Xiaohong Liu
STAR : Bridging Statistical and Agentic Reasoning for Large Model Performance Prediction
Feb 12, 2026Abstract:As comprehensive large model evaluation becomes prohibitively expensive, predicting model performance from limited observations has become essential. However, existing statistical methods struggle with pattern shifts, data sparsity, and lack of explanation, while pure LLM methods remain unreliable. We propose STAR, a framework that bridges data-driven STatistical expectations with knowledge-driven Agentic Reasoning. STAR leverages specialized retrievers to gather external knowledge and embeds semantic features into Constrained Probabilistic Matrix Factorization (CPMF) to generate statistical expectations with uncertainty. A reasoning module guided by Expectation Violation Theory (EVT) then refines predictions through intra-family analysis, cross-model comparison, and credibility-aware aggregation, producing adjustments with traceable explanations. Extensive experiments show that STAR consistently outperforms all baselines on both score-based and rank-based metrics, delivering a 14.46% gain in total score over the strongest statistical method under extreme sparsity, with only 1--2 observed scores per test model.
Light Up Your Face: A Physically Consistent Dataset and Diffusion Model for Face Fill-Light Enhancement
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Face fill-light enhancement (FFE) brightens underexposed faces by adding virtual fill light while keeping the original scene illumination and background unchanged. Most face relighting methods aim to reshape overall lighting, which can suppress the input illumination or modify the entire scene, leading to foreground-background inconsistency and mismatching practical FFE needs. To support scalable learning, we introduce LightYourFace-160K (LYF-160K), a large-scale paired dataset built with a physically consistent renderer that injects a disk-shaped area fill light controlled by six disentangled factors, producing 160K before-and-after pairs. We first pretrain a physics-aware lighting prompt (PALP) that embeds the 6D parameters into conditioning tokens, using an auxiliary planar-light reconstruction objective. Building on a pretrained diffusion backbone, we then train a fill-light diffusion (FiLitDiff), an efficient one-step model conditioned on physically grounded lighting codes, enabling controllable and high-fidelity fill lighting at low computational cost. Experiments on held-out paired sets demonstrate strong perceptual quality and competitive full-reference metrics, while better preserving background illumination. The dataset and model will be at https://github.com/gobunu/Light-Up-Your-Face.
Samba+: General and Accurate Salient Object Detection via A More Unified Mamba-based Framework
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Existing salient object detection (SOD) models are generally constrained by the limited receptive fields of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) and quadratic computational complexity of Transformers. Recently, the emerging state-space model, namely Mamba, has shown great potential in balancing global receptive fields and computational efficiency. As a solution, we propose Saliency Mamba (Samba), a pure Mamba-based architecture that flexibly handles various distinct SOD tasks, including RGB/RGB-D/RGB-T SOD, video SOD (VSOD), RGB-D VSOD, and visible-depth-thermal SOD. Specifically, we rethink the scanning strategy of Mamba for SOD, and introduce a saliency-guided Mamba block (SGMB) that features a spatial neighborhood scanning (SNS) algorithm to preserve the spatial continuity of salient regions. A context-aware upsampling (CAU) method is also proposed to promote hierarchical feature alignment and aggregation by modeling contextual dependencies. As one step further, to avoid the "task-specific" problem as in previous SOD solutions, we develop Samba+, which is empowered by training Samba in a multi-task joint manner, leading to a more unified and versatile model. Two crucial components that collaboratively tackle challenges encountered in input of arbitrary modalities and continual adaptation are investigated. Specifically, a hub-and-spoke graph attention (HGA) module facilitates adaptive cross-modal interactive fusion, and a modality-anchored continual learning (MACL) strategy alleviates inter-modal conflicts together with catastrophic forgetting. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Samba individually outperforms existing methods across six SOD tasks on 22 datasets with lower computational cost, whereas Samba+ achieves even superior results on these tasks and datasets by using a single trained versatile model. Additional results further demonstrate the potential of our Samba framework.
Prism: Efficient Test-Time Scaling via Hierarchical Search and Self-Verification for Discrete Diffusion Language Models
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Inference-time compute has re-emerged as a practical way to improve LLM reasoning. Most test-time scaling (TTS) algorithms rely on autoregressive decoding, which is ill-suited to discrete diffusion language models (dLLMs) due to their parallel decoding over the entire sequence. As a result, developing effective and efficient TTS methods to unlock dLLMs' full generative potential remains an underexplored challenge. To address this, we propose Prism (Pruning, Remasking, and Integrated Self-verification Method), an efficient TTS framework for dLLMs that (i) performs Hierarchical Trajectory Search (HTS) which dynamically prunes and reallocates compute in an early-to-mid denoising window, (ii) introduces Local branching with partial remasking to explore diverse implementations while preserving high-confidence tokens, and (iii) replaces external verifiers with Self-Verified Feedback (SVF) obtained via self-evaluation prompts on intermediate completions. Across four mathematical reasoning and code generation benchmarks on three dLLMs, including LLaDA 8B Instruct, Dream 7B Instruct, and LLaDA 2.0-mini, our Prism achieves a favorable performance-efficiency trade-off, matching best-of-N performance with substantially fewer function evaluations (NFE). The code is released at https://github.com/viiika/Prism.
Advances and Innovations in the Multi-Agent Robotic System (MARS) Challenge
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in multimodal large language models and vision-languageaction models have significantly driven progress in Embodied AI. As the field transitions toward more complex task scenarios, multi-agent system frameworks are becoming essential for achieving scalable, efficient, and collaborative solutions. This shift is fueled by three primary factors: increasing agent capabilities, enhancing system efficiency through task delegation, and enabling advanced human-agent interactions. To address the challenges posed by multi-agent collaboration, we propose the Multi-Agent Robotic System (MARS) Challenge, held at the NeurIPS 2025 Workshop on SpaVLE. The competition focuses on two critical areas: planning and control, where participants explore multi-agent embodied planning using vision-language models (VLMs) to coordinate tasks and policy execution to perform robotic manipulation in dynamic environments. By evaluating solutions submitted by participants, the challenge provides valuable insights into the design and coordination of embodied multi-agent systems, contributing to the future development of advanced collaborative AI systems.
dMLLM-TTS: Self-Verified and Efficient Test-Time Scaling for Diffusion Multi-Modal Large Language Models
Dec 22, 2025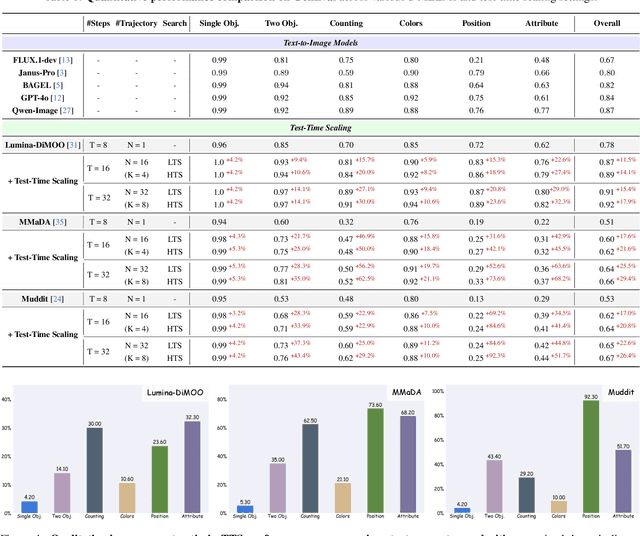
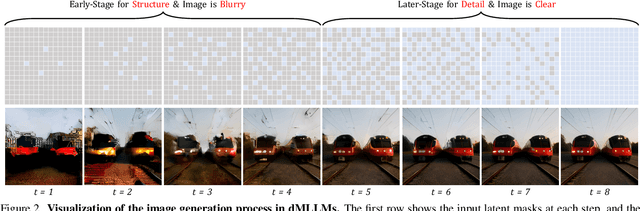
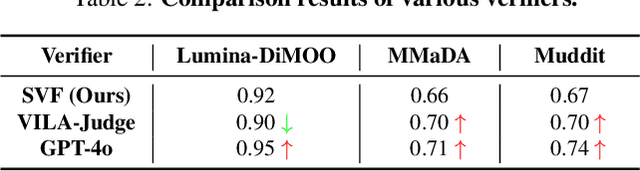
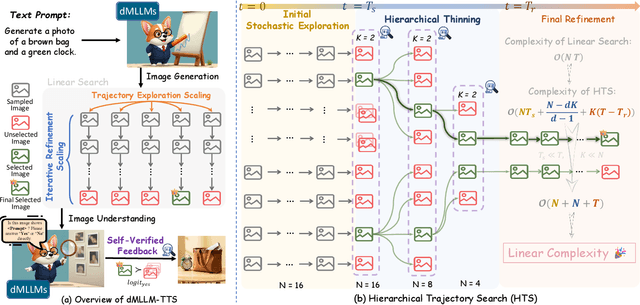
Abstract:Diffusion Multi-modal Large Language Models (dMLLMs) have recently emerged as a novel architecture unifying image generation and understanding. However, developing effective and efficient Test-Time Scaling (TTS) methods to unlock their full generative potential remains an underexplored challenge. To address this, we propose dMLLM-TTS, a novel framework operating on two complementary scaling axes: (1) trajectory exploration scaling to enhance the diversity of generated hypotheses, and (2) iterative refinement scaling for stable generation. Conventional TTS approaches typically perform linear search across these two dimensions, incurring substantial computational costs of O(NT) and requiring an external verifier for best-of-N selection. To overcome these limitations, we propose two innovations. First, we design an efficient hierarchical search algorithm with O(N+T) complexity that adaptively expands and prunes sampling trajectories. Second, we introduce a self-verified feedback mechanism that leverages the dMLLMs' intrinsic image understanding capabilities to assess text-image alignment, eliminating the need for external verifier. Extensive experiments on the GenEval benchmark across three representative dMLLMs (e.g., Lumina-DiMOO, MMaDA, Muddit) show that our framework substantially improves generation quality while achieving up to 6x greater efficiency than linear search. Project page: https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-DiMOO.
Using GUI Agent for Electronic Design Automation
Dec 12, 2025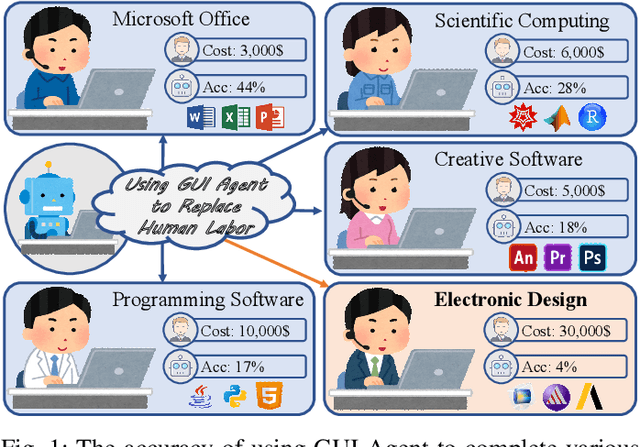
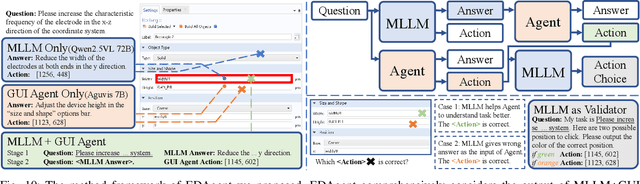
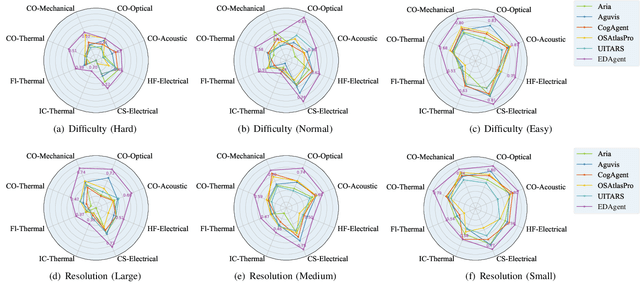
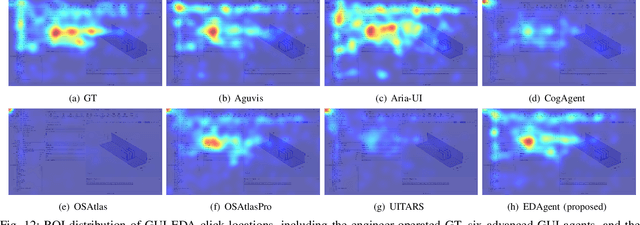
Abstract:Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents adopt an end-to-end paradigm that maps a screenshot to an action sequence, thereby automating repetitive tasks in virtual environments. However, existing GUI agents are evaluated almost exclusively on commodity software such as Microsoft Word and Excel. Professional Computer-Aided Design (CAD) suites promise an order-of-magnitude higher economic return, yet remain the weakest performance domain for existing agents and are still far from replacing expert Electronic-Design-Automation (EDA) engineers. We therefore present the first systematic study that deploys GUI agents for EDA workflows. Our contributions are: (1) a large-scale dataset named GUI-EDA, including 5 CAD tools and 5 physical domains, comprising 2,000+ high-quality screenshot-answer-action pairs recorded by EDA scientists and engineers during real-world component design; (2) a comprehensive benchmark that evaluates 30+ mainstream GUI agents, demonstrating that EDA tasks constitute a major, unsolved challenge; and (3) an EDA-specialized metric named EDAgent, equipped with a reflection mechanism that achieves reliable performance on industrial CAD software and, for the first time, outperforms Ph.D. students majored in Electrical Engineering. This work extends GUI agents from generic office automation to specialized, high-value engineering domains and offers a new avenue for advancing EDA productivity. The dataset will be released at: https://github.com/aiben-ch/GUI-EDA.
Embodied Image Compression
Dec 12, 2025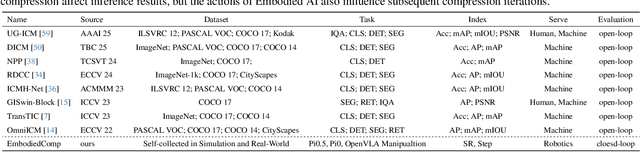
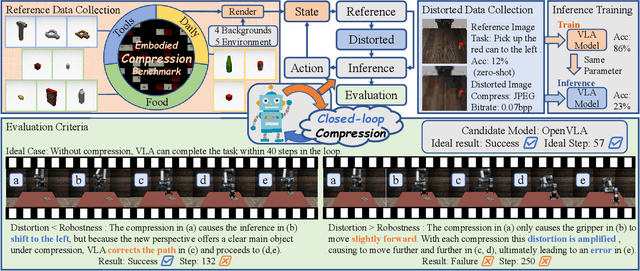
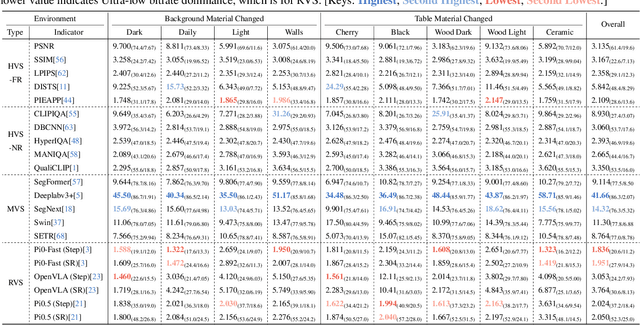
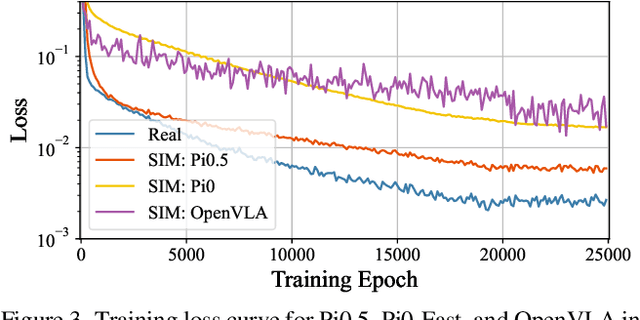
Abstract:Image Compression for Machines (ICM) has emerged as a pivotal research direction in the field of visual data compression. However, with the rapid evolution of machine intelligence, the target of compression has shifted from task-specific virtual models to Embodied agents operating in real-world environments. To address the communication constraints of Embodied AI in multi-agent systems and ensure real-time task execution, this paper introduces, for the first time, the scientific problem of Embodied Image Compression. We establish a standardized benchmark, EmbodiedComp, to facilitate systematic evaluation under ultra-low bitrate conditions in a closed-loop setting. Through extensive empirical studies in both simulated and real-world settings, we demonstrate that existing Vision-Language-Action models (VLAs) fail to reliably perform even simple manipulation tasks when compressed below the Embodied bitrate threshold. We anticipate that EmbodiedComp will catalyze the development of domain-specific compression tailored for Embodied agents , thereby accelerating the Embodied AI deployment in the Real-world.
ATLAS: A High-Difficulty, Multidisciplinary Benchmark for Frontier Scientific Reasoning
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has led to performance saturation on many established benchmarks, questioning their ability to distinguish frontier models. Concurrently, existing high-difficulty benchmarks often suffer from narrow disciplinary focus, oversimplified answer formats, and vulnerability to data contamination, creating a fidelity gap with real-world scientific inquiry. To address these challenges, we introduce ATLAS (AGI-Oriented Testbed for Logical Application in Science), a large-scale, high-difficulty, and cross-disciplinary evaluation suite composed of approximately 800 original problems. Developed by domain experts (PhD-level and above), ATLAS spans seven core scientific fields: mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, computer science, earth science, and materials science. Its key features include: (1) High Originality and Contamination Resistance, with all questions newly created or substantially adapted to prevent test data leakage; (2) Cross-Disciplinary Focus, designed to assess models' ability to integrate knowledge and reason across scientific domains; (3) High-Fidelity Answers, prioritizing complex, open-ended answers involving multi-step reasoning and LaTeX-formatted expressions over simple multiple-choice questions; and (4) Rigorous Quality Control, employing a multi-stage process of expert peer review and adversarial testing to ensure question difficulty, scientific value, and correctness. We also propose a robust evaluation paradigm using a panel of LLM judges for automated, nuanced assessment of complex answers. Preliminary results on leading models demonstrate ATLAS's effectiveness in differentiating their advanced scientific reasoning capabilities. We plan to develop ATLAS into a long-term, open, community-driven platform to provide a reliable "ruler" for progress toward Artificial General Intelligence.
GeoX-Bench: Benchmarking Cross-View Geo-Localization and Pose Estimation Capabilities of Large Multimodal Models
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across a wide range of tasks, however their knowledge and abilities in the cross-view geo-localization and pose estimation domains remain unexplored, despite potential benefits for navigation, autonomous driving, outdoor robotics, \textit{etc}. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textbf{GeoX-Bench}, a comprehensive \underline{Bench}mark designed to explore and evaluate the capabilities of LMMs in \underline{cross}-view \underline{Geo}-localization and pose estimation. Specifically, GeoX-Bench contains 10,859 panoramic-satellite image pairs spanning 128 cities in 49 countries, along with corresponding 755,976 question-answering (QA) pairs. Among these, 42,900 QA pairs are designated for benchmarking, while the remaining are intended to enhance the capabilities of LMMs. Based on GeoX-Bench, we evaluate the capabilities of 25 state-of-the-art LMMs on cross-view geo-localization and pose estimation tasks, and further explore the empowered capabilities of instruction-tuning. Our benchmark demonstrate that while current LMMs achieve impressive performance in geo-localization tasks, their effectiveness declines significantly on the more complex pose estimation tasks, highlighting a critical area for future improvement, and instruction-tuning LMMs on the training data of GeoX-Bench can significantly improve the cross-view geo-sense abilities. The GeoX-Bench is available at \textcolor{magenta}{https://github.com/IntMeGroup/GeoX-Bench}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge