Kaizhu Huang
SynthVerse: A Large-Scale Diverse Synthetic Dataset for Point Tracking
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Point tracking aims to follow visual points through complex motion, occlusion, and viewpoint changes, and has advanced rapidly with modern foundation models. Yet progress toward general point tracking remains constrained by limited high-quality data, as existing datasets often provide insufficient diversity and imperfect trajectory annotations. To this end, we introduce SynthVerse, a large-scale, diverse synthetic dataset specifically designed for point tracking. SynthVerse includes several new domains and object types missing from existing synthetic datasets, such as animated-film-style content, embodied manipulation, scene navigation, and articulated objects. SynthVerse substantially expands dataset diversity by covering a broader range of object categories and providing high-quality dynamic motions and interactions, enabling more robust training and evaluation for general point tracking. In addition, we establish a highly diverse point tracking benchmark to systematically evaluate state-of-the-art methods under broader domain shifts. Extensive experiments and analyses demonstrate that training with SynthVerse yields consistent improvements in generalization and reveal limitations of existing trackers under diverse settings.
Pareto-Guided Optimization for Uncertainty-Aware Medical Image Segmentation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Uncertainty in medical image segmentation is inherently non-uniform, with boundary regions exhibiting substantially higher ambiguity than interior areas. Conventional training treats all pixels equally, leading to unstable optimization during early epochs when predictions are unreliable. We argue that this instability hinders convergence toward Pareto-optimal solutions and propose a region-wise curriculum strategy that prioritizes learning from certain regions and gradually incorporates uncertain ones, reducing gradient variance. Methodologically, we introduce a Pareto-consistent loss that balances trade-offs between regional uncertainties by adaptively reshaping the loss landscape and constraining convergence dynamics between interior and boundary regions; this guides the model toward Pareto-approximate solutions. To address boundary ambiguity, we further develop a fuzzy labeling mechanism that maintains binary confidence in non-boundary areas while enabling smooth transitions near boundaries, stabilizing gradients, and expanding flat regions in the loss surface. Experiments on brain metastasis and non-metastatic tumor segmentation show consistent improvements across multiple configurations, with our method outperforming traditional crisp-set approaches in all tumor subregions.
Towards Faithful Reasoning in Comics for Small MLLMs
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Comic-based visual question answering (CVQA) poses distinct challenges to multimodal large language models (MLLMs) due to its reliance on symbolic abstraction, narrative logic, and humor, which differ from conventional VQA tasks. Although Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting is widely used to enhance MLLM reasoning, surprisingly, its direct application to CVQA often degrades performance, especially in small-scale models. Our theoretical and empirical analyses reveal that standard CoT in CVQA suffers from state entanglement, spurious transitions, and exploration inefficiency, with small models particularly vulnerable in resource-constrained settings. To address these issues, we propose a novel comic reasoning framework, designed to produce more faithful and transferable reasoning chains in small MLLMs. Specifically, our framework combines modular CoT generation with GRPO-based reinforcement fine-tuning and a novel structured reward. Beyond comic VQA, we further evaluate our approach on a broader class of humor-centric and abstract visual reasoning tasks, including meme understanding and editorial cartoon interpretation. Across five challenging benchmarks, our 3B model outperforms state-of-the-art methods, and plug-in experiments yield an additional average improvement of $\mathbf{12.1\%}$ across different MLLMs.
Can MLLMs Absorb Math Reasoning Abilities from LLMs as Free Lunch?
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Math reasoning has been one crucial ability of large language models (LLMs), where significant advancements have been achieved in recent years. However, most efforts focus on LLMs by curating high-quality annotation data and intricate training (or inference) paradigms, while the math reasoning performance of multi-modal LLMs (MLLMs) remains lagging behind. Since the MLLM typically consists of an LLM and a vision block, we wonder: Can MLLMs directly absorb math reasoning abilities from off-the-shelf math LLMs without tuning? Recent model-merging approaches may offer insights into this question. However, they overlook the alignment between the MLLM and LLM, where we find that there is a large gap between their parameter spaces, resulting in lower performance. Our empirical evidence reveals two key factors behind this issue: the identification of crucial reasoning-associated layers in the model and the mitigation of the gaps in parameter space. Based on the empirical insights, we propose IP-Merging that first identifies the reasoning-associated parameters in both MLLM and Math LLM, then projects them into the subspace of MLLM, aiming to maintain the alignment, and finally merges parameters in this subspace. IP-Merging is a tuning-free approach since parameters are directly adjusted. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our IP-Merging method can enhance the math reasoning ability of MLLMs directly from Math LLMs without compromising their other capabilities.
The Demon is in Ambiguity: Revisiting Situation Recognition with Single Positive Multi-Label Learning
Aug 29, 2025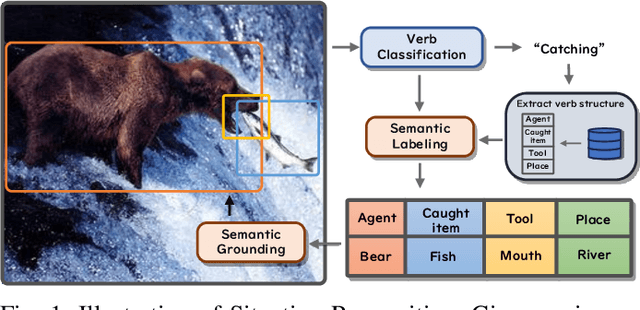
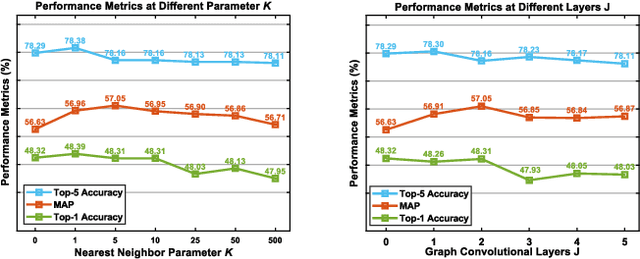
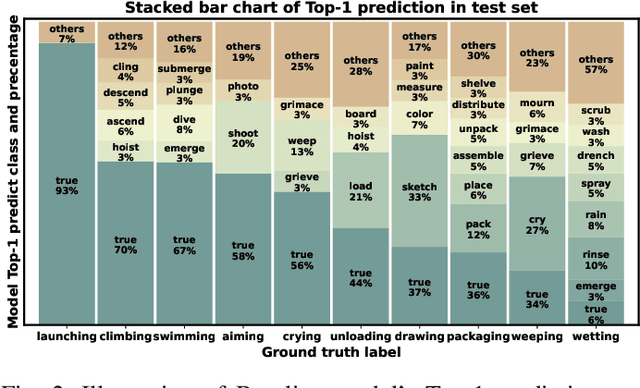
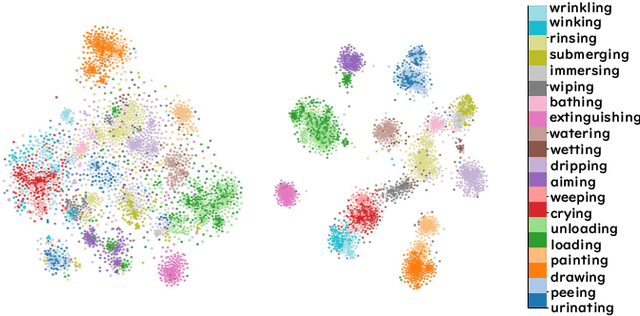
Abstract:Context recognition (SR) is a fundamental task in computer vision that aims to extract structured semantic summaries from images by identifying key events and their associated entities. Specifically, given an input image, the model must first classify the main visual events (verb classification), then identify the participating entities and their semantic roles (semantic role labeling), and finally localize these entities in the image (semantic role localization). Existing methods treat verb classification as a single-label problem, but we show through a comprehensive analysis that this formulation fails to address the inherent ambiguity in visual event recognition, as multiple verb categories may reasonably describe the same image. This paper makes three key contributions: First, we reveal through empirical analysis that verb classification is inherently a multi-label problem due to the ubiquitous semantic overlap between verb categories. Second, given the impracticality of fully annotating large-scale datasets with multiple labels, we propose to reformulate verb classification as a single positive multi-label learning (SPMLL) problem - a novel perspective in SR research. Third, we design a comprehensive multi-label evaluation benchmark for SR that is carefully designed to fairly evaluate model performance in a multi-label setting. To address the challenges of SPMLL, we futher develop the Graph Enhanced Verb Multilayer Perceptron (GE-VerbMLP), which combines graph neural networks to capture label correlations and adversarial training to optimize decision boundaries. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets show that our approach achieves more than 3\% MAP improvement while remaining competitive on traditional top-1 and top-5 accuracy metrics.
Exploiting Layer Normalization Fine-tuning in Visual Transformer Foundation Models for Classification
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:LayerNorm is pivotal in Vision Transformers (ViTs), yet its fine-tuning dynamics under data scarcity and domain shifts remain underexplored. This paper shows that shifts in LayerNorm parameters after fine-tuning (LayerNorm shifts) are indicative of the transitions between source and target domains; its efficacy is contingent upon the degree to which the target training samples accurately represent the target domain, as quantified by our proposed Fine-tuning Shift Ratio ($FSR$). Building on this, we propose a simple yet effective rescaling mechanism using a scalar $\lambda$ that is negatively correlated to $FSR$ to align learned LayerNorm shifts with those ideal shifts achieved under fully representative data, combined with a cyclic framework that further enhances the LayerNorm fine-tuning. Extensive experiments across natural and pathological images, in both in-distribution (ID) and out-of-distribution (OOD) settings, and various target training sample regimes validate our framework. Notably, OOD tasks tend to yield lower $FSR$ and higher $\lambda$ in comparison to ID cases, especially with scarce data, indicating under-represented target training samples. Moreover, ViTFs fine-tuned on pathological data behave more like ID settings, favoring conservative LayerNorm updates. Our findings illuminate the underexplored dynamics of LayerNorm in transfer learning and provide practical strategies for LayerNorm fine-tuning.
GeoSDF: Plane Geometry Diagram Synthesis via Signed Distance Field
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Plane Geometry Diagram Synthesis has been a crucial task in computer graphics, with applications ranging from educational tools to AI-driven mathematical reasoning. Traditionally, we rely on computer tools (e.g., Matplotlib and GeoGebra) to manually generate precise diagrams, but it usually requires huge, complicated calculations cost. Recently, researchers start to work on learning-based methods (e.g., Stable Diffusion and GPT4) to automatically generate diagrams, saving operational cost but usually suffering from limited realism and insufficient accuracy. In this paper, we propose a novel framework GeoSDF to automatically generate diagrams efficiently and accurately with Signed Distance Field (SDF). Specifically, we first represent geometric elements in the SDF, then construct a series of constraint functions to represent geometric relationships, next we optimize such constraint functions to get an optimized field of both elements and constraints, finally by rendering the optimized field, we can obtain the synthesized diagram. In our GeoSDF, we define a symbolic language to easily represent geometric elements and those constraints, and our synthesized geometry diagrams can be self-verified in the SDF, ensuring both mathematical accuracy and visual plausibility. In experiments, our GeoSDF synthesized both normal high-school level and IMO-level geometry diagrams. Through both qualitative and quantitative analysis, we can see that synthesized diagrams are realistic and accurate, and our synthesizing process is simple and efficient. Furthermore, we obtain a very high accuracy of solving geometry problems (over 95\% while the current SOTA accuracy is around 75%) by leveraging our self-verification property. All of these demonstrate the advantage of GeoSDF, paving the way for more sophisticated, accurate, and flexible generation of geometric diagrams for a wide array of applications.
DvD: Unleashing a Generative Paradigm for Document Dewarping via Coordinates-based Diffusion Model
May 28, 2025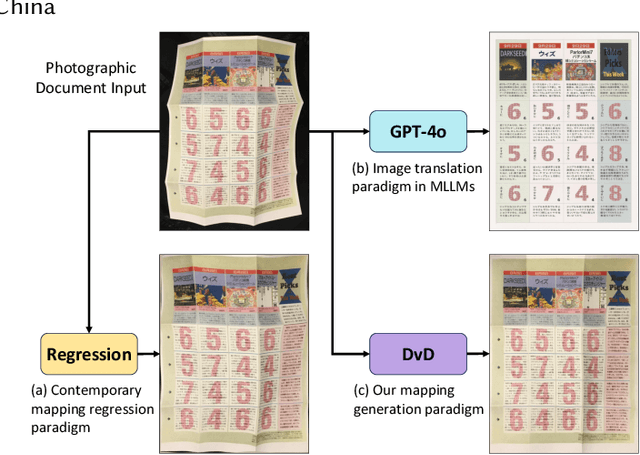
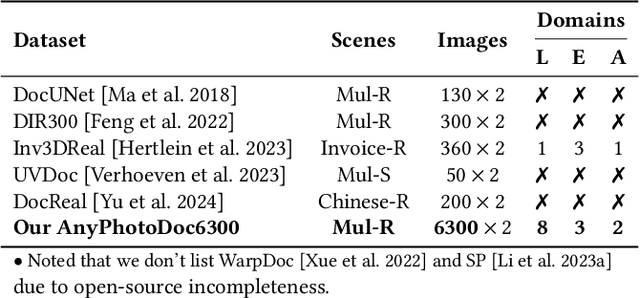
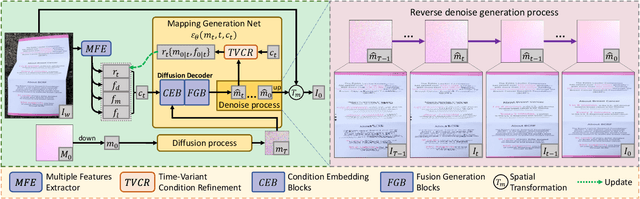
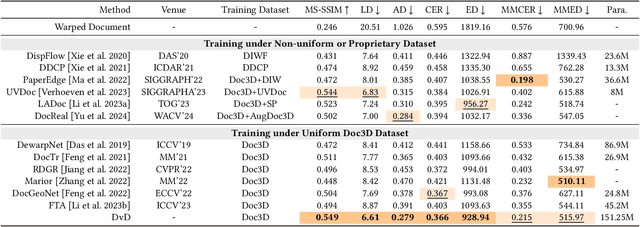
Abstract:Document dewarping aims to rectify deformations in photographic document images, thus improving text readability, which has attracted much attention and made great progress, but it is still challenging to preserve document structures. Given recent advances in diffusion models, it is natural for us to consider their potential applicability to document dewarping. However, it is far from straightforward to adopt diffusion models in document dewarping due to their unfaithful control on highly complex document images (e.g., 2000$\times$3000 resolution). In this paper, we propose DvD, the first generative model to tackle document \textbf{D}ewarping \textbf{v}ia a \textbf{D}iffusion framework. To be specific, DvD introduces a coordinate-level denoising instead of typical pixel-level denoising, generating a mapping for deformation rectification. In addition, we further propose a time-variant condition refinement mechanism to enhance the preservation of document structures. In experiments, we find that current document dewarping benchmarks can not evaluate dewarping models comprehensively. To this end, we present AnyPhotoDoc6300, a rigorously designed large-scale document dewarping benchmark comprising 6,300 real image pairs across three distinct domains, enabling fine-grained evaluation of dewarping models. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our proposed DvD can achieve state-of-the-art performance with acceptable computational efficiency on multiple metrics across various benchmarks including DocUNet, DIR300, and AnyPhotoDoc6300. The new benchmark and code will be publicly available.
Interpretable Zero-shot Learning with Infinite Class Concepts
May 06, 2025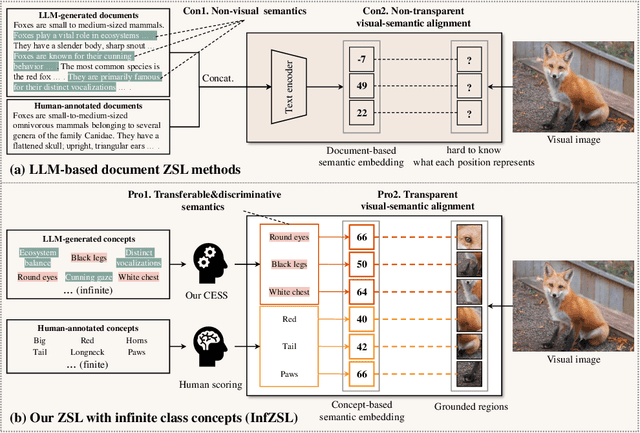
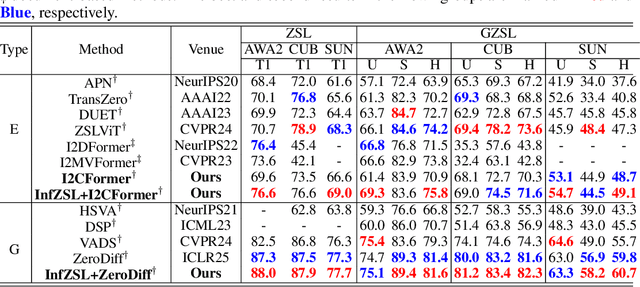
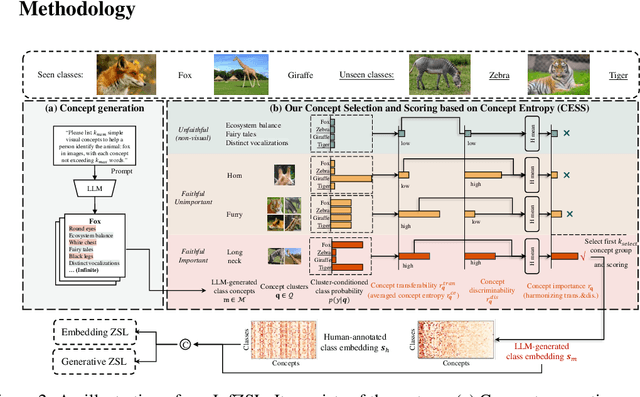
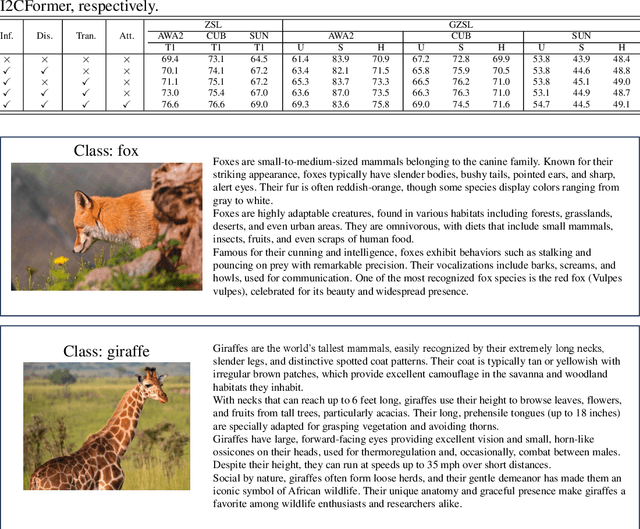
Abstract:Zero-shot learning (ZSL) aims to recognize unseen classes by aligning images with intermediate class semantics, like human-annotated concepts or class definitions. An emerging alternative leverages Large-scale Language Models (LLMs) to automatically generate class documents. However, these methods often face challenges with transparency in the classification process and may suffer from the notorious hallucination problem in LLMs, resulting in non-visual class semantics. This paper redefines class semantics in ZSL with a focus on transferability and discriminability, introducing a novel framework called Zero-shot Learning with Infinite Class Concepts (InfZSL). Our approach leverages the powerful capabilities of LLMs to dynamically generate an unlimited array of phrase-level class concepts. To address the hallucination challenge, we introduce an entropy-based scoring process that incorporates a ``goodness" concept selection mechanism, ensuring that only the most transferable and discriminative concepts are selected. Our InfZSL framework not only demonstrates significant improvements on three popular benchmark datasets but also generates highly interpretable, image-grounded concepts. Code will be released upon acceptance.
Unlock Pose Diversity: Accurate and Efficient Implicit Keypoint-based Spatiotemporal Diffusion for Audio-driven Talking Portrait
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Audio-driven single-image talking portrait generation plays a crucial role in virtual reality, digital human creation, and filmmaking. Existing approaches are generally categorized into keypoint-based and image-based methods. Keypoint-based methods effectively preserve character identity but struggle to capture fine facial details due to the fixed points limitation of the 3D Morphable Model. Moreover, traditional generative networks face challenges in establishing causality between audio and keypoints on limited datasets, resulting in low pose diversity. In contrast, image-based approaches produce high-quality portraits with diverse details using the diffusion network but incur identity distortion and expensive computational costs. In this work, we propose KDTalker, the first framework to combine unsupervised implicit 3D keypoint with a spatiotemporal diffusion model. Leveraging unsupervised implicit 3D keypoints, KDTalker adapts facial information densities, allowing the diffusion process to model diverse head poses and capture fine facial details flexibly. The custom-designed spatiotemporal attention mechanism ensures accurate lip synchronization, producing temporally consistent, high-quality animations while enhancing computational efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate that KDTalker achieves state-of-the-art performance regarding lip synchronization accuracy, head pose diversity, and execution efficiency.Our codes are available at https://github.com/chaolongy/KDTalker.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge