Luoqi Liu
Context Tokens are Anchors: Understanding the Repetition Curse in dMLLMs from an Information Flow Perspective
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Recent diffusion-based Multimodal Large Language Models (dMLLMs) suffer from high inference latency and therefore rely on caching techniques to accelerate decoding. However, the application of cache mechanisms often introduces undesirable repetitive text generation, a phenomenon we term the \textbf{Repeat Curse}. To better investigate underlying mechanism behind this issue, we analyze repetition generation through the lens of information flow. Our work reveals three key findings: (1) context tokens aggregate semantic information as anchors and guide the final predictions; (2) as information propagates across layers, the entropy of context tokens converges in deeper layers, reflecting the model's growing prediction certainty; (3) Repetition is typically linked to disruptions in the information flow of context tokens and to the inability of their entropy to converge in deeper layers. Based on these insights, we present \textbf{CoTA}, a plug-and-play method for mitigating repetition. CoTA enhances the attention of context tokens to preserve intrinsic information flow patterns, while introducing a penalty term to the confidence score during decoding to avoid outputs driven by uncertain context tokens. With extensive experiments, CoTA demonstrates significant effectiveness in alleviating repetition and achieves consistent performance improvements on general tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/ErikZ719/CoTA
Learning Stochastic Bridges for Video Object Removal via Video-to-Video Translation
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Existing video object removal methods predominantly rely on diffusion models following a noise-to-data paradigm, where generation starts from uninformative Gaussian noise. This approach discards the rich structural and contextual priors present in the original input video. Consequently, such methods often lack sufficient guidance, leading to incomplete object erasure or the synthesis of implausible content that conflicts with the scene's physical logic. In this paper, we reformulate video object removal as a video-to-video translation task via a stochastic bridge model. Unlike noise-initialized methods, our framework establishes a direct stochastic path from the source video (with objects) to the target video (objects removed). This bridge formulation effectively leverages the input video as a strong structural prior, guiding the model to perform precise removal while ensuring that the filled regions are logically consistent with the surrounding environment. To address the trade-off where strong bridge priors hinder the removal of large objects, we propose a novel adaptive mask modulation strategy. This mechanism dynamically modulates input embeddings based on mask characteristics, balancing background fidelity with generative flexibility. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach significantly outperforms existing methods in both visual quality and temporal consistency.
On Exact Editing of Flow-Based Diffusion Models
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Recent methods in flow-based diffusion editing have enabled direct transformations between source and target image distribution without explicit inversion. However, the latent trajectories in these methods often exhibit accumulated velocity errors, leading to semantic inconsistency and loss of structural fidelity. We propose Conditioned Velocity Correction (CVC), a principled framework that reformulates flow-based editing as a distribution transformation problem driven by a known source prior. CVC rethinks the role of velocity in inter-distribution transformation by introducing a dual-perspective velocity conversion mechanism. This mechanism explicitly decomposes the latent evolution into two components: a structure-preserving branch that remains consistent with the source trajectory, and a semantically-guided branch that drives a controlled deviation toward the target distribution. The conditional velocity field exhibits an absolute velocity error relative to the true underlying distribution trajectory, which inherently introduces potential instability and trajectory drift in the latent space. To address this quantifiable deviation and maintain fidelity to the true flow, we apply a posterior-consistent update to the resulting conditional velocity field. This update is derived from Empirical Bayes Inference and Tweedie correction, which ensures a mathematically grounded error compensation over time. Our method yields stable and interpretable latent dynamics, achieving faithful reconstruction alongside smooth local semantic conversion. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that CVC consistently achieves superior fidelity, better semantic alignment, and more reliable editing behavior across diverse tasks.
AlignGen: Boosting Personalized Image Generation with Cross-Modality Prior Alignment
May 28, 2025



Abstract:Personalized image generation aims to integrate user-provided concepts into text-to-image models, enabling the generation of customized content based on a given prompt. Recent zero-shot approaches, particularly those leveraging diffusion transformers, incorporate reference image information through multi-modal attention mechanism. This integration allows the generated output to be influenced by both the textual prior from the prompt and the visual prior from the reference image. However, we observe that when the prompt and reference image are misaligned, the generated results exhibit a stronger bias toward the textual prior, leading to a significant loss of reference content. To address this issue, we propose AlignGen, a Cross-Modality Prior Alignment mechanism that enhances personalized image generation by: 1) introducing a learnable token to bridge the gap between the textual and visual priors, 2) incorporating a robust training strategy to ensure proper prior alignment, and 3) employing a selective cross-modal attention mask within the multi-modal attention mechanism to further align the priors. Experimental results demonstrate that AlignGen outperforms existing zero-shot methods and even surpasses popular test-time optimization approaches.
GlyphMastero: A Glyph Encoder for High-Fidelity Scene Text Editing
May 08, 2025
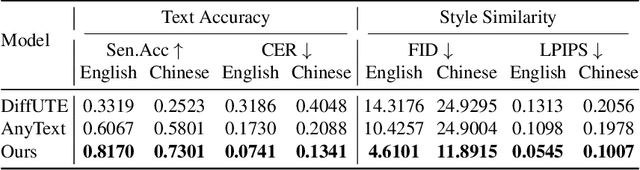
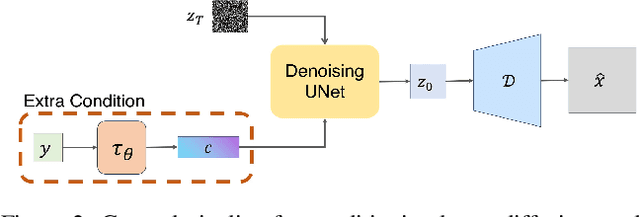
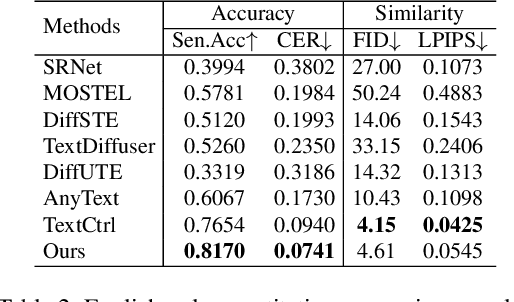
Abstract:Scene text editing, a subfield of image editing, requires modifying texts in images while preserving style consistency and visual coherence with the surrounding environment. While diffusion-based methods have shown promise in text generation, they still struggle to produce high-quality results. These methods often generate distorted or unrecognizable characters, particularly when dealing with complex characters like Chinese. In such systems, characters are composed of intricate stroke patterns and spatial relationships that must be precisely maintained. We present GlyphMastero, a specialized glyph encoder designed to guide the latent diffusion model for generating texts with stroke-level precision. Our key insight is that existing methods, despite using pretrained OCR models for feature extraction, fail to capture the hierarchical nature of text structures - from individual strokes to stroke-level interactions to overall character-level structure. To address this, our glyph encoder explicitly models and captures the cross-level interactions between local-level individual characters and global-level text lines through our novel glyph attention module. Meanwhile, our model implements a feature pyramid network to fuse the multi-scale OCR backbone features at the global-level. Through these cross-level and multi-scale fusions, we obtain more detailed glyph-aware guidance, enabling precise control over the scene text generation process. Our method achieves an 18.02\% improvement in sentence accuracy over the state-of-the-art multi-lingual scene text editing baseline, while simultaneously reducing the text-region Fr\'echet inception distance by 53.28\%.
DCEdit: Dual-Level Controlled Image Editing via Precisely Localized Semantics
Mar 21, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a novel approach to improving text-guided image editing using diffusion-based models. Text-guided image editing task poses key challenge of precisly locate and edit the target semantic, and previous methods fall shorts in this aspect. Our method introduces a Precise Semantic Localization strategy that leverages visual and textual self-attention to enhance the cross-attention map, which can serve as a regional cues to improve editing performance. Then we propose a Dual-Level Control mechanism for incorporating regional cues at both feature and latent levels, offering fine-grained control for more precise edits. To fully compare our methods with other DiT-based approaches, we construct the RW-800 benchmark, featuring high resolution images, long descriptive texts, real-world images, and a new text editing task. Experimental results on the popular PIE-Bench and RW-800 benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance of our approach in preserving background and providing accurate edits.
Memory Efficient Matting with Adaptive Token Routing
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Transformer-based models have recently achieved outstanding performance in image matting. However, their application to high-resolution images remains challenging due to the quadratic complexity of global self-attention. To address this issue, we propose MEMatte, a \textbf{m}emory-\textbf{e}fficient \textbf{m}atting framework for processing high-resolution images. MEMatte incorporates a router before each global attention block, directing informative tokens to the global attention while routing other tokens to a Lightweight Token Refinement Module (LTRM). Specifically, the router employs a local-global strategy to predict the routing probability of each token, and the LTRM utilizes efficient modules to simulate global attention. Additionally, we introduce a Batch-constrained Adaptive Token Routing (BATR) mechanism, which allows each router to dynamically route tokens based on image content and the stages of attention block in the network. Furthermore, we construct an ultra high-resolution image matting dataset, UHR-395, comprising 35,500 training images and 1,000 test images, with an average resolution of $4872\times6017$. This dataset is created by compositing 395 different alpha mattes across 11 categories onto various backgrounds, all with high-quality manual annotation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MEMatte outperforms existing methods on both high-resolution and real-world datasets, significantly reducing memory usage by approximately 88% and latency by 50% on the Composition-1K benchmark. Our code is available at https://github.com/linyiheng123/MEMatte.
SPDiffusion: Semantic Protection Diffusion for Multi-concept Text-to-image Generation
Sep 02, 2024



Abstract:Recent text-to-image models have achieved remarkable success in generating high-quality images. However, when tasked with multi-concept generation which creates images containing multiple characters or objects, existing methods often suffer from attribute confusion, resulting in severe text-image inconsistency. We found that attribute confusion occurs when a certain region of the latent features attend to multiple or incorrect prompt tokens. In this work, we propose novel Semantic Protection Diffusion (SPDiffusion) to protect the semantics of regions from the influence of irrelevant tokens, eliminating the confusion of non-corresponding attributes. In the SPDiffusion framework, we design a Semantic Protection Mask (SP-Mask) to represent the relevance of the regions and the tokens, and propose a Semantic Protection Cross-Attention (SP-Attn) to shield the influence of irrelevant tokens on specific regions in the generation process. To evaluate our method, we created a diverse multi-concept benchmark, and SPDiffusion achieves state-of-the-art results on this benchmark, proving its effectiveness. Our method can be combined with many other application methods or backbones, such as ControlNet, Story Diffusion, PhotoMaker and PixArt-alpha to enhance their multi-concept capabilities, demonstrating strong compatibility and scalability.
Draw Like an Artist: Complex Scene Generation with Diffusion Model via Composition, Painting, and Retouching
Aug 25, 2024
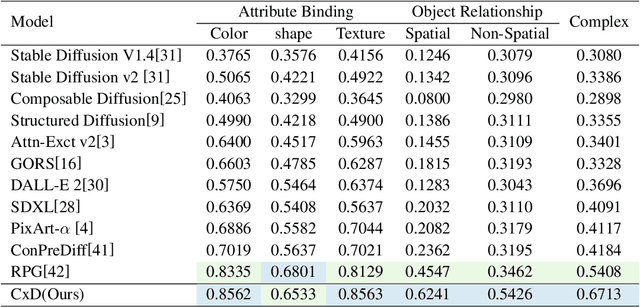
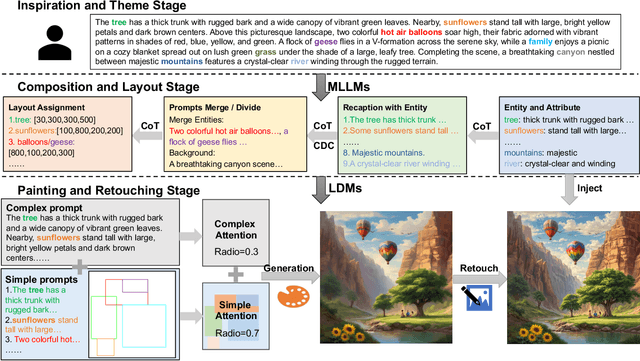
Abstract:Recent advances in text-to-image diffusion models have demonstrated impressive capabilities in image quality. However, complex scene generation remains relatively unexplored, and even the definition of `complex scene' itself remains unclear. In this paper, we address this gap by providing a precise definition of complex scenes and introducing a set of Complex Decomposition Criteria (CDC) based on this definition. Inspired by the artists painting process, we propose a training-free diffusion framework called Complex Diffusion (CxD), which divides the process into three stages: composition, painting, and retouching. Our method leverages the powerful chain-of-thought capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to decompose complex prompts based on CDC and to manage composition and layout. We then develop an attention modulation method that guides simple prompts to specific regions to complete the complex scene painting. Finally, we inject the detailed output of the LLM into a retouching model to enhance the image details, thus implementing the retouching stage. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms previous SOTA approaches, significantly improving the generation of high-quality, semantically consistent, and visually diverse images for complex scenes, even with intricate prompts.
SAM-REF: Rethinking Image-Prompt Synergy for Refinement in Segment Anything
Aug 22, 2024



Abstract:The advent of the Segment Anything Model (SAM) marks a significant milestone for interactive segmentation using generalist models. As a late fusion model, SAM extracts image embeddings once and merges them with prompts in later interactions. This strategy limits the models ability to extract detailed information from the prompted target zone. Current specialist models utilize the early fusion strategy that encodes the combination of images and prompts to target the prompted objects, yet repetitive complex computations on the images result in high latency. The key to these issues is efficiently synergizing the images and prompts. We propose SAM-REF, a two-stage refinement framework that fully integrates images and prompts globally and locally while maintaining the accuracy of early fusion and the efficiency of late fusion. The first-stage GlobalDiff Refiner is a lightweight early fusion network that combines the whole image and prompts, focusing on capturing detailed information for the entire object. The second-stage PatchDiff Refiner locates the object detail window according to the mask and prompts, then refines the local details of the object. Experimentally, we demonstrated the high effectiveness and efficiency of our method in tackling complex cases with multiple interactions. Our SAM-REF model outperforms the current state-of-the-art method in most metrics on segmentation quality without compromising efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge