Zicheng Zhang
RISE-Video: Can Video Generators Decode Implicit World Rules?
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:While generative video models have achieved remarkable visual fidelity, their capacity to internalize and reason over implicit world rules remains a critical yet under-explored frontier. To bridge this gap, we present RISE-Video, a pioneering reasoning-oriented benchmark for Text-Image-to-Video (TI2V) synthesis that shifts the evaluative focus from surface-level aesthetics to deep cognitive reasoning. RISE-Video comprises 467 meticulously human-annotated samples spanning eight rigorous categories, providing a structured testbed for probing model intelligence across diverse dimensions, ranging from commonsense and spatial dynamics to specialized subject domains. Our framework introduces a multi-dimensional evaluation protocol consisting of four metrics: \textit{Reasoning Alignment}, \textit{Temporal Consistency}, \textit{Physical Rationality}, and \textit{Visual Quality}. To further support scalable evaluation, we propose an automated pipeline leveraging Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) to emulate human-centric assessment. Extensive experiments on 11 state-of-the-art TI2V models reveal pervasive deficiencies in simulating complex scenarios under implicit constraints, offering critical insights for the advancement of future world-simulating generative models.
VideoAesBench: Benchmarking the Video Aesthetics Perception Capabilities of Large Multimodal Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) have demonstrated outstanding capabilities in various visual perception tasks, which has in turn made the evaluation of LMMs significant. However, the capability of video aesthetic quality assessment, which is a fundamental ability for human, remains underexplored for LMMs. To address this, we introduce VideoAesBench, a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating LMMs' understanding of video aesthetic quality. VideoAesBench has several significant characteristics: (1) Diverse content including 1,804 videos from multiple video sources including user-generated (UGC), AI-generated (AIGC), compressed, robotic-generated (RGC), and game videos. (2) Multiple question formats containing traditional single-choice questions, multi-choice questions, True or False questions, and a novel open-ended questions for video aesthetics description. (3) Holistic video aesthetics dimensions including visual form related questions from 5 aspects, visual style related questions from 4 aspects, and visual affectiveness questions from 3 aspects. Based on VideoAesBench, we benchmark 23 open-source and commercial large multimodal models. Our findings show that current LMMs only contain basic video aesthetics perception ability, their performance remains incomplete and imprecise. We hope our VideoAesBench can be served as a strong testbed and offer insights for explainable video aesthetics assessment.
Automated Safety Benchmarking: A Multi-agent Pipeline for LVLMs
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities in cross-modal tasks but face significant safety challenges, which undermine their reliability in real-world applications. Efforts have been made to build LVLM safety evaluation benchmarks to uncover their vulnerability. However, existing benchmarks are hindered by their labor-intensive construction process, static complexity, and limited discriminative power. Thus, they may fail to keep pace with rapidly evolving models and emerging risks. To address these limitations, we propose VLSafetyBencher, the first automated system for LVLM safety benchmarking. VLSafetyBencher introduces four collaborative agents: Data Preprocessing, Generation, Augmentation, and Selection agents to construct and select high-quality samples. Experiments validates that VLSafetyBencher can construct high-quality safety benchmarks within one week at a minimal cost. The generated benchmark effectively distinguish safety, with a safety rate disparity of 70% between the most and least safe models.
Q-Bench-Portrait: Benchmarking Multimodal Large Language Models on Portrait Image Quality Perception
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance on existing low-level vision benchmarks, which primarily focus on generic images. However, their capabilities to perceive and assess portrait images, a domain characterized by distinct structural and perceptual properties, remain largely underexplored. To this end, we introduce Q-Bench-Portrait, the first holistic benchmark specifically designed for portrait image quality perception, comprising 2,765 image-question-answer triplets and featuring (1) diverse portrait image sources, including natural, synthetic distortion, AI-generated, artistic, and computer graphics images; (2) comprehensive quality dimensions, covering technical distortions, AIGC-specific distortions, and aesthetics; and (3) a range of question formats, including single-choice, multiple-choice, true/false, and open-ended questions, at both global and local levels. Based on Q-Bench-Portrait, we evaluate 20 open-source and 5 closed-source MLLMs, revealing that although current models demonstrate some competence in portrait image perception, their performance remains limited and imprecise, with a clear gap relative to human judgments. We hope that the proposed benchmark will foster further research into enhancing the portrait image perception capabilities of both general-purpose and domain-specific MLLMs.
Enhancing Image Quality Assessment Ability of LMMs via Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have recently shown remarkable promise in low-level visual perception tasks, particularly in Image Quality Assessment (IQA), demonstrating strong zero-shot capability. However, achieving state-of-the-art performance often requires computationally expensive fine-tuning methods, which aim to align the distribution of quality-related token in output with image quality levels. Inspired by recent training-free works for LMM, we introduce IQARAG, a novel, training-free framework that enhances LMMs' IQA ability. IQARAG leverages Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to retrieve some semantically similar but quality-variant reference images with corresponding Mean Opinion Scores (MOSs) for input image. These retrieved images and input image are integrated into a specific prompt. Retrieved images provide the LMM with a visual perception anchor for IQA task. IQARAG contains three key phases: Retrieval Feature Extraction, Image Retrieval, and Integration & Quality Score Generation. Extensive experiments across multiple diverse IQA datasets, including KADID, KonIQ, LIVE Challenge, and SPAQ, demonstrate that the proposed IQARAG effectively boosts the IQA performance of LMMs, offering a resource-efficient alternative to fine-tuning for quality assessment.
EvolMem: A Cognitive-Driven Benchmark for Multi-Session Dialogue Memory
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Despite recent advances in understanding and leveraging long-range conversational memory, existing benchmarks still lack systematic evaluation of large language models(LLMs) across diverse memory dimensions, particularly in multi-session settings. In this work, we propose EvolMem, a new benchmark for assessing multi-session memory capabilities of LLMs and agent systems. EvolMem is grounded in cognitive psychology and encompasses both declarative and non-declarative memory, further decomposed into multiple fine-grained abilities. To construct the benchmark, we introduce a hybrid data synthesis framework that consists of topic-initiated generation and narrative-inspired transformations. This framework enables scalable generation of multi-session conversations with controllable complexity, accompanied by sample-specific evaluation guidelines. Extensive evaluation reveals that no LLM consistently outperforms others across all memory dimensions. Moreover, agent memory mechanisms do not necessarily enhance LLMs' capabilities and often exhibit notable efficiency limitations. Data and code will be released at https://github.com/shenye7436/EvolMem.
Embodied Image Compression
Dec 12, 2025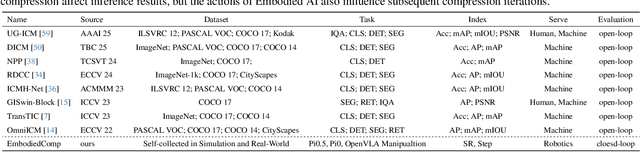
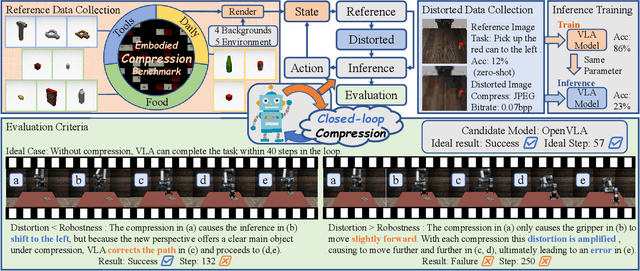
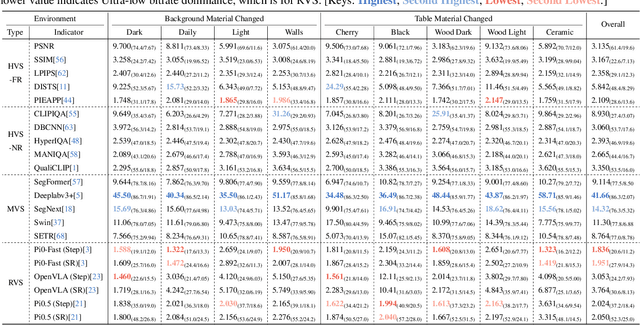
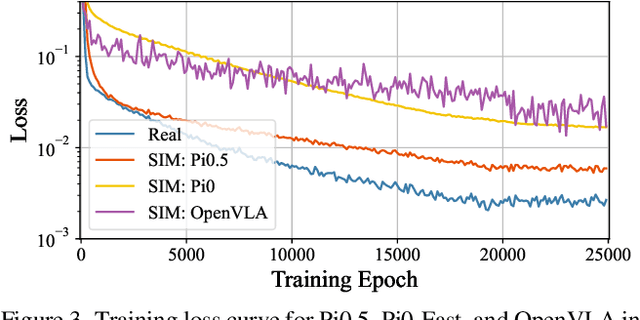
Abstract:Image Compression for Machines (ICM) has emerged as a pivotal research direction in the field of visual data compression. However, with the rapid evolution of machine intelligence, the target of compression has shifted from task-specific virtual models to Embodied agents operating in real-world environments. To address the communication constraints of Embodied AI in multi-agent systems and ensure real-time task execution, this paper introduces, for the first time, the scientific problem of Embodied Image Compression. We establish a standardized benchmark, EmbodiedComp, to facilitate systematic evaluation under ultra-low bitrate conditions in a closed-loop setting. Through extensive empirical studies in both simulated and real-world settings, we demonstrate that existing Vision-Language-Action models (VLAs) fail to reliably perform even simple manipulation tasks when compressed below the Embodied bitrate threshold. We anticipate that EmbodiedComp will catalyze the development of domain-specific compression tailored for Embodied agents , thereby accelerating the Embodied AI deployment in the Real-world.
Using GUI Agent for Electronic Design Automation
Dec 12, 2025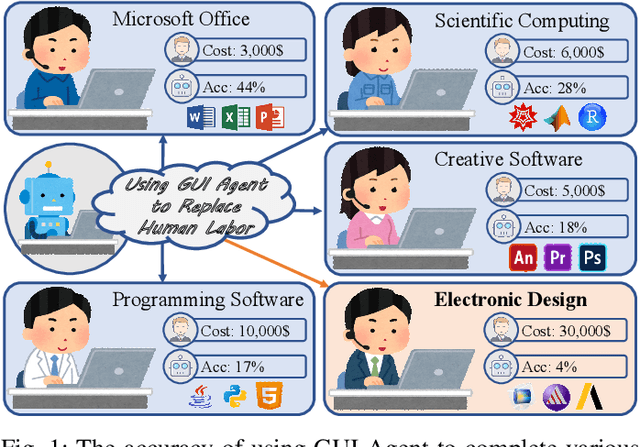
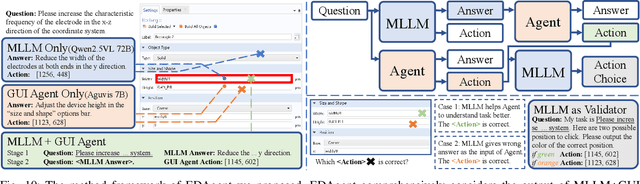
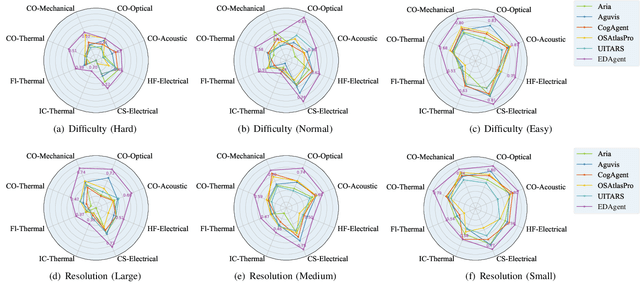
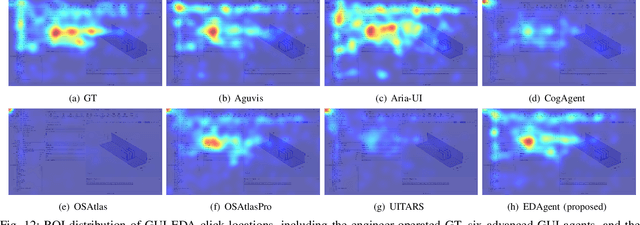
Abstract:Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents adopt an end-to-end paradigm that maps a screenshot to an action sequence, thereby automating repetitive tasks in virtual environments. However, existing GUI agents are evaluated almost exclusively on commodity software such as Microsoft Word and Excel. Professional Computer-Aided Design (CAD) suites promise an order-of-magnitude higher economic return, yet remain the weakest performance domain for existing agents and are still far from replacing expert Electronic-Design-Automation (EDA) engineers. We therefore present the first systematic study that deploys GUI agents for EDA workflows. Our contributions are: (1) a large-scale dataset named GUI-EDA, including 5 CAD tools and 5 physical domains, comprising 2,000+ high-quality screenshot-answer-action pairs recorded by EDA scientists and engineers during real-world component design; (2) a comprehensive benchmark that evaluates 30+ mainstream GUI agents, demonstrating that EDA tasks constitute a major, unsolved challenge; and (3) an EDA-specialized metric named EDAgent, equipped with a reflection mechanism that achieves reliable performance on industrial CAD software and, for the first time, outperforms Ph.D. students majored in Electrical Engineering. This work extends GUI agents from generic office automation to specialized, high-value engineering domains and offers a new avenue for advancing EDA productivity. The dataset will be released at: https://github.com/aiben-ch/GUI-EDA.
GeoX-Bench: Benchmarking Cross-View Geo-Localization and Pose Estimation Capabilities of Large Multimodal Models
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across a wide range of tasks, however their knowledge and abilities in the cross-view geo-localization and pose estimation domains remain unexplored, despite potential benefits for navigation, autonomous driving, outdoor robotics, \textit{etc}. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textbf{GeoX-Bench}, a comprehensive \underline{Bench}mark designed to explore and evaluate the capabilities of LMMs in \underline{cross}-view \underline{Geo}-localization and pose estimation. Specifically, GeoX-Bench contains 10,859 panoramic-satellite image pairs spanning 128 cities in 49 countries, along with corresponding 755,976 question-answering (QA) pairs. Among these, 42,900 QA pairs are designated for benchmarking, while the remaining are intended to enhance the capabilities of LMMs. Based on GeoX-Bench, we evaluate the capabilities of 25 state-of-the-art LMMs on cross-view geo-localization and pose estimation tasks, and further explore the empowered capabilities of instruction-tuning. Our benchmark demonstrate that while current LMMs achieve impressive performance in geo-localization tasks, their effectiveness declines significantly on the more complex pose estimation tasks, highlighting a critical area for future improvement, and instruction-tuning LMMs on the training data of GeoX-Bench can significantly improve the cross-view geo-sense abilities. The GeoX-Bench is available at \textcolor{magenta}{https://github.com/IntMeGroup/GeoX-Bench}.
A Multi-To-One Interview Paradigm for Efficient MLLM Evaluation
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:The rapid progress of Multi-Modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has spurred the creation of numerous benchmarks. However, conventional full-coverage Question-Answering evaluations suffer from high redundancy and low efficiency. Inspired by human interview processes, we propose a multi-to-one interview paradigm for efficient MLLM evaluation. Our framework consists of (i) a two-stage interview strategy with pre-interview and formal interview phases, (ii) dynamic adjustment of interviewer weights to ensure fairness, and (iii) an adaptive mechanism for question difficulty-level chosen. Experiments on different benchmarks show that the proposed paradigm achieves significantly higher correlation with full-coverage results than random sampling, with improvements of up to 17.6% in PLCC and 16.7% in SRCC, while reducing the number of required questions. These findings demonstrate that the proposed paradigm provides a reliable and efficient alternative for large-scale MLLM benchmarking.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge