Amarjeet Kumar
Multi-Class Segmentation of Aortic Branches and Zones in Computed Tomography Angiography: The AortaSeg24 Challenge
Feb 07, 2025



Abstract:Multi-class segmentation of the aorta in computed tomography angiography (CTA) scans is essential for diagnosing and planning complex endovascular treatments for patients with aortic dissections. However, existing methods reduce aortic segmentation to a binary problem, limiting their ability to measure diameters across different branches and zones. Furthermore, no open-source dataset is currently available to support the development of multi-class aortic segmentation methods. To address this gap, we organized the AortaSeg24 MICCAI Challenge, introducing the first dataset of 100 CTA volumes annotated for 23 clinically relevant aortic branches and zones. This dataset was designed to facilitate both model development and validation. The challenge attracted 121 teams worldwide, with participants leveraging state-of-the-art frameworks such as nnU-Net and exploring novel techniques, including cascaded models, data augmentation strategies, and custom loss functions. We evaluated the submitted algorithms using the Dice Similarity Coefficient (DSC) and Normalized Surface Distance (NSD), highlighting the approaches adopted by the top five performing teams. This paper presents the challenge design, dataset details, evaluation metrics, and an in-depth analysis of the top-performing algorithms. The annotated dataset, evaluation code, and implementations of the leading methods are publicly available to support further research. All resources can be accessed at https://aortaseg24.grand-challenge.org.
A Flexible 2.5D Medical Image Segmentation Approach with In-Slice and Cross-Slice Attention
Apr 30, 2024
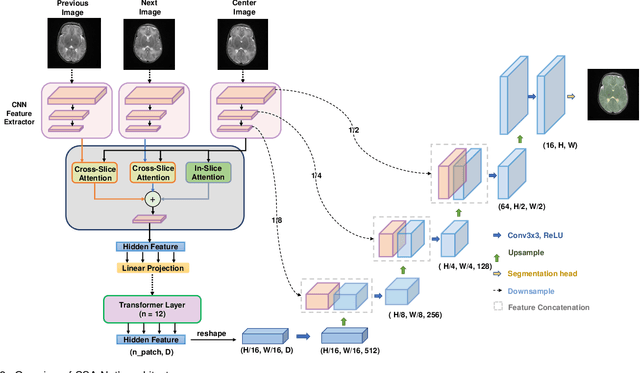
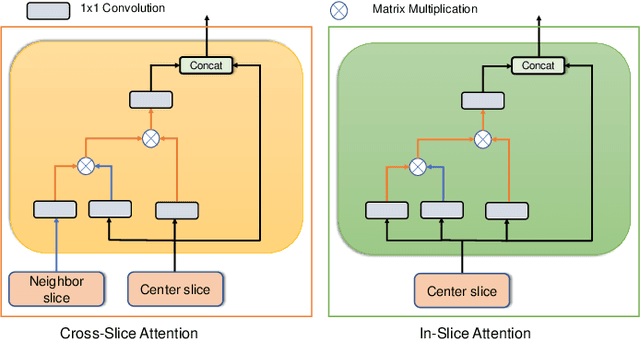
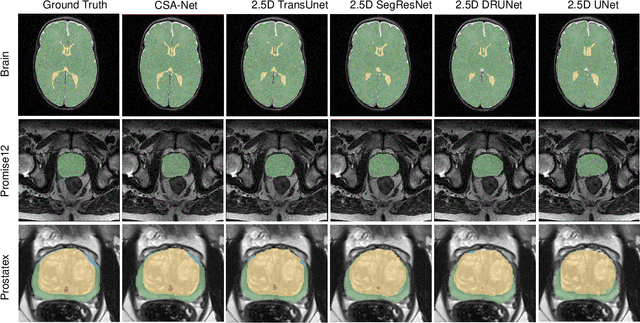
Abstract:Deep learning has become the de facto method for medical image segmentation, with 3D segmentation models excelling in capturing complex 3D structures and 2D models offering high computational efficiency. However, segmenting 2.5D images, which have high in-plane but low through-plane resolution, is a relatively unexplored challenge. While applying 2D models to individual slices of a 2.5D image is feasible, it fails to capture the spatial relationships between slices. On the other hand, 3D models face challenges such as resolution inconsistencies in 2.5D images, along with computational complexity and susceptibility to overfitting when trained with limited data. In this context, 2.5D models, which capture inter-slice correlations using only 2D neural networks, emerge as a promising solution due to their reduced computational demand and simplicity in implementation. In this paper, we introduce CSA-Net, a flexible 2.5D segmentation model capable of processing 2.5D images with an arbitrary number of slices through an innovative Cross-Slice Attention (CSA) module. This module uses the cross-slice attention mechanism to effectively capture 3D spatial information by learning long-range dependencies between the center slice (for segmentation) and its neighboring slices. Moreover, CSA-Net utilizes the self-attention mechanism to understand correlations among pixels within the center slice. We evaluated CSA-Net on three 2.5D segmentation tasks: (1) multi-class brain MRI segmentation, (2) binary prostate MRI segmentation, and (3) multi-class prostate MRI segmentation. CSA-Net outperformed leading 2D and 2.5D segmentation methods across all three tasks, demonstrating its efficacy and superiority. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/mirthAI/CSA-Net.
CIS-UNet: Multi-Class Segmentation of the Aorta in Computed Tomography Angiography via Context-Aware Shifted Window Self-Attention
Jan 23, 2024



Abstract:Advancements in medical imaging and endovascular grafting have facilitated minimally invasive treatments for aortic diseases. Accurate 3D segmentation of the aorta and its branches is crucial for interventions, as inaccurate segmentation can lead to erroneous surgical planning and endograft construction. Previous methods simplified aortic segmentation as a binary image segmentation problem, overlooking the necessity of distinguishing between individual aortic branches. In this paper, we introduce Context Infused Swin-UNet (CIS-UNet), a deep learning model designed for multi-class segmentation of the aorta and thirteen aortic branches. Combining the strengths of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Swin transformers, CIS-UNet adopts a hierarchical encoder-decoder structure comprising a CNN encoder, symmetric decoder, skip connections, and a novel Context-aware Shifted Window Self-Attention (CSW-SA) as the bottleneck block. Notably, CSW-SA introduces a unique utilization of the patch merging layer, distinct from conventional Swin transformers. It efficiently condenses the feature map, providing a global spatial context and enhancing performance when applied at the bottleneck layer, offering superior computational efficiency and segmentation accuracy compared to the Swin transformers. We trained our model on computed tomography (CT) scans from 44 patients and tested it on 15 patients. CIS-UNet outperformed the state-of-the-art SwinUNetR segmentation model, which is solely based on Swin transformers, by achieving a superior mean Dice coefficient of 0.713 compared to 0.697, and a mean surface distance of 2.78 mm compared to 3.39 mm. CIS-UNet's superior 3D aortic segmentation offers improved precision and optimization for planning endovascular treatments. Our dataset and code will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge