Anqi Li
RECAP: Resistance Capture in Text-based Mental Health Counseling with Large Language Models
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Recognizing and navigating client resistance is critical for effective mental health counseling, yet detecting such behaviors is particularly challenging in text-based interactions. Existing NLP approaches oversimplify resistance categories, ignore the sequential dynamics of therapeutic interventions, and offer limited interpretability. To address these limitations, we propose PsyFIRE, a theoretically grounded framework capturing 13 fine-grained resistance behaviors alongside collaborative interactions. Based on PsyFIRE, we construct the ClientResistance corpus with 23,930 annotated utterances from real-world Chinese text-based counseling, each supported by context-specific rationales. Leveraging this dataset, we develop RECAP, a two-stage framework that detects resistance and fine-grained resistance types with explanations. RECAP achieves 91.25% F1 for distinguishing collaboration and resistance and 66.58% macro-F1 for fine-grained resistance categories classification, outperforming leading prompt-based LLM baselines by over 20 points. Applied to a separate counseling dataset and a pilot study with 62 counselors, RECAP reveals the prevalence of resistance, its negative impact on therapeutic relationships and demonstrates its potential to improve counselors' understanding and intervention strategies.
A Unified 3D Object Perception Framework for Real-Time Outside-In Multi-Camera Systems
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Accurate 3D object perception and multi-target multi-camera (MTMC) tracking are fundamental for the digital transformation of industrial infrastructure. However, transitioning "inside-out" autonomous driving models to "outside-in" static camera networks presents significant challenges due to heterogeneous camera placements and extreme occlusion. In this paper, we present an adapted Sparse4D framework specifically optimized for large-scale infrastructure environments. Our system leverages absolute world-coordinate geometric priors and introduces an occlusion-aware ReID embedding module to maintain identity stability across distributed sensor networks. To bridge the Sim2Real domain gap without manual labeling, we employ a generative data augmentation strategy using the NVIDIA COSMOS framework, creating diverse environmental styles that enhance the model's appearance-invariance. Evaluated on the AI City Challenge 2025 benchmark, our camera-only framework achieves a state-of-the-art HOTA of $45.22$. Furthermore, we address real-time deployment constraints by developing an optimized TensorRT plugin for Multi-Scale Deformable Aggregation (MSDA). Our hardware-accelerated implementation achieves a $2.15\times$ speedup on modern GPU architectures, enabling a single Blackwell-class GPU to support over 64 concurrent camera streams.
HippMetric: A skeletal-representation-based framework for cross-sectional and longitudinal hippocampal substructural morphometry
Dec 22, 2025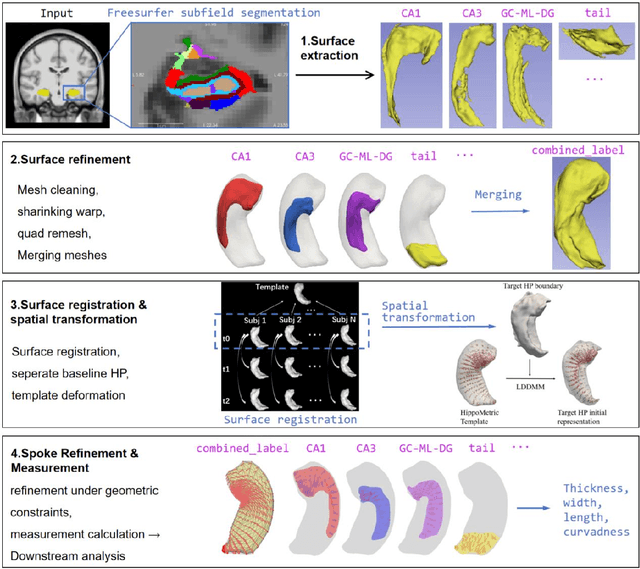
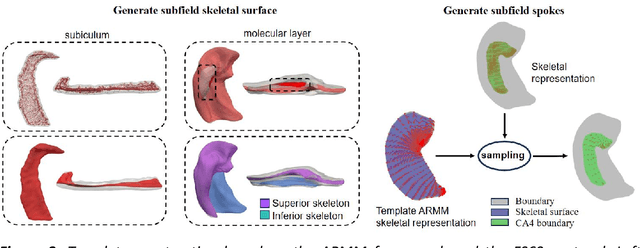
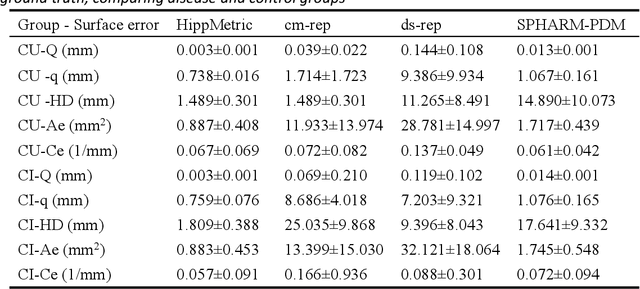
Abstract:Accurate characterization of hippocampal substructure is crucial for detecting subtle structural changes and identifying early neurodegenerative biomarkers. However, high inter-subject variability and complex folding pattern of human hippocampus hinder consistent cross-subject and longitudinal analysis. Most existing approaches rely on subject-specific modelling and lack a stable intrinsic coordinate system to accommodate anatomical variability, which limits their ability to establish reliable inter- and intra-individual correspondence. To address this, we propose HippMetric, a skeletal representation (s-rep)-based framework for hippocampal substructural morphometry and point-wise correspondence across individuals and scans. HippMetric builds on the Axis-Referenced Morphometric Model (ARMM) and employs a deformable skeletal coordinate system aligned with hippocampal anatomy and function, providing a biologically grounded reference for correspondence. Our framework comprises two core modules: a skeletal-based coordinate system that respects the hippocampus' conserved longitudinal lamellar architecture, in which functional units (lamellae) are stacked perpendicular to the long-axis, enabling anatomically consistent localization across subjects and time; and individualized s-reps generated through surface reconstruction, deformation, and geometrically constrained spoke refinement, enforcing boundary adherence, orthogonality and non-intersection to produce mathematically valid skeletal geometry. Extensive experiments on two international cohorts demonstrate that HippMetric achieves higher accuracy, reliability, and correspondence stability compared to existing shape models.
Parallel Sampling via Autospeculation
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:We present parallel algorithms to accelerate sampling via counting in two settings: any-order autoregressive models and denoising diffusion models. An any-order autoregressive model accesses a target distribution $μ$ on $[q]^n$ through an oracle that provides conditional marginals, while a denoising diffusion model accesses a target distribution $μ$ on $\mathbb{R}^n$ through an oracle that provides conditional means under Gaussian noise. Standard sequential sampling algorithms require $\widetilde{O}(n)$ time to produce a sample from $μ$ in either setting. We show that, by issuing oracle calls in parallel, the expected sampling time can be reduced to $\widetilde{O}(n^{1/2})$. This improves the previous $\widetilde{O}(n^{2/3})$ bound for any-order autoregressive models and yields the first parallel speedup for diffusion models in the high-accuracy regime, under the relatively mild assumption that the support of $μ$ is bounded. We introduce a novel technique to obtain our results: speculative rejection sampling. This technique leverages an auxiliary ``speculative'' distribution~$ν$ that approximates~$μ$ to accelerate sampling. Our technique is inspired by the well-studied ``speculative decoding'' techniques popular in large language models, but differs in key ways. Firstly, we use ``autospeculation,'' namely we build the speculation $ν$ out of the same oracle that defines~$μ$. In contrast, speculative decoding typically requires a separate, faster, but potentially less accurate ``draft'' model $ν$. Secondly, the key differentiating factor in our technique is that we make and accept speculations at a ``sequence'' level rather than at the level of single (or a few) steps. This last fact is key to unlocking our parallel runtime of $\widetilde{O}(n^{1/2})$.
TrackVLA: Embodied Visual Tracking in the Wild
May 29, 2025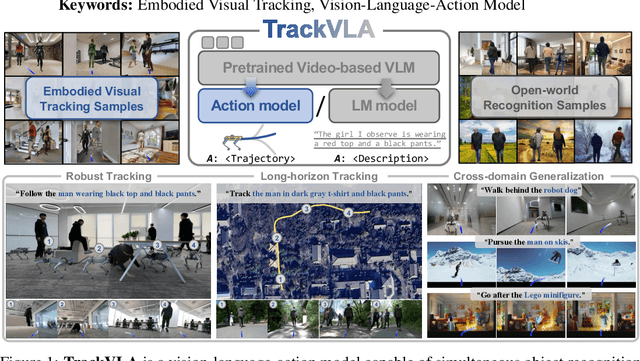
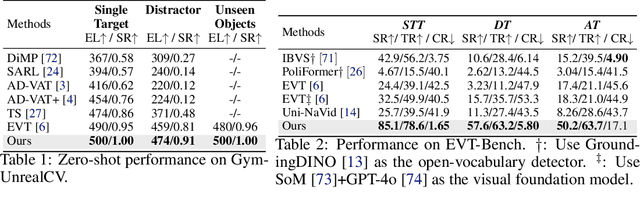
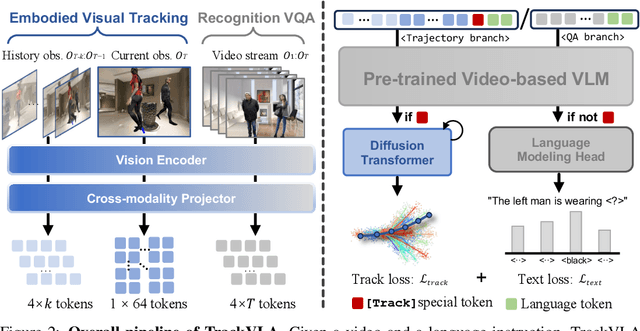
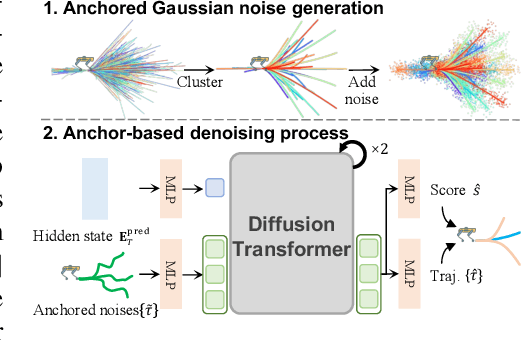
Abstract:Embodied visual tracking is a fundamental skill in Embodied AI, enabling an agent to follow a specific target in dynamic environments using only egocentric vision. This task is inherently challenging as it requires both accurate target recognition and effective trajectory planning under conditions of severe occlusion and high scene dynamics. Existing approaches typically address this challenge through a modular separation of recognition and planning. In this work, we propose TrackVLA, a Vision-Language-Action (VLA) model that learns the synergy between object recognition and trajectory planning. Leveraging a shared LLM backbone, we employ a language modeling head for recognition and an anchor-based diffusion model for trajectory planning. To train TrackVLA, we construct an Embodied Visual Tracking Benchmark (EVT-Bench) and collect diverse difficulty levels of recognition samples, resulting in a dataset of 1.7 million samples. Through extensive experiments in both synthetic and real-world environments, TrackVLA demonstrates SOTA performance and strong generalizability. It significantly outperforms existing methods on public benchmarks in a zero-shot manner while remaining robust to high dynamics and occlusion in real-world scenarios at 10 FPS inference speed. Our project page is: https://pku-epic.github.io/TrackVLA-web.
Plug-and-Play Posterior Sampling for Blind Inverse Problems
May 28, 2025


Abstract:We introduce Blind Plug-and-Play Diffusion Models (Blind-PnPDM) as a novel framework for solving blind inverse problems where both the target image and the measurement operator are unknown. Unlike conventional methods that rely on explicit priors or separate parameter estimation, our approach performs posterior sampling by recasting the problem into an alternating Gaussian denoising scheme. We leverage two diffusion models as learned priors: one to capture the distribution of the target image and another to characterize the parameters of the measurement operator. This PnP integration of diffusion models ensures flexibility and ease of adaptation. Our experiments on blind image deblurring show that Blind-PnPDM outperforms state-of-the-art methods in terms of both quantitative metrics and visual fidelity. Our results highlight the effectiveness of treating blind inverse problems as a sequence of denoising subproblems while harnessing the expressive power of diffusion-based priors.
FlowCut: Rethinking Redundancy via Information Flow for Efficient Vision-Language Models
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) excel at multimodal understanding but suffer from high computational costs due to redundant vision tokens. Existing pruning methods typically rely on single-layer attention scores to rank and prune redundant visual tokens to solve this inefficiency. However, as the interaction between tokens and layers is complicated, this raises a basic question: Is such a simple single-layer criterion sufficient to identify redundancy? To answer this question, we rethink the emergence of redundant visual tokens from a fundamental perspective: information flow, which models the interaction between tokens and layers by capturing how information moves between tokens across layers. We find (1) the CLS token acts as an information relay, which can simplify the complicated flow analysis; (2) the redundancy emerges progressively and dynamically via layer-wise attention concentration; and (3) relying solely on attention scores from single layers can lead to contradictory redundancy identification. Based on this, we propose FlowCut, an information-flow-aware pruning framework, mitigating the insufficiency of the current criterion for identifying redundant tokens and better aligning with the model's inherent behaviors. Extensive experiments show that FlowCut achieves superior results, outperforming SoTA by 1.6% on LLaVA-1.5-7B with 88.9% token reduction, and by 4.3% on LLaVA-NeXT-7B with 94.4% reduction, delivering 3.2x speed-up in the prefilling stage. Our code is available at https://github.com/TungChintao/FlowCut
Purity Law for Generalizable Neural TSP Solvers
May 07, 2025Abstract:Achieving generalization in neural approaches across different scales and distributions remains a significant challenge for the Traveling Salesman Problem~(TSP). A key obstacle is that neural networks often fail to learn robust principles for identifying universal patterns and deriving optimal solutions from diverse instances. In this paper, we first uncover Purity Law (PuLa), a fundamental structural principle for optimal TSP solutions, defining that edge prevalence grows exponentially with the sparsity of surrounding vertices. Statistically validated across diverse instances, PuLa reveals a consistent bias toward local sparsity in global optima. Building on this insight, we propose Purity Policy Optimization~(PUPO), a novel training paradigm that explicitly aligns characteristics of neural solutions with PuLa during the solution construction process to enhance generalization. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PUPO can be seamlessly integrated with popular neural solvers, significantly enhancing their generalization performance without incurring additional computational overhead during inference.
The Tenth NTIRE 2025 Image Denoising Challenge Report
Apr 16, 2025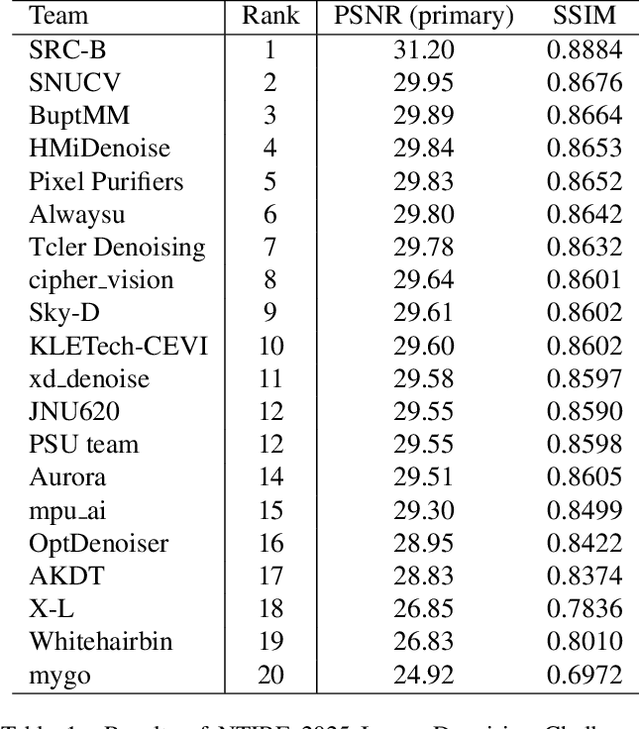


Abstract:This paper presents an overview of the NTIRE 2025 Image Denoising Challenge ({\sigma} = 50), highlighting the proposed methodologies and corresponding results. The primary objective is to develop a network architecture capable of achieving high-quality denoising performance, quantitatively evaluated using PSNR, without constraints on computational complexity or model size. The task assumes independent additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) with a fixed noise level of 50. A total of 290 participants registered for the challenge, with 20 teams successfully submitting valid results, providing insights into the current state-of-the-art in image denoising.
HAMSTER: Hierarchical Action Models For Open-World Robot Manipulation
Feb 08, 2025



Abstract:Large foundation models have shown strong open-world generalization to complex problems in vision and language, but similar levels of generalization have yet to be achieved in robotics. One fundamental challenge is the lack of robotic data, which are typically obtained through expensive on-robot operation. A promising remedy is to leverage cheaper, off-domain data such as action-free videos, hand-drawn sketches or simulation data. In this work, we posit that hierarchical vision-language-action (VLA) models can be more effective in utilizing off-domain data than standard monolithic VLA models that directly finetune vision-language models (VLMs) to predict actions. In particular, we study a class of hierarchical VLA models, where the high-level VLM is finetuned to produce a coarse 2D path indicating the desired robot end-effector trajectory given an RGB image and a task description. The intermediate 2D path prediction is then served as guidance to the low-level, 3D-aware control policy capable of precise manipulation. Doing so alleviates the high-level VLM from fine-grained action prediction, while reducing the low-level policy's burden on complex task-level reasoning. We show that, with the hierarchical design, the high-level VLM can transfer across significant domain gaps between the off-domain finetuning data and real-robot testing scenarios, including differences on embodiments, dynamics, visual appearances and task semantics, etc. In the real-robot experiments, we observe an average of 20% improvement in success rate across seven different axes of generalization over OpenVLA, representing a 50% relative gain. Visual results are provided at: https://hamster-robot.github.io/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge