Jun Chen
School of Electronics and Information, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an, China, Chongqing Institute for Brain and Intelligence, Guangyang Bay Laboratory, Chongqing, China
Kimi K2.5: Visual Agentic Intelligence
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:We introduce Kimi K2.5, an open-source multimodal agentic model designed to advance general agentic intelligence. K2.5 emphasizes the joint optimization of text and vision so that two modalities enhance each other. This includes a series of techniques such as joint text-vision pre-training, zero-vision SFT, and joint text-vision reinforcement learning. Building on this multimodal foundation, K2.5 introduces Agent Swarm, a self-directed parallel agent orchestration framework that dynamically decomposes complex tasks into heterogeneous sub-problems and executes them concurrently. Extensive evaluations show that Kimi K2.5 achieves state-of-the-art results across various domains including coding, vision, reasoning, and agentic tasks. Agent Swarm also reduces latency by up to $4.5\times$ over single-agent baselines. We release the post-trained Kimi K2.5 model checkpoint to facilitate future research and real-world applications of agentic intelligence.
HardSecBench: Benchmarking the Security Awareness of LLMs for Hardware Code Generation
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are being increasingly integrated into practical hardware and firmware development pipelines for code generation. Existing studies have primarily focused on evaluating the functional correctness of LLM-generated code, yet paid limited attention to its security issues. However, LLM-generated code that appears functionally sound may embed security flaws which could induce catastrophic damages after deployment. This critical research gap motivates us to design a benchmark for assessing security awareness under realistic specifications. In this work, we introduce HardSecBench, a benchmark with 924 tasks spanning Verilog Register Transfer Level (RTL) and firmware-level C, covering 76 hardware-relevant Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE) entries. Each task includes a structured specification, a secure reference implementation, and executable tests. To automate artifact synthesis, we propose a multi-agent pipeline that decouples synthesis from verification and grounds evaluation in execution evidence, enabling reliable evaluation. Using HardSecBench, we evaluate a range of LLMs on hardware and firmware code generation and find that models often satisfy functional requirements while still leaving security risks. We also find that security results vary with prompting. These findings highlight pressing challenges and offer actionable insights for future advancements in LLM-assisted hardware design. Our data and code will be released soon.
QASA: Quality-Guided K-Adaptive Slot Attention for Unsupervised Object-Centric Learning
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Slot Attention, an approach that binds different objects in a scene to a set of "slots", has become a leading method in unsupervised object-centric learning. Most methods assume a fixed slot count K, and to better accommodate the dynamic nature of object cardinality, a few works have explored K-adaptive variants. However, existing K-adaptive methods still suffer from two limitations. First, they do not explicitly constrain slot-binding quality, so low-quality slots lead to ambiguous feature attribution. Second, adding a slot-count penalty to the reconstruction objective creates conflicting optimization goals between reducing the number of active slots and maintaining reconstruction fidelity. As a result, they still lag significantly behind strong K-fixed baselines. To address these challenges, we propose Quality-Guided K-Adaptive Slot Attention (QASA). First, we decouple slot selection from reconstruction, eliminating the mutual constraints between the two objectives. Then, we propose an unsupervised Slot-Quality metric to assess per-slot quality, providing a principled signal for fine-grained slot--object binding. Based on this metric, we design a Quality-Guided Slot Selection scheme that dynamically selects a subset of high-quality slots and feeds them into our newly designed gated decoder for reconstruction during training. At inference, token-wise competition on slot attention yields a K-adaptive outcome. Experiments show that QASA substantially outperforms existing K-adaptive methods on both real and synthetic datasets. Moreover, on real-world datasets QASA surpasses K-fixed methods.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
VideoAuto-R1: Video Auto Reasoning via Thinking Once, Answering Twice
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning has emerged as a powerful tool for multimodal large language models on video understanding tasks. However, its necessity and advantages over direct answering remain underexplored. In this paper, we first demonstrate that for RL-trained video models, direct answering often matches or even surpasses CoT performance, despite CoT producing step-by-step analyses at a higher computational cost. Motivated by this, we propose VideoAuto-R1, a video understanding framework that adopts a reason-when-necessary strategy. During training, our approach follows a Thinking Once, Answering Twice paradigm: the model first generates an initial answer, then performs reasoning, and finally outputs a reviewed answer. Both answers are supervised via verifiable rewards. During inference, the model uses the confidence score of the initial answer to determine whether to proceed with reasoning. Across video QA and grounding benchmarks, VideoAuto-R1 achieves state-of-the-art accuracy with significantly improved efficiency, reducing the average response length by ~3.3x, e.g., from 149 to just 44 tokens. Moreover, we observe a low rate of thinking-mode activation on perception-oriented tasks, but a higher rate on reasoning-intensive tasks. This suggests that explicit language-based reasoning is generally beneficial but not always necessary.
Fast, accurate measurement of the worker populations of honey bee colonies using deep learning
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Honey bees play a crucial role in pollination, contributing significantly to global agriculture and ecosystems. Accurately estimating hive populations is essential for understanding the effects of environmental factors on bee colonies, yet traditional methods of counting bees are time-consuming, labor-intensive, and prone to human error, particularly in large-scale studies. In this paper, we present a deep learning-based solution for automating bee population counting using CSRNet and introduce ASUBEE, the FIRST high-resolution dataset specifically designed for this task. Our method employs density map estimation to predict bee populations, effectively addressing challenges such as occlusion and overlapping bees that are common in hive monitoring. We demonstrate that CSRNet achieves superior performance in terms of time efficiency, with a computation time of just 1 second per image, while delivering accurate counts even in complex and densely populated hive scenarios. Our findings show that deep learning approaches like CSRNet can dramatically enhance the efficiency of hive population assessments, providing a valuable tool for researchers and beekeepers alike. This work marks a significant advancement in applying AI technologies to ecological research, offering scalable and precise monitoring solutions for honey bee populations.
An LLM-based Framework for Human-Swarm Teaming Cognition in Disaster Search and Rescue
Nov 06, 2025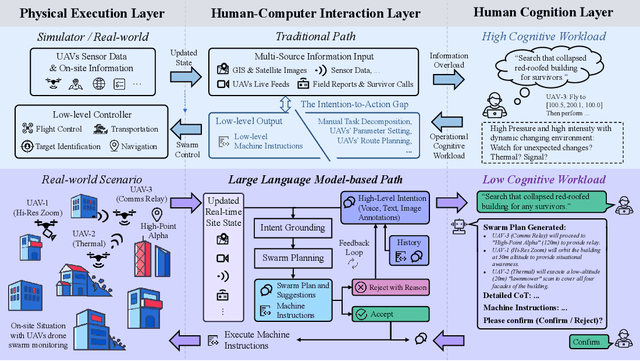
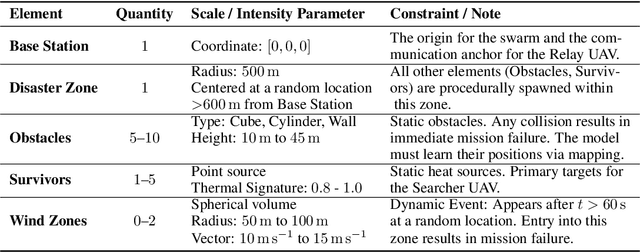
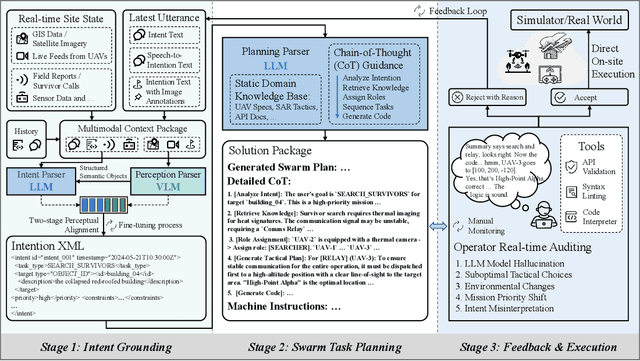
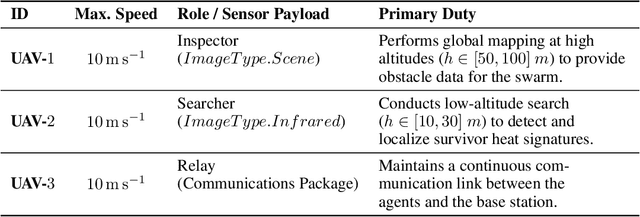
Abstract:Large-scale disaster Search And Rescue (SAR) operations are persistently challenged by complex terrain and disrupted communications. While Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) swarms offer a promising solution for tasks like wide-area search and supply delivery, yet their effective coordination places a significant cognitive burden on human operators. The core human-machine collaboration bottleneck lies in the ``intention-to-action gap'', which is an error-prone process of translating a high-level rescue objective into a low-level swarm command under high intensity and pressure. To bridge this gap, this study proposes a novel LLM-CRF system that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to model and augment human-swarm teaming cognition. The proposed framework initially captures the operator's intention through natural and multi-modal interactions with the device via voice or graphical annotations. It then employs the LLM as a cognitive engine to perform intention comprehension, hierarchical task decomposition, and mission planning for the UAV swarm. This closed-loop framework enables the swarm to act as a proactive partner, providing active feedback in real-time while reducing the need for manual monitoring and control, which considerably advances the efficacy of the SAR task. We evaluate the proposed framework in a simulated SAR scenario. Experimental results demonstrate that, compared to traditional order and command-based interfaces, the proposed LLM-driven approach reduced task completion time by approximately $64.2\%$ and improved task success rate by $7\%$. It also leads to a considerable reduction in subjective cognitive workload, with NASA-TLX scores dropping by $42.9\%$. This work establishes the potential of LLMs to create more intuitive and effective human-swarm collaborations in high-stakes scenarios.
Mind-Paced Speaking: A Dual-Brain Approach to Real-Time Reasoning in Spoken Language Models
Oct 10, 2025Abstract:Real-time Spoken Language Models (SLMs) struggle to leverage Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning due to the prohibitive latency of generating the entire thought process sequentially. Enabling SLMs to think while speaking, similar to humans, is attracting increasing attention. We present, for the first time, Mind-Paced Speaking (MPS), a brain-inspired framework that enables high-fidelity, real-time reasoning. Similar to how humans utilize distinct brain regions for thinking and responding, we propose a novel dual-brain approach, employing a "Formulation Brain" for high-level reasoning to pace and guide a separate "Articulation Brain" for fluent speech generation. This division of labor eliminates mode-switching, preserving the integrity of the reasoning process. Experiments show that MPS significantly outperforms existing think-while-speaking methods and achieves reasoning performance comparable to models that pre-compute the full CoT before speaking, while drastically reducing latency. Under a zero-latency configuration, the proposed method achieves an accuracy of 92.8% on the mathematical reasoning task Spoken-MQA and attains a score of 82.5 on the speech conversation task URO-Bench. Our work effectively bridges the gap between high-quality reasoning and real-time interaction.
AU-IQA: A Benchmark Dataset for Perceptual Quality Assessment of AI-Enhanced User-Generated Content
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:AI-based image enhancement techniques have been widely adopted in various visual applications, significantly improving the perceptual quality of user-generated content (UGC). However, the lack of specialized quality assessment models has become a significant limiting factor in this field, limiting user experience and hindering the advancement of enhancement methods. While perceptual quality assessment methods have shown strong performance on UGC and AIGC individually, their effectiveness on AI-enhanced UGC (AI-UGC) which blends features from both, remains largely unexplored. To address this gap, we construct AU-IQA, a benchmark dataset comprising 4,800 AI-UGC images produced by three representative enhancement types which include super-resolution, low-light enhancement, and denoising. On this dataset, we further evaluate a range of existing quality assessment models, including traditional IQA methods and large multimodal models. Finally, we provide a comprehensive analysis of how well current approaches perform in assessing the perceptual quality of AI-UGC. The access link to the AU-IQA is https://github.com/WNNGGU/AU-IQA-Dataset.
RetinexDual: Retinex-based Dual Nature Approach for Generalized Ultra-High-Definition Image Restoration
Aug 06, 2025Abstract:Advancements in image sensing have elevated the importance of Ultra-High-Definition Image Restoration (UHD IR). Traditional methods, such as extreme downsampling or transformation from the spatial to the frequency domain, encounter significant drawbacks: downsampling induces irreversible information loss in UHD images, while our frequency analysis reveals that pure frequency-domain approaches are ineffective for spatially confined image artifacts, primarily due to the loss of degradation locality. To overcome these limitations, we present RetinexDual, a novel Retinex theory-based framework designed for generalized UHD IR tasks. RetinexDual leverages two complementary sub-networks: the Scale-Attentive maMBA (SAMBA) and the Frequency Illumination Adaptor (FIA). SAMBA, responsible for correcting the reflectance component, utilizes a coarse-to-fine mechanism to overcome the causal modeling of mamba, which effectively reduces artifacts and restores intricate details. On the other hand, FIA ensures precise correction of color and illumination distortions by operating in the frequency domain and leveraging the global context provided by it. Evaluating RetinexDual on four UHD IR tasks, namely deraining, deblurring, dehazing, and Low-Light Image Enhancement (LLIE), shows that it outperforms recent methods qualitatively and quantitatively. Ablation studies demonstrate the importance of employing distinct designs for each branch in RetinexDual, as well as the effectiveness of its various components.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge