Yaochu Jin
IRIS: Implicit Reward-Guided Internal Sifting for Mitigating Multimodal Hallucination
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Hallucination remains a fundamental challenge for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). While Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) is a key alignment framework, existing approaches often rely heavily on costly external evaluators for scoring or rewriting, incurring off-policy learnability gaps and discretization loss. Due to the lack of access to internal states, such feedback overlooks the fine-grained conflicts between different modalities that lead to hallucinations during generation. To address this issue, we propose IRIS (Implicit Reward-Guided Internal Sifting), which leverages continuous implicit rewards in the native log-probability space to preserve full information density and capture internal modal competition. This on-policy paradigm eliminates learnability gaps by utilizing self-generated preference pairs. By sifting these pairs based on multimodal implicit rewards, IRIS ensures that optimization is driven by signals that directly resolve modal conflicts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that IRIS achieves highly competitive performance on key hallucination benchmarks using only 5.7k samples, without requiring any external feedback during preference alignment. These results confirm that IRIS provides an efficient and principled paradigm for mitigating MLLM hallucinations.
Scaling Behaviors of Evolutionary Algorithms on GPUs: When Does Parallelism Pay Off?
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Evolutionary algorithms (EAs) are increasingly implemented on graphics processing units (GPUs) to leverage parallel processing capabilities for enhanced efficiency. However, existing studies largely emphasize the raw speedup obtained by porting individual algorithms from CPUs to GPUs. Consequently, these studies offer limited insight into when and why GPU parallelism fundamentally benefits EAs. To address this gap, we investigate how GPU parallelism alters the behavior of EAs beyond simple acceleration metrics. We conduct a systematic empirical study of 16 representative EAs on 30 benchmark problems. Specifically, we compare CPU and GPU executions across a wide range of problem dimensionalities and population sizes. Our results reveal that the impact of GPU acceleration is highly heterogeneous and depends strongly on algorithmic structure. We further demonstrate that conventional fixed-budget evaluation based on the number of function evaluations (FEs) is inadequate for GPU execution. In contrast, fixed-time evaluation uncovers performance characteristics that are unobservable under small or practically constrained FE budgets, particularly for adaptive and exploration-oriented algorithms. Moreover, we identify distinct scaling regimes in which GPU parallelism is beneficial, saturates, or degrades as problem dimensionality and population size increase. Crucially, we show that large populations enabled by GPUs not only improve hardware utilization but also reveal algorithm-specific convergence and diversity dynamics that are difficult to observe under CPU-constrained settings. Consequently, our findings indicate that GPU parallelism is not strictly an implementation detail, but a pivotal factor that influences how EAs should be evaluated, compared, and designed for modern computing platforms.
Overlooked Safety Vulnerability in LLMs: Malicious Intelligent Optimization Algorithm Request and its Jailbreak
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:The widespread deployment of large language models (LLMs) has raised growing concerns about their misuse risks and associated safety issues. While prior studies have examined the safety of LLMs in general usage, code generation, and agent-based applications, their vulnerabilities in automated algorithm design remain underexplored. To fill this gap, this study investigates this overlooked safety vulnerability, with a particular focus on intelligent optimization algorithm design, given its prevalent use in complex decision-making scenarios. We introduce MalOptBench, a benchmark consisting of 60 malicious optimization algorithm requests, and propose MOBjailbreak, a jailbreak method tailored for this scenario. Through extensive evaluation of 13 mainstream LLMs including the latest GPT-5 and DeepSeek-V3.1, we reveal that most models remain highly susceptible to such attacks, with an average attack success rate of 83.59% and an average harmfulness score of 4.28 out of 5 on original harmful prompts, and near-complete failure under MOBjailbreak. Furthermore, we assess state-of-the-art plug-and-play defenses that can be applied to closed-source models, and find that they are only marginally effective against MOBjailbreak and prone to exaggerated safety behaviors. These findings highlight the urgent need for stronger alignment techniques to safeguard LLMs against misuse in algorithm design.
Self-motion as a structural prior for coherent and robust formation of cognitive maps
Dec 23, 2025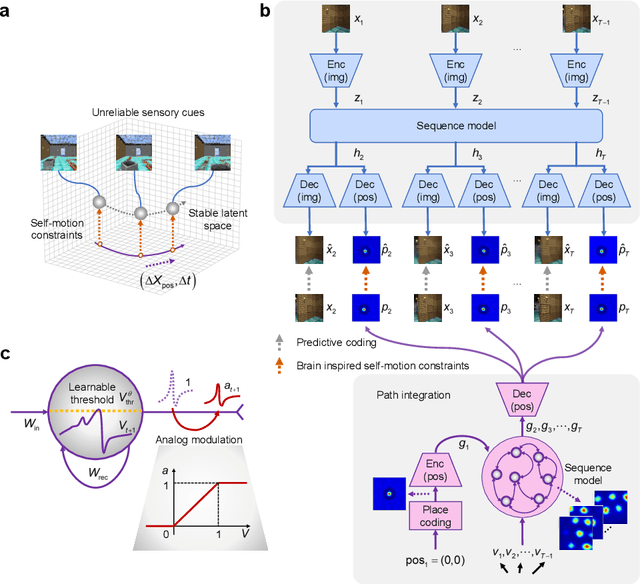
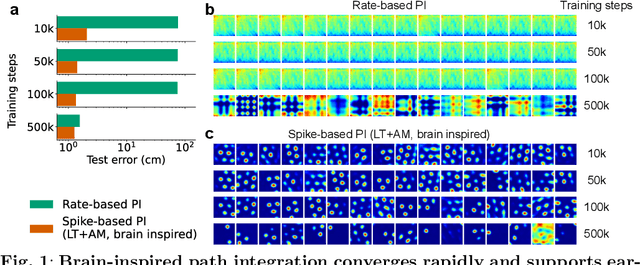
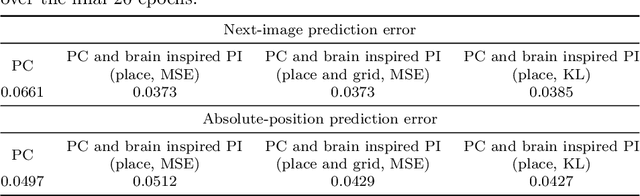
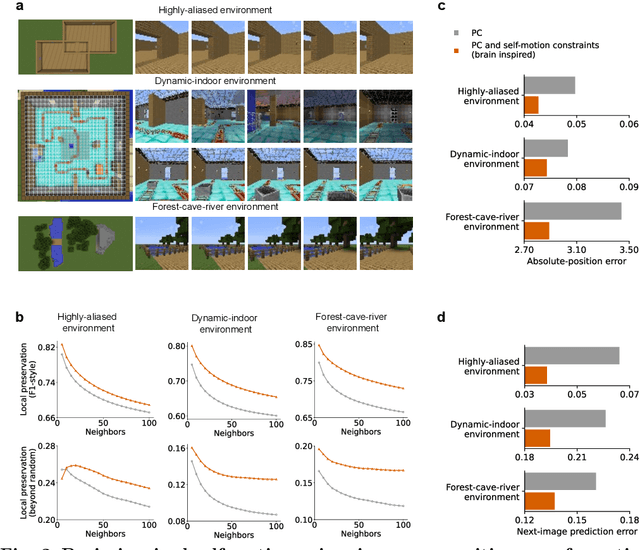
Abstract:Most computational accounts of cognitive maps assume that stability is achieved primarily through sensory anchoring, with self-motion contributing to incremental positional updates only. However, biological spatial representations often remain coherent even when sensory cues degrade or conflict, suggesting that self-motion may play a deeper organizational role. Here, we show that self-motion can act as a structural prior that actively organizes the geometry of learned cognitive maps. We embed a path-integration-based motion prior in a predictive-coding framework, implemented using a capacity-efficient, brain-inspired recurrent mechanism combining spiking dynamics, analog modulation and adaptive thresholds. Across highly aliased, dynamically changing and naturalistic environments, this structural prior consistently stabilizes map formation, improving local topological fidelity, global positional accuracy and next-step prediction under sensory ambiguity. Mechanistic analyses reveal that the motion prior itself encodes geometrically precise trajectories under tight constraints of internal states and generalizes zero-shot to unseen environments, outperforming simpler motion-based constraints. Finally, deployment on a quadrupedal robot demonstrates that motion-derived structural priors enhance online landmark-based navigation under real-world sensory variability. Together, these results reframe self-motion as an organizing scaffold for coherent spatial representations, showing how brain-inspired principles can systematically strengthen spatial intelligence in embodied artificial agents.
OmniMER: Indonesian Multimodal Emotion Recognition via Auxiliary-Enhanced LLM Adaptation
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Indonesian, spoken by over 200 million people, remains underserved in multimodal emotion recognition research despite its dominant presence on Southeast Asian social media platforms. We introduce IndoMER, the first multimodal emotion recognition benchmark for Indonesian, comprising 1,944 video segments from 203 speakers with temporally aligned text, audio, and visual annotations across seven emotion categories. The dataset exhibits realistic challenges including cross-modal inconsistency and long-tailed class distributions shaped by Indonesian cultural communication norms. To address these challenges, we propose OmniMER, a multimodal adaptation framework built upon Qwen2.5-Omni that enhances emotion recognition through three auxiliary modality-specific perception tasks: emotion keyword extraction for text, facial expression analysis for video, and prosody analysis for audio. These auxiliary tasks help the model identify emotion-relevant cues in each modality before fusion, reducing reliance on spurious correlations in low-resource settings. Experiments on IndoMER show that OmniMER achieves 0.582 Macro-F1 on sentiment classification and 0.454 on emotion recognition, outperforming the base model by 7.6 and 22.1 absolute points respectively. Cross-lingual evaluation on the Chinese CH-SIMS dataset further demonstrates the generalizability of the proposed framework. The dataset and code are publicly available. https://github.com/yanxm01/INDOMER
LacaDM: A Latent Causal Diffusion Model for Multiobjective Reinforcement Learning
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Multiobjective reinforcement learning (MORL) poses significant challenges due to the inherent conflicts between objectives and the difficulty of adapting to dynamic environments. Traditional methods often struggle to generalize effectively, particularly in large and complex state-action spaces. To address these limitations, we introduce the Latent Causal Diffusion Model (LacaDM), a novel approach designed to enhance the adaptability of MORL in discrete and continuous environments. Unlike existing methods that primarily address conflicts between objectives, LacaDM learns latent temporal causal relationships between environmental states and policies, enabling efficient knowledge transfer across diverse MORL scenarios. By embedding these causal structures within a diffusion model-based framework, LacaDM achieves a balance between conflicting objectives while maintaining strong generalization capabilities in previously unseen environments. Empirical evaluations on various tasks from the MOGymnasium framework demonstrate that LacaDM consistently outperforms the state-of-art baselines in terms of hypervolume, sparsity, and expected utility maximization, showcasing its effectiveness in complex multiobjective tasks.
Solver-Independent Automated Problem Formulation via LLMs for High-Cost Simulation-Driven Design
Dec 21, 2025Abstract:In the high-cost simulation-driven design domain, translating ambiguous design requirements into a mathematical optimization formulation is a bottleneck for optimizing product performance. This process is time-consuming and heavily reliant on expert knowledge. While large language models (LLMs) offer potential for automating this task, existing approaches either suffer from poor formalization that fails to accurately align with the design intent or rely on solver feedback for data filtering, which is unavailable due to the high simulation costs. To address this challenge, we propose APF, a framework for solver-independent, automated problem formulation via LLMs designed to automatically convert engineers' natural language requirements into executable optimization models. The core of this framework is an innovative pipeline for automatically generating high-quality data, which overcomes the difficulty of constructing suitable fine-tuning datasets in the absence of high-cost solver feedback with the help of data generation and test instance annotation. The generated high-quality dataset is used to perform supervised fine-tuning on LLMs, significantly enhancing their ability to generate accurate and executable optimization problem formulations. Experimental results on antenna design demonstrate that APF significantly outperforms the existing methods in both the accuracy of requirement formalization and the quality of resulting radiation efficiency curves in meeting the design goals.
Robustness of Probabilistic Models to Low-Quality Data: A Multi-Perspective Analysis
Dec 11, 2025



Abstract:A systematic, comparative investigation into the effects of low-quality data reveals a stark spectrum of robustness across modern probabilistic models. We find that autoregressive language models, from token prediction to sequence-to-sequence tasks, are remarkably resilient (for GPT-2, test NLL increases modestly from 2.87 to 3.59 despite 50% token corruption). By contrast, under the same levels of data corruption, class-conditional diffusion models degrade catastrophically (image-label consistency plummets by 56.81% relative to baseline), while classifiers show a moderate impact that diminishes with dataset scale. To explain these discrepancies, we analyze the results through a multi-perspective lens, integrating information theory, PAC learning, and gradient dynamics. These analyses suggest that robustness is heavily influenced by two key principles: the richness of conditioning information, which constrains the learning problem, and the absolute information content of the training data, which allows the signal from correct information to dominate statistical noise.
HCPO: Hierarchical Conductor-Based Policy Optimization in Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
Nov 15, 2025Abstract:In cooperative Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL), efficient exploration is crucial for optimizing the performance of joint policy. However, existing methods often update joint policies via independent agent exploration, without coordination among agents, which inherently constrains the expressive capacity and exploration of joint policies. To address this issue, we propose a conductor-based joint policy framework that directly enhances the expressive capacity of joint policies and coordinates exploration. In addition, we develop a Hierarchical Conductor-based Policy Optimization (HCPO) algorithm that instructs policy updates for the conductor and agents in a direction aligned with performance improvement. A rigorous theoretical guarantee further establishes the monotonicity of the joint policy optimization process. By deploying local conductors, HCPO retains centralized training benefits while eliminating inter-agent communication during execution. Finally, we evaluate HCPO on three challenging benchmarks: StarCraftII Multi-agent Challenge, Multi-agent MuJoCo, and Multi-agent Particle Environment. The results indicate that HCPO outperforms competitive MARL baselines regarding cooperative efficiency and stability.
OutSafe-Bench: A Benchmark for Multimodal Offensive Content Detection in Large Language Models
Nov 13, 2025



Abstract:Since Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) are increasingly being integrated into everyday tools and intelligent agents, growing concerns have arisen regarding their possible output of unsafe contents, ranging from toxic language and biased imagery to privacy violations and harmful misinformation. Current safety benchmarks remain highly limited in both modality coverage and performance evaluations, often neglecting the extensive landscape of content safety. In this work, we introduce OutSafe-Bench, the first most comprehensive content safety evaluation test suite designed for the multimodal era. OutSafe-Bench includes a large-scale dataset that spans four modalities, featuring over 18,000 bilingual (Chinese and English) text prompts, 4,500 images, 450 audio clips and 450 videos, all systematically annotated across nine critical content risk categories. In addition to the dataset, we introduce a Multidimensional Cross Risk Score (MCRS), a novel metric designed to model and assess overlapping and correlated content risks across different categories. To ensure fair and robust evaluation, we propose FairScore, an explainable automated multi-reviewer weighted aggregation framework. FairScore selects top-performing models as adaptive juries, thereby mitigating biases from single-model judgments and enhancing overall evaluation reliability. Our evaluation of nine state-of-the-art MLLMs reveals persistent and substantial safety vulnerabilities, underscoring the pressing need for robust safeguards in MLLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge