Saikat Roy
MedNeXt-v2: Scaling 3D ConvNeXts for Large-Scale Supervised Representation Learning in Medical Image Segmentation
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Large-scale supervised pretraining is rapidly reshaping 3D medical image segmentation. However, existing efforts focus primarily on increasing dataset size and overlook the question of whether the backbone network is an effective representation learner at scale. In this work, we address this gap by revisiting ConvNeXt-based architectures for volumetric segmentation and introducing MedNeXt-v2, a compound-scaled 3D ConvNeXt that leverages improved micro-architecture and data scaling to deliver state-of-the-art performance. First, we show that routinely used backbones in large-scale pretraining pipelines are often suboptimal. Subsequently, we use comprehensive backbone benchmarking prior to scaling and demonstrate that stronger from scratch performance reliably predicts stronger downstream performance after pretraining. Guided by these findings, we incorporate a 3D Global Response Normalization module and use depth, width, and context scaling to improve our architecture for effective representation learning. We pretrain MedNeXt-v2 on 18k CT volumes and demonstrate state-of-the-art performance when fine-tuning across six challenging CT and MR benchmarks (144 structures), showing consistent gains over seven publicly released pretrained models. Beyond improvements, our benchmarking of these models also reveals that stronger backbones yield better results on similar data, representation scaling disproportionately benefits pathological segmentation, and that modality-specific pretraining offers negligible benefit once full finetuning is applied. In conclusion, our results establish MedNeXt-v2 as a strong backbone for large-scale supervised representation learning in 3D Medical Image Segmentation. Our code and pretrained models are made available with the official nnUNet repository at: https://www.github.com/MIC-DKFZ/nnUNet
CRONOS: Continuous Time Reconstruction for 4D Medical Longitudinal Series
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Forecasting how 3D medical scans evolve over time is important for disease progression, treatment planning, and developmental assessment. Yet existing models either rely on a single prior scan, fixed grid times, or target global labels, which limits voxel-level forecasting under irregular sampling. We present CRONOS, a unified framework for many-to-one prediction from multiple past scans that supports both discrete (grid-based) and continuous (real-valued) timestamps in one model, to the best of our knowledge the first to achieve continuous sequence-to-image forecasting for 3D medical data. CRONOS learns a spatio-temporal velocity field that transports context volumes toward a target volume at an arbitrary time, while operating directly in 3D voxel space. Across three public datasets spanning Cine-MRI, perfusion CT, and longitudinal MRI, CRONOS outperforms other baselines, while remaining computationally competitive. We will release code and evaluation protocols to enable reproducible, multi-dataset benchmarking of multi-context, continuous-time forecasting.
Temporal Flow Matching for Learning Spatio-Temporal Trajectories in 4D Longitudinal Medical Imaging
Aug 29, 2025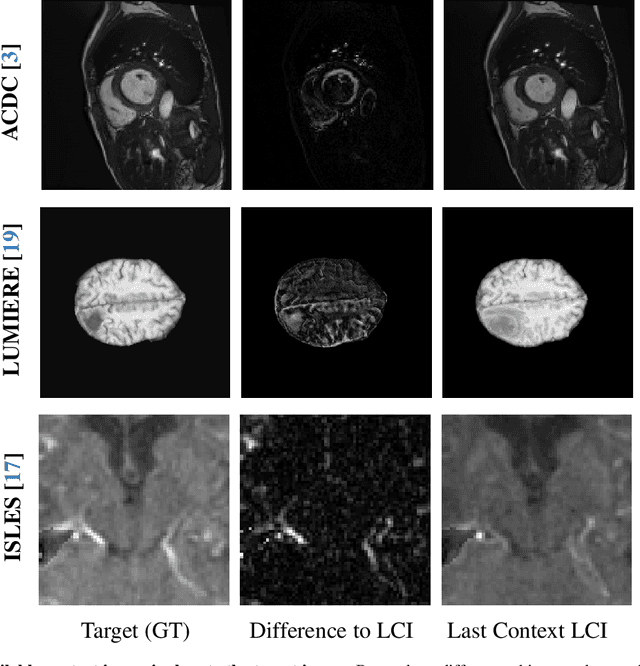
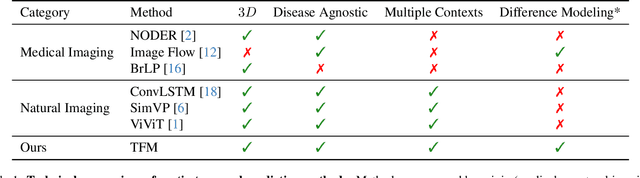
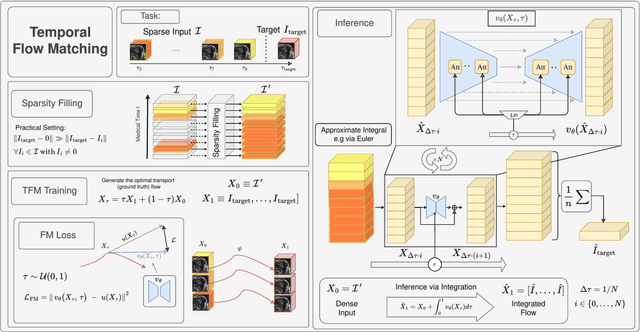
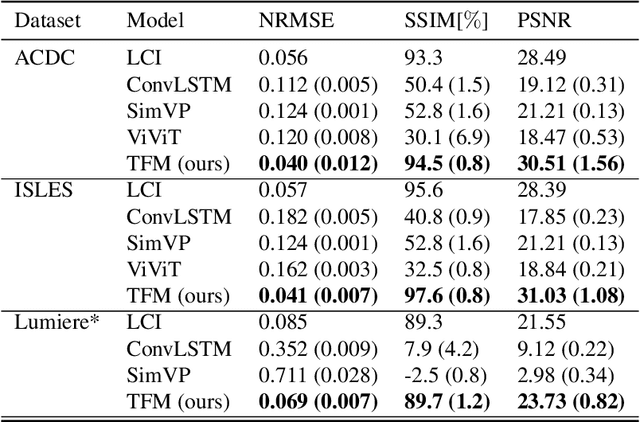
Abstract:Understanding temporal dynamics in medical imaging is crucial for applications such as disease progression modeling, treatment planning and anatomical development tracking. However, most deep learning methods either consider only single temporal contexts, or focus on tasks like classification or regression, limiting their ability for fine-grained spatial predictions. While some approaches have been explored, they are often limited to single timepoints, specific diseases or have other technical restrictions. To address this fundamental gap, we introduce Temporal Flow Matching (TFM), a unified generative trajectory method that (i) aims to learn the underlying temporal distribution, (ii) by design can fall back to a nearest image predictor, i.e. predicting the last context image (LCI), as a special case, and (iii) supports $3D$ volumes, multiple prior scans, and irregular sampling. Extensive benchmarks on three public longitudinal datasets show that TFM consistently surpasses spatio-temporal methods from natural imaging, establishing a new state-of-the-art and robust baseline for $4D$ medical image prediction.
Inclusive, Differentially Private Federated Learning for Clinical Data
May 28, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) offers a promising approach for training clinical AI models without centralizing sensitive patient data. However, its real-world adoption is hindered by challenges related to privacy, resource constraints, and compliance. Existing Differential Privacy (DP) approaches often apply uniform noise, which disproportionately degrades model performance, even among well-compliant institutions. In this work, we propose a novel compliance-aware FL framework that enhances DP by adaptively adjusting noise based on quantifiable client compliance scores. Additionally, we introduce a compliance scoring tool based on key healthcare and security standards to promote secure, inclusive, and equitable participation across diverse clinical settings. Extensive experiments on public datasets demonstrate that integrating under-resourced, less compliant clinics with highly regulated institutions yields accuracy improvements of up to 15% over traditional FL. This work advances FL by balancing privacy, compliance, and performance, making it a viable solution for real-world clinical workflows in global healthcare.
Primus: Enforcing Attention Usage for 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 03, 2025
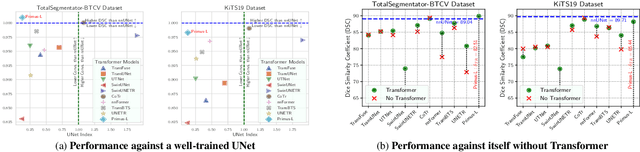
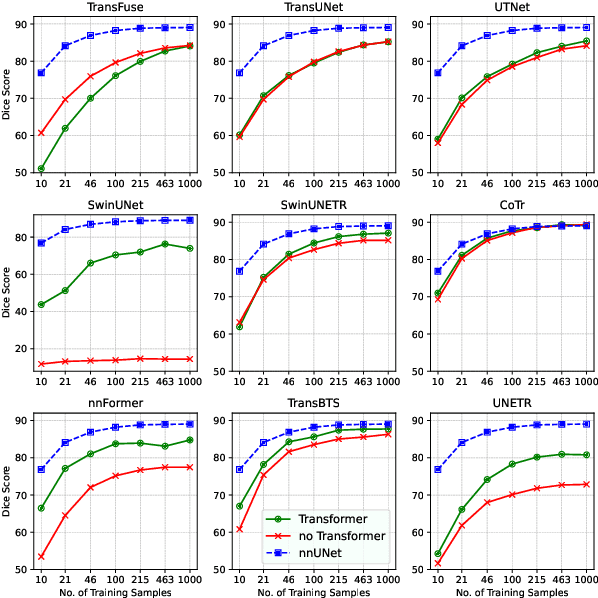
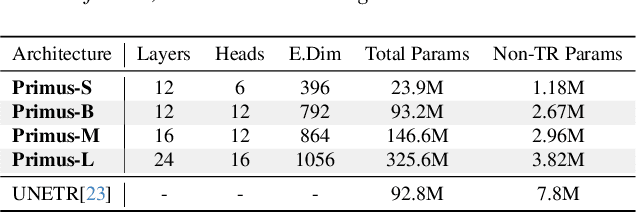
Abstract:Transformers have achieved remarkable success across multiple fields, yet their impact on 3D medical image segmentation remains limited with convolutional networks still dominating major benchmarks. In this work, we a) analyze current Transformer-based segmentation models and identify critical shortcomings, particularly their over-reliance on convolutional blocks. Further, we demonstrate that in some architectures, performance is unaffected by the absence of the Transformer, thereby demonstrating their limited effectiveness. To address these challenges, we move away from hybrid architectures and b) introduce a fully Transformer-based segmentation architecture, termed Primus. Primus leverages high-resolution tokens, combined with advances in positional embeddings and block design, to maximally leverage its Transformer blocks. Through these adaptations Primus surpasses current Transformer-based methods and competes with state-of-the-art convolutional models on multiple public datasets. By doing so, we create the first pure Transformer architecture and take a significant step towards making Transformers state-of-the-art for 3D medical image segmentation.
LesionLocator: Zero-Shot Universal Tumor Segmentation and Tracking in 3D Whole-Body Imaging
Feb 28, 2025Abstract:In this work, we present LesionLocator, a framework for zero-shot longitudinal lesion tracking and segmentation in 3D medical imaging, establishing the first end-to-end model capable of 4D tracking with dense spatial prompts. Our model leverages an extensive dataset of 23,262 annotated medical scans, as well as synthesized longitudinal data across diverse lesion types. The diversity and scale of our dataset significantly enhances model generalizability to real-world medical imaging challenges and addresses key limitations in longitudinal data availability. LesionLocator outperforms all existing promptable models in lesion segmentation by nearly 10 dice points, reaching human-level performance, and achieves state-of-the-art results in lesion tracking, with superior lesion retrieval and segmentation accuracy. LesionLocator not only sets a new benchmark in universal promptable lesion segmentation and automated longitudinal lesion tracking but also provides the first open-access solution of its kind, releasing our synthetic 4D dataset and model to the community, empowering future advancements in medical imaging. Code is available at: www.github.com/MIC-DKFZ/LesionLocator
Investigating the Feasibility of Patch-based Inference for Generalized Diffusion Priors in Inverse Problems for Medical Images
Jan 25, 2025Abstract:Plug-and-play approaches to solving inverse problems such as restoration and super-resolution have recently benefited from Diffusion-based generative priors for natural as well as medical images. However, solutions often use the standard albeit computationally intensive route of training and inferring with the whole image on the diffusion prior. While patch-based approaches to evaluating diffusion priors in plug-and-play methods have received some interest, they remain an open area of study. In this work, we explore the feasibility of the usage of patches for training and inference of a diffusion prior on MRI images. We explore the minor adaptation necessary for artifact avoidance, the performance and the efficiency of memory usage of patch-based methods as well as the adaptability of whole image training to patch-based evaluation - evaluating across multiple plug-and-play methods, tasks and datasets.
ScaleMAI: Accelerating the Development of Trusted Datasets and AI Models
Jan 06, 2025

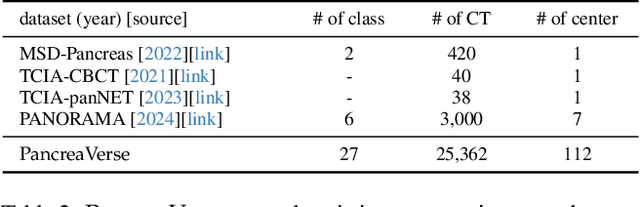

Abstract:Building trusted datasets is critical for transparent and responsible Medical AI (MAI) research, but creating even small, high-quality datasets can take years of effort from multidisciplinary teams. This process often delays AI benefits, as human-centric data creation and AI-centric model development are treated as separate, sequential steps. To overcome this, we propose ScaleMAI, an agent of AI-integrated data curation and annotation, allowing data quality and AI performance to improve in a self-reinforcing cycle and reducing development time from years to months. We adopt pancreatic tumor detection as an example. First, ScaleMAI progressively creates a dataset of 25,362 CT scans, including per-voxel annotations for benign/malignant tumors and 24 anatomical structures. Second, through progressive human-in-the-loop iterations, ScaleMAI provides Flagship AI Model that can approach the proficiency of expert annotators (30-year experience) in detecting pancreatic tumors. Flagship Model significantly outperforms models developed from smaller, fixed-quality datasets, with substantial gains in tumor detection (+14%), segmentation (+5%), and classification (72%) on three prestigious benchmarks. In summary, ScaleMAI transforms the speed, scale, and reliability of medical dataset creation, paving the way for a variety of impactful, data-driven applications.
Touchstone Benchmark: Are We on the Right Way for Evaluating AI Algorithms for Medical Segmentation?
Nov 06, 2024



Abstract:How can we test AI performance? This question seems trivial, but it isn't. Standard benchmarks often have problems such as in-distribution and small-size test sets, oversimplified metrics, unfair comparisons, and short-term outcome pressure. As a consequence, good performance on standard benchmarks does not guarantee success in real-world scenarios. To address these problems, we present Touchstone, a large-scale collaborative segmentation benchmark of 9 types of abdominal organs. This benchmark is based on 5,195 training CT scans from 76 hospitals around the world and 5,903 testing CT scans from 11 additional hospitals. This diverse test set enhances the statistical significance of benchmark results and rigorously evaluates AI algorithms across various out-of-distribution scenarios. We invited 14 inventors of 19 AI algorithms to train their algorithms, while our team, as a third party, independently evaluated these algorithms on three test sets. In addition, we also evaluated pre-existing AI frameworks--which, differing from algorithms, are more flexible and can support different algorithms--including MONAI from NVIDIA, nnU-Net from DKFZ, and numerous other open-source frameworks. We are committed to expanding this benchmark to encourage more innovation of AI algorithms for the medical domain.
nnU-Net Revisited: A Call for Rigorous Validation in 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Apr 15, 2024



Abstract:The release of nnU-Net marked a paradigm shift in 3D medical image segmentation, demonstrating that a properly configured U-Net architecture could still achieve state-of-the-art results. Despite this, the pursuit of novel architectures, and the respective claims of superior performance over the U-Net baseline, continued. In this study, we demonstrate that many of these recent claims fail to hold up when scrutinized for common validation shortcomings, such as the use of inadequate baselines, insufficient datasets, and neglected computational resources. By meticulously avoiding these pitfalls, we conduct a thorough and comprehensive benchmarking of current segmentation methods including CNN-based, Transformer-based, and Mamba-based approaches. In contrast to current beliefs, we find that the recipe for state-of-the-art performance is 1) employing CNN-based U-Net models, including ResNet and ConvNeXt variants, 2) using the nnU-Net framework, and 3) scaling models to modern hardware resources. These results indicate an ongoing innovation bias towards novel architectures in the field and underscore the need for more stringent validation standards in the quest for scientific progress.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge