling process. Experiments on three datasets with different scales show that our PDPP model can achieve the state-of-the-art performance on multiple metrics, even without the task supervision. Code and trained models are available at https://github.com/MCG-NJU/PDPP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge