Zhaoqing Wang
MMGen: Unified Multi-modal Image Generation and Understanding in One Go
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:A unified diffusion framework for multi-modal generation and understanding has the transformative potential to achieve seamless and controllable image diffusion and other cross-modal tasks. In this paper, we introduce MMGen, a unified framework that integrates multiple generative tasks into a single diffusion model. This includes: (1) multi-modal category-conditioned generation, where multi-modal outputs are generated simultaneously through a single inference process, given category information; (2) multi-modal visual understanding, which accurately predicts depth, surface normals, and segmentation maps from RGB images; and (3) multi-modal conditioned generation, which produces corresponding RGB images based on specific modality conditions and other aligned modalities. Our approach develops a novel diffusion transformer that flexibly supports multi-modal output, along with a simple modality-decoupling strategy to unify various tasks. Extensive experiments and applications demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of MMGen across diverse tasks and conditions, highlighting its potential for applications that require simultaneous generation and understanding.
MF-VITON: High-Fidelity Mask-Free Virtual Try-On with Minimal Input
Mar 11, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in Virtual Try-On (VITON) have significantly improved image realism and garment detail preservation, driven by powerful text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models. However, existing methods often rely on user-provided masks, introducing complexity and performance degradation due to imperfect inputs, as shown in Fig.1(a). To address this, we propose a Mask-Free VITON (MF-VITON) framework that achieves realistic VITON using only a single person image and a target garment, eliminating the requirement for auxiliary masks. Our approach introduces a novel two-stage pipeline: (1) We leverage existing Mask-based VITON models to synthesize a high-quality dataset. This dataset contains diverse, realistic pairs of person images and corresponding garments, augmented with varied backgrounds to mimic real-world scenarios. (2) The pre-trained Mask-based model is fine-tuned on the generated dataset, enabling garment transfer without mask dependencies. This stage simplifies the input requirements while preserving garment texture and shape fidelity. Our framework achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance regarding garment transfer accuracy and visual realism. Notably, the proposed Mask-Free model significantly outperforms existing Mask-based approaches, setting a new benchmark and demonstrating a substantial lead over previous approaches. For more details, visit our project page: https://zhenchenwan.github.io/MF-VITON/.
OVGaussian: Generalizable 3D Gaussian Segmentation with Open Vocabularies
Dec 31, 2024Abstract:Open-vocabulary scene understanding using 3D Gaussian (3DGS) representations has garnered considerable attention. However, existing methods mostly lift knowledge from large 2D vision models into 3DGS on a scene-by-scene basis, restricting the capabilities of open-vocabulary querying within their training scenes so that lacking the generalizability to novel scenes. In this work, we propose \textbf{OVGaussian}, a generalizable \textbf{O}pen-\textbf{V}ocabulary 3D semantic segmentation framework based on the 3D \textbf{Gaussian} representation. We first construct a large-scale 3D scene dataset based on 3DGS, dubbed \textbf{SegGaussian}, which provides detailed semantic and instance annotations for both Gaussian points and multi-view images. To promote semantic generalization across scenes, we introduce Generalizable Semantic Rasterization (GSR), which leverages a 3D neural network to learn and predict the semantic property for each 3D Gaussian point, where the semantic property can be rendered as multi-view consistent 2D semantic maps. In the next, we propose a Cross-modal Consistency Learning (CCL) framework that utilizes open-vocabulary annotations of 2D images and 3D Gaussians within SegGaussian to train the 3D neural network capable of open-vocabulary semantic segmentation across Gaussian-based 3D scenes. Experimental results demonstrate that OVGaussian significantly outperforms baseline methods, exhibiting robust cross-scene, cross-domain, and novel-view generalization capabilities. Code and the SegGaussian dataset will be released. (https://github.com/runnanchen/OVGaussian).
PanoSLAM: Panoptic 3D Scene Reconstruction via Gaussian SLAM
Dec 31, 2024



Abstract:Understanding geometric, semantic, and instance information in 3D scenes from sequential video data is essential for applications in robotics and augmented reality. However, existing Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) methods generally focus on either geometric or semantic reconstruction. In this paper, we introduce PanoSLAM, the first SLAM system to integrate geometric reconstruction, 3D semantic segmentation, and 3D instance segmentation within a unified framework. Our approach builds upon 3D Gaussian Splatting, modified with several critical components to enable efficient rendering of depth, color, semantic, and instance information from arbitrary viewpoints. To achieve panoptic 3D scene reconstruction from sequential RGB-D videos, we propose an online Spatial-Temporal Lifting (STL) module that transfers 2D panoptic predictions from vision models into 3D Gaussian representations. This STL module addresses the challenges of label noise and inconsistencies in 2D predictions by refining the pseudo labels across multi-view inputs, creating a coherent 3D representation that enhances segmentation accuracy. Our experiments show that PanoSLAM outperforms recent semantic SLAM methods in both mapping and tracking accuracy. For the first time, it achieves panoptic 3D reconstruction of open-world environments directly from the RGB-D video. (https://github.com/runnanchen/PanoSLAM)
TED-VITON: Transformer-Empowered Diffusion Models for Virtual Try-On
Nov 26, 2024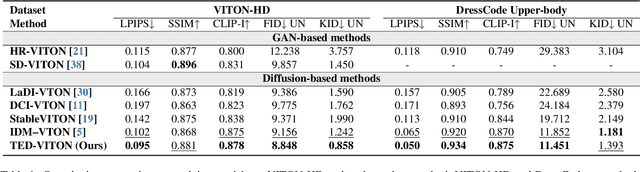
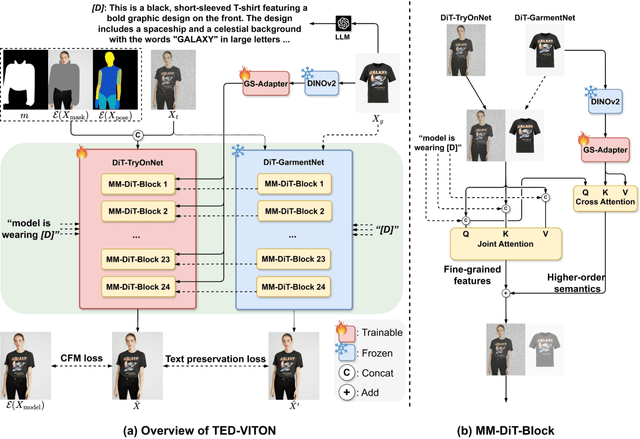


Abstract:Recent advancements in Virtual Try-On (VTO) have demonstrated exceptional efficacy in generating realistic images and preserving garment details, largely attributed to the robust generative capabilities of text-to-image (T2I) diffusion backbones. However, the T2I models that underpin these methods have become outdated, thereby limiting the potential for further improvement in VTO. Additionally, current methods face notable challenges in accurately rendering text on garments without distortion and preserving fine-grained details, such as textures and material fidelity. The emergence of Diffusion Transformer (DiT) based T2I models has showcased impressive performance and offers a promising opportunity for advancing VTO. Directly applying existing VTO techniques to transformer-based T2I models is ineffective due to substantial architectural differences, which hinder their ability to fully leverage the models' advanced capabilities for improved text generation. To address these challenges and unlock the full potential of DiT-based T2I models for VTO, we propose TED-VITON, a novel framework that integrates a Garment Semantic (GS) Adapter for enhancing garment-specific features, a Text Preservation Loss to ensure accurate and distortion-free text rendering, and a constraint mechanism to generate prompts by optimizing Large Language Model (LLM). These innovations enable state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in visual quality and text fidelity, establishing a new benchmark for VTO task.
Beyond Gaussians: Fast and High-Fidelity 3D Splatting with Linear Kernels
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have substantially improved novel view synthesis, enabling high-quality reconstruction and real-time rendering. However, blurring artifacts, such as floating primitives and over-reconstruction, remain challenging. Current methods address these issues by refining scene structure, enhancing geometric representations, addressing blur in training images, improving rendering consistency, and optimizing density control, yet the role of kernel design remains underexplored. We identify the soft boundaries of Gaussian ellipsoids as one of the causes of these artifacts, limiting detail capture in high-frequency regions. To bridge this gap, we introduce 3D Linear Splatting (3DLS), which replaces Gaussian kernels with linear kernels to achieve sharper and more precise results, particularly in high-frequency regions. Through evaluations on three datasets, 3DLS demonstrates state-of-the-art fidelity and accuracy, along with a 30% FPS improvement over baseline 3DGS. The implementation will be made publicly available upon acceptance.
LaVin-DiT: Large Vision Diffusion Transformer
Nov 18, 2024Abstract:This paper presents the Large Vision Diffusion Transformer (LaVin-DiT), a scalable and unified foundation model designed to tackle over 20 computer vision tasks in a generative framework. Unlike existing large vision models directly adapted from natural language processing architectures, which rely on less efficient autoregressive techniques and disrupt spatial relationships essential for vision data, LaVin-DiT introduces key innovations to optimize generative performance for vision tasks. First, to address the high dimensionality of visual data, we incorporate a spatial-temporal variational autoencoder that encodes data into a continuous latent space. Second, for generative modeling, we develop a joint diffusion transformer that progressively produces vision outputs. Third, for unified multi-task training, in-context learning is implemented. Input-target pairs serve as task context, which guides the diffusion transformer to align outputs with specific tasks within the latent space. During inference, a task-specific context set and test data as queries allow LaVin-DiT to generalize across tasks without fine-tuning. Trained on extensive vision datasets, the model is scaled from 0.1B to 3.4B parameters, demonstrating substantial scalability and state-of-the-art performance across diverse vision tasks. This work introduces a novel pathway for large vision foundation models, underscoring the promising potential of diffusion transformers. The code and models will be open-sourced.
Training-Free Robust Interactive Video Object Segmentation
Jun 08, 2024



Abstract:Interactive video object segmentation is a crucial video task, having various applications from video editing to data annotating. However, current approaches struggle to accurately segment objects across diverse domains. Recently, Segment Anything Model (SAM) introduces interactive visual prompts and demonstrates impressive performance across different domains. In this paper, we propose a training-free prompt tracking framework for interactive video object segmentation (I-PT), leveraging the powerful generalization of SAM. Although point tracking efficiently captures the pixel-wise information of objects in a video, points tend to be unstable when tracked over a long period, resulting in incorrect segmentation. Towards fast and robust interaction, we jointly adopt sparse points and boxes tracking, filtering out unstable points and capturing object-wise information. To better integrate reference information from multiple interactions, we introduce a cross-round space-time module (CRSTM), which adaptively aggregates mask features from previous rounds and frames, enhancing the segmentation stability. Our framework has demonstrated robust zero-shot video segmentation results on popular VOS datasets with interaction types, including DAVIS 2017, YouTube-VOS 2018, and MOSE 2023, maintaining a good tradeoff between performance and interaction time.
Open-Vocabulary Segmentation with Unpaired Mask-Text Supervision
Feb 14, 2024Abstract:Contemporary cutting-edge open-vocabulary segmentation approaches commonly rely on image-mask-text triplets, yet this restricted annotation is labour-intensive and encounters scalability hurdles in complex real-world scenarios. Although some methods are proposed to reduce the annotation cost with only text supervision, the incompleteness of supervision severely limits the versatility and performance. In this paper, we liberate the strict correspondence between masks and texts by using independent image-mask and image-text pairs, which can be easily collected respectively. With this unpaired mask-text supervision, we propose a new weakly-supervised open-vocabulary segmentation framework (Uni-OVSeg) that leverages confident pairs of mask predictions and entities in text descriptions. Using the independent image-mask and image-text pairs, we predict a set of binary masks and associate them with entities by resorting to the CLIP embedding space. However, the inherent noise in the correspondence between masks and entities poses a significant challenge when obtaining reliable pairs. In light of this, we advocate using the large vision-language model (LVLM) to refine text descriptions and devise a multi-scale ensemble to stablise the matching between masks and entities. Compared to text-only weakly-supervised methods, our Uni-OVSeg achieves substantial improvements of 15.5% mIoU on the ADE20K datasets, and even surpasses fully-supervised methods on the challenging PASCAL Context-459 dataset.
IDEAL: Influence-Driven Selective Annotations Empower In-Context Learners in Large Language Models
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:In-context learning is a promising paradigm that utilizes in-context examples as prompts for the predictions of large language models. These prompts are crucial for achieving strong performance. However, since the prompts need to be sampled from a large volume of annotated examples, finding the right prompt may result in high annotation costs. To address this challenge, this paper introduces an influence-driven selective annotation method that aims to minimize annotation costs while improving the quality of in-context examples. The essence of our method is to select a pivotal subset from a large-scale unlabeled data pool to annotate for the subsequent sampling of prompts. Specifically, a directed graph is first constructed to represent unlabeled data. Afterward, the influence of candidate unlabeled subsets is quantified with a diffusion process. A simple yet effective greedy algorithm for unlabeled data selection is lastly introduced. It iteratively selects the data if it provides a maximum marginal gain with respect to quantified influence. Compared with previous efforts on selective annotations, our influence-driven method works in an end-to-end manner, avoids an intractable explicit balance between data diversity and representativeness, and enjoys theoretical support. Experiments confirm the superiority of the proposed method on various benchmarks, achieving better performance under lower time consumption during subset selection. The project page is available at https://skzhang1.github.io/IDEAL/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge