Han Yu
Federated Learning Playground
Feb 23, 2026Abstract:We present Federated Learning Playground, an interactive browser-based platform inspired by and extends TensorFlow Playground that teaches core Federated Learning (FL) concepts. Users can experiment with heterogeneous client data distributions, model hyperparameters, and aggregation algorithms directly in the browser without coding or system setup, and observe their effects on client and global models through real-time visualizations, gaining intuition for challenges such as non-IID data, local overfitting, and scalability. The playground serves as an easy to use educational tool, lowering the entry barrier for newcomers to distributed AI while also offering a sandbox for rapidly prototyping and comparing FL methods. By democratizing exploration of FL, it promotes broader understanding and adoption of this important paradigm.
TextResNet: Decoupling and Routing Optimization Signals in Compound AI Systems via Deep Residual Tuning
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Textual Gradient-style optimizers (TextGrad) enable gradient-like feedback propagation through compound AI systems. However, they do not work well for deep chains. The root cause of this limitation stems from the Semantic Entanglement problem in these extended workflows. In standard textual backpropagation, feedback signals mix local critiques with upstream contexts, leading to Attribution Ambiguity. To address this challenge, we propose TextResNet, a framework that reformulates the optimization process to achieve precise signal routing via four key innovations. Firstly, in the forward pass, it enforces Additive Semantic Deltas to preserve an Identity Highway for gradient flow. Secondly, in the backward pass, it introduces Semantic Gradient Decomposition via a Semantic Projector to disentangle feedback into causally independent subspaces. Thirdly, it implements Causal Routing, which routes projected signals to their specific components. Finally, it performs Density-Aware Optimization Scheduling to leverage the disentangled signals to dynamically allocate resources to key system bottlenecks. Our results show that TextResNet not only achieves superior performance compared to TextGrad, but also exhibits remarkable stability for agentic tasks in compound AI systems where baselines collapse. Code is available at https://github.com/JeanDiable/TextResNet.
AnomSeer: Reinforcing Multimodal LLMs to Reason for Time-Series Anomaly Detection
Feb 09, 2026Abstract:Time-series anomaly detection (TSAD) with multimodal large language models (MLLMs) is an emerging area, yet a persistent challenge remains: MLLMs rely on coarse time-series heuristics but struggle with multi-dimensional, detailed reasoning, which is vital for understanding complex time-series data. We present AnomSeer to address this by reinforcing the model to ground its reasoning in precise, structural details of time series, unifying anomaly classification, localization, and explanation. At its core, an expert chain-of-thought trace is generated to provide a verifiable, fine-grained reasoning from classical analyses (e.g., statistical measures, frequency transforms). Building on this, we propose a novel time-series grounded policy optimization (TimerPO) that incorporates two additional components beyond standard reinforcement learning: a time-series grounded advantage based on optimal transport and an orthogonal projection to ensure this auxiliary granular signal does not interfere with the primary detection objective. Across diverse anomaly scenarios, AnomSeer, with Qwen2.5-VL-3B/7B-Instruct, outperforms larger commercial baselines (e.g., GPT-4o) in classification and localization accuracy, particularly on point- and frequency-driven exceptions. Moreover, it produces plausible time-series reasoning traces that support its conclusions.
Rethinking LoRA for Data Heterogeneous Federated Learning: Subspace and State Alignment
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) is widely used for federated fine-tuning. Yet under non-IID settings, it can substantially underperform full-parameter fine-tuning. Through with-high-probability robustness analysis, we uncover that this gap can be attributed to two coupled mismatches: (i) update-space mismatch, where clients optimize in a low-rank subspace but aggregation occurs in the full space; and (ii) optimizer-state mismatch, where unsynchronized adaptive states amplify drift across rounds. We propose FedGaLore, which combines client-side GaLore-style gradient-subspace optimization with server-side drift-robust synchronization of projected second-moment states via spectral shared-signal extraction, to address this challenge. Across NLU, vision, and NLG benchmarks, FedGaLore improves robustness and accuracy over state-of-the-art federated LoRA baselines in non-IID settings.
Robust and Generalized Humanoid Motion Tracking
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Learning a general humanoid whole-body controller is challenging because practical reference motions can exhibit noise and inconsistencies after being transferred to the robot domain, and local defects may be amplified by closed-loop execution, causing drift or failure in highly dynamic and contact-rich behaviors. We propose a dynamics-conditioned command aggregation framework that uses a causal temporal encoder to summarize recent proprioception and a multi-head cross-attention command encoder to selectively aggregate a context window based on the current dynamics. We further integrate a fall recovery curriculum with random unstable initialization and an annealed upward assistance force to improve robustness and disturbance rejection. The resulting policy requires only about 3.5 hours of motion data and supports single-stage end-to-end training without distillation. The proposed method is evaluated under diverse reference inputs and challenging motion regimes, demonstrating zero-shot transfer to unseen motions as well as robust sim-to-real transfer on a physical humanoid robot.
A Federated and Parameter-Efficient Framework for Large Language Model Training in Medicine
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong performance on medical benchmarks, including question answering and diagnosis. To enable their use in clinical settings, LLMs are typically further adapted through continued pretraining or post-training using clinical data. However, most medical LLMs are trained on data from a single institution, which faces limitations in generalizability and safety in heterogeneous systems. Federated learning (FL) is a promising solution for enabling collaborative model development across healthcare institutions. Yet applying FL to LLMs in medicine remains fundamentally limited. First, conventional FL requires transmitting the full model during each communication round, which becomes impractical for multi-billion-parameter LLMs given the limited computational resources. Second, many FL algorithms implicitly assume data homogeneity, whereas real-world clinical data are highly heterogeneous across patients, diseases, and institutional practices. We introduce the model-agnostic and parameter-efficient federated learning framework for adapting LLMs to medical applications. Fed-MedLoRA transmits only low-rank adapter parameters, reducing communication and computation overhead, while Fed-MedLoRA+ further incorporates adaptive, data-aware aggregation to improve convergence under cross-site heterogeneity. We apply the framework to clinical information extraction (IE), which transforms patient narratives into structured medical entities and relations. Accuracy was assessed across five patient cohorts through comparisons with BERT models, and LLaMA-3 and DeepSeek-R1, GPT-4o models. Evaluation settings included (1) in-domain training and testing, (2) external validation on independent cohorts, and (3) a low-resource new-site adaptation scenario using real-world clinical notes from the Yale New Haven Health System.
Textual Equilibrium Propagation for Deep Compound AI Systems
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed as part of compound AI systems that coordinate multiple modules (e.g., retrievers, tools, verifiers) over long-horizon workflows. Recent approaches that propagate textual feedback globally (e.g., TextGrad) make it feasible to optimize such pipelines, but we find that performance degrades as system depth grows. In particular, long-horizon agentic workflows exhibit two depth-scaling failure modes: 1) exploding textual gradient, where textual feedback grows exponentially with depth, leading to prohibitively long message and amplifies evaluation biases; and 2) vanishing textual gradient, where limited long-context ability causes models overemphasize partial feedback and compression of lengthy feedback causes downstream messages to lose specificity gradually as they propagate many hops upstream. To mitigate these issues, we introduce Textual Equilibrium Propagation (TEP), a local learning principle inspired by Equilibrium Propagation in energy-based models. TEP includes two phases: 1) a free phase where a local LLM critics iteratively refine prompts until reaching equilibrium (no further improvements are suggested); and 2) a nudged phase which applies proximal prompt edits with bounded modification intensity, using task-level objectives that propagate via forward signaling rather than backward feedback chains. This design supports local prompt optimization followed by controlled adaptation toward global goals without the computational burden and signal degradation of global textual backpropagation. Across long-horizon QA benchmarks and multi-agent tool-use dataset, TEP consistently improves accuracy and efficiency over global propagation methods such as TextGrad. The gains grows with depth, while preserving the practicality of black-box LLM components in deep compound AI system.
Generating Risky Samples with Conformity Constraints via Diffusion Models
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:Although neural networks achieve promising performance in many tasks, they may still fail when encountering some examples and bring about risks to applications. To discover risky samples, previous literature attempts to search for patterns of risky samples within existing datasets or inject perturbation into them. Yet in this way the diversity of risky samples is limited by the coverage of existing datasets. To overcome this limitation, recent works adopt diffusion models to produce new risky samples beyond the coverage of existing datasets. However, these methods struggle in the conformity between generated samples and expected categories, which could introduce label noise and severely limit their effectiveness in applications. To address this issue, we propose RiskyDiff that incorporates the embeddings of both texts and images as implicit constraints of category conformity. We also design a conformity score to further explicitly strengthen the category conformity, as well as introduce the mechanisms of embedding screening and risky gradient guidance to boost the risk of generated samples. Extensive experiments reveal that RiskyDiff greatly outperforms existing methods in terms of the degree of risk, generation quality, and conformity with conditioned categories. We also empirically show the generalization ability of the models can be enhanced by augmenting training data with generated samples of high conformity.
Hybrid Iterative Detection for OTFS: Interplay between Local L-MMSE and Global Message Passing
Dec 16, 2025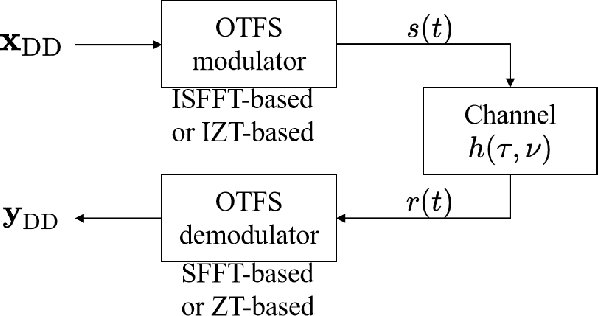
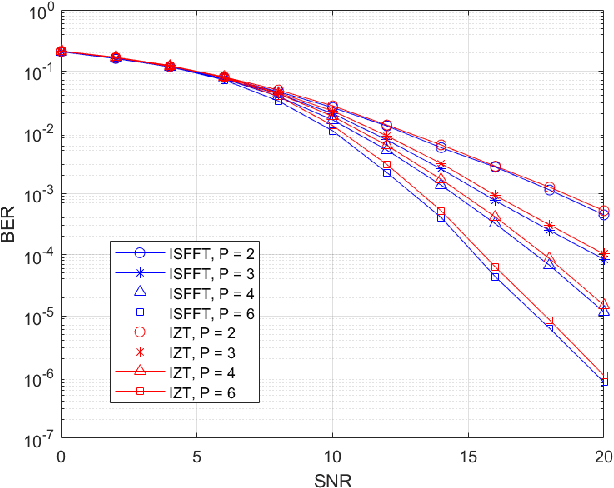
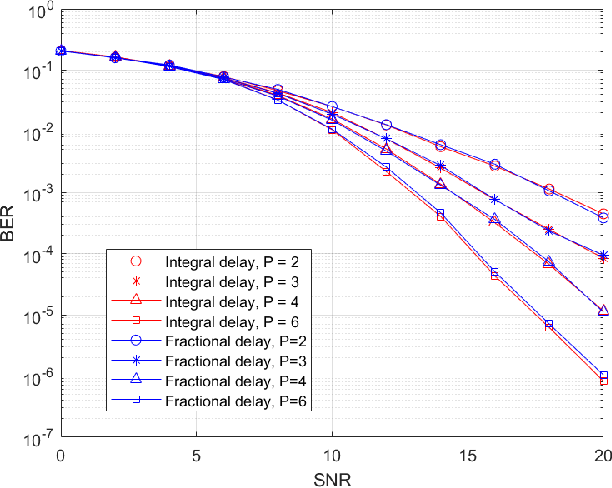
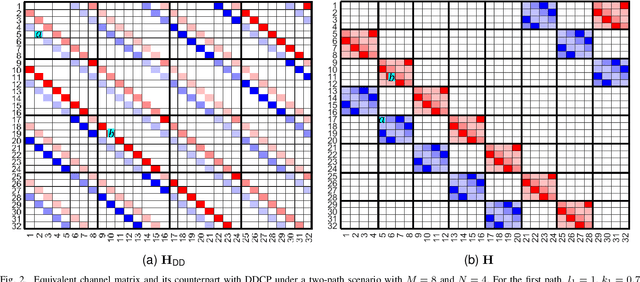
Abstract:Orthogonal time frequency space (OTFS) modulation has emerged as a robust solution for high-mobility wireless communications. However, conventional detection algorithms, such as linear equalizers and message passing (MP) methods, either suffer from noise enhancement or fail under complex doubly-selective channels, especially in the presence of fractional delay and Doppler shifts. In this paper, we propose a hybrid low-complexity iterative detection framework that combines linear minimum mean square error (L-MMSE) estimation with MP-based probabilistic inference. The key idea is to apply a new delay-Doppler (DD) commutation precoder (DDCP) to the DD domain signal vector, such that the resulting effective channel matrix exhibits a structured form with several locally dense blocks that are sparsely inter-connected. This precoding structure enables a hybrid iterative detection strategy, where a low-dimensional L-MMSE estimation is applied to the dense blocks, while MP is utilized to exploit the sparse inter-block connections. Furthermore, we provide a detailed complexity analysis, which shows that the proposed scheme incurs lower computational cost compared to the full-size L-MMSE detection. The simulation results of convergence performance confirm that the proposed hybrid MP detection achieves fast and reliable convergence with controlled complexity. In terms of error performance, simulation results demonstrate that our scheme achieves significantly better bit error rate (BER) under various channel conditions. Particularly in multipath scenarios, the BER performance of the proposed method closely approaches the matched filter bound (MFB), indicating its near-optimal error performance.
Enhancing Logical Expressiveness in Graph Neural Networks via Path-Neighbor Aggregation
Nov 13, 2025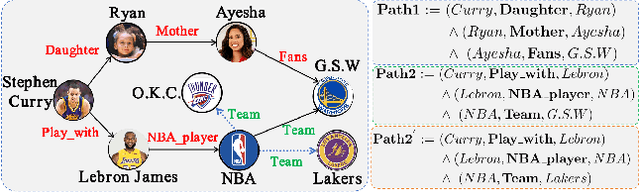
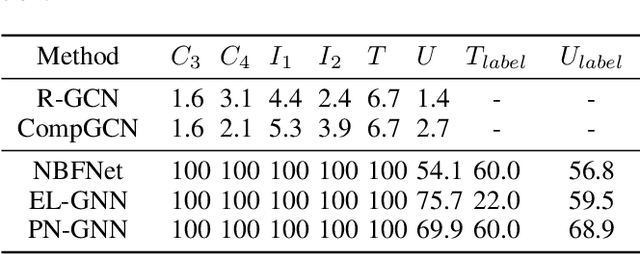
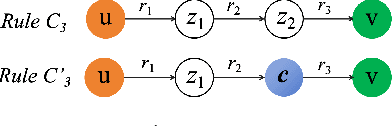
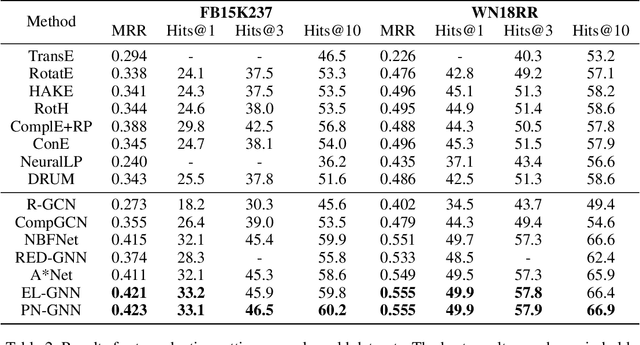
Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) can effectively model structural information of graphs, making them widely used in knowledge graph (KG) reasoning. However, existing studies on the expressive power of GNNs mainly focuses on simple single-relation graphs, and there is still insufficient discussion on the power of GNN to express logical rules in KGs. How to enhance the logical expressive power of GNNs is still a key issue. Motivated by this, we propose Path-Neighbor enhanced GNN (PN-GNN), a method to enhance the logical expressive power of GNN by aggregating node-neighbor embeddings on the reasoning path. First, we analyze the logical expressive power of existing GNN-based methods and point out the shortcomings of the expressive power of these methods. Then, we theoretically investigate the logical expressive power of PN-GNN, showing that it not only has strictly stronger expressive power than C-GNN but also that its $(k+1)$-hop logical expressiveness is strictly superior to that of $k$-hop. Finally, we evaluate the logical expressive power of PN-GNN on six synthetic datasets and two real-world datasets. Both theoretical analysis and extensive experiments confirm that PN-GNN enhances the expressive power of logical rules without compromising generalization, as evidenced by its competitive performance in KG reasoning tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge