Wenping Wang
Joint Orientation and Weight Optimization for Robust Watertight Surface Reconstruction via Dirichlet-Regularized Winding Fields
Feb 14, 2026Abstract:We propose Dirichlet Winding Reconstruction (DiWR), a robust method for reconstructing watertight surfaces from unoriented point clouds with non-uniform sampling, noise, and outliers. Our method uses the generalized winding number (GWN) field as the target implicit representation and jointly optimizes point orientations, per-point area weights, and confidence coefficients in a single pipeline. The optimization minimizes the Dirichlet energy of the induced winding field together with additional GWN-based constraints, allowing DiWR to compensate for non-uniform sampling, reduce the impact of noise, and downweight outliers during reconstruction, with no reliance on separate preprocessing. We evaluate DiWR on point clouds from 3D Gaussian Splatting, a computer-vision pipeline, and corrupted graphics benchmarks. Experiments show that DiWR produces plausible watertight surfaces on these challenging inputs and outperforms both traditional multi-stage pipelines and recent joint orientation-reconstruction methods.
MTPano: Multi-Task Panoramic Scene Understanding via Label-Free Integration of Dense Prediction Priors
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Comprehensive panoramic scene understanding is critical for immersive applications, yet it remains challenging due to the scarcity of high-resolution, multi-task annotations. While perspective foundation models have achieved success through data scaling, directly adapting them to the panoramic domain often fails due to severe geometric distortions and coordinate system discrepancies. Furthermore, the underlying relations between diverse dense prediction tasks in spherical spaces are underexplored. To address these challenges, we propose MTPano, a robust multi-task panoramic foundation model established by a label-free training pipeline. First, to circumvent data scarcity, we leverage powerful perspective dense priors. We project panoramic images into perspective patches to generate accurate, domain-gap-free pseudo-labels using off-the-shelf foundation models, which are then re-projected to serve as patch-wise supervision. Second, to tackle the interference between task types, we categorize tasks into rotation-invariant (e.g., depth, segmentation) and rotation-variant (e.g., surface normals) groups. We introduce the Panoramic Dual BridgeNet, which disentangles these feature streams via geometry-aware modulation layers that inject absolute position and ray direction priors. To handle the distortion from equirectangular projections (ERP), we incorporate ERP token mixers followed by a dual-branch BridgeNet for interactions with gradient truncation, facilitating beneficial cross-task information sharing while blocking conflicting gradients from incompatible task attributes. Additionally, we introduce auxiliary tasks (image gradient, point map, etc.) to fertilize the cross-task learning process. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MTPano achieves state-of-the-art performance on multiple benchmarks and delivers competitive results against task-specific panoramic specialist foundation models.
EgoReAct: Egocentric Video-Driven 3D Human Reaction Generation
Dec 28, 2025Abstract:Humans exhibit adaptive, context-sensitive responses to egocentric visual input. However, faithfully modeling such reactions from egocentric video remains challenging due to the dual requirements of strictly causal generation and precise 3D spatial alignment. To tackle this problem, we first construct the Human Reaction Dataset (HRD) to address data scarcity and misalignment by building a spatially aligned egocentric video-reaction dataset, as existing datasets (e.g., ViMo) suffer from significant spatial inconsistency between the egocentric video and reaction motion, e.g., dynamically moving motions are always paired with fixed-camera videos. Leveraging HRD, we present EgoReAct, the first autoregressive framework that generates 3D-aligned human reaction motions from egocentric video streams in real-time. We first compress the reaction motion into a compact yet expressive latent space via a Vector Quantised-Variational AutoEncoder and then train a Generative Pre-trained Transformer for reaction generation from the visual input. EgoReAct incorporates 3D dynamic features, i.e., metric depth, and head dynamics during the generation, which effectively enhance spatial grounding. Extensive experiments demonstrate that EgoReAct achieves remarkably higher realism, spatial consistency, and generation efficiency compared with prior methods, while maintaining strict causality during generation. We will release code, models, and data upon acceptance.
UniSER: A Foundation Model for Unified Soft Effects Removal
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Digital images are often degraded by soft effects such as lens flare, haze, shadows, and reflections, which reduce aesthetics even though the underlying pixels remain partially visible. The prevailing works address these degradations in isolation, developing highly specialized, specialist models that lack scalability and fail to exploit the shared underlying essences of these restoration problems. While specialist models are limited, recent large-scale pretrained generalist models offer powerful, text-driven image editing capabilities. while recent general-purpose systems (e.g., GPT-4o, Flux Kontext, Nano Banana) require detailed prompts and often fail to achieve robust removal on these fine-grained tasks or preserve identity of the scene. Leveraging the common essence of soft effects, i.e., semi-transparent occlusions, we introduce a foundational versatile model UniSER, capable of addressing diverse degradations caused by soft effects within a single framework. Our methodology centers on curating a massive 3.8M-pair dataset to ensure robustness and generalization, which includes novel, physically-plausible data to fill critical gaps in public benchmarks, and a tailored training pipeline that fine-tunes a Diffusion Transformer to learn robust restoration priors from this diverse data, integrating fine-grained mask and strength controls. This synergistic approach allows UniSER to significantly outperform both specialist and generalist models, achieving robust, high-fidelity restoration in the wild.
Dynamic Gaussian Scene Reconstruction from Unsynchronized Videos
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Multi-view video reconstruction plays a vital role in computer vision, enabling applications in film production, virtual reality, and motion analysis. While recent advances such as 4D Gaussian Splatting (4DGS) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in dynamic scene reconstruction, they typically rely on the assumption that input video streams are temporally synchronized. However, in real-world scenarios, this assumption often fails due to factors like camera trigger delays or independent recording setups, leading to temporal misalignment across views and reduced reconstruction quality. To address this challenge, a novel temporal alignment strategy is proposed for high-quality 4DGS reconstruction from unsynchronized multi-view videos. Our method features a coarse-to-fine alignment module that estimates and compensates for each camera's time shift. The method first determines a coarse, frame-level offset and then refines it to achieve sub-frame accuracy. This strategy can be integrated as a readily integrable module into existing 4DGS frameworks, enhancing their robustness when handling asynchronous data. Experiments show that our approach effectively processes temporally misaligned videos and significantly enhances baseline methods.
SPGen: Spherical Projection as Consistent and Flexible Representation for Single Image 3D Shape Generation
Sep 16, 2025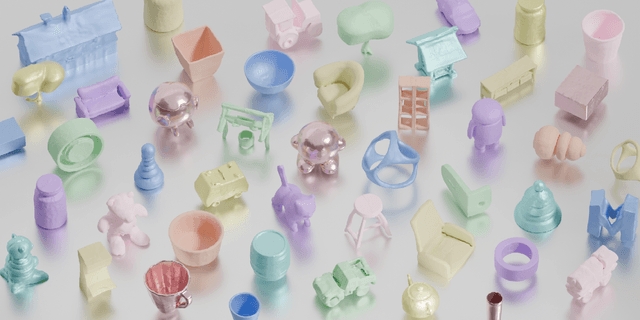
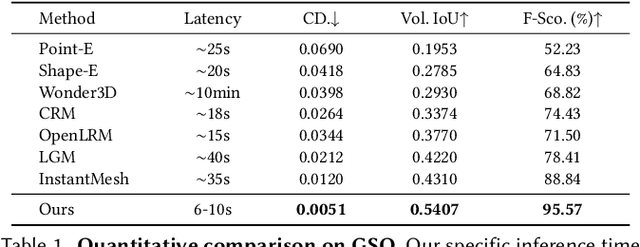
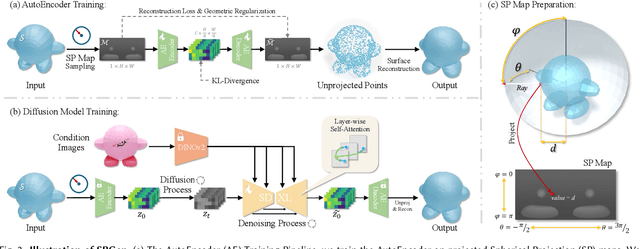
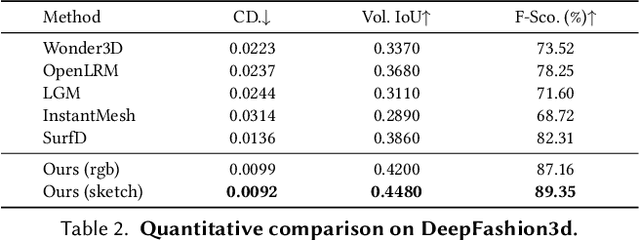
Abstract:Existing single-view 3D generative models typically adopt multiview diffusion priors to reconstruct object surfaces, yet they remain prone to inter-view inconsistencies and are unable to faithfully represent complex internal structure or nontrivial topologies. In particular, we encode geometry information by projecting it onto a bounding sphere and unwrapping it into a compact and structural multi-layer 2D Spherical Projection (SP) representation. Operating solely in the image domain, SPGen offers three key advantages simultaneously: (1) Consistency. The injective SP mapping encodes surface geometry with a single viewpoint which naturally eliminates view inconsistency and ambiguity; (2) Flexibility. Multi-layer SP maps represent nested internal structures and support direct lifting to watertight or open 3D surfaces; (3) Efficiency. The image-domain formulation allows the direct inheritance of powerful 2D diffusion priors and enables efficient finetuning with limited computational resources. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SPGen significantly outperforms existing baselines in geometric quality and computational efficiency.
Reconstructing 4D Spatial Intelligence: A Survey
Jul 28, 2025



Abstract:Reconstructing 4D spatial intelligence from visual observations has long been a central yet challenging task in computer vision, with broad real-world applications. These range from entertainment domains like movies, where the focus is often on reconstructing fundamental visual elements, to embodied AI, which emphasizes interaction modeling and physical realism. Fueled by rapid advances in 3D representations and deep learning architectures, the field has evolved quickly, outpacing the scope of previous surveys. Additionally, existing surveys rarely offer a comprehensive analysis of the hierarchical structure of 4D scene reconstruction. To address this gap, we present a new perspective that organizes existing methods into five progressive levels of 4D spatial intelligence: (1) Level 1 -- reconstruction of low-level 3D attributes (e.g., depth, pose, and point maps); (2) Level 2 -- reconstruction of 3D scene components (e.g., objects, humans, structures); (3) Level 3 -- reconstruction of 4D dynamic scenes; (4) Level 4 -- modeling of interactions among scene components; and (5) Level 5 -- incorporation of physical laws and constraints. We conclude the survey by discussing the key challenges at each level and highlighting promising directions for advancing toward even richer levels of 4D spatial intelligence. To track ongoing developments, we maintain an up-to-date project page: https://github.com/yukangcao/Awesome-4D-Spatial-Intelligence.
MOSPA: Human Motion Generation Driven by Spatial Audio
Jul 16, 2025Abstract:Enabling virtual humans to dynamically and realistically respond to diverse auditory stimuli remains a key challenge in character animation, demanding the integration of perceptual modeling and motion synthesis. Despite its significance, this task remains largely unexplored. Most previous works have primarily focused on mapping modalities like speech, audio, and music to generate human motion. As of yet, these models typically overlook the impact of spatial features encoded in spatial audio signals on human motion. To bridge this gap and enable high-quality modeling of human movements in response to spatial audio, we introduce the first comprehensive Spatial Audio-Driven Human Motion (SAM) dataset, which contains diverse and high-quality spatial audio and motion data. For benchmarking, we develop a simple yet effective diffusion-based generative framework for human MOtion generation driven by SPatial Audio, termed MOSPA, which faithfully captures the relationship between body motion and spatial audio through an effective fusion mechanism. Once trained, MOSPA could generate diverse realistic human motions conditioned on varying spatial audio inputs. We perform a thorough investigation of the proposed dataset and conduct extensive experiments for benchmarking, where our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on this task. Our model and dataset will be open-sourced upon acceptance. Please refer to our supplementary video for more details.
SURPRISE3D: A Dataset for Spatial Understanding and Reasoning in Complex 3D Scenes
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:The integration of language and 3D perception is critical for embodied AI and robotic systems to perceive, understand, and interact with the physical world. Spatial reasoning, a key capability for understanding spatial relationships between objects, remains underexplored in current 3D vision-language research. Existing datasets often mix semantic cues (e.g., object name) with spatial context, leading models to rely on superficial shortcuts rather than genuinely interpreting spatial relationships. To address this gap, we introduce S\textsc{urprise}3D, a novel dataset designed to evaluate language-guided spatial reasoning segmentation in complex 3D scenes. S\textsc{urprise}3D consists of more than 200k vision language pairs across 900+ detailed indoor scenes from ScanNet++ v2, including more than 2.8k unique object classes. The dataset contains 89k+ human-annotated spatial queries deliberately crafted without object name, thereby mitigating shortcut biases in spatial understanding. These queries comprehensively cover various spatial reasoning skills, such as relative position, narrative perspective, parametric perspective, and absolute distance reasoning. Initial benchmarks demonstrate significant challenges for current state-of-the-art expert 3D visual grounding methods and 3D-LLMs, underscoring the necessity of our dataset and the accompanying 3D Spatial Reasoning Segmentation (3D-SRS) benchmark suite. S\textsc{urprise}3D and 3D-SRS aim to facilitate advancements in spatially aware AI, paving the way for effective embodied interaction and robotic planning. The code and datasets can be found in https://github.com/liziwennba/SUPRISE.
NeuVAS: Neural Implicit Surfaces for Variational Shape Modeling
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Neural implicit shape representation has drawn significant attention in recent years due to its smoothness, differentiability, and topological flexibility. However, directly modeling the shape of a neural implicit surface, especially as the zero-level set of a neural signed distance function (SDF), with sparse geometric control is still a challenging task. Sparse input shape control typically includes 3D curve networks or, more generally, 3D curve sketches, which are unstructured and cannot be connected to form a curve network, and therefore more difficult to deal with. While 3D curve networks or curve sketches provide intuitive shape control, their sparsity and varied topology pose challenges in generating high-quality surfaces to meet such curve constraints. In this paper, we propose NeuVAS, a variational approach to shape modeling using neural implicit surfaces constrained under sparse input shape control, including unstructured 3D curve sketches as well as connected 3D curve networks. Specifically, we introduce a smoothness term based on a functional of surface curvatures to minimize shape variation of the zero-level set surface of a neural SDF. We also develop a new technique to faithfully model G0 sharp feature curves as specified in the input curve sketches. Comprehensive comparisons with the state-of-the-art methods demonstrate the significant advantages of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge