Ziye Chen
Michael Pokorny
RIMO: An Easy-to-Evaluate, Hard-to-Solve Olympiad Benchmark for Advanced Mathematical Reasoning
Sep 09, 2025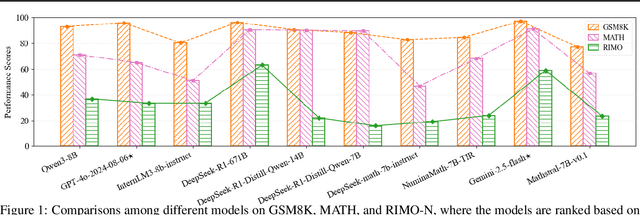
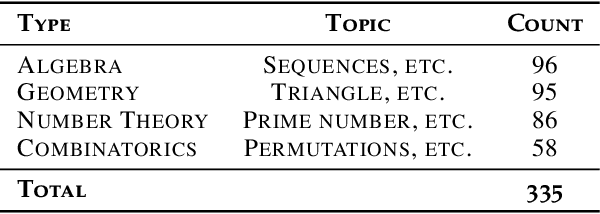
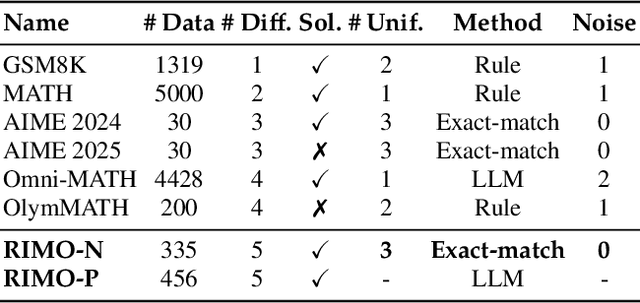
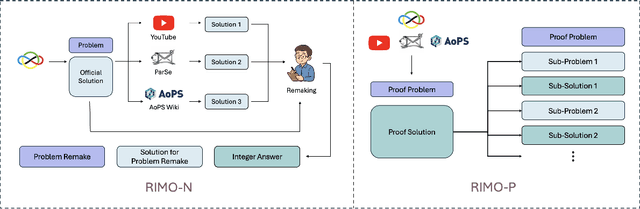
Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) reach high scores on established mathematical benchmarks, such as GSM8K and MATH, the research community has turned to International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) problems to push the evaluation frontier. However, existing Olympiad-level benchmarks suffer from practical constraints that introduce grading noise and potential bias, such as heterogeneous answer formats requiring model-based judges and a reliance on potentially flawed solutions. We introduce RIMO, a two-track benchmark designed to preserve peak Olympiad difficulty while eliminating this evaluation noise. The first track, RIMO-N, rewrites 335 IMO problems to admit a single, unique integer answer, allowing for deterministic correctness checking. The second track, RIMO-P, features 456 proof problems with expert-checked solutions, which are decomposed into a sequence of sub-problems to evaluate the step-by-step reasoning process via an automated grading system. Our benchmarking of ten frontier LLMs, including GPT-4o and Gemini 2.5 Flash, reveals that while these systems excel on older benchmarks, their performance drops sharply on RIMO. These results highlight a substantial gap between current LLM capabilities and actual Olympiad-level reasoning. By providing a challenging yet easy-to-evaluate suite, RIMO offers a high-resolution yardstick for future research, presenting a clear target for closing the profound reasoning gap our findings expose.
Agent-Centric Personalized Multiple Clustering with Multi-Modal LLMs
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:Personalized multiple clustering aims to generate diverse partitions of a dataset based on different user-specific aspects, rather than a single clustering. It has recently drawn research interest for accommodating varying user preferences. Recent approaches primarily use CLIP embeddings with proxy learning to extract representations biased toward user clustering preferences. However, CLIP primarily focuses on coarse image-text alignment, lacking a deep contextual understanding of user interests. To overcome these limitations, we propose an agent-centric personalized clustering framework that leverages multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) as agents to comprehensively traverse a relational graph to search for clusters based on user interests. Due to the advanced reasoning mechanism of MLLMs, the obtained clusters align more closely with user-defined criteria than those obtained from CLIP-based representations. To reduce computational overhead, we shorten the agents' traversal path by constructing a relational graph using user-interest-biased embeddings extracted by MLLMs. A large number of weakly connected edges can be filtered out based on embedding similarity, facilitating an efficient traversal search for agents. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves NMI scores of 0.9667 and 0.9481 on the Card Order and Card Suits benchmarks, respectively, largely improving the SOTA model by over 140%.
Humanity's Last Exam
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Benchmarks are important tools for tracking the rapid advancements in large language model (LLM) capabilities. However, benchmarks are not keeping pace in difficulty: LLMs now achieve over 90\% accuracy on popular benchmarks like MMLU, limiting informed measurement of state-of-the-art LLM capabilities. In response, we introduce Humanity's Last Exam (HLE), a multi-modal benchmark at the frontier of human knowledge, designed to be the final closed-ended academic benchmark of its kind with broad subject coverage. HLE consists of 3,000 questions across dozens of subjects, including mathematics, humanities, and the natural sciences. HLE is developed globally by subject-matter experts and consists of multiple-choice and short-answer questions suitable for automated grading. Each question has a known solution that is unambiguous and easily verifiable, but cannot be quickly answered via internet retrieval. State-of-the-art LLMs demonstrate low accuracy and calibration on HLE, highlighting a significant gap between current LLM capabilities and the expert human frontier on closed-ended academic questions. To inform research and policymaking upon a clear understanding of model capabilities, we publicly release HLE at https://lastexam.ai.
Open-Vocabulary Segmentation with Unpaired Mask-Text Supervision
Feb 14, 2024Abstract:Contemporary cutting-edge open-vocabulary segmentation approaches commonly rely on image-mask-text triplets, yet this restricted annotation is labour-intensive and encounters scalability hurdles in complex real-world scenarios. Although some methods are proposed to reduce the annotation cost with only text supervision, the incompleteness of supervision severely limits the versatility and performance. In this paper, we liberate the strict correspondence between masks and texts by using independent image-mask and image-text pairs, which can be easily collected respectively. With this unpaired mask-text supervision, we propose a new weakly-supervised open-vocabulary segmentation framework (Uni-OVSeg) that leverages confident pairs of mask predictions and entities in text descriptions. Using the independent image-mask and image-text pairs, we predict a set of binary masks and associate them with entities by resorting to the CLIP embedding space. However, the inherent noise in the correspondence between masks and entities poses a significant challenge when obtaining reliable pairs. In light of this, we advocate using the large vision-language model (LVLM) to refine text descriptions and devise a multi-scale ensemble to stablise the matching between masks and entities. Compared to text-only weakly-supervised methods, our Uni-OVSeg achieves substantial improvements of 15.5% mIoU on the ADE20K datasets, and even surpasses fully-supervised methods on the challenging PASCAL Context-459 dataset.
An Efficient Transformer for Simultaneous Learning of BEV and Lane Representations in 3D Lane Detection
Jun 08, 2023
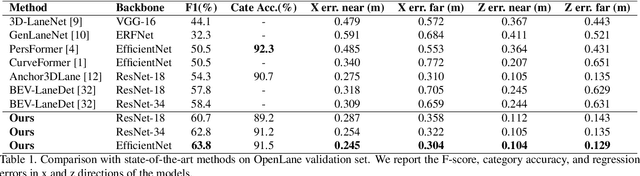

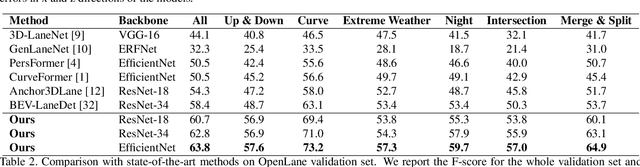
Abstract:Accurately detecting lane lines in 3D space is crucial for autonomous driving. Existing methods usually first transform image-view features into bird-eye-view (BEV) by aid of inverse perspective mapping (IPM), and then detect lane lines based on the BEV features. However, IPM ignores the changes in road height, leading to inaccurate view transformations. Additionally, the two separate stages of the process can cause cumulative errors and increased complexity. To address these limitations, we propose an efficient transformer for 3D lane detection. Different from the vanilla transformer, our model contains a decomposed cross-attention mechanism to simultaneously learn lane and BEV representations. The mechanism decomposes the cross-attention between image-view and BEV features into the one between image-view and lane features, and the one between lane and BEV features, both of which are supervised with ground-truth lane lines. Our method obtains 2D and 3D lane predictions by applying the lane features to the image-view and BEV features, respectively. This allows for a more accurate view transformation than IPM-based methods, as the view transformation is learned from data with a supervised cross-attention. Additionally, the cross-attention between lane and BEV features enables them to adjust to each other, resulting in more accurate lane detection than the two separate stages. Finally, the decomposed cross-attention is more efficient than the original one. Experimental results on OpenLane and ONCE-3DLanes demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of our method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge