Lei Yang
Towards Next-Generation SLAM: A Survey on 3DGS-SLAM Focusing on Performance, Robustness, and Future Directions
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Traditional Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) systems often face limitations including coarse rendering quality, insufficient recovery of scene details, and poor robustness in dynamic environments. 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), with its efficient explicit representation and high-quality rendering capabilities, offers a new reconstruction paradigm for SLAM. This survey comprehensively reviews key technical approaches for integrating 3DGS with SLAM. We analyze performance optimization of representative methods across four critical dimensions: rendering quality, tracking accuracy, reconstruction speed, and memory consumption, delving into their design principles and breakthroughs. Furthermore, we examine methods for enhancing the robustness of 3DGS-SLAM in complex environments such as motion blur and dynamic environments. Finally, we discuss future challenges and development trends in this area. This survey aims to provide a technical reference for researchers and foster the development of next-generation SLAM systems characterized by high fidelity, efficiency, and robustness.
UV-M3TL: A Unified and Versatile Multimodal Multi-Task Learning Framework for Assistive Driving Perception
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) need to understand human driver behavior while perceiving their navigation context, but jointly learning these heterogeneous tasks would cause inter-task negative transfer and impair system performance. Here, we propose a Unified and Versatile Multimodal Multi-Task Learning (UV-M3TL) framework to simultaneously recognize driver behavior, driver emotion, vehicle behavior, and traffic context, while mitigating inter-task negative transfer. Our framework incorporates two core components: dual-branch spatial channel multimodal embedding (DB-SCME) and adaptive feature-decoupled multi-task loss (AFD-Loss). DB-SCME enhances cross-task knowledge transfer while mitigating task conflicts by employing a dual-branch structure to explicitly model salient task-shared and task-specific features. AFD-Loss improves the stability of joint optimization while guiding the model to learn diverse multi-task representations by introducing an adaptive weighting mechanism based on learning dynamics and feature decoupling constraints. We evaluate our method on the AIDE dataset, and the experimental results demonstrate that UV-M3TL achieves state-of-the-art performance across all four tasks. To further prove the versatility, we evaluate UV-M3TL on additional public multi-task perception benchmarks (BDD100K, CityScapes, NYUD-v2, and PASCAL-Context), where it consistently delivers strong performance across diverse task combinations, attaining state-of-the-art results on most tasks.
SOUP: Token-level Single-sample Mix-policy Reinforcement Learning for Large Language Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:On-policy reinforcement learning (RL) methods widely used for language model post-training, like Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), often suffer from limited exploration and early saturation due to low sampling diversity. While off-policy data can help, current approaches that mix entire trajectories cause significant policy mismatch and instability. In this work, we propose the $\textbf{S}$ingle-sample Mix-p$\textbf{O}$licy $\textbf{U}$nified $\textbf{P}$aradigm (SOUP), a framework that unifies off- and on-policy learning within individual samples at the token level. It confines off-policy influence to the prefix of a generated sequence sampled from historical policies, while the continuation is generated on-policy. Through token-level importance ratios, SOUP effectively leverages off-policy information while preserving training stability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SOUP consistently outperforms standard on-policy training and existing off-policy extensions. Our further analysis clarifies how our fine-grained, single-sample mix-policy training can improve both exploration and final performance in LLM RL.
Meta-Cognitive Reinforcement Learning with Self-Doubt and Recovery
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Robust reinforcement learning methods typically focus on suppressing unreliable experiences or corrupted rewards, but they lack the ability to reason about the reliability of their own learning process. As a result, such methods often either overreact to noise by becoming overly conservative or fail catastrophically when uncertainty accumulates. In this work, we propose a meta-cognitive reinforcement learning framework that enables an agent to assess, regulate, and recover its learning behavior based on internally estimated reliability signals. The proposed method introduces a meta-trust variable driven by Value Prediction Error Stability (VPES), which modulates learning dynamics via fail-safe regulation and gradual trust recovery. Experiments on continuous-control benchmarks with reward corruption demonstrate that recovery-enabled meta-cognitive control achieves higher average returns and significantly reduces late-stage training failures compared to strong robustness baselines.
Training instability in deep learning follows low-dimensional dynamical principles
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Deep learning systems achieve remarkable empirical performance, yet the stability of the training process itself remains poorly understood. Training unfolds as a high-dimensional dynamical system in which small perturbations to optimization, data, parameters, or learning signals can induce abrupt and irreversible collapse, undermining reproducibility and scalability. We propose a unified dynamical perspective that characterizes training stability as an intrinsic property of learning systems, organized along four interacting dimensions: optimization, environmental/data, parametric, and learning-signal stability. We operationalize this perspective through controlled perturbation auditing of training trajectories, probing how learning dynamics respond to structured disturbances without modifying learning algorithms. Across reinforcement learning and large language model training, we identify three recurring regularities: high final performance is frequently decoupled from training stability; controlled stochasticity consistently buffers learning dynamics across paradigms; and deviations in low-dimensional latent meta-states systematically precede observable performance collapse. Together, these findings establish training stability as a measurable and comparable dynamical property of learning systems, providing a descriptive foundation for studying learning dynamics beyond final performance outcomes.
Learning to Trust Experience: A Monitor-Trust-Regulator Framework for Learning under Unobservable Feedback Reliability
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Learning under unobservable feedback reliability poses a distinct challenge beyond optimization robustness: a system must decide whether to learn from an experience, not only how to learn stably. We study this setting as Epistemic Identifiability under Unobservable Reliability (EIUR), where each experience has a latent credibility, reliable and unreliable feedback can be locally indistinguishable, and data are generated in a closed loop by the learner's own evolving beliefs and actions. In EIUR, standard robust learning can converge stably yet form high-confidence, systematically wrong beliefs. We propose metacognitive regulation as a practical response: a second, introspective control loop that infers experience credibility from endogenous evidence in the learner's internal dynamics. We formalize this as a modular Monitor-Trust-Regulator (MTR) decomposition and instantiate it with self-diagnosis, which maintains a slowly varying experience-trust variable that softly modulates learning updates, without exogenous reliability labels or an explicit corruption model. Empirically, in the EIUR regimes studied here, self-diagnosis is associated with improved epistemic identifiability. In reinforcement learning, it enables calibrated skepticism and recovery under systematically corrupted rewards. In supervised learning, it exposes a critical dissociation: performance recovery does not imply epistemic recovery. Accuracy can rebound while internal belief dynamics remain locked-in by early misleading data, a failure detectable only through introspective diagnostics. Together, MTR and self-diagnosis provide an organizing abstraction and a concrete design template for intrinsic reliability assessment in autonomous learning under unobservable reliability.
Radiance-Field Reinforced Pretraining: Scaling Localization Models with Unlabeled Wireless Signals
Dec 08, 2025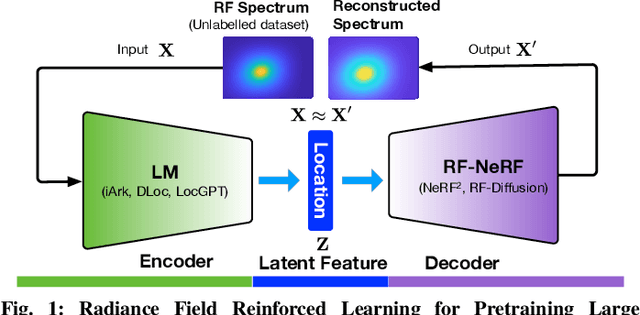
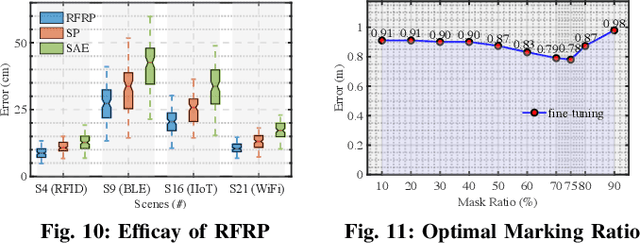
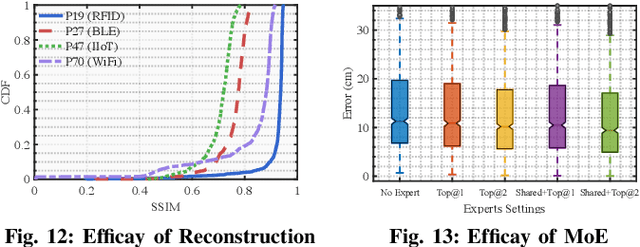
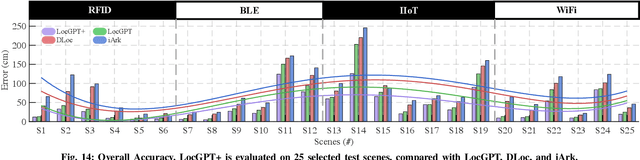
Abstract:Radio frequency (RF)-based indoor localization offers significant promise for applications such as indoor navigation, augmented reality, and pervasive computing. While deep learning has greatly enhanced localization accuracy and robustness, existing localization models still face major challenges in cross-scene generalization due to their reliance on scene-specific labeled data. To address this, we introduce Radiance-Field Reinforced Pretraining (RFRP). This novel self-supervised pretraining framework couples a large localization model (LM) with a neural radio-frequency radiance field (RF-NeRF) in an asymmetrical autoencoder architecture. In this design, the LM encodes received RF spectra into latent, position-relevant representations, while the RF-NeRF decodes them to reconstruct the original spectra. This alignment between input and output enables effective representation learning using large-scale, unlabeled RF data, which can be collected continuously with minimal effort. To this end, we collected RF samples at 7,327,321 positions across 100 diverse scenes using four common wireless technologies--RFID, BLE, WiFi, and IIoT. Data from 75 scenes were used for training, and the remaining 25 for evaluation. Experimental results show that the RFRP-pretrained LM reduces localization error by over 40% compared to non-pretrained models and by 21% compared to those pretrained using supervised learning.
Scaling Spatial Intelligence with Multimodal Foundation Models
Nov 17, 2025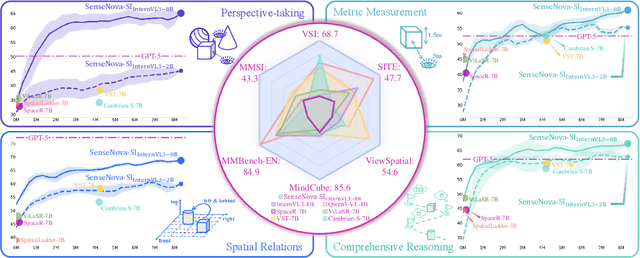
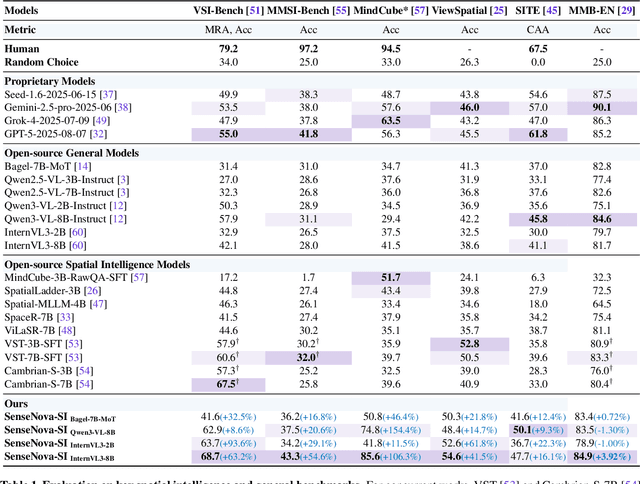
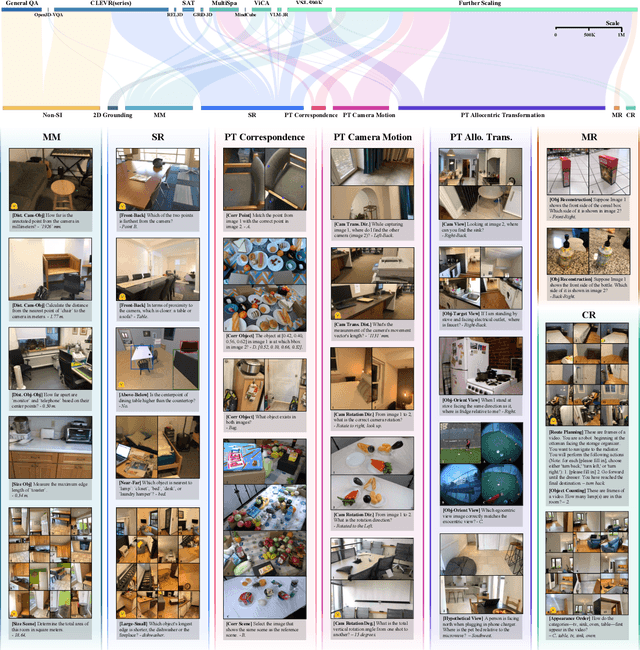
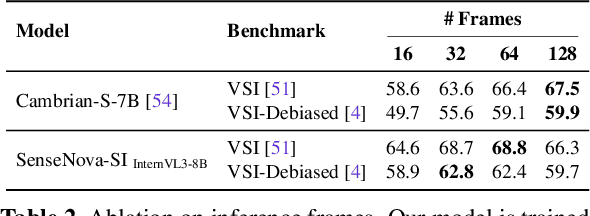
Abstract:Despite remarkable progress, multimodal foundation models still exhibit surprising deficiencies in spatial intelligence. In this work, we explore scaling up multimodal foundation models to cultivate spatial intelligence within the SenseNova-SI family, built upon established multimodal foundations including visual understanding models (i.e., Qwen3-VL and InternVL3) and unified understanding and generation models (i.e., Bagel). We take a principled approach to constructing high-performing and robust spatial intelligence by systematically curating SenseNova-SI-8M: eight million diverse data samples under a rigorous taxonomy of spatial capabilities. SenseNova-SI demonstrates unprecedented performance across a broad range of spatial intelligence benchmarks: 68.7% on VSI-Bench, 43.3% on MMSI, 85.6% on MindCube, 54.6% on ViewSpatial, and 50.1% on SITE, while maintaining strong general multimodal understanding (e.g., 84.9% on MMBench-En). More importantly, we analyze the impact of data scaling, discuss early signs of emergent generalization capabilities enabled by diverse data training, analyze the risk of overfitting and language shortcuts, present a preliminary study on spatial chain-of-thought reasoning, and validate the potential downstream application. SenseNova-SI is an ongoing project, and this report will be updated continuously. All newly trained multimodal foundation models are publicly released to facilitate further research in this direction.
DGFusion: Dual-guided Fusion for Robust Multi-Modal 3D Object Detection
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:As a critical task in autonomous driving perception systems, 3D object detection is used to identify and track key objects, such as vehicles and pedestrians. However, detecting distant, small, or occluded objects (hard instances) remains a challenge, which directly compromises the safety of autonomous driving systems. We observe that existing multi-modal 3D object detection methods often follow a single-guided paradigm, failing to account for the differences in information density of hard instances between modalities. In this work, we propose DGFusion, based on the Dual-guided paradigm, which fully inherits the advantages of the Point-guide-Image paradigm and integrates the Image-guide-Point paradigm to address the limitations of the single paradigms. The core of DGFusion, the Difficulty-aware Instance Pair Matcher (DIPM), performs instance-level feature matching based on difficulty to generate easy and hard instance pairs, while the Dual-guided Modules exploit the advantages of both pair types to enable effective multi-modal feature fusion. Experimental results demonstrate that our DGFusion outperforms the baseline methods, with respective improvements of +1.0\% mAP, +0.8\% NDS, and +1.3\% average recall on nuScenes. Extensive experiments demonstrate consistent robustness gains for hard instance detection across ego-distance, size, visibility, and small-scale training scenarios.
Cross-Modal Unlearning via Influential Neuron Path Editing in Multimodal Large Language Models
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) extend foundation models to real-world applications by integrating inputs such as text and vision. However, their broad knowledge capacity raises growing concerns about privacy leakage, toxicity mitigation, and intellectual property violations. Machine Unlearning (MU) offers a practical solution by selectively forgetting targeted knowledge while preserving overall model utility. When applied to MLLMs, existing neuron-editing-based MU approaches face two fundamental challenges: (1) forgetting becomes inconsistent across modalities because existing point-wise attribution methods fail to capture the structured, layer-by-layer information flow that connects different modalities; and (2) general knowledge performance declines when sensitive neurons that also support important reasoning paths are pruned, as this disrupts the model's ability to generalize. To alleviate these limitations, we propose a multimodal influential neuron path editor (MIP-Editor) for MU. Our approach introduces modality-specific attribution scores to identify influential neuron paths responsible for encoding forget-set knowledge and applies influential-path-aware neuron-editing via representation misdirection. This strategy also enables effective and coordinated forgetting across modalities while preserving the model's general capabilities. Experimental results demonstrate that MIP-Editor achieves a superior unlearning performance on multimodal tasks, with a maximum forgetting rate of 87.75% and up to 54.26% improvement in general knowledge retention. On textual tasks, MIP-Editor achieves up to 80.65% forgetting and preserves 77.9% of general performance. Codes are available at https://github.com/PreckLi/MIP-Editor.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge