Lina Liu
Decentralized Optimization on Compact Submanifolds by Quantized Riemannian Gradient Tracking
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:This paper considers the problem of decentralized optimization on compact submanifolds, where a finite sum of smooth (possibly non-convex) local functions is minimized by $n$ agents forming an undirected and connected graph. However, the efficiency of distributed optimization is often hindered by communication bottlenecks. To mitigate this, we propose the Quantized Riemannian Gradient Tracking (Q-RGT) algorithm, where agents update their local variables using quantized gradients. The introduction of quantization noise allows our algorithm to bypass the constraints of the accurate Riemannian projection operator (such as retraction), further improving iterative efficiency. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first algorithm to achieve an $\mathcal{O}(1/K)$ convergence rate in the presence of quantization, matching the convergence rate of methods without quantization. Additionally, we explicitly derive lower bounds on decentralized consensus associated with a function of quantization levels. Numerical experiments demonstrate that Q-RGT performs comparably to non-quantized methods while reducing communication bottlenecks and computational overhead.
CMD: Constraining Multimodal Distribution for Domain Adaptation in Stereo Matching
Apr 30, 2025Abstract:Recently, learning-based stereo matching methods have achieved great improvement in public benchmarks, where soft argmin and smooth L1 loss play a core contribution to their success. However, in unsupervised domain adaptation scenarios, we observe that these two operations often yield multimodal disparity probability distributions in target domains, resulting in degraded generalization. In this paper, we propose a novel approach, Constrain Multi-modal Distribution (CMD), to address this issue. Specifically, we introduce \textit{uncertainty-regularized minimization} and \textit{anisotropic soft argmin} to encourage the network to produce predominantly unimodal disparity distributions in the target domain, thereby improving prediction accuracy. Experimentally, we apply the proposed method to multiple representative stereo-matching networks and conduct domain adaptation from synthetic data to unlabeled real-world scenes. Results consistently demonstrate improved generalization in both top-performing and domain-adaptable stereo-matching models. The code for CMD will be available at: \href{https://github.com/gallenszl/CMD}{https://github.com/gallenszl/CMD}.
MAG: Multi-Modal Aligned Autoregressive Co-Speech Gesture Generation without Vector Quantization
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:This work focuses on full-body co-speech gesture generation. Existing methods typically employ an autoregressive model accompanied by vector-quantized tokens for gesture generation, which results in information loss and compromises the realism of the generated gestures. To address this, inspired by the natural continuity of real-world human motion, we propose MAG, a novel multi-modal aligned framework for high-quality and diverse co-speech gesture synthesis without relying on discrete tokenization. Specifically, (1) we introduce a motion-text-audio-aligned variational autoencoder (MTA-VAE), which leverages pre-trained WavCaps' text and audio embeddings to enhance both semantic and rhythmic alignment with motion, ultimately producing more realistic gestures. (2) Building on this, we propose a multimodal masked autoregressive model (MMAG) that enables autoregressive modeling in continuous motion embeddings through diffusion without vector quantization. To further ensure multi-modal consistency, MMAG incorporates a hybrid granularity audio-text fusion block, which serves as conditioning for diffusion process. Extensive experiments on two benchmark datasets demonstrate that MAG achieves stateof-the-art performance both quantitatively and qualitatively, producing highly realistic and diverse co-speech gestures.The code will be released to facilitate future research.
Dual-branch Graph Feature Learning for NLOS Imaging
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:The domain of non-line-of-sight (NLOS) imaging is advancing rapidly, offering the capability to reveal occluded scenes that are not directly visible. However, contemporary NLOS systems face several significant challenges: (1) The computational and storage requirements are profound due to the inherent three-dimensional grid data structure, which restricts practical application. (2) The simultaneous reconstruction of albedo and depth information requires a delicate balance using hyperparameters in the loss function, rendering the concurrent reconstruction of texture and depth information difficult. This paper introduces the innovative methodology, \xnet, which integrates an albedo-focused reconstruction branch dedicated to albedo information recovery and a depth-focused reconstruction branch that extracts geometrical structure, to overcome these obstacles. The dual-branch framework segregates content delivery to the respective reconstructions, thereby enhancing the quality of the retrieved data. To our knowledge, we are the first to employ the GNN as a fundamental component to transform dense NLOS grid data into sparse structural features for efficient reconstruction. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our method attains the highest level of performance among existing methods across synthetic and real data. https://github.com/Nicholassu/DG-NLOS.
Analog Beamforming Aided by Full-Dimension One-Bit Chains
Sep 10, 2024



Abstract:This paper investigates the design of analog beamforming at the receiver in millimeter-wave (mmWave) multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems, aided by full digital chains featuring 1-bit ADCs. We advocate utilizing these full digital chains to facilitate rapid channel estimation and beam acquisition for subsequent communication, even without prior knowledge of the training pilots. To balance energy consumption and implementation costs, we opt for 1-bit ADCs. We propose a two-stage maximum likelihood (ML)-based algorithm to estimate angles of arrival (AoAs) and facilitate the design of analog beamforming to maximize the received signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). We validate our proposed beamforming schemes in narrowband coherent channels through synthetic testing and in wideband coherent channels, particularly under the 3GPP clustered-delay-line (CDL)-C channel model.
GaussianGrasper: 3D Language Gaussian Splatting for Open-vocabulary Robotic Grasping
Mar 14, 2024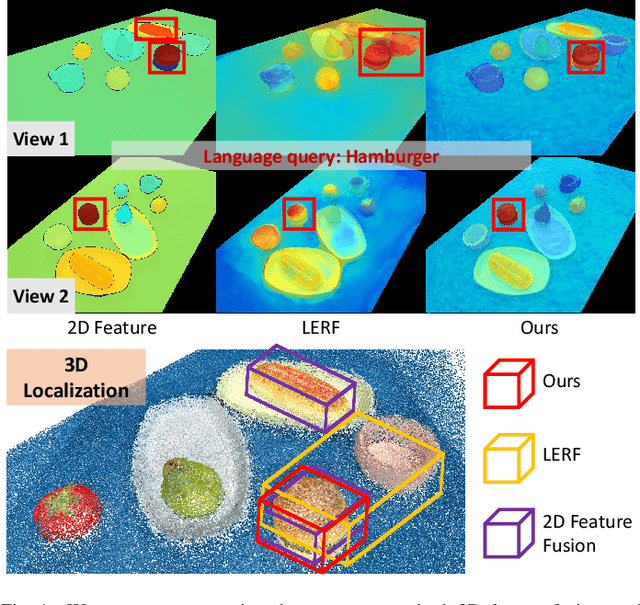
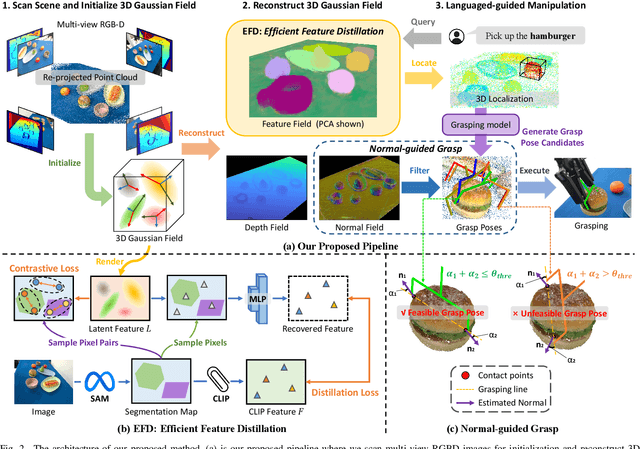
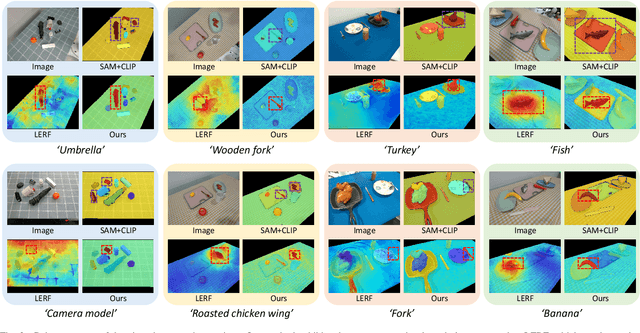

Abstract:Constructing a 3D scene capable of accommodating open-ended language queries, is a pivotal pursuit, particularly within the domain of robotics. Such technology facilitates robots in executing object manipulations based on human language directives. To tackle this challenge, some research efforts have been dedicated to the development of language-embedded implicit fields. However, implicit fields (e.g. NeRF) encounter limitations due to the necessity of processing a large number of input views for reconstruction, coupled with their inherent inefficiencies in inference. Thus, we present the GaussianGrasper, which utilizes 3D Gaussian Splatting to explicitly represent the scene as a collection of Gaussian primitives. Our approach takes a limited set of RGB-D views and employs a tile-based splatting technique to create a feature field. In particular, we propose an Efficient Feature Distillation (EFD) module that employs contrastive learning to efficiently and accurately distill language embeddings derived from foundational models. With the reconstructed geometry of the Gaussian field, our method enables the pre-trained grasping model to generate collision-free grasp pose candidates. Furthermore, we propose a normal-guided grasp module to select the best grasp pose. Through comprehensive real-world experiments, we demonstrate that GaussianGrasper enables robots to accurately query and grasp objects with language instructions, providing a new solution for language-guided manipulation tasks. Data and codes can be available at https://github.com/MrSecant/GaussianGrasper.
Self-supervised Event-based Monocular Depth Estimation using Cross-modal Consistency
Jan 14, 2024Abstract:An event camera is a novel vision sensor that can capture per-pixel brightness changes and output a stream of asynchronous ``events''. It has advantages over conventional cameras in those scenes with high-speed motions and challenging lighting conditions because of the high temporal resolution, high dynamic range, low bandwidth, low power consumption, and no motion blur. Therefore, several supervised monocular depth estimation from events is proposed to address scenes difficult for conventional cameras. However, depth annotation is costly and time-consuming. In this paper, to lower the annotation cost, we propose a self-supervised event-based monocular depth estimation framework named EMoDepth. EMoDepth constrains the training process using the cross-modal consistency from intensity frames that are aligned with events in the pixel coordinate. Moreover, in inference, only events are used for monocular depth prediction. Additionally, we design a multi-scale skip-connection architecture to effectively fuse features for depth estimation while maintaining high inference speed. Experiments on MVSEC and DSEC datasets demonstrate that our contributions are effective and that the accuracy can outperform existing supervised event-based and unsupervised frame-based methods.
Semi-Supervised Learning for Visual Bird's Eye View Semantic Segmentation
Aug 28, 2023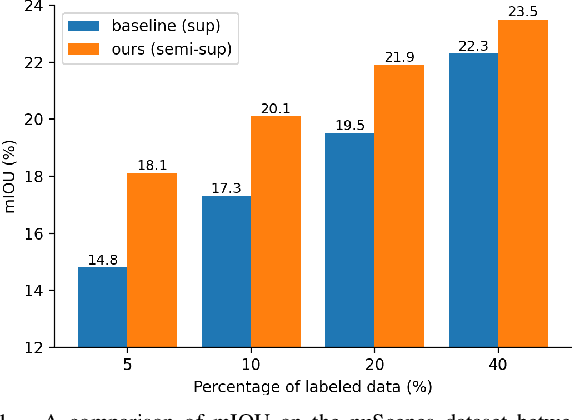
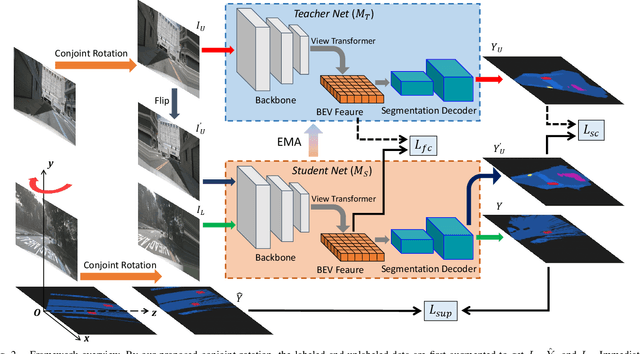
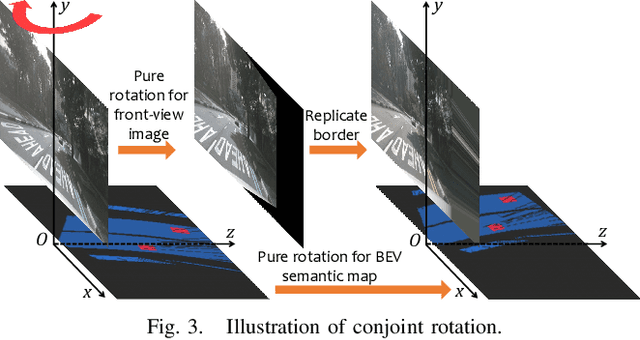
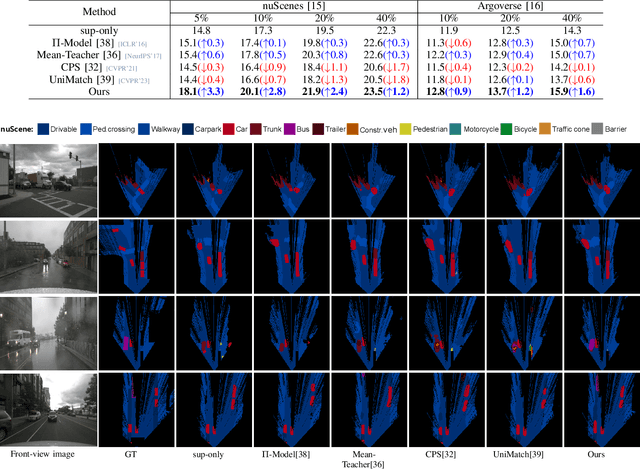
Abstract:Visual bird's eye view (BEV) semantic segmentation helps autonomous vehicles understand the surrounding environment only from images, including static elements (e.g., roads) and dynamic elements (e.g., vehicles, pedestrians). However, the high cost of annotation procedures of full-supervised methods limits the capability of the visual BEV semantic segmentation, which usually needs HD maps, 3D object bounding boxes, and camera extrinsic matrixes. In this paper, we present a novel semi-supervised framework for visual BEV semantic segmentation to boost performance by exploiting unlabeled images during the training. A consistency loss that makes full use of unlabeled data is then proposed to constrain the model on not only semantic prediction but also the BEV feature. Furthermore, we propose a novel and effective data augmentation method named conjoint rotation which reasonably augments the dataset while maintaining the geometric relationship between the front-view images and the BEV semantic segmentation. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes and Argoverse datasets show that our semi-supervised framework can effectively improve prediction accuracy. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work that explores improving visual BEV semantic segmentation performance using unlabeled data. The code will be publicly available.
Digging into Depth Priors for Outdoor Neural Radiance Fields
Aug 08, 2023Abstract:Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) have demonstrated impressive performance in vision and graphics tasks, such as novel view synthesis and immersive reality. However, the shape-radiance ambiguity of radiance fields remains a challenge, especially in the sparse viewpoints setting. Recent work resorts to integrating depth priors into outdoor NeRF training to alleviate the issue. However, the criteria for selecting depth priors and the relative merits of different priors have not been thoroughly investigated. Moreover, the relative merits of selecting different approaches to use the depth priors is also an unexplored problem. In this paper, we provide a comprehensive study and evaluation of employing depth priors to outdoor neural radiance fields, covering common depth sensing technologies and most application ways. Specifically, we conduct extensive experiments with two representative NeRF methods equipped with four commonly-used depth priors and different depth usages on two widely used outdoor datasets. Our experimental results reveal several interesting findings that can potentially benefit practitioners and researchers in training their NeRF models with depth priors. Project Page: https://cwchenwang.github.io/outdoor-nerf-depth
FG-Depth: Flow-Guided Unsupervised Monocular Depth Estimation
Jan 20, 2023



Abstract:The great potential of unsupervised monocular depth estimation has been demonstrated by many works due to low annotation cost and impressive accuracy comparable to supervised methods. To further improve the performance, recent works mainly focus on designing more complex network structures and exploiting extra supervised information, e.g., semantic segmentation. These methods optimize the models by exploiting the reconstructed relationship between the target and reference images in varying degrees. However, previous methods prove that this image reconstruction optimization is prone to get trapped in local minima. In this paper, our core idea is to guide the optimization with prior knowledge from pretrained Flow-Net. And we show that the bottleneck of unsupervised monocular depth estimation can be broken with our simple but effective framework named FG-Depth. In particular, we propose (i) a flow distillation loss to replace the typical photometric loss that limits the capacity of the model and (ii) a prior flow based mask to remove invalid pixels that bring the noise in training loss. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of each component, and our approach achieves state-of-the-art results on both KITTI and NYU-Depth-v2 datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge