Tassilo Wald
MedNeXt-v2: Scaling 3D ConvNeXts for Large-Scale Supervised Representation Learning in Medical Image Segmentation
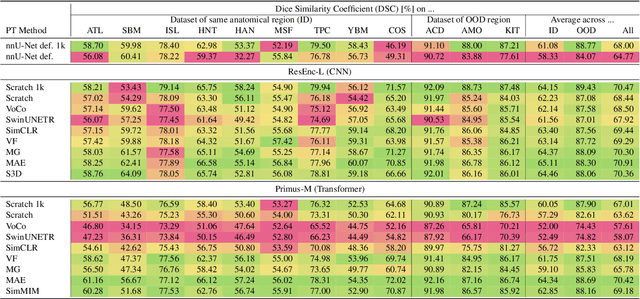
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Large-scale supervised pretraining is rapidly reshaping 3D medical image segmentation. However, existing efforts focus primarily on increasing dataset size and overlook the question of whether the backbone network is an effective representation learner at scale. In this work, we address this gap by revisiting ConvNeXt-based architectures for volumetric segmentation and introducing MedNeXt-v2, a compound-scaled 3D ConvNeXt that leverages improved micro-architecture and data scaling to deliver state-of-the-art performance. First, we show that routinely used backbones in large-scale pretraining pipelines are often suboptimal. Subsequently, we use comprehensive backbone benchmarking prior to scaling and demonstrate that stronger from scratch performance reliably predicts stronger downstream performance after pretraining. Guided by these findings, we incorporate a 3D Global Response Normalization module and use depth, width, and context scaling to improve our architecture for effective representation learning. We pretrain MedNeXt-v2 on 18k CT volumes and demonstrate state-of-the-art performance when fine-tuning across six challenging CT and MR benchmarks (144 structures), showing consistent gains over seven publicly released pretrained models. Beyond improvements, our benchmarking of these models also reveals that stronger backbones yield better results on similar data, representation scaling disproportionately benefits pathological segmentation, and that modality-specific pretraining offers negligible benefit once full finetuning is applied. In conclusion, our results establish MedNeXt-v2 as a strong backbone for large-scale supervised representation learning in 3D Medical Image Segmentation. Our code and pretrained models are made available with the official nnUNet repository at: https://www.github.com/MIC-DKFZ/nnUNet
The Missing Piece: A Case for Pre-Training in 3D Medical Object Detection
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Large-scale pre-training holds the promise to advance 3D medical object detection, a crucial component of accurate computer-aided diagnosis. Yet, it remains underexplored compared to segmentation, where pre-training has already demonstrated significant benefits. Existing pre-training approaches for 3D object detection rely on 2D medical data or natural image pre-training, failing to fully leverage 3D volumetric information. In this work, we present the first systematic study of how existing pre-training methods can be integrated into state-of-the-art detection architectures, covering both CNNs and Transformers. Our results show that pre-training consistently improves detection performance across various tasks and datasets. Notably, reconstruction-based self-supervised pre-training outperforms supervised pre-training, while contrastive pre-training provides no clear benefit for 3D medical object detection. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/nnDetection-finetuning.
* MICCAI 2025
Large Scale Supervised Pretraining For Traumatic Brain Injury Segmentation
Apr 09, 2025
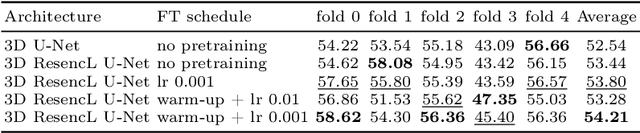
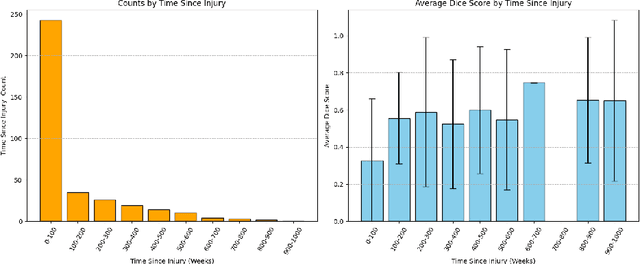
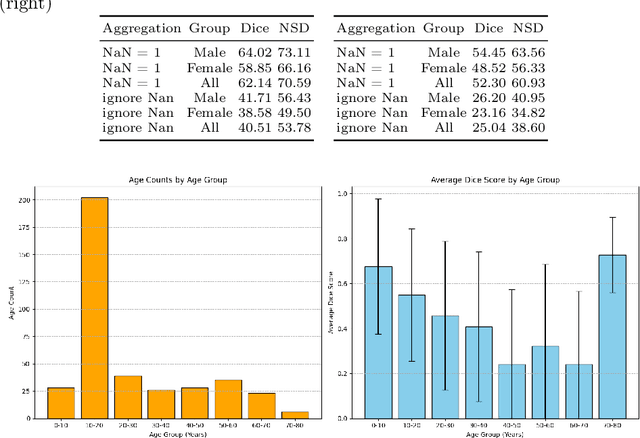
Abstract:The segmentation of lesions in Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury (msTBI) presents a significant challenge in neuroimaging due to the diverse characteristics of these lesions, which vary in size, shape, and distribution across brain regions and tissue types. This heterogeneity complicates traditional image processing techniques, resulting in critical errors in tasks such as image registration and brain parcellation. To address these challenges, the AIMS-TBI Segmentation Challenge 2024 aims to advance innovative segmentation algorithms specifically designed for T1-weighted MRI data, the most widely utilized imaging modality in clinical practice. Our proposed solution leverages a large-scale multi-dataset supervised pretraining approach inspired by the MultiTalent method. We train a Resenc L network on a comprehensive collection of datasets covering various anatomical and pathological structures, which equips the model with a robust understanding of brain anatomy and pathology. Following this, the model is fine-tuned on msTBI-specific data to optimize its performance for the unique characteristics of T1-weighted MRI scans and outperforms the baseline without pretraining up to 2 Dice points.
nnInteractive: Redefining 3D Promptable Segmentation
Mar 11, 2025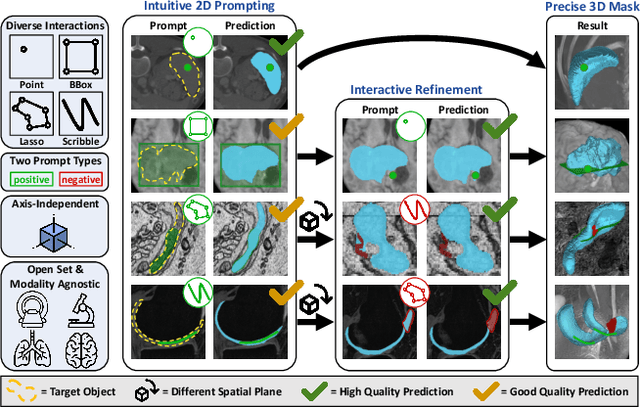
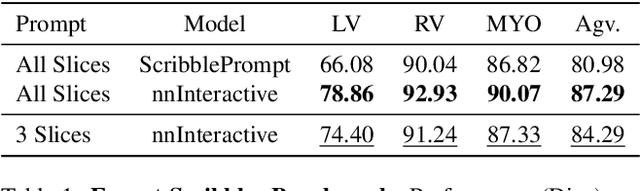
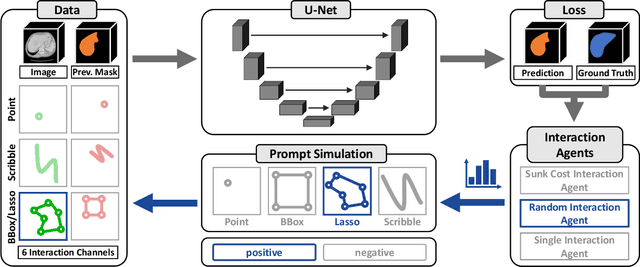
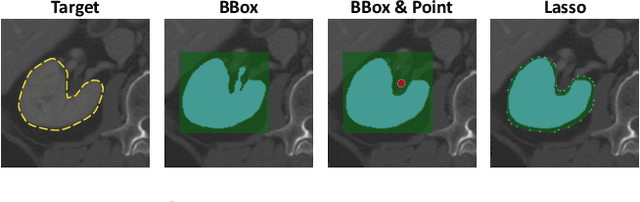
Abstract:Accurate and efficient 3D segmentation is essential for both clinical and research applications. While foundation models like SAM have revolutionized interactive segmentation, their 2D design and domain shift limitations make them ill-suited for 3D medical images. Current adaptations address some of these challenges but remain limited, either lacking volumetric awareness, offering restricted interactivity, or supporting only a small set of structures and modalities. Usability also remains a challenge, as current tools are rarely integrated into established imaging platforms and often rely on cumbersome web-based interfaces with restricted functionality. We introduce nnInteractive, the first comprehensive 3D interactive open-set segmentation method. It supports diverse prompts-including points, scribbles, boxes, and a novel lasso prompt-while leveraging intuitive 2D interactions to generate full 3D segmentations. Trained on 120+ diverse volumetric 3D datasets (CT, MRI, PET, 3D Microscopy, etc.), nnInteractive sets a new state-of-the-art in accuracy, adaptability, and usability. Crucially, it is the first method integrated into widely used image viewers (e.g., Napari, MITK), ensuring broad accessibility for real-world clinical and research applications. Extensive benchmarking demonstrates that nnInteractive far surpasses existing methods, setting a new standard for AI-driven interactive 3D segmentation. nnInteractive is publicly available: https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/napari-nninteractive (Napari plugin), https://www.mitk.org/MITK-nnInteractive (MITK integration), https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/nnInteractive (Python backend).
Primus: Enforcing Attention Usage for 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 03, 2025
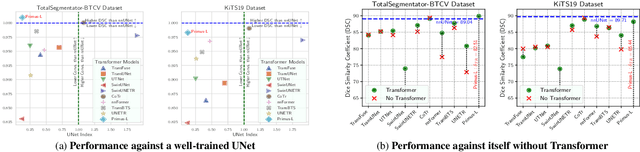
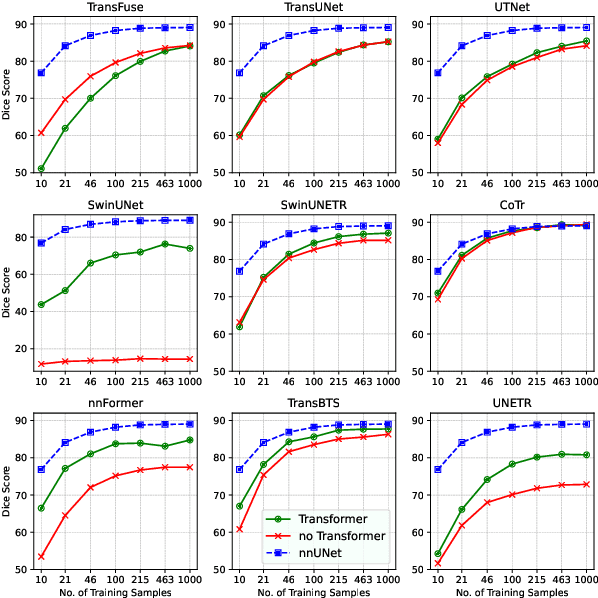
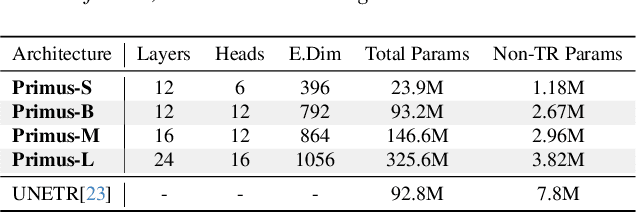
Abstract:Transformers have achieved remarkable success across multiple fields, yet their impact on 3D medical image segmentation remains limited with convolutional networks still dominating major benchmarks. In this work, we a) analyze current Transformer-based segmentation models and identify critical shortcomings, particularly their over-reliance on convolutional blocks. Further, we demonstrate that in some architectures, performance is unaffected by the absence of the Transformer, thereby demonstrating their limited effectiveness. To address these challenges, we move away from hybrid architectures and b) introduce a fully Transformer-based segmentation architecture, termed Primus. Primus leverages high-resolution tokens, combined with advances in positional embeddings and block design, to maximally leverage its Transformer blocks. Through these adaptations Primus surpasses current Transformer-based methods and competes with state-of-the-art convolutional models on multiple public datasets. By doing so, we create the first pure Transformer architecture and take a significant step towards making Transformers state-of-the-art for 3D medical image segmentation.
LesionLocator: Zero-Shot Universal Tumor Segmentation and Tracking in 3D Whole-Body Imaging
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:In this work, we present LesionLocator, a framework for zero-shot longitudinal lesion tracking and segmentation in 3D medical imaging, establishing the first end-to-end model capable of 4D tracking with dense spatial prompts. Our model leverages an extensive dataset of 23,262 annotated medical scans, as well as synthesized longitudinal data across diverse lesion types. The diversity and scale of our dataset significantly enhances model generalizability to real-world medical imaging challenges and addresses key limitations in longitudinal data availability. LesionLocator outperforms all existing promptable models in lesion segmentation by nearly 10 dice points, reaching human-level performance, and achieves state-of-the-art results in lesion tracking, with superior lesion retrieval and segmentation accuracy. LesionLocator not only sets a new benchmark in universal promptable lesion segmentation and automated longitudinal lesion tracking but also provides the first open-access solution of its kind, releasing our synthetic 4D dataset and model to the community, empowering future advancements in medical imaging. Code is available at: www.github.com/MIC-DKFZ/LesionLocator
A Unified Framework for Foreground and Anonymization Area Segmentation in CT and MRI Data
Jan 08, 2025



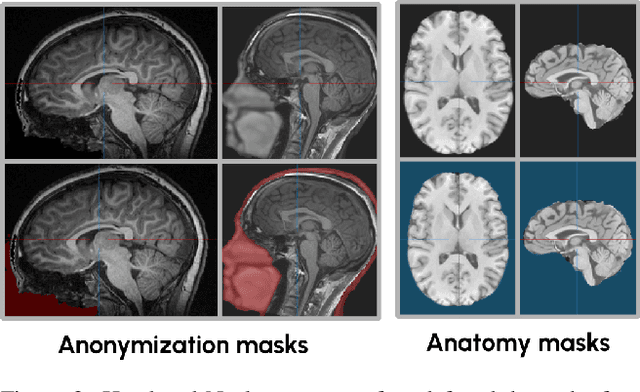
Abstract:This study presents an open-source toolkit to address critical challenges in preprocessing data for self-supervised learning (SSL) for 3D medical imaging, focusing on data privacy and computational efficiency. The toolkit comprises two main components: a segmentation network that delineates foreground regions to optimize data sampling and thus reduce training time, and a segmentation network that identifies anonymized regions, preventing erroneous supervision in reconstruction-based SSL methods. Experimental results demonstrate high robustness, with mean Dice scores exceeding 98.5 across all anonymization methods and surpassing 99.5 for foreground segmentation tasks, highlighting the efficacy of the toolkit in supporting SSL applications in 3D medical imaging for both CT and MRI images. The weights and code is available at https://github.com/MIC-DKFZ/Foreground-and-Anonymization-Area-Segmentation.
An OpenMind for 3D medical vision self-supervised learning
Dec 22, 2024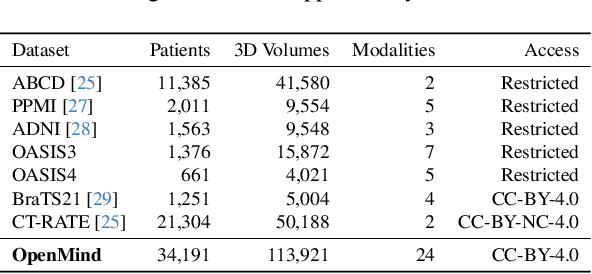
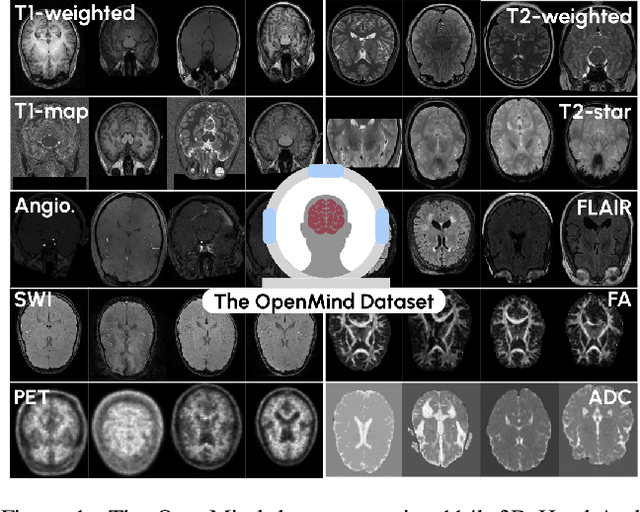
Abstract:The field of 3D medical vision self-supervised learning lacks consistency and standardization. While many methods have been developed it is impossible to identify the current state-of-the-art, due to i) varying and small pre-training datasets, ii) varying architectures, and iii) being evaluated on differing downstream datasets. In this paper we bring clarity to this field and lay the foundation for further method advancements: We a) publish the largest publicly available pre-training dataset comprising 114k 3D brain MRI volumes and b) benchmark existing SSL methods under common architectures and c) provide the code of our framework publicly to facilitate rapid adoption and reproduction. This pre-print \textit{only describes} the dataset contribution (a); Data, benchmark, and codebase will be made available shortly.
INTRABENCH: Interactive Radiological Benchmark
Nov 12, 2024



Abstract:Current interactive segmentation approaches, inspired by the success of META's Segment Anything model, have achieved notable advancements, however, they come with substantial limitations that hinder their practical application in real clinical scenarios. These include unrealistic human interaction requirements, such as slice-by-slice operations for 2D models on 3D data, a lack of iterative refinement, and insufficient evaluation experiments. These shortcomings prevent accurate assessment of model performance and lead to inconsistent outcomes across studies. IntRaBench overcomes these challenges by offering a comprehensive and reproducible framework for evaluating interactive segmentation methods in realistic, clinically relevant scenarios. It includes diverse datasets, target structures, and segmentation models, and provides a flexible codebase that allows seamless integration of new models and prompting strategies. Additionally, we introduce advanced techniques to minimize clinician interaction, ensuring fair comparisons between 2D and 3D models. By open-sourcing IntRaBench, we invite the research community to integrate their models and prompting techniques, ensuring continuous and transparent evaluation of interactive segmentation models in 3D medical imaging.
Touchstone Benchmark: Are We on the Right Way for Evaluating AI Algorithms for Medical Segmentation?
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:How can we test AI performance? This question seems trivial, but it isn't. Standard benchmarks often have problems such as in-distribution and small-size test sets, oversimplified metrics, unfair comparisons, and short-term outcome pressure. As a consequence, good performance on standard benchmarks does not guarantee success in real-world scenarios. To address these problems, we present Touchstone, a large-scale collaborative segmentation benchmark of 9 types of abdominal organs. This benchmark is based on 5,195 training CT scans from 76 hospitals around the world and 5,903 testing CT scans from 11 additional hospitals. This diverse test set enhances the statistical significance of benchmark results and rigorously evaluates AI algorithms across various out-of-distribution scenarios. We invited 14 inventors of 19 AI algorithms to train their algorithms, while our team, as a third party, independently evaluated these algorithms on three test sets. In addition, we also evaluated pre-existing AI frameworks--which, differing from algorithms, are more flexible and can support different algorithms--including MONAI from NVIDIA, nnU-Net from DKFZ, and numerous other open-source frameworks. We are committed to expanding this benchmark to encourage more innovation of AI algorithms for the medical domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge