Karim Lekadir
FUGC: Benchmarking Semi-Supervised Learning Methods for Cervical Segmentation
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Accurate segmentation of cervical structures in transvaginal ultrasound (TVS) is critical for assessing the risk of spontaneous preterm birth (PTB), yet the scarcity of labeled data limits the performance of supervised learning approaches. This paper introduces the Fetal Ultrasound Grand Challenge (FUGC), the first benchmark for semi-supervised learning in cervical segmentation, hosted at ISBI 2025. FUGC provides a dataset of 890 TVS images, including 500 training images, 90 validation images, and 300 test images. Methods were evaluated using the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC), Hausdorff Distance (HD), and runtime (RT), with a weighted combination of 0.4/0.4/0.2. The challenge attracted 10 teams with 82 participants submitting innovative solutions. The best-performing methods for each individual metric achieved 90.26\% mDSC, 38.88 mHD, and 32.85 ms RT, respectively. FUGC establishes a standardized benchmark for cervical segmentation, demonstrates the efficacy of semi-supervised methods with limited labeled data, and provides a foundation for AI-assisted clinical PTB risk assessment.
Agent-Based Output Drift Detection for Breast Cancer Response Prediction in a Multisite Clinical Decision Support System
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:Modern clinical decision support systems can concurrently serve multiple, independent medical imaging institutions, but their predictive performance may degrade across sites due to variations in patient populations, imaging hardware, and acquisition protocols. Continuous surveillance of predictive model outputs offers a safe and reliable approach for identifying such distributional shifts without ground truth labels. However, most existing methods rely on centralized monitoring of aggregated predictions, overlooking site-specific drift dynamics. We propose an agent-based framework for detecting drift and assessing its severity in multisite clinical AI systems. To evaluate its effectiveness, we simulate a multi-center environment for output-based drift detection, assigning each site a drift monitoring agent that performs batch-wise comparisons of model outputs against a reference distribution. We analyse several multi-center monitoring schemes, that differ in how the reference is obtained (site-specific, global, production-only and adaptive), alongside a centralized baseline. Results on real-world breast cancer imaging data using a pathological complete response prediction model shows that all multi-center schemes outperform centralized monitoring, with F1-score improvements up to 10.3% in drift detection. In the absence of site-specific references, the adaptive scheme performs best, with F1-scores of 74.3% for drift detection and 83.7% for drift severity classification. These findings suggest that adaptive, site-aware agent-based drift monitoring can enhance reliability of multisite clinical decision support systems.
MedSapiens: Taking a Pose to Rethink Medical Imaging Landmark Detection
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:This paper does not introduce a novel architecture; instead, it revisits a fundamental yet overlooked baseline: adapting human-centric foundation models for anatomical landmark detection in medical imaging. While landmark detection has traditionally relied on domain-specific models, the emergence of large-scale pre-trained vision models presents new opportunities. In this study, we investigate the adaptation of Sapiens, a human-centric foundation model designed for pose estimation, to medical imaging through multi-dataset pretraining, establishing a new state of the art across multiple datasets. Our proposed model, MedSapiens, demonstrates that human-centric foundation models, inherently optimized for spatial pose localization, provide strong priors for anatomical landmark detection, yet this potential has remained largely untapped. We benchmark MedSapiens against existing state-of-the-art models, achieving up to 5.26% improvement over generalist models and up to 21.81% improvement over specialist models in the average success detection rate (SDR). To further assess MedSapiens adaptability to novel downstream tasks with few annotations, we evaluate its performance in limited-data settings, achieving 2.69% improvement over the few-shot state of the art in SDR. Code and model weights are available at https://github.com/xmed-lab/MedSapiens .
Clinically-guided Data Synthesis for Laryngeal Lesion Detection
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Although computer-aided diagnosis (CADx) and detection (CADe) systems have made significant progress in various medical domains, their application is still limited in specialized fields such as otorhinolaryngology. In the latter, current assessment methods heavily depend on operator expertise, and the high heterogeneity of lesions complicates diagnosis, with biopsy persisting as the gold standard despite its substantial costs and risks. A critical bottleneck for specialized endoscopic CADx/e systems is the lack of well-annotated datasets with sufficient variability for real-world generalization. This study introduces a novel approach that exploits a Latent Diffusion Model (LDM) coupled with a ControlNet adapter to generate laryngeal endoscopic image-annotation pairs, guided by clinical observations. The method addresses data scarcity by conditioning the diffusion process to produce realistic, high-quality, and clinically relevant image features that capture diverse anatomical conditions. The proposed approach can be leveraged to expand training datasets for CADx/e models, empowering the assessment process in laryngology. Indeed, during a downstream task of detection, the addition of only 10% synthetic data improved the detection rate of laryngeal lesions by 9% when the model was internally tested and 22.1% on out-of-domain external data. Additionally, the realism of the generated images was evaluated by asking 5 expert otorhinolaryngologists with varying expertise to rate their confidence in distinguishing synthetic from real images. This work has the potential to accelerate the development of automated tools for laryngeal disease diagnosis, offering a solution to data scarcity and demonstrating the applicability of synthetic data in real-world scenarios.
Federated learning in low-resource settings: A chest imaging study in Africa -- Challenges and lessons learned
May 20, 2025Abstract:This study explores the use of Federated Learning (FL) for tuberculosis (TB) diagnosis using chest X-rays in low-resource settings across Africa. FL allows hospitals to collaboratively train AI models without sharing raw patient data, addressing privacy concerns and data scarcity that hinder traditional centralized models. The research involved hospitals and research centers in eight African countries. Most sites used local datasets, while Ghana and The Gambia used public ones. The study compared locally trained models with a federated model built across all institutions to evaluate FL's real-world feasibility. Despite its promise, implementing FL in sub-Saharan Africa faces challenges such as poor infrastructure, unreliable internet, limited digital literacy, and weak AI regulations. Some institutions were also reluctant to share model updates due to data control concerns. In conclusion, FL shows strong potential for enabling AI-driven healthcare in underserved regions, but broader adoption will require improvements in infrastructure, education, and regulatory support.
Calibration and Uncertainty for multiRater Volume Assessment in multiorgan Segmentation (CURVAS) challenge results
May 13, 2025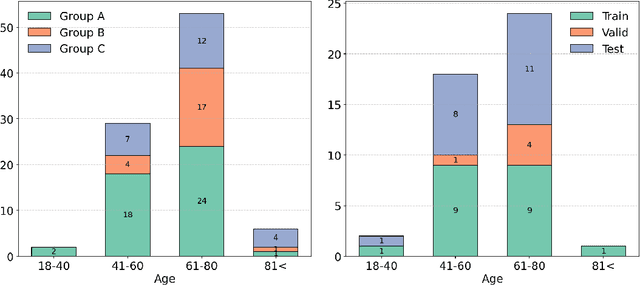
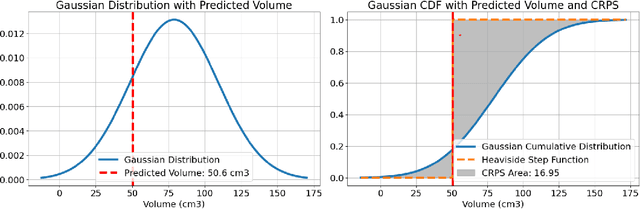

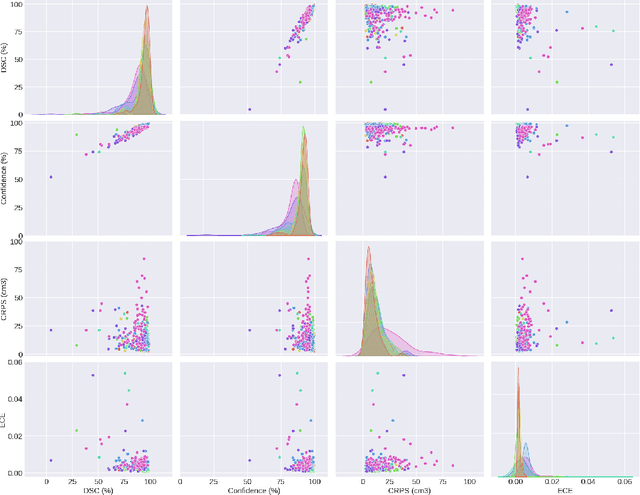
Abstract:Deep learning (DL) has become the dominant approach for medical image segmentation, yet ensuring the reliability and clinical applicability of these models requires addressing key challenges such as annotation variability, calibration, and uncertainty estimation. This is why we created the Calibration and Uncertainty for multiRater Volume Assessment in multiorgan Segmentation (CURVAS), which highlights the critical role of multiple annotators in establishing a more comprehensive ground truth, emphasizing that segmentation is inherently subjective and that leveraging inter-annotator variability is essential for robust model evaluation. Seven teams participated in the challenge, submitting a variety of DL models evaluated using metrics such as Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC), Expected Calibration Error (ECE), and Continuous Ranked Probability Score (CRPS). By incorporating consensus and dissensus ground truth, we assess how DL models handle uncertainty and whether their confidence estimates align with true segmentation performance. Our findings reinforce the importance of well-calibrated models, as better calibration is strongly correlated with the quality of the results. Furthermore, we demonstrate that segmentation models trained on diverse datasets and enriched with pre-trained knowledge exhibit greater robustness, particularly in cases deviating from standard anatomical structures. Notably, the best-performing models achieved high DSC and well-calibrated uncertainty estimates. This work underscores the need for multi-annotator ground truth, thorough calibration assessments, and uncertainty-aware evaluations to develop trustworthy and clinically reliable DL-based medical image segmentation models.
Segmentation variability and radiomics stability for predicting Triple-Negative Breast Cancer subtype using Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Apr 02, 2025



Abstract:Most papers caution against using predictive models for disease stratification based on unselected radiomic features, as these features are affected by contouring variability. Instead, they advocate for the use of the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) as a measure of stability for feature selection. However, the direct effect of segmentation variability on the predictive models is rarely studied. This study investigates the impact of segmentation variability on feature stability and predictive performance in radiomics-based prediction of Triple-Negative Breast Cancer (TNBC) subtype using Magnetic Resonance Imaging. A total of 244 images from the Duke dataset were used, with segmentation variability introduced through modifications of manual segmentations. For each mask, explainable radiomic features were selected using the Shapley Additive exPlanations method and used to train logistic regression models. Feature stability across segmentations was assessed via ICC, Pearson's correlation, and reliability scores quantifying the relationship between feature stability and segmentation variability. Results indicate that segmentation accuracy does not significantly impact predictive performance. While incorporating peritumoral information may reduce feature reproducibility, it does not diminish feature predictive capability. Moreover, feature selection in predictive models is not inherently tied to feature stability with respect to segmentation, suggesting that an overreliance on ICC or reliability scores for feature selection might exclude valuable predictive features.
Federated nnU-Net for Privacy-Preserving Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 04, 2025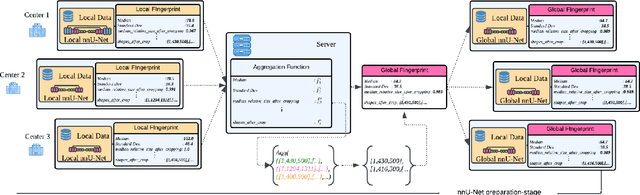
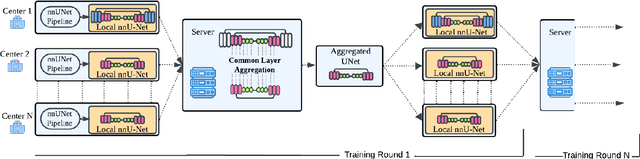
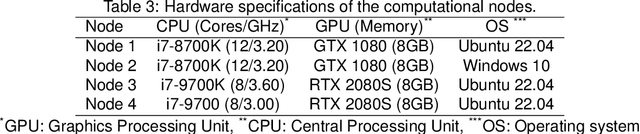
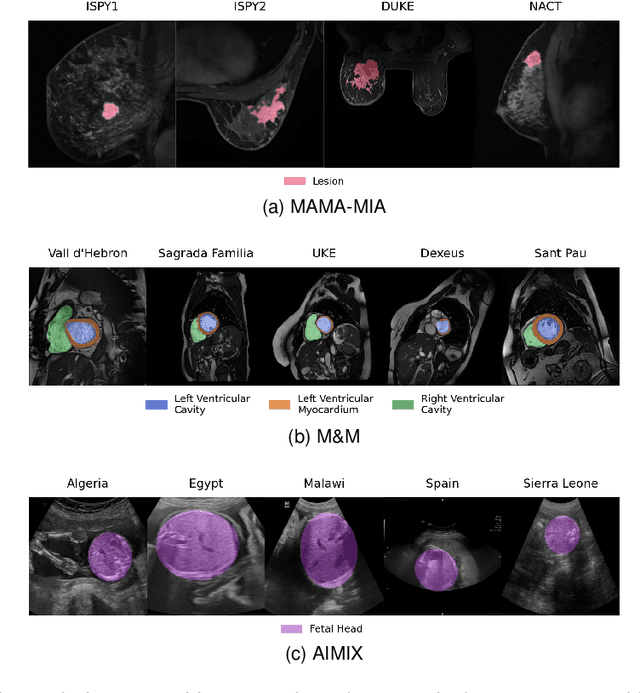
Abstract:The nnU-Net framework has played a crucial role in medical image segmentation and has become the gold standard in multitudes of applications targeting different diseases, organs, and modalities. However, so far it has been used primarily in a centralized approach where the data collected from hospitals are stored in one center and used to train the nnU-Net. This centralized approach has various limitations, such as leakage of sensitive patient information and violation of patient privacy. Federated learning is one of the approaches to train a segmentation model in a decentralized manner that helps preserve patient privacy. In this paper, we propose FednnU-Net, a federated learning extension of nnU-Net. We introduce two novel federated learning methods to the nnU-Net framework - Federated Fingerprint Extraction (FFE) and Asymmetric Federated Averaging (AsymFedAvg) - and experimentally show their consistent performance for breast, cardiac and fetal segmentation using 6 datasets representing samples from 18 institutions. Additionally, to further promote research and deployment of decentralized training in privacy constrained institutions, we make our plug-n-play framework public. The source-code is available at https://github.com/faildeny/FednnUNet .
Efficient MedSAMs: Segment Anything in Medical Images on Laptop
Dec 20, 2024


Abstract:Promptable segmentation foundation models have emerged as a transformative approach to addressing the diverse needs in medical images, but most existing models require expensive computing, posing a big barrier to their adoption in clinical practice. In this work, we organized the first international competition dedicated to promptable medical image segmentation, featuring a large-scale dataset spanning nine common imaging modalities from over 20 different institutions. The top teams developed lightweight segmentation foundation models and implemented an efficient inference pipeline that substantially reduced computational requirements while maintaining state-of-the-art segmentation accuracy. Moreover, the post-challenge phase advanced the algorithms through the design of performance booster and reproducibility tasks, resulting in improved algorithms and validated reproducibility of the winning solution. Furthermore, the best-performing algorithms have been incorporated into the open-source software with a user-friendly interface to facilitate clinical adoption. The data and code are publicly available to foster the further development of medical image segmentation foundation models and pave the way for impactful real-world applications.
Simulating Dynamic Tumor Contrast Enhancement in Breast MRI using Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks
Sep 27, 2024Abstract:This paper presents a method for virtual contrast enhancement in breast MRI, offering a promising non-invasive alternative to traditional contrast agent-based DCE-MRI acquisition. Using a conditional generative adversarial network, we predict DCE-MRI images, including jointly-generated sequences of multiple corresponding DCE-MRI timepoints, from non-contrast-enhanced MRIs, enabling tumor localization and characterization without the associated health risks. Furthermore, we qualitatively and quantitatively evaluate the synthetic DCE-MRI images, proposing a multi-metric Scaled Aggregate Measure (SAMe), assessing their utility in a tumor segmentation downstream task, and conclude with an analysis of the temporal patterns in multi-sequence DCE-MRI generation. Our approach demonstrates promising results in generating realistic and useful DCE-MRI sequences, highlighting the potential of virtual contrast enhancement for improving breast cancer diagnosis and treatment, particularly for patients where contrast agent administration is contraindicated.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge