Carlos Martín-Isla
Federated learning in low-resource settings: A chest imaging study in Africa -- Challenges and lessons learned
May 20, 2025Abstract:This study explores the use of Federated Learning (FL) for tuberculosis (TB) diagnosis using chest X-rays in low-resource settings across Africa. FL allows hospitals to collaboratively train AI models without sharing raw patient data, addressing privacy concerns and data scarcity that hinder traditional centralized models. The research involved hospitals and research centers in eight African countries. Most sites used local datasets, while Ghana and The Gambia used public ones. The study compared locally trained models with a federated model built across all institutions to evaluate FL's real-world feasibility. Despite its promise, implementing FL in sub-Saharan Africa faces challenges such as poor infrastructure, unreliable internet, limited digital literacy, and weak AI regulations. Some institutions were also reluctant to share model updates due to data control concerns. In conclusion, FL shows strong potential for enabling AI-driven healthcare in underserved regions, but broader adoption will require improvements in infrastructure, education, and regulatory support.
Federated nnU-Net for Privacy-Preserving Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 04, 2025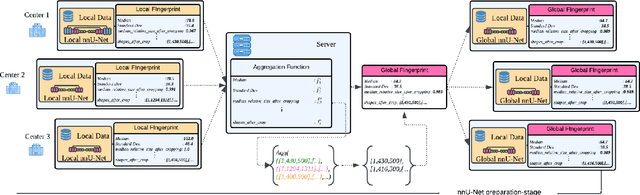
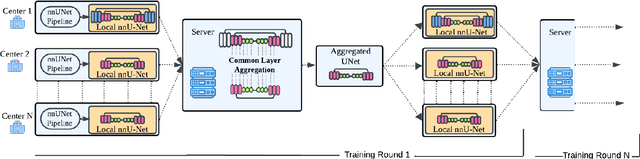
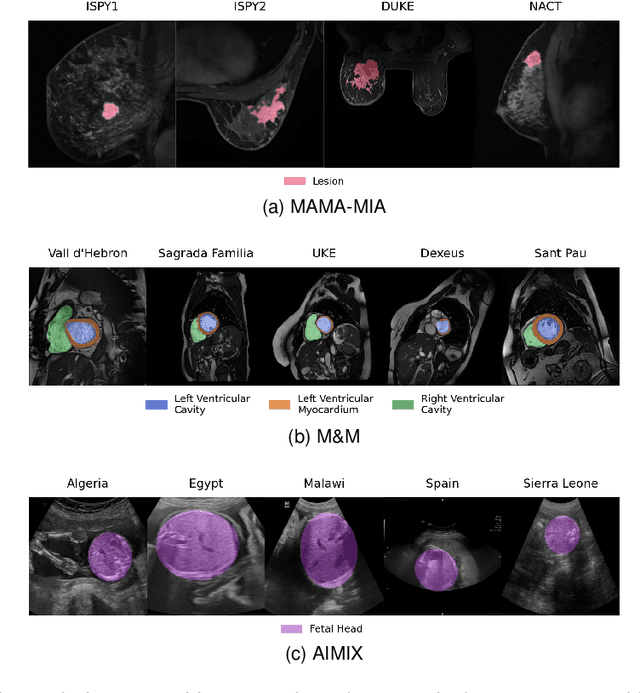
Abstract:The nnU-Net framework has played a crucial role in medical image segmentation and has become the gold standard in multitudes of applications targeting different diseases, organs, and modalities. However, so far it has been used primarily in a centralized approach where the data collected from hospitals are stored in one center and used to train the nnU-Net. This centralized approach has various limitations, such as leakage of sensitive patient information and violation of patient privacy. Federated learning is one of the approaches to train a segmentation model in a decentralized manner that helps preserve patient privacy. In this paper, we propose FednnU-Net, a federated learning extension of nnU-Net. We introduce two novel federated learning methods to the nnU-Net framework - Federated Fingerprint Extraction (FFE) and Asymmetric Federated Averaging (AsymFedAvg) - and experimentally show their consistent performance for breast, cardiac and fetal segmentation using 6 datasets representing samples from 18 institutions. Additionally, to further promote research and deployment of decentralized training in privacy constrained institutions, we make our plug-n-play framework public. The source-code is available at https://github.com/faildeny/FednnUNet .
Efficient MedSAMs: Segment Anything in Medical Images on Laptop
Dec 20, 2024


Abstract:Promptable segmentation foundation models have emerged as a transformative approach to addressing the diverse needs in medical images, but most existing models require expensive computing, posing a big barrier to their adoption in clinical practice. In this work, we organized the first international competition dedicated to promptable medical image segmentation, featuring a large-scale dataset spanning nine common imaging modalities from over 20 different institutions. The top teams developed lightweight segmentation foundation models and implemented an efficient inference pipeline that substantially reduced computational requirements while maintaining state-of-the-art segmentation accuracy. Moreover, the post-challenge phase advanced the algorithms through the design of performance booster and reproducibility tasks, resulting in improved algorithms and validated reproducibility of the winning solution. Furthermore, the best-performing algorithms have been incorporated into the open-source software with a user-friendly interface to facilitate clinical adoption. The data and code are publicly available to foster the further development of medical image segmentation foundation models and pave the way for impactful real-world applications.
Democratizing AI in Africa: FL for Low-Resource Edge Devices
Aug 30, 2024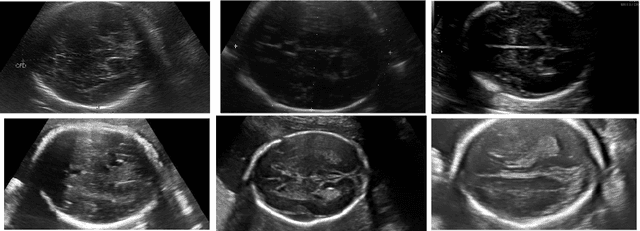
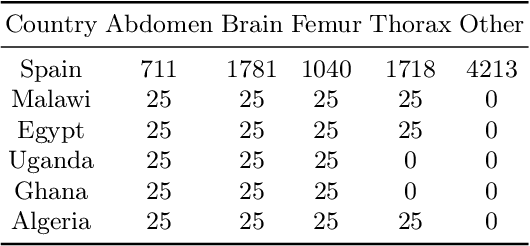
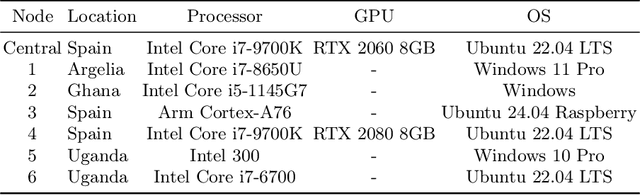
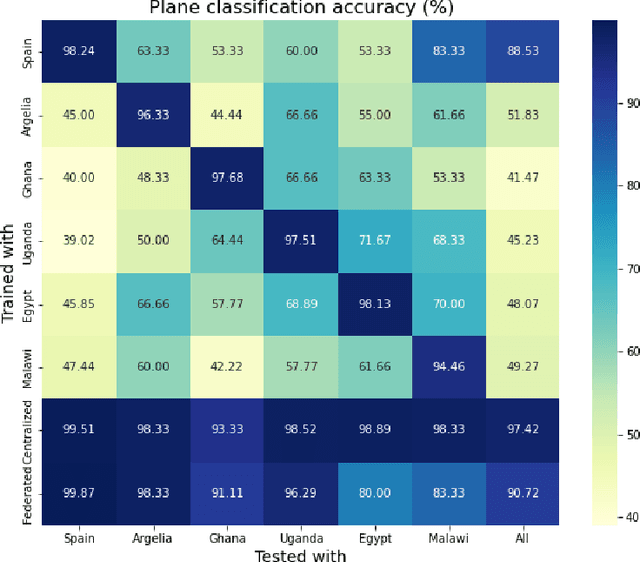
Abstract:Africa faces significant challenges in healthcare delivery due to limited infrastructure and access to advanced medical technologies. This study explores the use of federated learning to overcome these barriers, focusing on perinatal health. We trained a fetal plane classifier using perinatal data from five African countries: Algeria, Ghana, Egypt, Malawi, and Uganda, along with data from Spanish hospitals. To incorporate the lack of computational resources in the analysis, we considered a heterogeneous set of devices, including a Raspberry Pi and several laptops, for model training. We demonstrate comparative performance between a centralized and a federated model, despite the compute limitations, and a significant improvement in model generalizability when compared to models trained only locally. These results show the potential for a future implementation at a large scale of a federated learning platform to bridge the accessibility gap and improve model generalizability with very little requirements.
MAMA-MIA: A Large-Scale Multi-Center Breast Cancer DCE-MRI Benchmark Dataset with Expert Segmentations
Jun 19, 2024Abstract:Current research in breast cancer Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), especially with Artificial Intelligence (AI), faces challenges due to the lack of expert segmentations. To address this, we introduce the MAMA-MIA dataset, comprising 1506 multi-center dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI cases with expert segmentations of primary tumors and non-mass enhancement areas. These cases were sourced from four publicly available collections in The Cancer Imaging Archive (TCIA). Initially, we trained a deep learning model to automatically segment the cases, generating preliminary segmentations that significantly reduced expert segmentation time. Sixteen experts, averaging 9 years of experience in breast cancer, then corrected these segmentations, resulting in the final expert segmentations. Additionally, two radiologists conducted a visual inspection of the automatic segmentations to support future quality control studies. Alongside the expert segmentations, we provide 49 harmonized demographic and clinical variables and the pretrained weights of the well-known nnUNet architecture trained using the DCE-MRI full-images and expert segmentations. This dataset aims to accelerate the development and benchmarking of deep learning models and foster innovation in breast cancer diagnostics and treatment planning.
Why is the winner the best?
Mar 30, 2023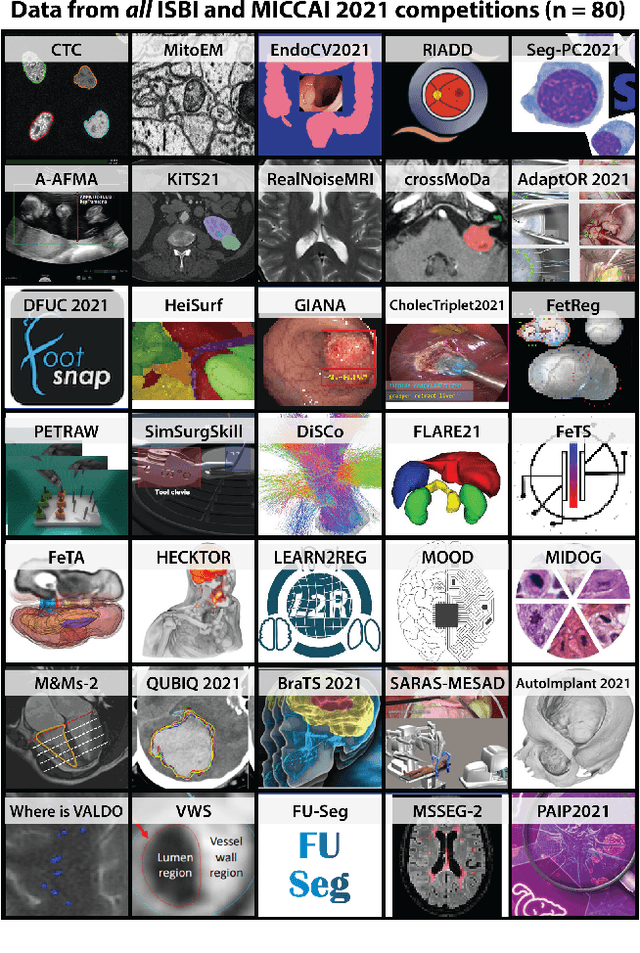
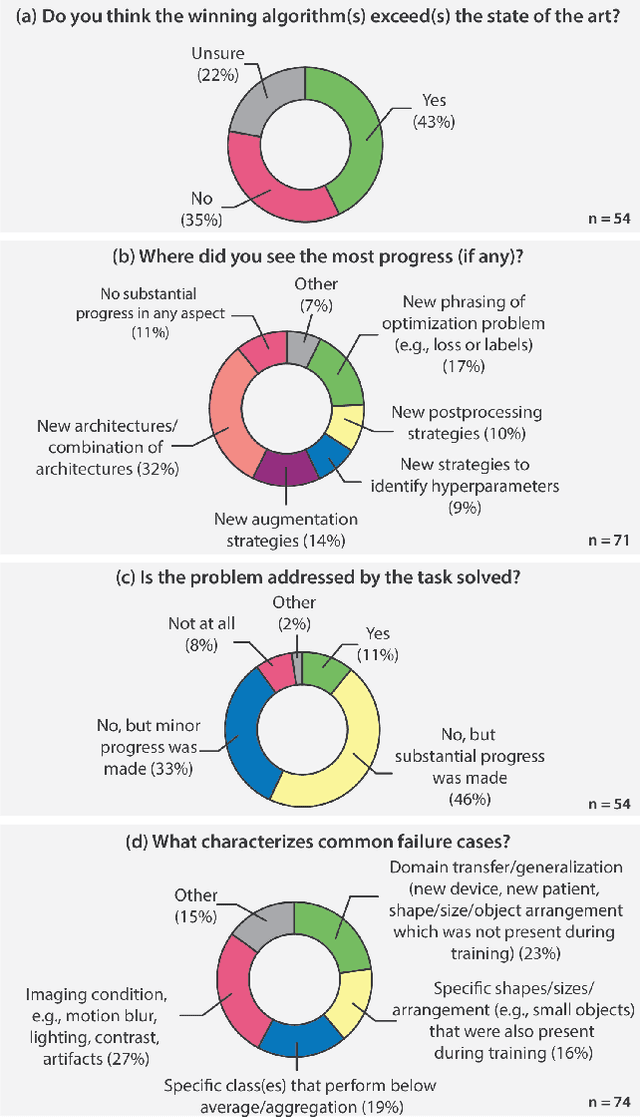
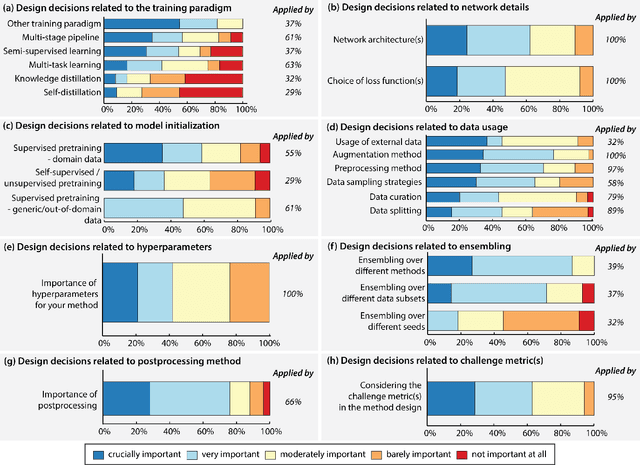
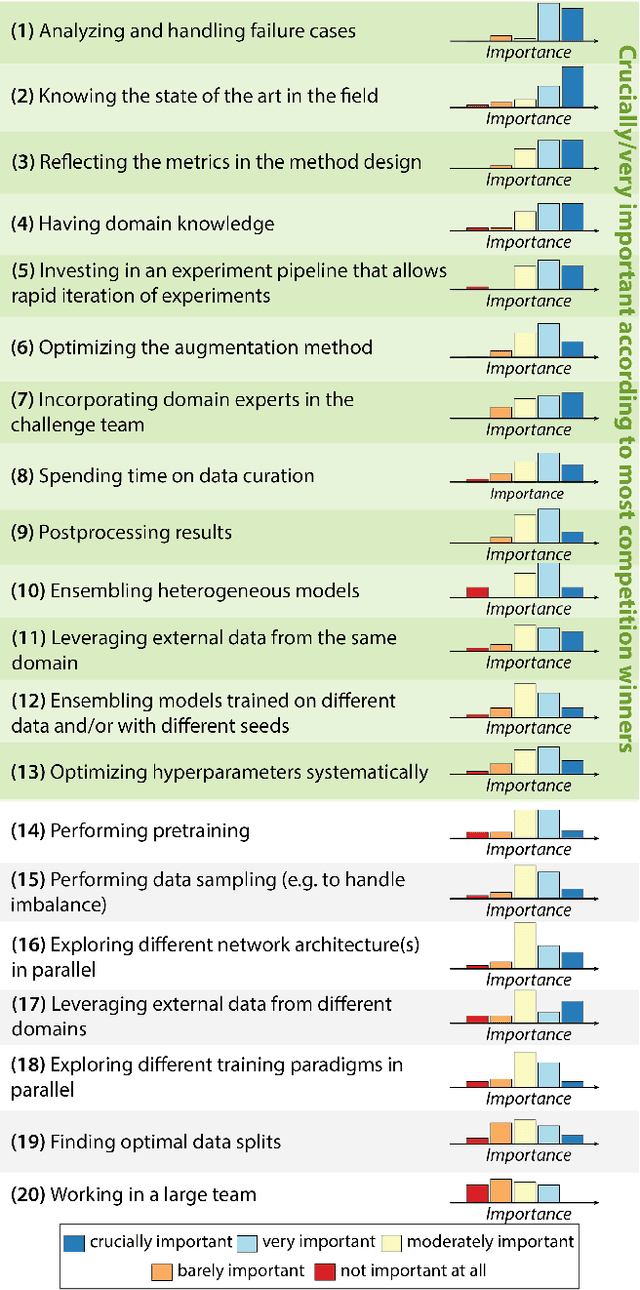
Abstract:International benchmarking competitions have become fundamental for the comparative performance assessment of image analysis methods. However, little attention has been given to investigating what can be learnt from these competitions. Do they really generate scientific progress? What are common and successful participation strategies? What makes a solution superior to a competing method? To address this gap in the literature, we performed a multi-center study with all 80 competitions that were conducted in the scope of IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021. Statistical analyses performed based on comprehensive descriptions of the submitted algorithms linked to their rank as well as the underlying participation strategies revealed common characteristics of winning solutions. These typically include the use of multi-task learning (63%) and/or multi-stage pipelines (61%), and a focus on augmentation (100%), image preprocessing (97%), data curation (79%), and postprocessing (66%). The "typical" lead of a winning team is a computer scientist with a doctoral degree, five years of experience in biomedical image analysis, and four years of experience in deep learning. Two core general development strategies stood out for highly-ranked teams: the reflection of the metrics in the method design and the focus on analyzing and handling failure cases. According to the organizers, 43% of the winning algorithms exceeded the state of the art but only 11% completely solved the respective domain problem. The insights of our study could help researchers (1) improve algorithm development strategies when approaching new problems, and (2) focus on open research questions revealed by this work.
Biomedical image analysis competitions: The state of current participation practice
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:The number of international benchmarking competitions is steadily increasing in various fields of machine learning (ML) research and practice. So far, however, little is known about the common practice as well as bottlenecks faced by the community in tackling the research questions posed. To shed light on the status quo of algorithm development in the specific field of biomedical imaging analysis, we designed an international survey that was issued to all participants of challenges conducted in conjunction with the IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021 conferences (80 competitions in total). The survey covered participants' expertise and working environments, their chosen strategies, as well as algorithm characteristics. A median of 72% challenge participants took part in the survey. According to our results, knowledge exchange was the primary incentive (70%) for participation, while the reception of prize money played only a minor role (16%). While a median of 80 working hours was spent on method development, a large portion of participants stated that they did not have enough time for method development (32%). 25% perceived the infrastructure to be a bottleneck. Overall, 94% of all solutions were deep learning-based. Of these, 84% were based on standard architectures. 43% of the respondents reported that the data samples (e.g., images) were too large to be processed at once. This was most commonly addressed by patch-based training (69%), downsampling (37%), and solving 3D analysis tasks as a series of 2D tasks. K-fold cross-validation on the training set was performed by only 37% of the participants and only 50% of the participants performed ensembling based on multiple identical models (61%) or heterogeneous models (39%). 48% of the respondents applied postprocessing steps.
Multi-center, multi-vendor automated segmentation of left ventricular anatomy in contrast-enhanced MRI
Oct 28, 2021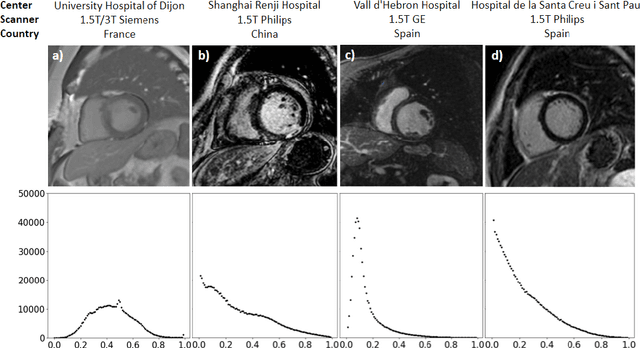
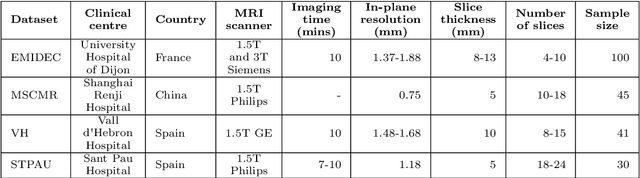
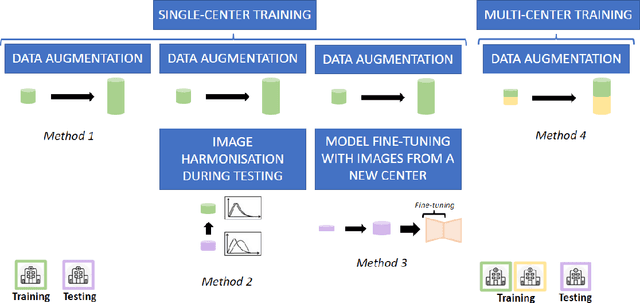
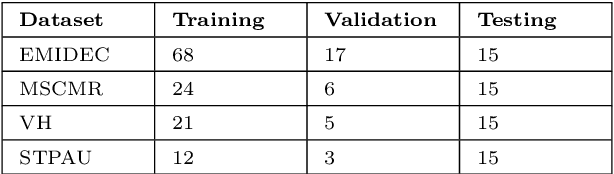
Abstract:Accurate delineation of the left ventricular boundaries in late gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (LGE-MRI) is an essential step for scar tissue quantification and patient-specific assessment of myocardial infarction. Many deep-learning techniques have been proposed to perform automatic segmentations of the left ventricle (LV) in LGE-MRI showing segmentations as accurate as those obtained by expert cardiologists. Thus far, the existing models have been overwhelmingly developed and evaluated with LGE-MRI datasets from single clinical centers. However, in practice, LGE-MRI images vary significantly between clinical centers within and across countries, in particular due to differences in the MRI scanners, imaging conditions, contrast injection protocols and local clinical practise. This work investigates for the first time multi-center and multi-vendor LV segmentation in LGE-MRI, by proposing, implementing and evaluating in detail several strategies to enhance model generalizability across clinical cites. These include data augmentation to artificially augment the image variability in the training sample, image harmonization to align the distributions of LGE-MRI images across centers, and transfer learning to adjust existing single-center models to unseen images from new clinical sites. The results obtained based on a new multi-center LGE-MRI dataset acquired in four clinical centers in Spain, France and China, show that the combination of data augmentation and transfer learning can lead to single-center models that generalize well to new clinical centers not included in the original training. The proposed framework shows the potential for developing clinical tools for automated LV segmentation in LGE-MRI that can be deployed in multiple clinical centers across distinct geographical locations.
Combining Multi-Sequence and Synthetic Images for Improved Segmentation of Late Gadolinium Enhancement Cardiac MRI
Sep 03, 2019



Abstract:Accurate segmentation of the cardiac boundaries in late gadolinium enhancement magnetic resonance images (LGE-MRI) is a fundamental step for accurate quantification of scar tissue. However, while there are many solutions for automatic cardiac segmentation of cine images, the presence of scar tissue can make the correct delineation of the myocardium in LGE-MRI challenging even for human experts. As part of the Multi-Sequence Cardiac MR Segmentation Challenge, we propose a solution for LGE-MRI segmentation based on two components. First, a generative adversarial network is trained for the task of modality-to-modality translation between cine and LGE-MRI sequences to obtain extra synthetic images for both modalities. Second, a deep learning model is trained for segmentation with different combinations of original, augmented and synthetic sequences. Our results based on three magnetic resonance sequences (LGE, bSSFP and T2) from 45 different patients show that the multi-sequence model training integrating synthetic images and data augmentation improves in the segmentation over conventional training with real datasets. In conclusion, the accuracy of the segmentation of LGE-MRI images can be improved by using complementary information provided by non-contrast MRI sequences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge