Shiming Chen
Prototype-Guided Curriculum Learning for Zero-Shot Learning
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:In Zero-Shot Learning (ZSL), embedding-based methods enable knowledge transfer from seen to unseen classes by learning a visual-semantic mapping from seen-class images to class-level semantic prototypes (e.g., attributes). However, these semantic prototypes are manually defined and may introduce noisy supervision for two main reasons: (i) instance-level mismatch: variations in perspective, occlusion, and annotation bias will cause discrepancies between individual sample and the class-level semantic prototypes; and (ii) class-level imprecision: the manually defined semantic prototypes may not accurately reflect the true semantics of the class. Consequently, the visual-semantic mapping will be misled, reducing the effectiveness of knowledge transfer to unseen classes. In this work, we propose a prototype-guided curriculum learning framework (dubbed as CLZSL), which mitigates instance-level mismatches through a Prototype-Guided Curriculum Learning (PCL) module and addresses class-level imprecision via a Prototype Update (PUP) module. Specifically, the PCL module prioritizes samples with high cosine similarity between their visual mappings and the class-level semantic prototypes, and progressively advances to less-aligned samples, thereby reducing the interference of instance-level mismatches to achieve accurate visual-semantic mapping. Besides, the PUP module dynamically updates the class-level semantic prototypes by leveraging the visual mappings learned from instances, thereby reducing class-level imprecision and further improving the visual-semantic mapping. Experiments were conducted on standard benchmark datasets-AWA2, SUN, and CUB-to verify the effectiveness of our method.
GenZSL: Generative Zero-Shot Learning Via Inductive Variational Autoencoder
May 17, 2025Abstract:Remarkable progress in zero-shot learning (ZSL) has been achieved using generative models. However, existing generative ZSL methods merely generate (imagine) the visual features from scratch guided by the strong class semantic vectors annotated by experts, resulting in suboptimal generative performance and limited scene generalization. To address these and advance ZSL, we propose an inductive variational autoencoder for generative zero-shot learning, dubbed GenZSL. Mimicking human-level concept learning, GenZSL operates by inducting new class samples from similar seen classes using weak class semantic vectors derived from target class names (i.e., CLIP text embedding). To ensure the generation of informative samples for training an effective ZSL classifier, our GenZSL incorporates two key strategies. Firstly, it employs class diversity promotion to enhance the diversity of class semantic vectors. Secondly, it utilizes target class-guided information boosting criteria to optimize the model. Extensive experiments conducted on three popular benchmark datasets showcase the superiority and potential of our GenZSL with significant efficacy and efficiency over f-VAEGAN, e.g., 24.7% performance gains and more than $60\times$ faster training speed on AWA2. Codes are available at https://github.com/shiming-chen/GenZSL.
Interpretable Zero-shot Learning with Infinite Class Concepts
May 06, 2025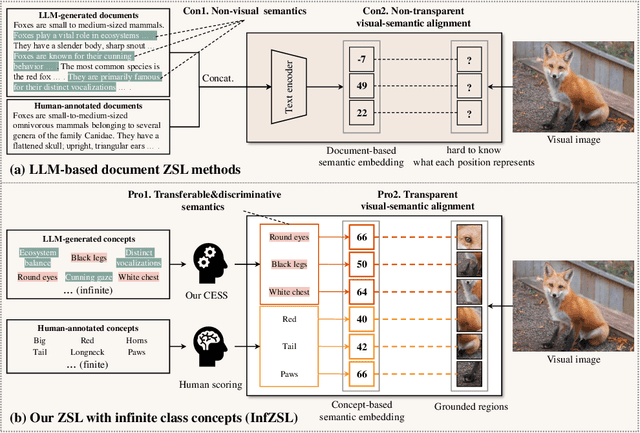
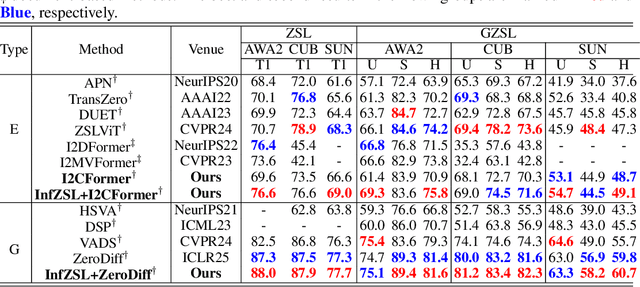
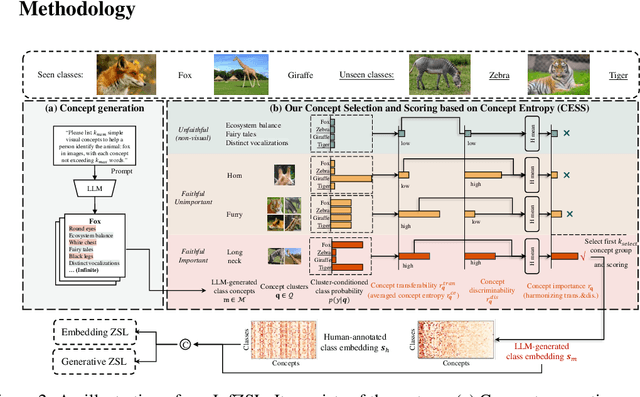
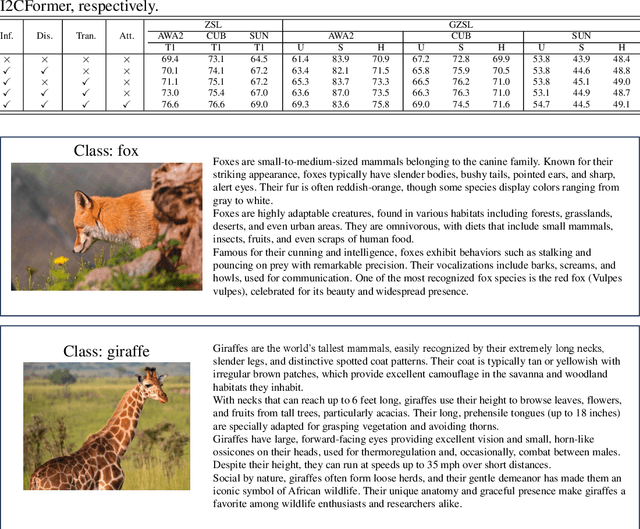
Abstract:Zero-shot learning (ZSL) aims to recognize unseen classes by aligning images with intermediate class semantics, like human-annotated concepts or class definitions. An emerging alternative leverages Large-scale Language Models (LLMs) to automatically generate class documents. However, these methods often face challenges with transparency in the classification process and may suffer from the notorious hallucination problem in LLMs, resulting in non-visual class semantics. This paper redefines class semantics in ZSL with a focus on transferability and discriminability, introducing a novel framework called Zero-shot Learning with Infinite Class Concepts (InfZSL). Our approach leverages the powerful capabilities of LLMs to dynamically generate an unlimited array of phrase-level class concepts. To address the hallucination challenge, we introduce an entropy-based scoring process that incorporates a ``goodness" concept selection mechanism, ensuring that only the most transferable and discriminative concepts are selected. Our InfZSL framework not only demonstrates significant improvements on three popular benchmark datasets but also generates highly interpretable, image-grounded concepts. Code will be released upon acceptance.
Toward Realistic Camouflaged Object Detection: Benchmarks and Method
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:Camouflaged object detection (COD) primarily relies on semantic or instance segmentation methods. While these methods have made significant advancements in identifying the contours of camouflaged objects, they may be inefficient or cost-effective for tasks that only require the specific location of the object. Object detection algorithms offer an optimized solution for Realistic Camouflaged Object Detection (RCOD) in such cases. However, detecting camouflaged objects remains a formidable challenge due to the high degree of similarity between the features of the objects and their backgrounds. Unlike segmentation methods that perform pixel-wise comparisons to differentiate between foreground and background, object detectors omit this analysis, further aggravating the challenge. To solve this problem, we propose a camouflage-aware feature refinement (CAFR) strategy. Since camouflaged objects are not rare categories, CAFR fully utilizes a clear perception of the current object within the prior knowledge of large models to assist detectors in deeply understanding the distinctions between background and foreground. Specifically, in CAFR, we introduce the Adaptive Gradient Propagation (AGP) module that fine-tunes all feature extractor layers in large detection models to fully refine class-specific features from camouflaged contexts. We then design the Sparse Feature Refinement (SFR) module that optimizes the transformer-based feature extractor to focus primarily on capturing class-specific features in camouflaged scenarios. To facilitate the assessment of RCOD tasks, we manually annotate the labels required for detection on three existing segmentation COD datasets, creating a new benchmark for RCOD tasks. Code and datasets are available at: https://github.com/zhimengXin/RCOD.
Improved Feature Generating Framework for Transductive Zero-shot Learning
Dec 24, 2024Abstract:Feature Generative Adversarial Networks have emerged as powerful generative models in producing high-quality representations of unseen classes within the scope of Zero-shot Learning (ZSL). This paper delves into the pivotal influence of unseen class priors within the framework of transductive ZSL (TZSL) and illuminates the finding that even a marginal prior bias can result in substantial accuracy declines. Our extensive analysis uncovers that this inefficacy fundamentally stems from the utilization of an unconditional unseen discriminator - a core component in existing TZSL. We further establish that the detrimental effects of this component are inevitable unless the generator perfectly fits class-specific distributions. Building on these insights, we introduce our Improved Feature Generation Framework, termed I-VAEGAN, which incorporates two novel components: Pseudo-conditional Feature Adversarial (PFA) learning and Variational Embedding Regression (VER). PFA circumvents the need for prior estimation by explicitly injecting the predicted semantics as pseudo conditions for unseen classes premised by precise semantic regression. Meanwhile, VER utilizes reconstructive pre-training to learn class statistics, obtaining better semantic regression. Our I-VAEGAN achieves state-of-the-art TZSL accuracy across various benchmarks and priors. Our code would be released upon acceptance.
Discriminative Image Generation with Diffusion Models for Zero-Shot Learning
Dec 23, 2024



Abstract:Generative Zero-Shot Learning (ZSL) methods synthesize class-related features based on predefined class semantic prototypes, showcasing superior performance. However, this feature generation paradigm falls short of providing interpretable insights. In addition, existing approaches rely on semantic prototypes annotated by human experts, which exhibit a significant limitation in their scalability to generalized scenes. To overcome these deficiencies, a natural solution is to generate images for unseen classes using text prompts. To this end, We present DIG-ZSL, a novel Discriminative Image Generation framework for Zero-Shot Learning. Specifically, to ensure the generation of discriminative images for training an effective ZSL classifier, we learn a discriminative class token (DCT) for each unseen class under the guidance of a pre-trained category discrimination model (CDM). Harnessing DCTs, we can generate diverse and high-quality images, which serve as informative unseen samples for ZSL tasks. In this paper, the extensive experiments and visualizations on four datasets show that our DIG-ZSL: (1) generates diverse and high-quality images, (2) outperforms previous state-of-the-art nonhuman-annotated semantic prototype-based methods by a large margin, and (3) achieves comparable or better performance than baselines that leverage human-annotated semantic prototypes. The codes will be made available upon acceptance of the paper.
Visual-Semantic Graph Matching Net for Zero-Shot Learning
Nov 18, 2024Abstract:Zero-shot learning (ZSL) aims to leverage additional semantic information to recognize unseen classes. To transfer knowledge from seen to unseen classes, most ZSL methods often learn a shared embedding space by simply aligning visual embeddings with semantic prototypes. However, methods trained under this paradigm often struggle to learn robust embedding space because they align the two modalities in an isolated manner among classes, which ignore the crucial class relationship during the alignment process. To address the aforementioned challenges, this paper proposes a Visual-Semantic Graph Matching Net, termed as VSGMN, which leverages semantic relationships among classes to aid in visual-semantic embedding. VSGMN employs a Graph Build Network (GBN) and a Graph Matching Network (GMN) to achieve two-stage visual-semantic alignment. Specifically, GBN first utilizes an embedding-based approach to build visual and semantic graphs in the semantic space and align the embedding with its prototype for first-stage alignment. Additionally, to supplement unseen class relations in these graphs, GBN also build the unseen class nodes based on semantic relationships. In the second stage, GMN continuously integrates neighbor and cross-graph information into the constructed graph nodes, and aligns the node relationships between the two graphs under the class relationship constraint. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that VSGMN achieves superior performance in both conventional and generalized ZSL scenarios. The implementation of our VSGMN and experimental results are available at github: https://github.com/dbwfd/VSGMN
ZeroMamba: Exploring Visual State Space Model for Zero-Shot Learning
Aug 27, 2024Abstract:Zero-shot learning (ZSL) aims to recognize unseen classes by transferring semantic knowledge from seen classes to unseen ones, guided by semantic information. To this end, existing works have demonstrated remarkable performance by utilizing global visual features from Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) or Vision Transformers (ViTs) for visual-semantic interactions. Due to the limited receptive fields of CNNs and the quadratic complexity of ViTs, however, these visual backbones achieve suboptimal visual-semantic interactions. In this paper, motivated by the visual state space model (i.e., Vision Mamba), which is capable of capturing long-range dependencies and modeling complex visual dynamics, we propose a parameter-efficient ZSL framework called ZeroMamba to advance ZSL. Our ZeroMamba comprises three key components: Semantic-aware Local Projection (SLP), Global Representation Learning (GRL), and Semantic Fusion (SeF). Specifically, SLP integrates semantic embeddings to map visual features to local semantic-related representations, while GRL encourages the model to learn global semantic representations. SeF combines these two semantic representations to enhance the discriminability of semantic features. We incorporate these designs into Vision Mamba, forming an end-to-end ZSL framework. As a result, the learned semantic representations are better suited for classification. Through extensive experiments on four prominent ZSL benchmarks, ZeroMamba demonstrates superior performance, significantly outperforming the state-of-the-art (i.e., CNN-based and ViT-based) methods under both conventional ZSL (CZSL) and generalized ZSL (GZSL) settings. Code is available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/ZeroMamba.
Adapting Large Multimodal Models to Distribution Shifts: The Role of In-Context Learning
May 20, 2024Abstract:Recent studies indicate that large multimodal models (LMMs) are highly robust against natural distribution shifts, often surpassing previous baselines. Despite this, domain-specific adaptation is still necessary, particularly in specialized areas like healthcare. Due to the impracticality of fine-tuning LMMs given their vast parameter space, this work investigates in-context learning (ICL) as an effective alternative for enhancing LMMs' adaptability. We find that the success of ICL heavily relies on the choice of demonstration, mirroring challenges seen in large language models but introducing unique complexities for LMMs facing distribution shifts. Our study addresses this by evaluating an unsupervised ICL method, TopKNearestPR, which selects in-context examples through a nearest example search based on feature similarity. We uncover that its effectiveness is limited by the deficiencies of pre-trained vision encoders under distribution shift scenarios. To address these challenges, we propose InvariantSelectPR, a novel method leveraging Class-conditioned Contrastive Invariance (CCI) for more robust demonstration selection. Specifically, CCI enhances pre-trained vision encoders by improving their discriminative capabilities across different classes and ensuring invariance to domain-specific variations. This enhancement allows the encoders to effectively identify and retrieve the most informative examples, which are then used to guide LMMs in adapting to new query samples under varying distributions. Our experiments show that InvariantSelectPR substantially improves the adaptability of LMMs, achieving significant performance gains on benchmark datasets, with a 34.2%$\uparrow$ accuracy increase in 7-shot on Camelyon17 and 16.9%$\uparrow$ increase in 7-shot on HAM10000 compared to the baseline zero-shot performance.
Visual-Augmented Dynamic Semantic Prototype for Generative Zero-Shot Learning
Apr 23, 2024



Abstract:Generative Zero-shot learning (ZSL) learns a generator to synthesize visual samples for unseen classes, which is an effective way to advance ZSL. However, existing generative methods rely on the conditions of Gaussian noise and the predefined semantic prototype, which limit the generator only optimized on specific seen classes rather than characterizing each visual instance, resulting in poor generalizations (\textit{e.g.}, overfitting to seen classes). To address this issue, we propose a novel Visual-Augmented Dynamic Semantic prototype method (termed VADS) to boost the generator to learn accurate semantic-visual mapping by fully exploiting the visual-augmented knowledge into semantic conditions. In detail, VADS consists of two modules: (1) Visual-aware Domain Knowledge Learning module (VDKL) learns the local bias and global prior of the visual features (referred to as domain visual knowledge), which replace pure Gaussian noise to provide richer prior noise information; (2) Vision-Oriented Semantic Updation module (VOSU) updates the semantic prototype according to the visual representations of the samples. Ultimately, we concatenate their output as a dynamic semantic prototype, which serves as the condition of the generator. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our VADS achieves superior CZSL and GZSL performances on three prominent datasets and outperforms other state-of-the-art methods with averaging increases by 6.4\%, 5.9\% and 4.2\% on SUN, CUB and AWA2, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge