Fabian Isensee
Finally Outshining the Random Baseline: A Simple and Effective Solution for Active Learning in 3D Biomedical Imaging
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Active learning (AL) has the potential to drastically reduce annotation costs in 3D biomedical image segmentation, where expert labeling of volumetric data is both time-consuming and expensive. Yet, existing AL methods are unable to consistently outperform improved random sampling baselines adapted to 3D data, leaving the field without a reliable solution. We introduce Class-stratified Scheduled Power Predictive Entropy (ClaSP PE), a simple and effective query strategy that addresses two key limitations of standard uncertainty-based AL methods: class imbalance and redundancy in early selections. ClaSP PE combines class-stratified querying to ensure coverage of underrepresented structures and log-scale power noising with a decaying schedule to enforce query diversity in early-stage AL and encourage exploitation later. In our evaluation on 24 experimental settings using four 3D biomedical datasets within the comprehensive nnActive benchmark, ClaSP PE is the only method that generally outperforms improved random baselines in terms of both segmentation quality with statistically significant gains, whilst remaining annotation efficient. Furthermore, we explicitly simulate the real-world application by testing our method on four previously unseen datasets without manual adaptation, where all experiment parameters are set according to predefined guidelines. The results confirm that ClaSP PE robustly generalizes to novel tasks without requiring dataset-specific tuning. Within the nnActive framework, we present compelling evidence that an AL method can consistently outperform random baselines adapted to 3D segmentation, in terms of both performance and annotation efficiency in a realistic, close-to-production scenario. Our open-source implementation and clear deployment guidelines make it readily applicable in practice. Code is at https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/nnActive.
MedNeXt-v2: Scaling 3D ConvNeXts for Large-Scale Supervised Representation Learning in Medical Image Segmentation
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Large-scale supervised pretraining is rapidly reshaping 3D medical image segmentation. However, existing efforts focus primarily on increasing dataset size and overlook the question of whether the backbone network is an effective representation learner at scale. In this work, we address this gap by revisiting ConvNeXt-based architectures for volumetric segmentation and introducing MedNeXt-v2, a compound-scaled 3D ConvNeXt that leverages improved micro-architecture and data scaling to deliver state-of-the-art performance. First, we show that routinely used backbones in large-scale pretraining pipelines are often suboptimal. Subsequently, we use comprehensive backbone benchmarking prior to scaling and demonstrate that stronger from scratch performance reliably predicts stronger downstream performance after pretraining. Guided by these findings, we incorporate a 3D Global Response Normalization module and use depth, width, and context scaling to improve our architecture for effective representation learning. We pretrain MedNeXt-v2 on 18k CT volumes and demonstrate state-of-the-art performance when fine-tuning across six challenging CT and MR benchmarks (144 structures), showing consistent gains over seven publicly released pretrained models. Beyond improvements, our benchmarking of these models also reveals that stronger backbones yield better results on similar data, representation scaling disproportionately benefits pathological segmentation, and that modality-specific pretraining offers negligible benefit once full finetuning is applied. In conclusion, our results establish MedNeXt-v2 as a strong backbone for large-scale supervised representation learning in 3D Medical Image Segmentation. Our code and pretrained models are made available with the official nnUNet repository at: https://www.github.com/MIC-DKFZ/nnUNet
VoxTell: Free-Text Promptable Universal 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:We introduce VoxTell, a vision-language model for text-prompted volumetric medical image segmentation. It maps free-form descriptions, from single words to full clinical sentences, to 3D masks. Trained on 62K+ CT, MRI, and PET volumes spanning over 1K anatomical and pathological classes, VoxTell uses multi-stage vision-language fusion across decoder layers to align textual and visual features at multiple scales. It achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot performance across modalities on unseen datasets, excelling on familiar concepts while generalizing to related unseen classes. Extensive experiments further demonstrate strong cross-modality transfer, robustness to linguistic variations and clinical language, as well as accurate instance-specific segmentation from real-world text. Code is available at: https://www.github.com/MIC-DKFZ/VoxTell
Towards Interactive Lesion Segmentation in Whole-Body PET/CT with Promptable Models
Aug 29, 2025Abstract:Whole-body PET/CT is a cornerstone of oncological imaging, yet accurate lesion segmentation remains challenging due to tracer heterogeneity, physiological uptake, and multi-center variability. While fully automated methods have advanced substantially, clinical practice benefits from approaches that keep humans in the loop to efficiently refine predicted masks. The autoPET/CT IV challenge addresses this need by introducing interactive segmentation tasks based on simulated user prompts. In this work, we present our submission to Task 1. Building on the winning autoPET III nnU-Net pipeline, we extend the framework with promptable capabilities by encoding user-provided foreground and background clicks as additional input channels. We systematically investigate representations for spatial prompts and demonstrate that Euclidean Distance Transform (EDT) encodings consistently outperform Gaussian kernels. Furthermore, we propose online simulation of user interactions and a custom point sampling strategy to improve robustness under realistic prompting conditions. Our ensemble of EDT-based models, trained with and without external data, achieves the strongest cross-validation performance, reducing both false positives and false negatives compared to baseline models. These results highlight the potential of promptable models to enable efficient, user-guided segmentation workflows in multi-tracer, multi-center PET/CT. Code is publicly available at https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/autoPET-interactive
nnLandmark: A Self-Configuring Method for 3D Medical Landmark Detection
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Landmark detection plays a crucial role in medical imaging tasks that rely on precise spatial localization, including specific applications in diagnosis, treatment planning, image registration, and surgical navigation. However, manual annotation is labor-intensive and requires expert knowledge. While deep learning shows promise in automating this task, progress is hindered by limited public datasets, inconsistent benchmarks, and non-standardized baselines, restricting reproducibility, fair comparisons, and model generalizability. This work introduces nnLandmark, a self-configuring deep learning framework for 3D medical landmark detection, adapting nnU-Net to perform heatmap-based regression. By leveraging nnU-Net's automated configuration, nnLandmark eliminates the need for manual parameter tuning, offering out-of-the-box usability. It achieves state-of-the-art accuracy across two public datasets, with a mean radial error (MRE) of 1.5 mm on the Mandibular Molar Landmark (MML) dental CT dataset and 1.2 mm for anatomical fiducials on a brain MRI dataset (AFIDs), where nnLandmark aligns with the inter-rater variability of 1.5 mm. With its strong generalization, reproducibility, and ease of deployment, nnLandmark establishes a reliable baseline for 3D landmark detection, supporting research in anatomical localization and clinical workflows that depend on precise landmark identification. The code will be available soon.
Large Scale Supervised Pretraining For Traumatic Brain Injury Segmentation
Apr 09, 2025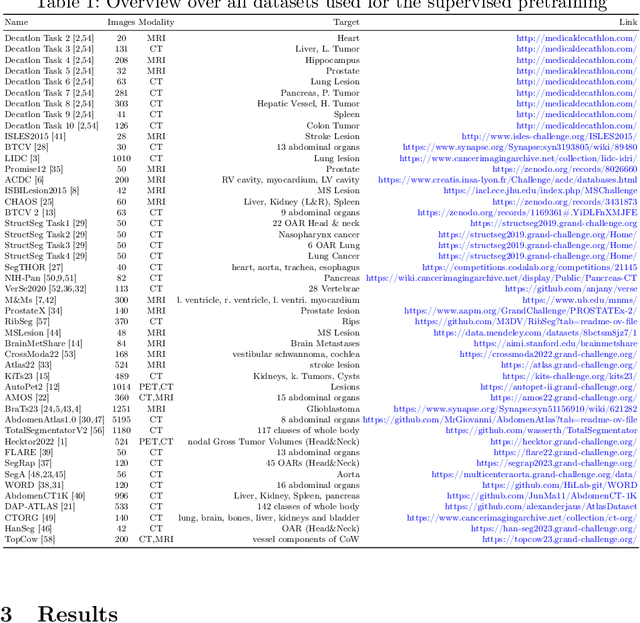
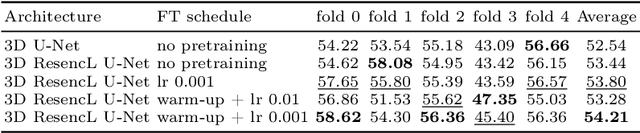
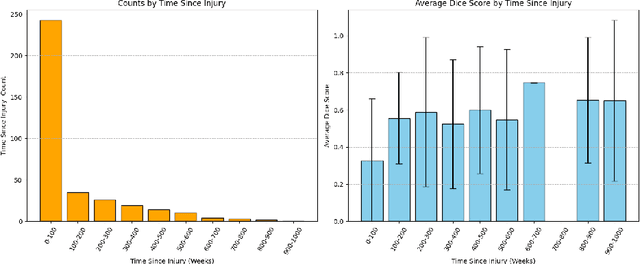
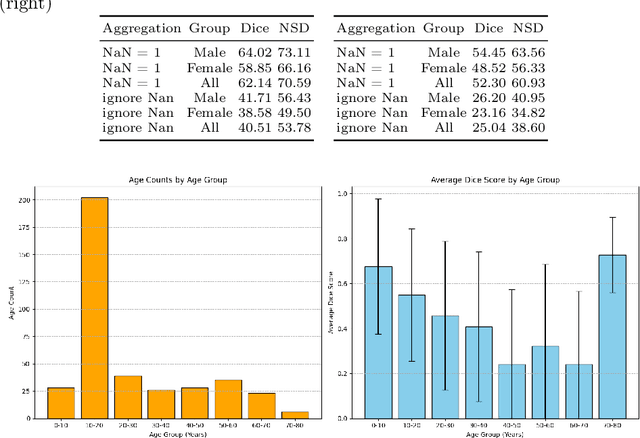
Abstract:The segmentation of lesions in Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (msTBI) presents a significant challenge in neuroimaging due to the diverse characteristics of these lesions, which vary in size, shape, and distribution across brain regions and tissue types. This heterogeneity complicates traditional image processing techniques, resulting in critical errors in tasks such as image registration and brain parcellation. To address these challenges, the AIMS-TBI Segmentation Challenge 2024 aims to advance innovative segmentation algorithms specifically designed for T1-weighted MRI data, the most widely utilized imaging modality in clinical practice. Our proposed solution leverages a large-scale multi-dataset supervised pretraining approach inspired by the MultiTalent method. We train a Resenc L network on a comprehensive collection of datasets covering various anatomical and pathological structures, which equips the model with a robust understanding of brain anatomy and pathology. Following this, the model is fine-tuned on msTBI-specific data to optimize its performance for the unique characteristics of T1-weighted MRI scans and outperforms the baseline without pretraining up to 2 Dice points.
Benchmark of Segmentation Techniques for Pelvic Fracture in CT and X-ray: Summary of the PENGWIN 2024 Challenge
Apr 03, 2025Abstract:The segmentation of pelvic fracture fragments in CT and X-ray images is crucial for trauma diagnosis, surgical planning, and intraoperative guidance. However, accurately and efficiently delineating the bone fragments remains a significant challenge due to complex anatomy and imaging limitations. The PENGWIN challenge, organized as a MICCAI 2024 satellite event, aimed to advance automated fracture segmentation by benchmarking state-of-the-art algorithms on these complex tasks. A diverse dataset of 150 CT scans was collected from multiple clinical centers, and a large set of simulated X-ray images was generated using the DeepDRR method. Final submissions from 16 teams worldwide were evaluated under a rigorous multi-metric testing scheme. The top-performing CT algorithm achieved an average fragment-wise intersection over union (IoU) of 0.930, demonstrating satisfactory accuracy. However, in the X-ray task, the best algorithm attained an IoU of 0.774, highlighting the greater challenges posed by overlapping anatomical structures. Beyond the quantitative evaluation, the challenge revealed methodological diversity in algorithm design. Variations in instance representation, such as primary-secondary classification versus boundary-core separation, led to differing segmentation strategies. Despite promising results, the challenge also exposed inherent uncertainties in fragment definition, particularly in cases of incomplete fractures. These findings suggest that interactive segmentation approaches, integrating human decision-making with task-relevant information, may be essential for improving model reliability and clinical applicability.
nnInteractive: Redefining 3D Promptable Segmentation
Mar 11, 2025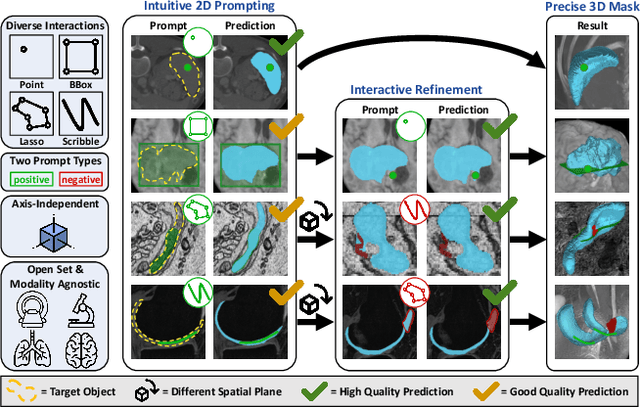
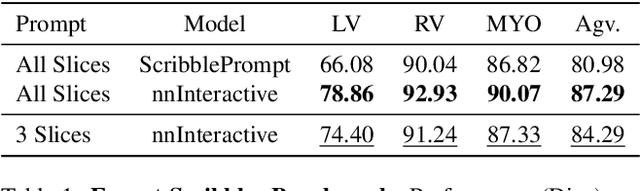
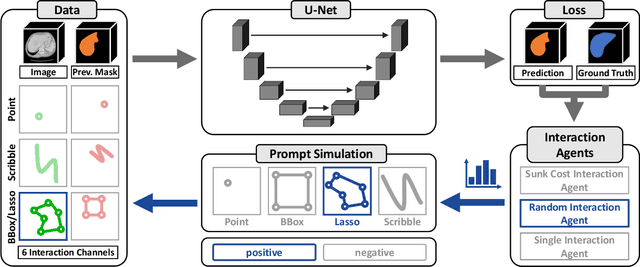
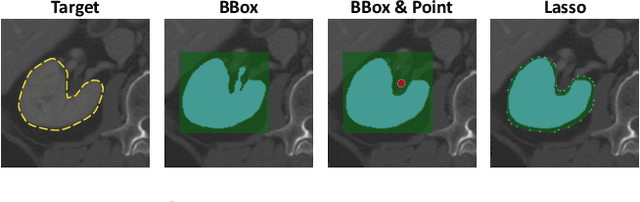
Abstract:Accurate and efficient 3D segmentation is essential for both clinical and research applications. While foundation models like SAM have revolutionized interactive segmentation, their 2D design and domain shift limitations make them ill-suited for 3D medical images. Current adaptations address some of these challenges but remain limited, either lacking volumetric awareness, offering restricted interactivity, or supporting only a small set of structures and modalities. Usability also remains a challenge, as current tools are rarely integrated into established imaging platforms and often rely on cumbersome web-based interfaces with restricted functionality. We introduce nnInteractive, the first comprehensive 3D interactive open-set segmentation method. It supports diverse prompts-including points, scribbles, boxes, and a novel lasso prompt-while leveraging intuitive 2D interactions to generate full 3D segmentations. Trained on 120+ diverse volumetric 3D datasets (CT, MRI, PET, 3D Microscopy, etc.), nnInteractive sets a new state-of-the-art in accuracy, adaptability, and usability. Crucially, it is the first method integrated into widely used image viewers (e.g., Napari, MITK), ensuring broad accessibility for real-world clinical and research applications. Extensive benchmarking demonstrates that nnInteractive far surpasses existing methods, setting a new standard for AI-driven interactive 3D segmentation. nnInteractive is publicly available: https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/napari-nninteractive (Napari plugin), https://www.mitk.org/MITK-nnInteractive (MITK integration), https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/nnInteractive (Python backend).
Primus: Enforcing Attention Usage for 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 03, 2025
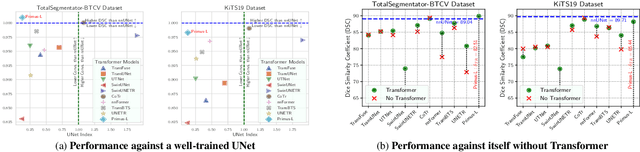
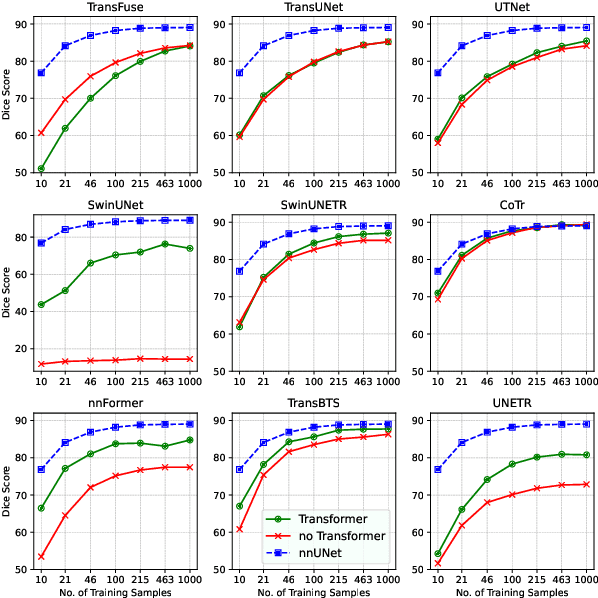
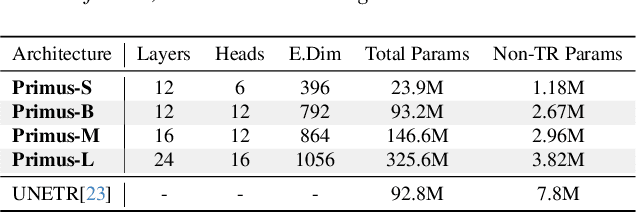
Abstract:Transformers have achieved remarkable success across multiple fields, yet their impact on 3D medical image segmentation remains limited with convolutional networks still dominating major benchmarks. In this work, we a) analyze current Transformer-based segmentation models and identify critical shortcomings, particularly their over-reliance on convolutional blocks. Further, we demonstrate that in some architectures, performance is unaffected by the absence of the Transformer, thereby demonstrating their limited effectiveness. To address these challenges, we move away from hybrid architectures and b) introduce a fully Transformer-based segmentation architecture, termed Primus. Primus leverages high-resolution tokens, combined with advances in positional embeddings and block design, to maximally leverage its Transformer blocks. Through these adaptations Primus surpasses current Transformer-based methods and competes with state-of-the-art convolutional models on multiple public datasets. By doing so, we create the first pure Transformer architecture and take a significant step towards making Transformers state-of-the-art for 3D medical image segmentation.
Bridging vision language model (VLM) evaluation gaps with a framework for scalable and cost-effective benchmark generation
Feb 21, 2025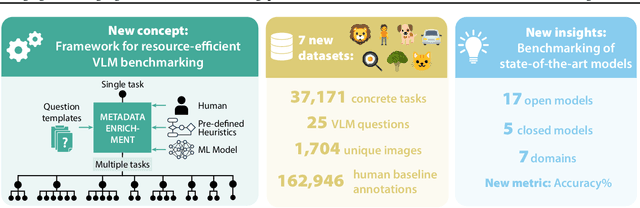
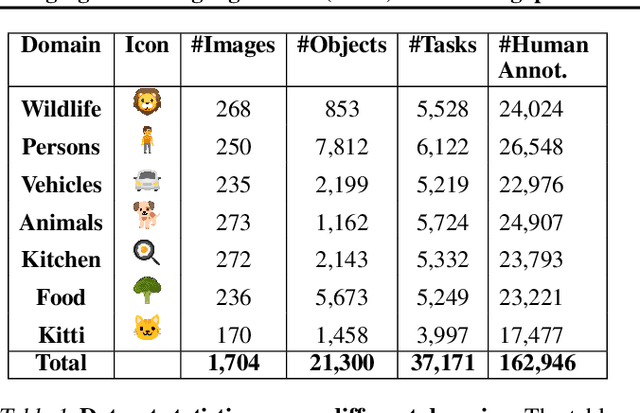
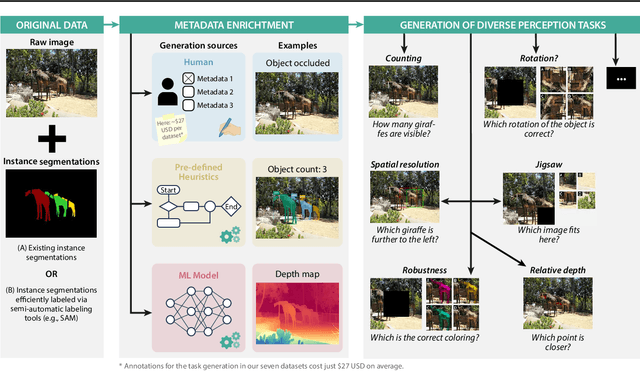
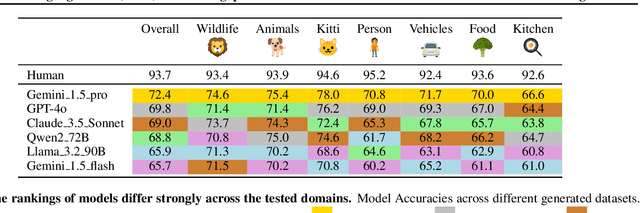
Abstract:Reliable evaluation of AI models is critical for scientific progress and practical application. While existing VLM benchmarks provide general insights into model capabilities, their heterogeneous designs and limited focus on a few imaging domains pose significant challenges for both cross-domain performance comparison and targeted domain-specific evaluation. To address this, we propose three key contributions: (1) a framework for the resource-efficient creation of domain-specific VLM benchmarks enabled by task augmentation for creating multiple diverse tasks from a single existing task, (2) the release of new VLM benchmarks for seven domains, created according to the same homogeneous protocol and including 162,946 thoroughly human-validated answers, and (3) an extensive benchmarking of 22 state-of-the-art VLMs on a total of 37,171 tasks, revealing performance variances across domains and tasks, thereby supporting the need for tailored VLM benchmarks. Adoption of our methodology will pave the way for the resource-efficient domain-specific selection of models and guide future research efforts toward addressing core open questions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge