Yingjie Zhou
Q-Agent: Quality-Driven Chain-of-Thought Image Restoration Agent through Robust Multimodal Large Language Model
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:Image restoration (IR) often faces various complex and unknown degradations in real-world scenarios, such as noise, blurring, compression artifacts, and low resolution, etc. Training specific models for specific degradation may lead to poor generalization. To handle multiple degradations simultaneously, All-in-One models might sacrifice performance on certain types of degradation and still struggle with unseen degradations during training. Existing IR agents rely on multimodal large language models (MLLM) and a time-consuming rolling-back selection strategy neglecting image quality. As a result, they may misinterpret degradations and have high time and computational costs to conduct unnecessary IR tasks with redundant order. To address these, we propose a Quality-Driven agent (Q-Agent) via Chain-of-Thought (CoT) restoration. Specifically, our Q-Agent consists of robust degradation perception and quality-driven greedy restoration. The former module first fine-tunes MLLM, and uses CoT to decompose multi-degradation perception into single-degradation perception tasks to enhance the perception of MLLMs. The latter employs objective image quality assessment (IQA) metrics to determine the optimal restoration sequence and execute the corresponding restoration algorithms. Experimental results demonstrate that our Q-Agent achieves superior IR performance compared to existing All-in-One models.
From Dense to Sparse: Event Response for Enhanced Residential Load Forecasting
Jan 08, 2025


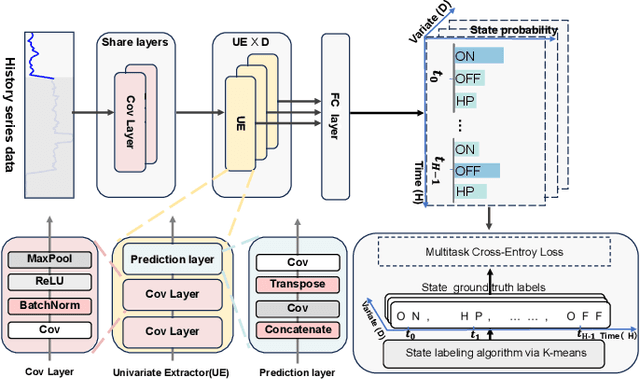
Abstract:Residential load forecasting (RLF) is crucial for resource scheduling in power systems. Most existing methods utilize all given load records (dense data) to indiscriminately extract the dependencies between historical and future time series. However, there exist important regular patterns residing in the event-related associations among different appliances (sparse knowledge), which have yet been ignored. In this paper, we propose an Event-Response Knowledge Guided approach (ERKG) for RLF by incorporating the estimation of electricity usage events for different appliances, mining event-related sparse knowledge from the load series. With ERKG, the event-response estimation enables portraying the electricity consumption behaviors of residents, revealing regular variations in appliance operational states. To be specific, ERKG consists of knowledge extraction and guidance: i) a forecasting model is designed for the electricity usage events by estimating appliance operational states, aiming to extract the event-related sparse knowledge; ii) a novel knowledge-guided mechanism is established by fusing such state estimates of the appliance events into the RLF model, which can give particular focuses on the patterns of users' electricity consumption behaviors. Notably, ERKG can flexibly serve as a plug-in module to boost the capability of existing forecasting models by leveraging event response. In numerical experiments, extensive comparisons and ablation studies have verified the effectiveness of our ERKG, e.g., over 8% MAE can be reduced on the tested state-of-the-art forecasting models.
Ultrasound-QBench: Can LLMs Aid in Quality Assessment of Ultrasound Imaging?
Jan 06, 2025



Abstract:With the dramatic upsurge in the volume of ultrasound examinations, low-quality ultrasound imaging has gradually increased due to variations in operator proficiency and imaging circumstances, imposing a severe burden on diagnosis accuracy and even entailing the risk of restarting the diagnosis in critical cases. To assist clinicians in selecting high-quality ultrasound images and ensuring accurate diagnoses, we introduce Ultrasound-QBench, a comprehensive benchmark that systematically evaluates multimodal large language models (MLLMs) on quality assessment tasks of ultrasound images. Ultrasound-QBench establishes two datasets collected from diverse sources: IVUSQA, consisting of 7,709 images, and CardiacUltraQA, containing 3,863 images. These images encompassing common ultrasound imaging artifacts are annotated by professional ultrasound experts and classified into three quality levels: high, medium, and low. To better evaluate MLLMs, we decompose the quality assessment task into three dimensionalities: qualitative classification, quantitative scoring, and comparative assessment. The evaluation of 7 open-source MLLMs as well as 1 proprietary MLLMs demonstrates that MLLMs possess preliminary capabilities for low-level visual tasks in ultrasound image quality classification. We hope this benchmark will inspire the research community to delve deeper into uncovering and enhancing the untapped potential of MLLMs for medical imaging tasks.
LLM-Virus: Evolutionary Jailbreak Attack on Large Language Models
Dec 28, 2024



Abstract:While safety-aligned large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used as the cornerstone for powerful systems such as multi-agent frameworks to solve complex real-world problems, they still suffer from potential adversarial queries, such as jailbreak attacks, which attempt to induce harmful content. Researching attack methods allows us to better understand the limitations of LLM and make trade-offs between helpfulness and safety. However, existing jailbreak attacks are primarily based on opaque optimization techniques (e.g. token-level gradient descent) and heuristic search methods like LLM refinement, which fall short in terms of transparency, transferability, and computational cost. In light of these limitations, we draw inspiration from the evolution and infection processes of biological viruses and propose LLM-Virus, a jailbreak attack method based on evolutionary algorithm, termed evolutionary jailbreak. LLM-Virus treats jailbreak attacks as both an evolutionary and transfer learning problem, utilizing LLMs as heuristic evolutionary operators to ensure high attack efficiency, transferability, and low time cost. Our experimental results on multiple safety benchmarks show that LLM-Virus achieves competitive or even superior performance compared to existing attack methods.
WiFi CSI Based Temporal Activity Detection Via Dual Pyramid Network
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:We address the challenge of WiFi-based temporal activity detection and propose an efficient Dual Pyramid Network that integrates Temporal Signal Semantic Encoders and Local Sensitive Response Encoders. The Temporal Signal Semantic Encoder splits feature learning into high and low-frequency components, using a novel Signed Mask-Attention mechanism to emphasize important areas and downplay unimportant ones, with the features fused using ContraNorm. The Local Sensitive Response Encoder captures fluctuations without learning. These feature pyramids are then combined using a new cross-attention fusion mechanism. We also introduce a dataset with over 2,114 activity segments across 553 WiFi CSI samples, each lasting around 85 seconds. Extensive experiments show our method outperforms challenging baselines. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/AVC2-UESTC/WiFiTAD.
MEMO-Bench: A Multiple Benchmark for Text-to-Image and Multimodal Large Language Models on Human Emotion Analysis
Nov 18, 2024



Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) has demonstrated significant capabilities in various fields, and in areas such as human-computer interaction (HCI), embodied intelligence, and the design and animation of virtual digital humans, both practitioners and users are increasingly concerned with AI's ability to understand and express emotion. Consequently, the question of whether AI can accurately interpret human emotions remains a critical challenge. To date, two primary classes of AI models have been involved in human emotion analysis: generative models and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). To assess the emotional capabilities of these two classes of models, this study introduces MEMO-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark consisting of 7,145 portraits, each depicting one of six different emotions, generated by 12 Text-to-Image (T2I) models. Unlike previous works, MEMO-Bench provides a framework for evaluating both T2I models and MLLMs in the context of sentiment analysis. Additionally, a progressive evaluation approach is employed, moving from coarse-grained to fine-grained metrics, to offer a more detailed and comprehensive assessment of the sentiment analysis capabilities of MLLMs. The experimental results demonstrate that existing T2I models are more effective at generating positive emotions than negative ones. Meanwhile, although MLLMs show a certain degree of effectiveness in distinguishing and recognizing human emotions, they fall short of human-level accuracy, particularly in fine-grained emotion analysis. The MEMO-Bench will be made publicly available to support further research in this area.
Q-Bench-Video: Benchmarking the Video Quality Understanding of LMMs
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:With the rising interest in research on Large Multi-modal Models (LMMs) for video understanding, many studies have emphasized general video comprehension capabilities, neglecting the systematic exploration into video quality understanding. To address this oversight, we introduce Q-Bench-Video in this paper, a new benchmark specifically designed to evaluate LMMs' proficiency in discerning video quality. a) To ensure video source diversity, Q-Bench-Video encompasses videos from natural scenes, AI-generated Content (AIGC), and Computer Graphics (CG). b) Building on the traditional multiple-choice questions format with the Yes-or-No and What-How categories, we include Open-ended questions to better evaluate complex scenarios. Additionally, we incorporate the video pair quality comparison question to enhance comprehensiveness. c) Beyond the traditional Technical, Aesthetic, and Temporal distortions, we have expanded our evaluation aspects to include the dimension of AIGC distortions, which addresses the increasing demand for video generation. Finally, we collect a total of 2,378 question-answer pairs and test them on 12 open-source & 5 proprietary LMMs. Our findings indicate that while LMMs have a foundational understanding of video quality, their performance remains incomplete and imprecise, with a notable discrepancy compared to human performance. Through Q-Bench-Video, we seek to catalyze community interest, stimulate further research, and unlock the untapped potential of LMMs to close the gap in video quality understanding.
3DGCQA: A Quality Assessment Database for 3D AI-Generated Contents
Sep 12, 2024



Abstract:Although 3D generated content (3DGC) offers advantages in reducing production costs and accelerating design timelines, its quality often falls short when compared to 3D professionally generated content. Common quality issues frequently affect 3DGC, highlighting the importance of timely and effective quality assessment. Such evaluations not only ensure a higher standard of 3DGCs for end-users but also provide critical insights for advancing generative technologies. To address existing gaps in this domain, this paper introduces a novel 3DGC quality assessment dataset, 3DGCQA, built using 7 representative Text-to-3D generation methods. During the dataset's construction, 50 fixed prompts are utilized to generate contents across all methods, resulting in the creation of 313 textured meshes that constitute the 3DGCQA dataset. The visualization intuitively reveals the presence of 6 common distortion categories in the generated 3DGCs. To further explore the quality of the 3DGCs, subjective quality assessment is conducted by evaluators, whose ratings reveal significant variation in quality across different generation methods. Additionally, several objective quality assessment algorithms are tested on the 3DGCQA dataset. The results expose limitations in the performance of existing algorithms and underscore the need for developing more specialized quality assessment methods. To provide a valuable resource for future research and development in 3D content generation and quality assessment, the dataset has been open-sourced in https://github.com/zyj-2000/3DGCQA.
TSI-Bench: Benchmarking Time Series Imputation
Jun 18, 2024Abstract:Effective imputation is a crucial preprocessing step for time series analysis. Despite the development of numerous deep learning algorithms for time series imputation, the community lacks standardized and comprehensive benchmark platforms to effectively evaluate imputation performance across different settings. Moreover, although many deep learning forecasting algorithms have demonstrated excellent performance, whether their modeling achievements can be transferred to time series imputation tasks remains unexplored. To bridge these gaps, we develop TSI-Bench, the first (to our knowledge) comprehensive benchmark suite for time series imputation utilizing deep learning techniques. The TSI-Bench pipeline standardizes experimental settings to enable fair evaluation of imputation algorithms and identification of meaningful insights into the influence of domain-appropriate missingness ratios and patterns on model performance. Furthermore, TSI-Bench innovatively provides a systematic paradigm to tailor time series forecasting algorithms for imputation purposes. Our extensive study across 34,804 experiments, 28 algorithms, and 8 datasets with diverse missingness scenarios demonstrates TSI-Bench's effectiveness in diverse downstream tasks and potential to unlock future directions in time series imputation research and analysis. The source code and experiment logs are available at https://github.com/WenjieDu/AwesomeImputation.
A-Bench: Are LMMs Masters at Evaluating AI-generated Images?
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:How to accurately and efficiently assess AI-generated images (AIGIs) remains a critical challenge for generative models. Given the high costs and extensive time commitments required for user studies, many researchers have turned towards employing large multi-modal models (LMMs) as AIGI evaluators, the precision and validity of which are still questionable. Furthermore, traditional benchmarks often utilize mostly natural-captured content rather than AIGIs to test the abilities of LMMs, leading to a noticeable gap for AIGIs. Therefore, we introduce A-Bench in this paper, a benchmark designed to diagnose whether LMMs are masters at evaluating AIGIs. Specifically, A-Bench is organized under two key principles: 1) Emphasizing both high-level semantic understanding and low-level visual quality perception to address the intricate demands of AIGIs. 2) Various generative models are utilized for AIGI creation, and various LMMs are employed for evaluation, which ensures a comprehensive validation scope. Ultimately, 2,864 AIGIs from 16 text-to-image models are sampled, each paired with question-answers annotated by human experts, and tested across 18 leading LMMs. We hope that A-Bench will significantly enhance the evaluation process and promote the generation quality for AIGIs. The benchmark is available at https://github.com/Q-Future/A-Bench.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge