Chunyi Li
Automated Safety Benchmarking: A Multi-agent Pipeline for LVLMs
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities in cross-modal tasks but face significant safety challenges, which undermine their reliability in real-world applications. Efforts have been made to build LVLM safety evaluation benchmarks to uncover their vulnerability. However, existing benchmarks are hindered by their labor-intensive construction process, static complexity, and limited discriminative power. Thus, they may fail to keep pace with rapidly evolving models and emerging risks. To address these limitations, we propose VLSafetyBencher, the first automated system for LVLM safety benchmarking. VLSafetyBencher introduces four collaborative agents: Data Preprocessing, Generation, Augmentation, and Selection agents to construct and select high-quality samples. Experiments validates that VLSafetyBencher can construct high-quality safety benchmarks within one week at a minimal cost. The generated benchmark effectively distinguish safety, with a safety rate disparity of 70% between the most and least safe models.
Embodied Image Compression
Dec 12, 2025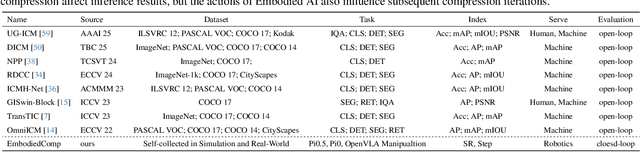
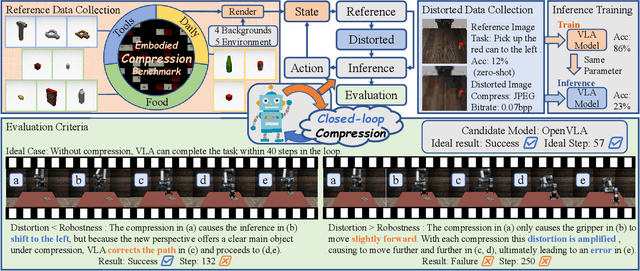
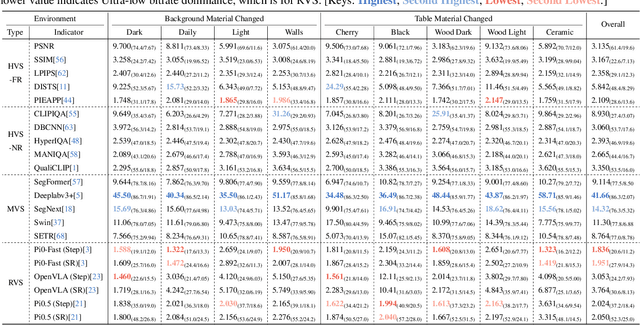
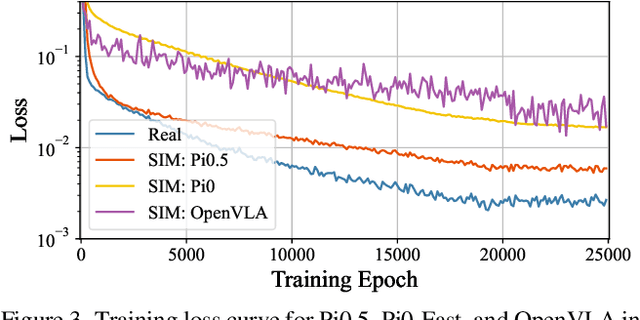
Abstract:Image Compression for Machines (ICM) has emerged as a pivotal research direction in the field of visual data compression. However, with the rapid evolution of machine intelligence, the target of compression has shifted from task-specific virtual models to Embodied agents operating in real-world environments. To address the communication constraints of Embodied AI in multi-agent systems and ensure real-time task execution, this paper introduces, for the first time, the scientific problem of Embodied Image Compression. We establish a standardized benchmark, EmbodiedComp, to facilitate systematic evaluation under ultra-low bitrate conditions in a closed-loop setting. Through extensive empirical studies in both simulated and real-world settings, we demonstrate that existing Vision-Language-Action models (VLAs) fail to reliably perform even simple manipulation tasks when compressed below the Embodied bitrate threshold. We anticipate that EmbodiedComp will catalyze the development of domain-specific compression tailored for Embodied agents , thereby accelerating the Embodied AI deployment in the Real-world.
Using GUI Agent for Electronic Design Automation
Dec 12, 2025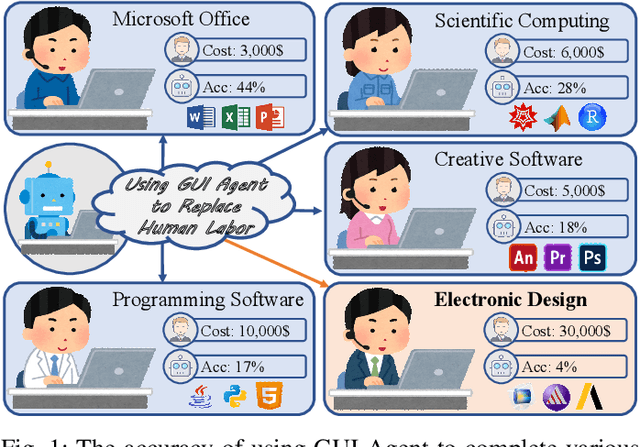
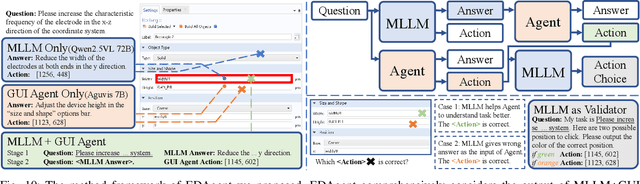
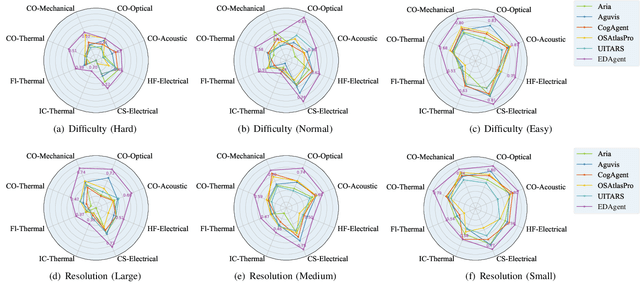
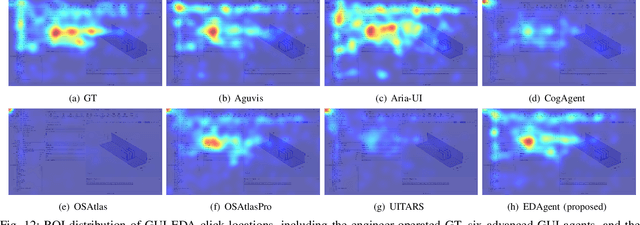
Abstract:Graphical User Interface (GUI) agents adopt an end-to-end paradigm that maps a screenshot to an action sequence, thereby automating repetitive tasks in virtual environments. However, existing GUI agents are evaluated almost exclusively on commodity software such as Microsoft Word and Excel. Professional Computer-Aided Design (CAD) suites promise an order-of-magnitude higher economic return, yet remain the weakest performance domain for existing agents and are still far from replacing expert Electronic-Design-Automation (EDA) engineers. We therefore present the first systematic study that deploys GUI agents for EDA workflows. Our contributions are: (1) a large-scale dataset named GUI-EDA, including 5 CAD tools and 5 physical domains, comprising 2,000+ high-quality screenshot-answer-action pairs recorded by EDA scientists and engineers during real-world component design; (2) a comprehensive benchmark that evaluates 30+ mainstream GUI agents, demonstrating that EDA tasks constitute a major, unsolved challenge; and (3) an EDA-specialized metric named EDAgent, equipped with a reflection mechanism that achieves reliable performance on industrial CAD software and, for the first time, outperforms Ph.D. students majored in Electrical Engineering. This work extends GUI agents from generic office automation to specialized, high-value engineering domains and offers a new avenue for advancing EDA productivity. The dataset will be released at: https://github.com/aiben-ch/GUI-EDA.
GeoX-Bench: Benchmarking Cross-View Geo-Localization and Pose Estimation Capabilities of Large Multimodal Models
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:Large multimodal models (LMMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across a wide range of tasks, however their knowledge and abilities in the cross-view geo-localization and pose estimation domains remain unexplored, despite potential benefits for navigation, autonomous driving, outdoor robotics, \textit{etc}. To bridge this gap, we introduce \textbf{GeoX-Bench}, a comprehensive \underline{Bench}mark designed to explore and evaluate the capabilities of LMMs in \underline{cross}-view \underline{Geo}-localization and pose estimation. Specifically, GeoX-Bench contains 10,859 panoramic-satellite image pairs spanning 128 cities in 49 countries, along with corresponding 755,976 question-answering (QA) pairs. Among these, 42,900 QA pairs are designated for benchmarking, while the remaining are intended to enhance the capabilities of LMMs. Based on GeoX-Bench, we evaluate the capabilities of 25 state-of-the-art LMMs on cross-view geo-localization and pose estimation tasks, and further explore the empowered capabilities of instruction-tuning. Our benchmark demonstrate that while current LMMs achieve impressive performance in geo-localization tasks, their effectiveness declines significantly on the more complex pose estimation tasks, highlighting a critical area for future improvement, and instruction-tuning LMMs on the training data of GeoX-Bench can significantly improve the cross-view geo-sense abilities. The GeoX-Bench is available at \textcolor{magenta}{https://github.com/IntMeGroup/GeoX-Bench}.
Data Assessment for Embodied Intelligence
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:In embodied intelligence, datasets play a pivotal role, serving as both a knowledge repository and a conduit for information transfer. The two most critical attributes of a dataset are the amount of information it provides and how easily this information can be learned by models. However, the multimodal nature of embodied data makes evaluating these properties particularly challenging. Prior work has largely focused on diversity, typically counting tasks and scenes or evaluating isolated modalities, which fails to provide a comprehensive picture of dataset diversity. On the other hand, the learnability of datasets has received little attention and is usually assessed post-hoc through model training, an expensive, time-consuming process that also lacks interpretability, offering little guidance on how to improve a dataset. In this work, we address both challenges by introducing two principled, data-driven tools. First, we construct a unified multimodal representation for each data sample and, based on it, propose diversity entropy, a continuous measure that characterizes the amount of information contained in a dataset. Second, we introduce the first interpretable, data-driven algorithm to efficiently quantify dataset learnability without training, enabling researchers to assess a dataset's learnability immediately upon its release. We validate our algorithm on both simulated and real-world embodied datasets, demonstrating that it yields faithful, actionable insights that enable researchers to jointly improve diversity and learnability. We hope this work provides a foundation for designing higher-quality datasets that advance the development of embodied intelligence.
AU-IQA: A Benchmark Dataset for Perceptual Quality Assessment of AI-Enhanced User-Generated Content
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:AI-based image enhancement techniques have been widely adopted in various visual applications, significantly improving the perceptual quality of user-generated content (UGC). However, the lack of specialized quality assessment models has become a significant limiting factor in this field, limiting user experience and hindering the advancement of enhancement methods. While perceptual quality assessment methods have shown strong performance on UGC and AIGC individually, their effectiveness on AI-enhanced UGC (AI-UGC) which blends features from both, remains largely unexplored. To address this gap, we construct AU-IQA, a benchmark dataset comprising 4,800 AI-UGC images produced by three representative enhancement types which include super-resolution, low-light enhancement, and denoising. On this dataset, we further evaluate a range of existing quality assessment models, including traditional IQA methods and large multimodal models. Finally, we provide a comprehensive analysis of how well current approaches perform in assessing the perceptual quality of AI-UGC. The access link to the AU-IQA is https://github.com/WNNGGU/AU-IQA-Dataset.
The Ever-Evolving Science Exam
Jul 22, 2025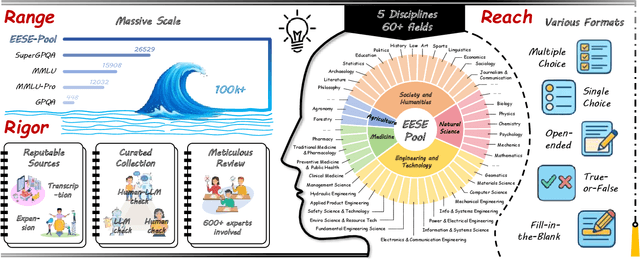
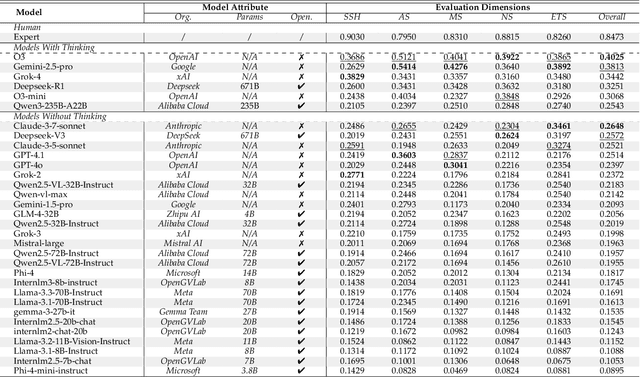
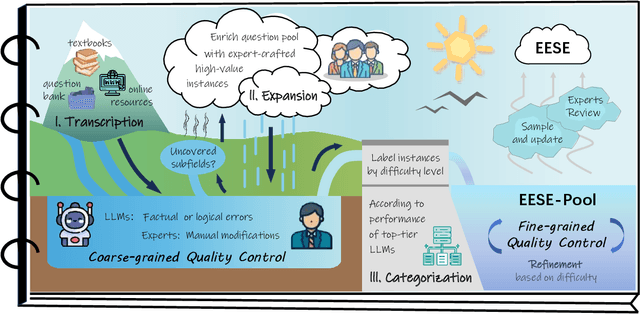
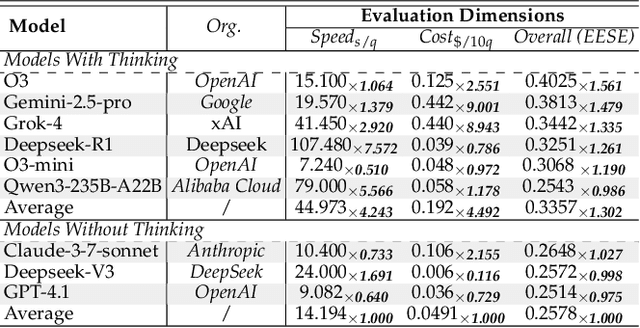
Abstract:As foundation models grow rapidly in capability and deployment, evaluating their scientific understanding becomes increasingly critical. Existing science benchmarks have made progress towards broad **Range**, wide **Reach**, and high **Rigor**, yet they often face two major challenges: **data leakage risks** that compromise benchmarking validity, and **evaluation inefficiency** due to large-scale testing. To address these issues, we introduce the **Ever-Evolving Science Exam (EESE)**, a dynamic benchmark designed to reliably assess scientific capabilities in foundation models. Our approach consists of two components: 1) a non-public **EESE-Pool** with over 100K expertly constructed science instances (question-answer pairs) across 5 disciplines and 500+ subfields, built through a multi-stage pipeline ensuring **Range**, **Reach**, and **Rigor**, 2) a periodically updated 500-instance subset **EESE**, sampled and validated to enable leakage-resilient, low-overhead evaluations. Experiments on 32 open- and closed-source models demonstrate that EESE effectively differentiates the strengths and weaknesses of models in scientific fields and cognitive dimensions. Overall, EESE provides a robust, scalable, and forward-compatible solution for science benchmark design, offering a realistic measure of how well foundation models handle science questions. The project page is at: https://github.com/aiben-ch/EESE.
Scaling-up Perceptual Video Quality Assessment
May 28, 2025Abstract:The data scaling law has been shown to significantly enhance the performance of large multi-modal models (LMMs) across various downstream tasks. However, in the domain of perceptual video quality assessment (VQA), the potential of scaling law remains unprecedented due to the scarcity of labeled resources and the insufficient scale of datasets. To address this, we propose \textbf{OmniVQA}, an efficient framework designed to efficiently build high-quality, human-in-the-loop VQA multi-modal instruction databases (MIDBs). We then scale up to create \textbf{OmniVQA-Chat-400K}, the largest MIDB in the VQA field concurrently. Our focus is on the technical and aesthetic quality dimensions, with abundant in-context instruction data to provide fine-grained VQA knowledge. Additionally, we have built the \textbf{OmniVQA-MOS-20K} dataset to enhance the model's quantitative quality rating capabilities. We then introduce a \textbf{complementary} training strategy that effectively leverages the knowledge from datasets for quality understanding and quality rating tasks. Furthermore, we propose the \textbf{OmniVQA-FG (fine-grain)-Benchmark} to evaluate the fine-grained performance of the models. Our results demonstrate that our models achieve state-of-the-art performance in both quality understanding and rating tasks.
Perceptual Quality Assessment for Embodied AI
May 22, 2025
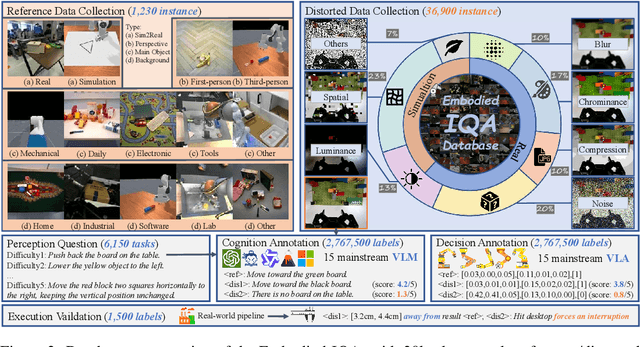


Abstract:Embodied AI has developed rapidly in recent years, but it is still mainly deployed in laboratories, with various distortions in the Real-world limiting its application. Traditionally, Image Quality Assessment (IQA) methods are applied to predict human preferences for distorted images; however, there is no IQA method to assess the usability of an image in embodied tasks, namely, the perceptual quality for robots. To provide accurate and reliable quality indicators for future embodied scenarios, we first propose the topic: IQA for Embodied AI. Specifically, we (1) based on the Mertonian system and meta-cognitive theory, constructed a perception-cognition-decision-execution pipeline and defined a comprehensive subjective score collection process; (2) established the Embodied-IQA database, containing over 36k reference/distorted image pairs, with more than 5m fine-grained annotations provided by Vision Language Models/Vision Language Action-models/Real-world robots; (3) trained and validated the performance of mainstream IQA methods on Embodied-IQA, demonstrating the need to develop more accurate quality indicators for Embodied AI. We sincerely hope that through evaluation, we can promote the application of Embodied AI under complex distortions in the Real-world. Project page: https://github.com/lcysyzxdxc/EmbodiedIQA
PuzzleBench: A Fully Dynamic Evaluation Framework for Large Multimodal Models on Puzzle Solving
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Large Multimodal Models (LMMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities across a wide range of multimodal tasks, achieving ever-increasing performance on various evaluation benchmarks. However, existing benchmarks are typically static and often overlap with pre-training datasets, leading to fixed complexity constraints and substantial data contamination issues. Meanwhile, manually annotated datasets are labor-intensive, time-consuming, and subject to human bias and inconsistency, leading to reliability and reproducibility issues. To address these problems, we propose a fully dynamic multimodal evaluation framework, named Open-ended Visual Puzzle Generation (OVPG), which aims to generate fresh, diverse, and verifiable evaluation data automatically in puzzle-solving tasks. Specifically, the OVPG pipeline consists of a raw material sampling module, a visual content generation module, and a puzzle rule design module, which ensures that each evaluation instance is primitive, highly randomized, and uniquely solvable, enabling continual adaptation to the evolving capabilities of LMMs. Built upon OVPG, we construct PuzzleBench, a dynamic and scalable benchmark comprising 11,840 VQA samples. It features six carefully designed puzzle tasks targeting three core LMM competencies, visual recognition, logical reasoning, and context understanding. PuzzleBench differs from static benchmarks that quickly become outdated. It enables ongoing dataset refreshing through OVPG and a rich set of open-ended puzzle designs, allowing seamless adaptation to the evolving capabilities of LMMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge