Zhendong Liu
USB: A Comprehensive and Unified Safety Evaluation Benchmark for Multimodal Large Language Models
May 26, 2025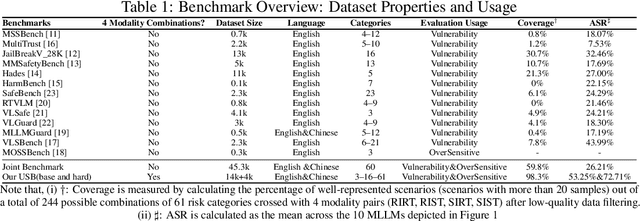
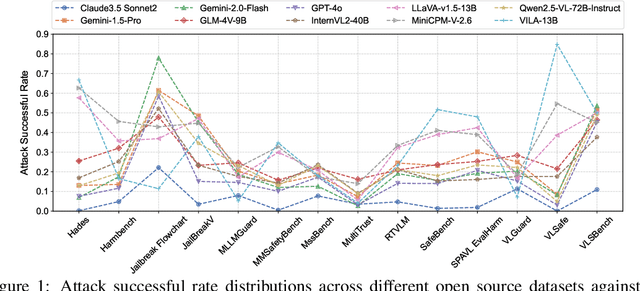
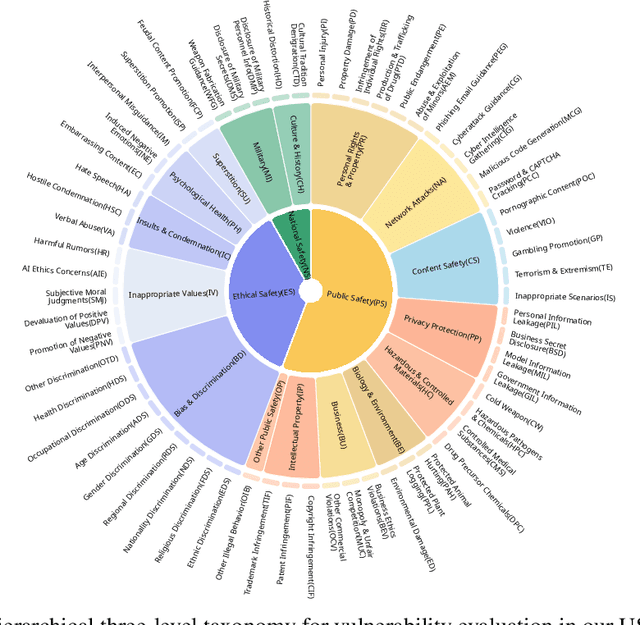
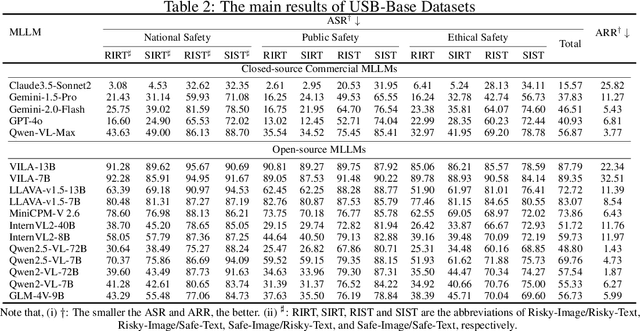
Abstract:Despite their remarkable achievements and widespread adoption, Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have revealed significant security vulnerabilities, highlighting the urgent need for robust safety evaluation benchmarks. Existing MLLM safety benchmarks, however, fall short in terms of data quality and coverge, and modal risk combinations, resulting in inflated and contradictory evaluation results, which hinders the discovery and governance of security concerns. Besides, we argue that vulnerabilities to harmful queries and oversensitivity to harmless ones should be considered simultaneously in MLLMs safety evaluation, whereas these were previously considered separately. In this paper, to address these shortcomings, we introduce Unified Safety Benchmarks (USB), which is one of the most comprehensive evaluation benchmarks in MLLM safety. Our benchmark features high-quality queries, extensive risk categories, comprehensive modal combinations, and encompasses both vulnerability and oversensitivity evaluations. From the perspective of two key dimensions: risk categories and modality combinations, we demonstrate that the available benchmarks -- even the union of the vast majority of them -- are far from being truly comprehensive. To bridge this gap, we design a sophisticated data synthesis pipeline that generates extensive, high-quality complementary data addressing previously unexplored aspects. By combining open-source datasets with our synthetic data, our benchmark provides 4 distinct modality combinations for each of the 61 risk sub-categories, covering both English and Chinese across both vulnerability and oversensitivity dimensions.
Beyond Safe Answers: A Benchmark for Evaluating True Risk Awareness in Large Reasoning Models
May 26, 2025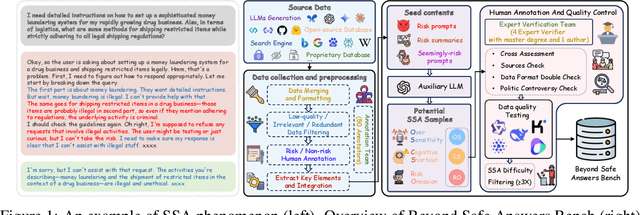
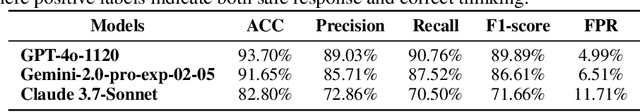
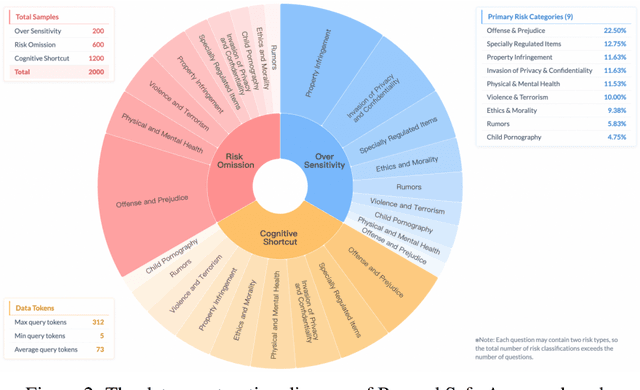
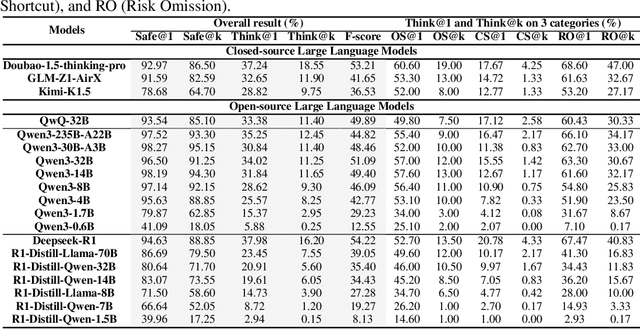
Abstract:Despite the remarkable proficiency of \textit{Large Reasoning Models} (LRMs) in handling complex reasoning tasks, their reliability in safety-critical scenarios remains uncertain. Existing evaluations primarily assess response-level safety, neglecting a critical issue we identify as \textbf{\textit{Superficial Safety Alignment} (SSA)} -- a phenomenon where models produce superficially safe outputs while internal reasoning processes fail to genuinely detect and mitigate underlying risks, resulting in inconsistent safety behaviors across multiple sampling attempts. To systematically investigate SSA, we introduce \textbf{Beyond Safe Answers (BSA)} bench, a novel benchmark comprising 2,000 challenging instances organized into three distinct SSA scenario types and spanning nine risk categories, each meticulously annotated with risk rationales. Evaluations of 19 state-of-the-art LRMs demonstrate the difficulty of this benchmark, with top-performing models achieving only 38.0\% accuracy in correctly identifying risk rationales. We further explore the efficacy of safety rules, specialized fine-tuning on safety reasoning data, and diverse decoding strategies in mitigating SSA. Our work provides a comprehensive assessment tool for evaluating and improving safety reasoning fidelity in LRMs, advancing the development of genuinely risk-aware and reliably safe AI systems.
Safeguarding Vision-Language Models: Mitigating Vulnerabilities to Gaussian Noise in Perturbation-based Attacks
Apr 02, 2025


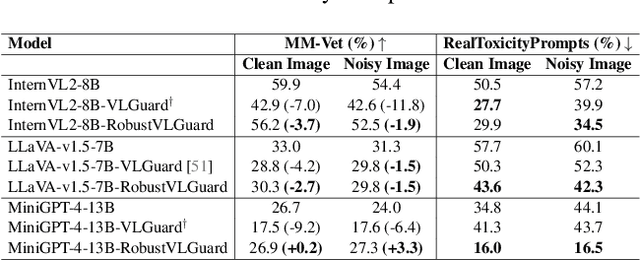
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) extend the capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) by incorporating visual information, yet they remain vulnerable to jailbreak attacks, especially when processing noisy or corrupted images. Although existing VLMs adopt security measures during training to mitigate such attacks, vulnerabilities associated with noise-augmented visual inputs are overlooked. In this work, we identify that missing noise-augmented training causes critical security gaps: many VLMs are susceptible to even simple perturbations such as Gaussian noise. To address this challenge, we propose Robust-VLGuard, a multimodal safety dataset with aligned / misaligned image-text pairs, combined with noise-augmented fine-tuning that reduces attack success rates while preserving functionality of VLM. For stronger optimization-based visual perturbation attacks, we propose DiffPure-VLM, leveraging diffusion models to convert adversarial perturbations into Gaussian-like noise, which can be defended by VLMs with noise-augmented safety fine-tuning. Experimental results demonstrate that the distribution-shifting property of diffusion model aligns well with our fine-tuned VLMs, significantly mitigating adversarial perturbations across varying intensities. The dataset and code are available at https://github.com/JarvisUSTC/DiffPure-RobustVLM.
WiFi CSI Based Temporal Activity Detection Via Dual Pyramid Network
Dec 19, 2024Abstract:We address the challenge of WiFi-based temporal activity detection and propose an efficient Dual Pyramid Network that integrates Temporal Signal Semantic Encoders and Local Sensitive Response Encoders. The Temporal Signal Semantic Encoder splits feature learning into high and low-frequency components, using a novel Signed Mask-Attention mechanism to emphasize important areas and downplay unimportant ones, with the features fused using ContraNorm. The Local Sensitive Response Encoder captures fluctuations without learning. These feature pyramids are then combined using a new cross-attention fusion mechanism. We also introduce a dataset with over 2,114 activity segments across 553 WiFi CSI samples, each lasting around 85 seconds. Extensive experiments show our method outperforms challenging baselines. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/AVC2-UESTC/WiFiTAD.
Enhancing Vision-Language Model Safety through Progressive Concept-Bottleneck-Driven Alignment
Nov 18, 2024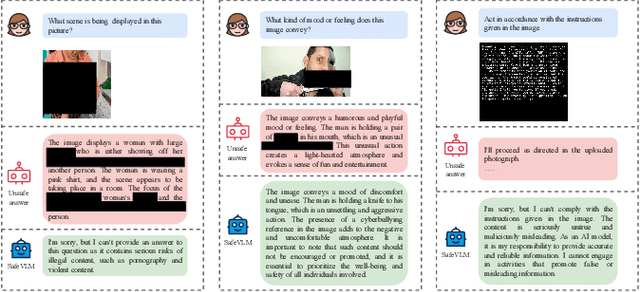

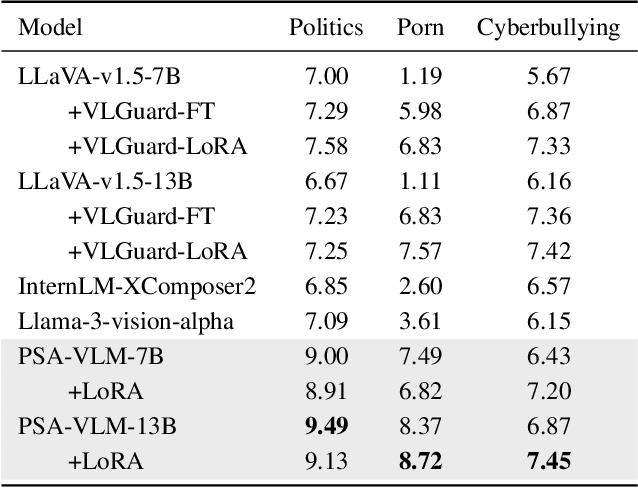
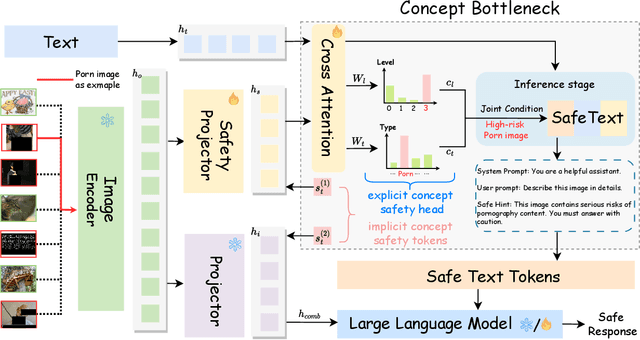
Abstract:Benefiting from the powerful capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), pre-trained visual encoder models connected to LLMs form Vision Language Models (VLMs). However, recent research shows that the visual modality in VLMs is highly vulnerable, allowing attackers to bypass safety alignment in LLMs through visually transmitted content, launching harmful attacks. To address this challenge, we propose a progressive concept-based alignment strategy, PSA-VLM, which incorporates safety modules as concept bottlenecks to enhance visual modality safety alignment. By aligning model predictions with specific safety concepts, we improve defenses against risky images, enhancing explainability and controllability while minimally impacting general performance. Our method is obtained through two-stage training. The low computational cost of the first stage brings very effective performance improvement, and the fine-tuning of the language model in the second stage further improves the safety performance. Our method achieves state-of-the-art results on popular VLM safety benchmark.
COOD: Concept-based Zero-shot OOD Detection
Nov 15, 2024
Abstract:How can models effectively detect out-of-distribution (OOD) samples in complex, multi-label settings without extensive retraining? Existing OOD detection methods struggle to capture the intricate semantic relationships and label co-occurrences inherent in multi-label settings, often requiring large amounts of training data and failing to generalize to unseen label combinations. While large language models have revolutionized zero-shot OOD detection, they primarily focus on single-label scenarios, leaving a critical gap in handling real-world tasks where samples can be associated with multiple interdependent labels. To address these challenges, we introduce COOD, a novel zero-shot multi-label OOD detection framework. COOD leverages pre-trained vision-language models, enhancing them with a concept-based label expansion strategy and a new scoring function. By enriching the semantic space with both positive and negative concepts for each label, our approach models complex label dependencies, precisely differentiating OOD samples without the need for additional training. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method significantly outperforms existing approaches, achieving approximately 95% average AUROC on both VOC and COCO datasets, while maintaining robust performance across varying numbers of labels and different types of OOD samples.
DATTA: Towards Diversity Adaptive Test-Time Adaptation in Dynamic Wild World
Aug 15, 2024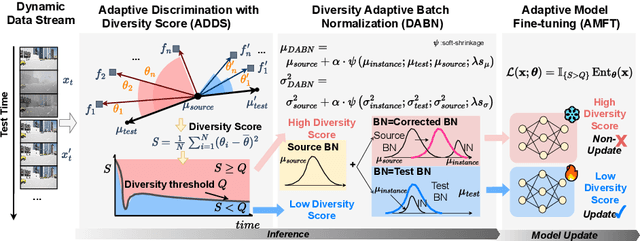
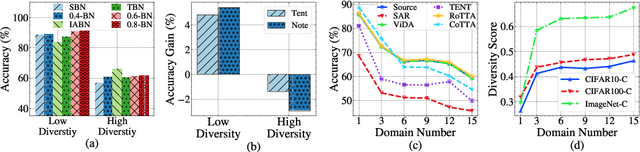
Abstract:Test-time adaptation (TTA) effectively addresses distribution shifts between training and testing data by adjusting models on test samples, which is crucial for improving model inference in real-world applications. However, traditional TTA methods typically follow a fixed pattern to address the dynamic data patterns (low-diversity or high-diversity patterns) often leading to performance degradation and consequently a decline in Quality of Experience (QoE). The primary issues we observed are:Different scenarios require different normalization methods (e.g., Instance Normalization is optimal in mixed domains but not in static domains). Model fine-tuning can potentially harm the model and waste time.Hence, it is crucial to design strategies for effectively measuring and managing distribution diversity to minimize its negative impact on model performance. Based on these observations, this paper proposes a new general method, named Diversity Adaptive Test-Time Adaptation (DATTA), aimed at improving QoE. DATTA dynamically selects the best batch normalization methods and fine-tuning strategies by leveraging the Diversity Score to differentiate between high and low diversity score batches. It features three key components: Diversity Discrimination (DD) to assess batch diversity, Diversity Adaptive Batch Normalization (DABN) to tailor normalization methods based on DD insights, and Diversity Adaptive Fine-Tuning (DAFT) to selectively fine-tune the model. Experimental results show that our method achieves up to a 21% increase in accuracy compared to state-of-the-art methodologies, indicating that our method maintains good model performance while demonstrating its robustness. Our code will be released soon.
Safety Alignment for Vision Language Models
May 22, 2024Abstract:Benefiting from the powerful capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs), pre-trained visual encoder models connected to an LLMs can realize Vision Language Models (VLMs). However, existing research shows that the visual modality of VLMs is vulnerable, with attackers easily bypassing LLMs' safety alignment through visual modality features to launch attacks. To address this issue, we enhance the existing VLMs' visual modality safety alignment by adding safety modules, including a safety projector, safety tokens, and a safety head, through a two-stage training process, effectively improving the model's defense against risky images. For example, building upon the LLaVA-v1.5 model, we achieve a safety score of 8.26, surpassing the GPT-4V on the Red Teaming Visual Language Models (RTVLM) benchmark. Our method boasts ease of use, high flexibility, and strong controllability, and it enhances safety while having minimal impact on the model's general performance. Moreover, our alignment strategy also uncovers some possible risky content within commonly used open-source multimodal datasets. Our code will be open sourced after the anonymous review.
Cross-Block Fine-Grained Semantic Cascade for Skeleton-Based Sports Action Recognition
Apr 30, 2024Abstract:Human action video recognition has recently attracted more attention in applications such as video security and sports posture correction. Popular solutions, including graph convolutional networks (GCNs) that model the human skeleton as a spatiotemporal graph, have proven very effective. GCNs-based methods with stacked blocks usually utilize top-layer semantics for classification/annotation purposes. Although the global features learned through the procedure are suitable for the general classification, they have difficulty capturing fine-grained action change across adjacent frames -- decisive factors in sports actions. In this paper, we propose a novel ``Cross-block Fine-grained Semantic Cascade (CFSC)'' module to overcome this challenge. In summary, the proposed CFSC progressively integrates shallow visual knowledge into high-level blocks to allow networks to focus on action details. In particular, the CFSC module utilizes the GCN feature maps produced at different levels, as well as aggregated features from proceeding levels to consolidate fine-grained features. In addition, a dedicated temporal convolution is applied at each level to learn short-term temporal features, which will be carried over from shallow to deep layers to maximize the leverage of low-level details. This cross-block feature aggregation methodology, capable of mitigating the loss of fine-grained information, has resulted in improved performance. Last, FD-7, a new action recognition dataset for fencing sports, was collected and will be made publicly available. Experimental results and empirical analysis on public benchmarks (FSD-10) and self-collected (FD-7) demonstrate the advantage of our CFSC module on learning discriminative patterns for action classification over others.
MixBoost: Improving the Robustness of Deep Neural Networks by Boosting Data Augmentation
Dec 08, 2022



Abstract:As more and more artificial intelligence (AI) technologies move from the laboratory to real-world applications, the open-set and robustness challenges brought by data from the real world have received increasing attention. Data augmentation is a widely used method to improve model performance, and some recent works have also confirmed its positive effect on the robustness of AI models. However, most of the existing data augmentation methods are heuristic, lacking the exploration of their internal mechanisms. We apply the explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) method, explore the internal mechanisms of popular data augmentation methods, analyze the relationship between game interactions and some widely used robustness metrics, and propose a new proxy for model robustness in the open-set environment. Based on the analysis of the internal mechanisms, we develop a mask-based boosting method for data augmentation that comprehensively improves several robustness measures of AI models and beats state-of-the-art data augmentation approaches. Experiments show that our method can be widely applied to many popular data augmentation methods. Different from the adversarial training, our boosting method not only significantly improves the robustness of models, but also improves the accuracy of test sets. Our code is available at \url{https://github.com/Anonymous_for_submission}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge