Yixiong Zou
SwimBird: Eliciting Switchable Reasoning Mode in Hybrid Autoregressive MLLMs
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have made remarkable progress in multimodal perception and reasoning by bridging vision and language. However, most existing MLLMs perform reasoning primarily with textual CoT, which limits their effectiveness on vision-intensive tasks. Recent approaches inject a fixed number of continuous hidden states as "visual thoughts" into the reasoning process and improve visual performance, but often at the cost of degraded text-based logical reasoning. We argue that the core limitation lies in a rigid, pre-defined reasoning pattern that cannot adaptively choose the most suitable thinking modality for different user queries. We introduce SwimBird, a reasoning-switchable MLLM that dynamically switches among three reasoning modes conditioned on the input: (1) text-only reasoning, (2) vision-only reasoning (continuous hidden states as visual thoughts), and (3) interleaved vision-text reasoning. To enable this capability, we adopt a hybrid autoregressive formulation that unifies next-token prediction for textual thoughts with next-embedding prediction for visual thoughts, and design a systematic reasoning-mode curation strategy to construct SwimBird-SFT-92K, a diverse supervised fine-tuning dataset covering all three reasoning patterns. By enabling flexible, query-adaptive mode selection, SwimBird preserves strong textual logic while substantially improving performance on vision-dense tasks. Experiments across diverse benchmarks covering textual reasoning and challenging visual understanding demonstrate that SwimBird achieves state-of-the-art results and robust gains over prior fixed-pattern multimodal reasoning methods.
Sketch-in-Latents: Eliciting Unified Reasoning in MLLMs
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) excel at visual understanding tasks through text reasoning, they often fall short in scenarios requiring visual imagination. Unlike current works that take predefined external toolkits or generate images during thinking, however, humans can form flexible visual-text imagination and interactions during thinking without predefined toolkits, where one important reason is that humans construct the visual-text thinking process in a unified space inside the brain. Inspired by this capability, given that current MLLMs already encode visual and text information in the same feature space, we hold that visual tokens can be seamlessly inserted into the reasoning process carried by text tokens, where ideally, all visual imagination processes can be encoded by the latent features. To achieve this goal, we propose Sketch-in-Latents (SkiLa), a novel paradigm for unified multi-modal reasoning that expands the auto-regressive capabilities of MLLMs to natively generate continuous visual embeddings, termed latent sketch tokens, as visual thoughts. During multi-step reasoning, the model dynamically alternates between textual thinking mode for generating textual think tokens and visual sketching mode for generating latent sketch tokens. A latent visual semantics reconstruction mechanism is proposed to ensure these latent sketch tokens are semantically grounded. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SkiLa achieves superior performance on vision-centric tasks while exhibiting strong generalization to diverse general multi-modal benchmarks. Codes will be released at https://github.com/TungChintao/SkiLa.
Decoupling Template Bias in CLIP: Harnessing Empty Prompts for Enhanced Few-Shot Learning
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:The Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP) model excels in few-shot learning by aligning visual and textual representations. Our study shows that template-sample similarity (TSS), defined as the resemblance between a text template and an image sample, introduces bias. This bias leads the model to rely on template proximity rather than true sample-to-category alignment, reducing both accuracy and robustness in classification. We present a framework that uses empty prompts, textual inputs that convey the idea of "emptiness" without category information. These prompts capture unbiased template features and offset TSS bias. The framework employs two stages. During pre-training, empty prompts reveal and reduce template-induced bias within the CLIP encoder. During few-shot fine-tuning, a bias calibration loss enforces correct alignment between images and their categories, ensuring the model focuses on relevant visual cues. Experiments across multiple benchmarks demonstrate that our template correction method significantly reduces performance fluctuations caused by TSS, yielding higher classification accuracy and stronger robustness. The repository of this project is available at https://github.com/zhenyuZ-HUST/Decoupling-Template-Bias-in-CLIP.
Start Small, Think Big: Curriculum-based Relative Policy Optimization for Visual Grounding
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has recently shown significant promise across various NLP and computer vision tasks by explicitly generating intermediate reasoning steps. However, we find that reinforcement learning (RL)-based fine-tuned CoT reasoning can paradoxically degrade performance in Visual Grounding tasks, particularly as CoT outputs become lengthy or complex. Additionally, our analysis reveals that increased dataset size does not always enhance performance due to varying data complexities. Motivated by these findings, we propose Curriculum-based Relative Policy Optimization (CuRPO), a novel training strategy that leverages CoT length and generalized Intersection over Union (gIoU) rewards as complexity indicators to progressively structure training data from simpler to more challenging examples. Extensive experiments on RefCOCO, RefCOCO+, RefCOCOg, and LISA datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. CuRPO consistently outperforms existing methods, including Visual-RFT, with notable improvements of up to +12.52 mAP on RefCOCO. Moreover, CuRPO exhibits exceptional efficiency and robustness, delivering strong localization performance even in few-shot learning scenarios, particularly benefiting tasks characterized by ambiguous and intricate textual descriptions.The code is released on https://github.com/qyoung-yan/CuRPO.
Adapter Naturally Serves as Decoupler for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Semantic Segmentation
Jun 09, 2025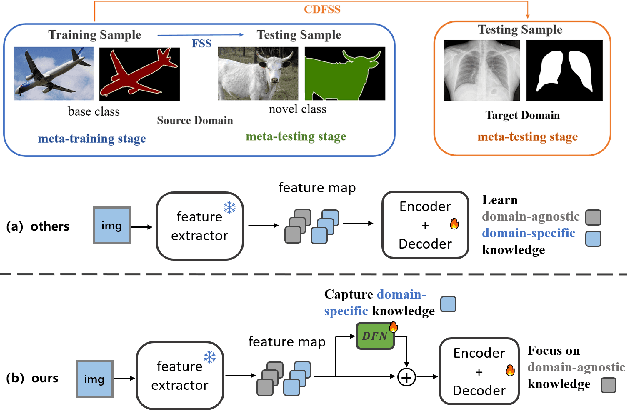
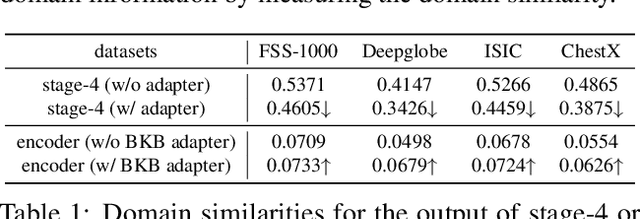
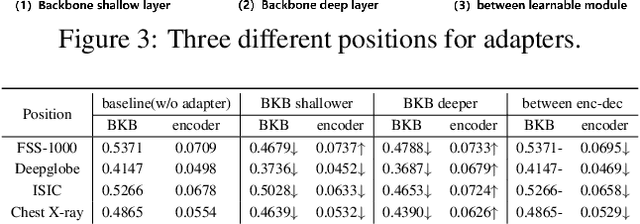
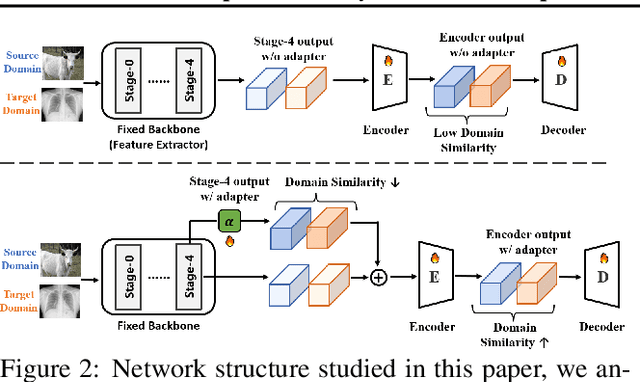
Abstract:Cross-domain few-shot segmentation (CD-FSS) is proposed to pre-train the model on a source-domain dataset with sufficient samples, and then transfer the model to target-domain datasets where only a few samples are available for efficient fine-tuning. There are majorly two challenges in this task: (1) the domain gap and (2) fine-tuning with scarce data. To solve these challenges, we revisit the adapter-based methods, and discover an intriguing insight not explored in previous works: the adapter not only helps the fine-tuning of downstream tasks but also naturally serves as a domain information decoupler. Then, we delve into this finding for an interpretation, and find the model's inherent structure could lead to a natural decoupling of domain information. Building upon this insight, we propose the Domain Feature Navigator (DFN), which is a structure-based decoupler instead of loss-based ones like current works, to capture domain-specific information, thereby directing the model's attention towards domain-agnostic knowledge. Moreover, to prevent the potential excessive overfitting of DFN during the source-domain training, we further design the SAM-SVN method to constrain DFN from learning sample-specific knowledge. On target domains, we freeze the model and fine-tune the DFN to learn target-specific knowledge specific. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method surpasses the state-of-the-art method in CD-FSS significantly by 2.69% and 4.68% MIoU in 1-shot and 5-shot scenarios, respectively.
FlowCut: Rethinking Redundancy via Information Flow for Efficient Vision-Language Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) excel at multimodal understanding but suffer from high computational costs due to redundant vision tokens. Existing pruning methods typically rely on single-layer attention scores to rank and prune redundant visual tokens to solve this inefficiency. However, as the interaction between tokens and layers is complicated, this raises a basic question: Is such a simple single-layer criterion sufficient to identify redundancy? To answer this question, we rethink the emergence of redundant visual tokens from a fundamental perspective: information flow, which models the interaction between tokens and layers by capturing how information moves between tokens across layers. We find (1) the CLS token acts as an information relay, which can simplify the complicated flow analysis; (2) the redundancy emerges progressively and dynamically via layer-wise attention concentration; and (3) relying solely on attention scores from single layers can lead to contradictory redundancy identification. Based on this, we propose FlowCut, an information-flow-aware pruning framework, mitigating the insufficiency of the current criterion for identifying redundant tokens and better aligning with the model's inherent behaviors. Extensive experiments show that FlowCut achieves superior results, outperforming SoTA by 1.6% on LLaVA-1.5-7B with 88.9% token reduction, and by 4.3% on LLaVA-NeXT-7B with 94.4% reduction, delivering 3.2x speed-up in the prefilling stage. Our code is available at https://github.com/TungChintao/FlowCut
NTIRE 2025 Challenge on Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection: Methods and Results
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Cross-Domain Few-Shot Object Detection (CD-FSOD) poses significant challenges to existing object detection and few-shot detection models when applied across domains. In conjunction with NTIRE 2025, we organized the 1st CD-FSOD Challenge, aiming to advance the performance of current object detectors on entirely novel target domains with only limited labeled data. The challenge attracted 152 registered participants, received submissions from 42 teams, and concluded with 13 teams making valid final submissions. Participants approached the task from diverse perspectives, proposing novel models that achieved new state-of-the-art (SOTA) results under both open-source and closed-source settings. In this report, we present an overview of the 1st NTIRE 2025 CD-FSOD Challenge, highlighting the proposed solutions and summarizing the results submitted by the participants.
The Devil is in Low-Level Features for Cross-Domain Few-Shot Segmentation
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Cross-Domain Few-Shot Segmentation (CDFSS) is proposed to transfer the pixel-level segmentation capabilities learned from large-scale source-domain datasets to downstream target-domain datasets, with only a few annotated images per class. In this paper, we focus on a well-observed but unresolved phenomenon in CDFSS: for target domains, particularly those distant from the source domain, segmentation performance peaks at the very early epochs, and declines sharply as the source-domain training proceeds. We delve into this phenomenon for an interpretation: low-level features are vulnerable to domain shifts, leading to sharper loss landscapes during the source-domain training, which is the devil of CDFSS. Based on this phenomenon and interpretation, we further propose a method that includes two plug-and-play modules: one to flatten the loss landscapes for low-level features during source-domain training as a novel sharpness-aware minimization method, and the other to directly supplement target-domain information to the model during target-domain testing by low-level-based calibration. Extensive experiments on four target datasets validate our rationale and demonstrate that our method surpasses the state-of-the-art method in CDFSS signifcantly by 3.71% and 5.34% average MIoU in 1-shot and 5-shot scenarios, respectively.
Training-free Anomaly Event Detection via LLM-guided Symbolic Pattern Discovery
Feb 09, 2025



Abstract:Anomaly event detection plays a crucial role in various real-world applications. However, current approaches predominantly rely on supervised learning, which faces significant challenges: the requirement for extensive labeled training data and lack of interpretability in decision-making processes. To address these limitations, we present a training-free framework that integrates open-set object detection with symbolic regression, powered by Large Language Models (LLMs) for efficient symbolic pattern discovery. The LLMs guide the symbolic reasoning process, establishing logical relationships between detected entities. Through extensive experiments across multiple domains, our framework demonstrates several key advantages: (1) achieving superior detection accuracy through direct reasoning without any training process; (2) providing highly interpretable logical expressions that are readily comprehensible to humans; and (3) requiring minimal annotation effort - approximately 1% of the data needed by traditional training-based methods.To facilitate comprehensive evaluation and future research, we introduce two datasets: a large-scale private dataset containing over 110,000 annotated images covering various anomaly scenarios including construction site safety violations, illegal fishing activities, and industrial hazards, along with a public benchmark dataset of 5,000 samples with detailed anomaly event annotations. Code is available at here.
Toward Realistic Camouflaged Object Detection: Benchmarks and Method
Jan 13, 2025



Abstract:Camouflaged object detection (COD) primarily relies on semantic or instance segmentation methods. While these methods have made significant advancements in identifying the contours of camouflaged objects, they may be inefficient or cost-effective for tasks that only require the specific location of the object. Object detection algorithms offer an optimized solution for Realistic Camouflaged Object Detection (RCOD) in such cases. However, detecting camouflaged objects remains a formidable challenge due to the high degree of similarity between the features of the objects and their backgrounds. Unlike segmentation methods that perform pixel-wise comparisons to differentiate between foreground and background, object detectors omit this analysis, further aggravating the challenge. To solve this problem, we propose a camouflage-aware feature refinement (CAFR) strategy. Since camouflaged objects are not rare categories, CAFR fully utilizes a clear perception of the current object within the prior knowledge of large models to assist detectors in deeply understanding the distinctions between background and foreground. Specifically, in CAFR, we introduce the Adaptive Gradient Propagation (AGP) module that fine-tunes all feature extractor layers in large detection models to fully refine class-specific features from camouflaged contexts. We then design the Sparse Feature Refinement (SFR) module that optimizes the transformer-based feature extractor to focus primarily on capturing class-specific features in camouflaged scenarios. To facilitate the assessment of RCOD tasks, we manually annotate the labels required for detection on three existing segmentation COD datasets, creating a new benchmark for RCOD tasks. Code and datasets are available at: https://github.com/zhimengXin/RCOD.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge