Raphael Stock
Primus: Enforcing Attention Usage for 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Mar 03, 2025
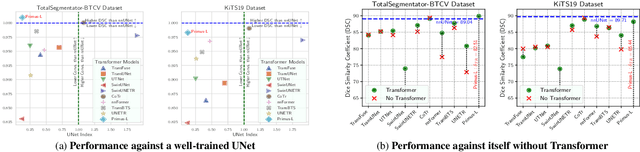
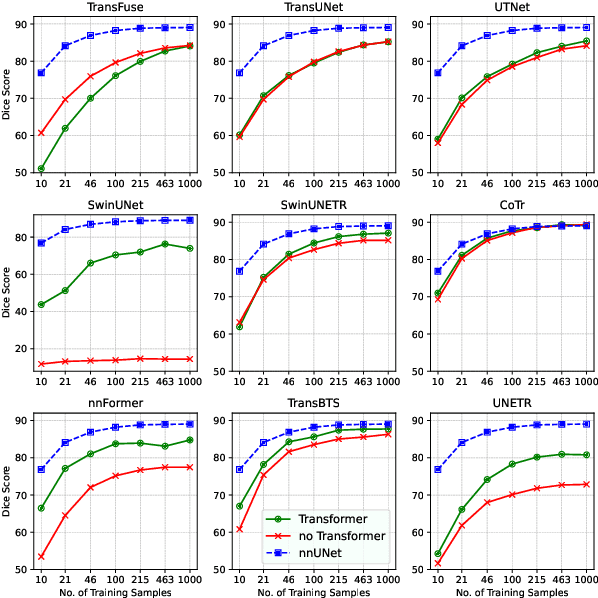
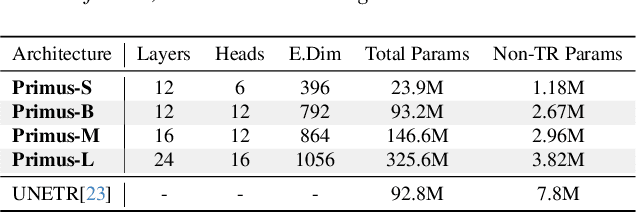
Abstract:Transformers have achieved remarkable success across multiple fields, yet their impact on 3D medical image segmentation remains limited with convolutional networks still dominating major benchmarks. In this work, we a) analyze current Transformer-based segmentation models and identify critical shortcomings, particularly their over-reliance on convolutional blocks. Further, we demonstrate that in some architectures, performance is unaffected by the absence of the Transformer, thereby demonstrating their limited effectiveness. To address these challenges, we move away from hybrid architectures and b) introduce a fully Transformer-based segmentation architecture, termed Primus. Primus leverages high-resolution tokens, combined with advances in positional embeddings and block design, to maximally leverage its Transformer blocks. Through these adaptations Primus surpasses current Transformer-based methods and competes with state-of-the-art convolutional models on multiple public datasets. By doing so, we create the first pure Transformer architecture and take a significant step towards making Transformers state-of-the-art for 3D medical image segmentation.
Tumor Detection, Segmentation and Classification Challenge on Automated 3D Breast Ultrasound: The TDSC-ABUS Challenge
Jan 26, 2025



Abstract:Breast cancer is one of the most common causes of death among women worldwide. Early detection helps in reducing the number of deaths. Automated 3D Breast Ultrasound (ABUS) is a newer approach for breast screening, which has many advantages over handheld mammography such as safety, speed, and higher detection rate of breast cancer. Tumor detection, segmentation, and classification are key components in the analysis of medical images, especially challenging in the context of 3D ABUS due to the significant variability in tumor size and shape, unclear tumor boundaries, and a low signal-to-noise ratio. The lack of publicly accessible, well-labeled ABUS datasets further hinders the advancement of systems for breast tumor analysis. Addressing this gap, we have organized the inaugural Tumor Detection, Segmentation, and Classification Challenge on Automated 3D Breast Ultrasound 2023 (TDSC-ABUS2023). This initiative aims to spearhead research in this field and create a definitive benchmark for tasks associated with 3D ABUS image analysis. In this paper, we summarize the top-performing algorithms from the challenge and provide critical analysis for ABUS image examination. We offer the TDSC-ABUS challenge as an open-access platform at https://tdsc-abus2023.grand-challenge.org/ to benchmark and inspire future developments in algorithmic research.
PSFHS Challenge Report: Pubic Symphysis and Fetal Head Segmentation from Intrapartum Ultrasound Images
Sep 17, 2024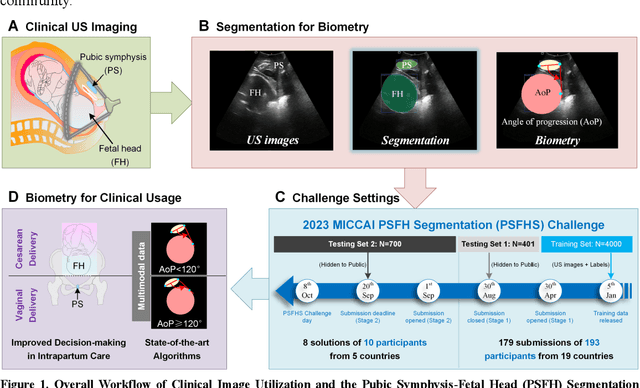
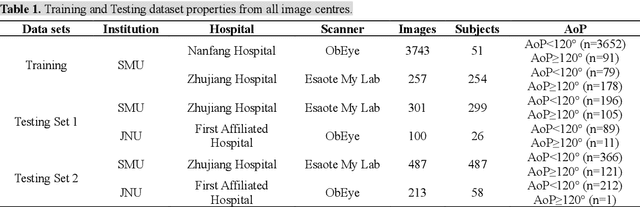
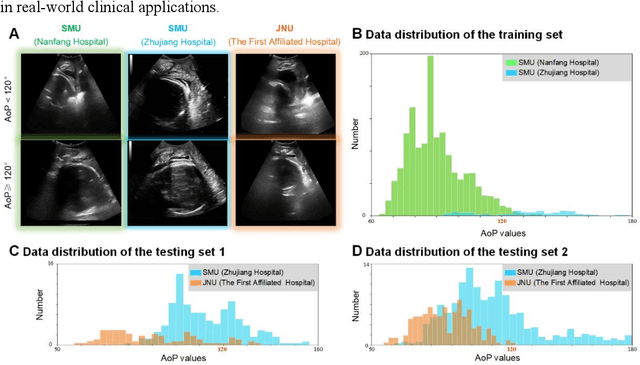

Abstract:Segmentation of the fetal and maternal structures, particularly intrapartum ultrasound imaging as advocated by the International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and Gynecology (ISUOG) for monitoring labor progression, is a crucial first step for quantitative diagnosis and clinical decision-making. This requires specialized analysis by obstetrics professionals, in a task that i) is highly time- and cost-consuming and ii) often yields inconsistent results. The utility of automatic segmentation algorithms for biometry has been proven, though existing results remain suboptimal. To push forward advancements in this area, the Grand Challenge on Pubic Symphysis-Fetal Head Segmentation (PSFHS) was held alongside the 26th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention (MICCAI 2023). This challenge aimed to enhance the development of automatic segmentation algorithms at an international scale, providing the largest dataset to date with 5,101 intrapartum ultrasound images collected from two ultrasound machines across three hospitals from two institutions. The scientific community's enthusiastic participation led to the selection of the top 8 out of 179 entries from 193 registrants in the initial phase to proceed to the competition's second stage. These algorithms have elevated the state-of-the-art in automatic PSFHS from intrapartum ultrasound images. A thorough analysis of the results pinpointed ongoing challenges in the field and outlined recommendations for future work. The top solutions and the complete dataset remain publicly available, fostering further advancements in automatic segmentation and biometry for intrapartum ultrasound imaging.
Visual Prompt Engineering for Medical Vision Language Models in Radiology
Aug 28, 2024



Abstract:Medical image classification in radiology faces significant challenges, particularly in generalizing to unseen pathologies. In contrast, CLIP offers a promising solution by leveraging multimodal learning to improve zero-shot classification performance. However, in the medical domain, lesions can be small and might not be well represented in the embedding space. Therefore, in this paper, we explore the potential of visual prompt engineering to enhance the capabilities of Vision Language Models (VLMs) in radiology. Leveraging BiomedCLIP, trained on extensive biomedical image-text pairs, we investigate the impact of embedding visual markers directly within radiological images to guide the model's attention to critical regions. Our evaluation on the JSRT dataset, focusing on lung nodule malignancy classification, demonstrates that incorporating visual prompts $\unicode{x2013}$ such as arrows, circles, and contours $\unicode{x2013}$ significantly improves classification metrics including AUROC, AUPRC, F1 score, and accuracy. Moreover, the study provides attention maps, showcasing enhanced model interpretability and focus on clinically relevant areas. These findings underscore the efficacy of visual prompt engineering as a straightforward yet powerful approach to advance VLM performance in medical image analysis.
Simulation-based Inference for Model Parameterization on Analog Neuromorphic Hardware
Mar 28, 2023Abstract:The BrainScaleS-2 (BSS-2) system implements physical models of neurons as well as synapses and aims for an energy-efficient and fast emulation of biological neurons. When replicating neuroscientific experiment results, a major challenge is finding suitable model parameters. This study investigates the suitability of the sequential neural posterior estimation (SNPE) algorithm for parameterizing a multi-compartmental neuron model emulated on the BSS-2 analog neuromorphic hardware system. In contrast to other optimization methods such as genetic algorithms or stochastic searches, the SNPE algorithms belongs to the class of approximate Bayesian computing (ABC) methods and estimates the posterior distribution of the model parameters; access to the posterior allows classifying the confidence in parameter estimations and unveiling correlation between model parameters. In previous applications, the SNPE algorithm showed a higher computational efficiency than traditional ABC methods. For our multi-compartmental model, we show that the approximated posterior is in agreement with experimental observations and that the identified correlation between parameters is in agreement with theoretical expectations. Furthermore, we show that the algorithm can deal with high-dimensional observations and parameter spaces. These results suggest that the SNPE algorithm is a promising approach for automating the parameterization of complex models, especially when dealing with characteristic properties of analog neuromorphic substrates, such as trial-to-trial variations or limited parameter ranges.
A Scalable Approach to Modeling on Accelerated Neuromorphic Hardware
Mar 21, 2022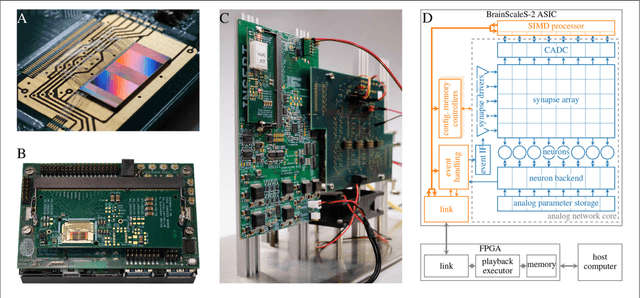
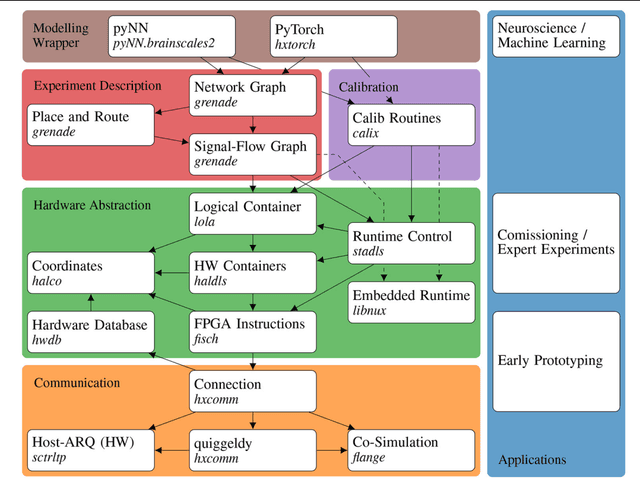
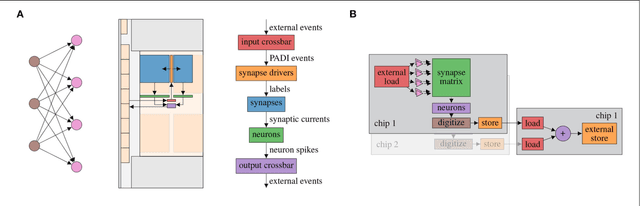
Abstract:Neuromorphic systems open up opportunities to enlarge the explorative space for computational research. However, it is often challenging to unite efficiency and usability. This work presents the software aspects of this endeavor for the BrainScaleS-2 system, a hybrid accelerated neuromorphic hardware architecture based on physical modeling. We introduce key aspects of the BrainScaleS-2 Operating System: experiment workflow, API layering, software design, and platform operation. We present use cases to discuss and derive requirements for the software and showcase the implementation. The focus lies on novel system and software features such as multi-compartmental neurons, fast re-configuration for hardware-in-the-loop training, applications for the embedded processors, the non-spiking operation mode, interactive platform access, and sustainable hardware/software co-development. Finally, we discuss further developments in terms of hardware scale-up, system usability and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge