Qingyun Wu
Live-Evo: Online Evolution of Agentic Memory from Continuous Feedback
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language model (LLM) agents are increasingly equipped with memory, which are stored experience and reusable guidance that can improve task-solving performance. Recent \emph{self-evolving} systems update memory based on interaction outcomes, but most existing evolution pipelines are developed for static train/test splits and only approximate online learning by folding static benchmarks, making them brittle under true distribution shift and continuous feedback. We introduce \textsc{Live-Evo}, an online self-evolving memory system that learns from a stream of incoming data over time. \textsc{Live-Evo} decouples \emph{what happened} from \emph{how to use it} via an Experience Bank and a Meta-Guideline Bank, compiling task-adaptive guidelines from retrieved experiences for each task. To manage memory online, \textsc{Live-Evo} maintains experience weights and updates them from feedback: experiences that consistently help are reinforced and retrieved more often, while misleading or stale experiences are down-weighted and gradually forgotten, analogous to reinforcement and decay in human memory. On the live \textit{Prophet Arena} benchmark over a 10-week horizon, \textsc{Live-Evo} improves Brier score by 20.8\% and increases market returns by 12.9\%, while also transferring to deep-research benchmarks with consistent gains over strong baselines. Our code is available at https://github.com/ag2ai/Live-Evo.
Do Images Speak Louder than Words? Investigating the Effect of Textual Misinformation in VLMs
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have shown strong multimodal reasoning capabilities on Visual-Question-Answering (VQA) benchmarks. However, their robustness against textual misinformation remains under-explored. While existing research has studied the effect of misinformation in text-only domains, it is not clear how VLMs arbitrate between contradictory information from different modalities. To bridge the gap, we first propose the CONTEXT-VQA (i.e., Conflicting Text) dataset, consisting of image-question pairs together with systematically generated persuasive prompts that deliberately conflict with visual evidence. Then, a thorough evaluation framework is designed and executed to benchmark the susceptibility of various models to these conflicting multimodal inputs. Comprehensive experiments over 11 state-of-the-art VLMs reveal that these models are indeed vulnerable to misleading textual prompts, often overriding clear visual evidence in favor of the conflicting text, and show an average performance drop of over 48.2% after only one round of persuasive conversation. Our findings highlight a critical limitation in current VLMs and underscore the need for improved robustness against textual manipulation.
Sliding Window Attention Adaptation
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:The self-attention mechanism in Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) scales quadratically with input length, making long-context inference expensive. Sliding window attention (SWA) reduces this cost to linear complexity, but naively enabling complete SWA at inference-time for models pretrained with full attention (FA) causes severe long-context performance degradation due to training-inference mismatch. This makes us wonder: Can FA-pretrained LLMs be well adapted to SWA without pretraining? We investigate this by proposing Sliding Window Attention Adaptation (SWAA), a set of practical recipes that combine five methods for better adaptation: (1) applying SWA only during prefilling; (2) preserving "sink" tokens; (3) interleaving FA/SWA layers; (4) chain-of-thought (CoT); and (5) fine-tuning. Our experiments show that SWA adaptation is feasible while non-trivial: no single method suffices, yet specific synergistic combinations effectively recover the original long-context performance. We further analyze the performance-efficiency trade-offs of different SWAA configurations and provide recommended recipes for diverse scenarios, which can greatly and fundamentally accelerate LLM long-context inference speed by up to 100%. Our code is available at https://github.com/yuyijiong/sliding-window-attention-adaptation
A Survey of Self-Evolving Agents: On Path to Artificial Super Intelligence
Jul 28, 2025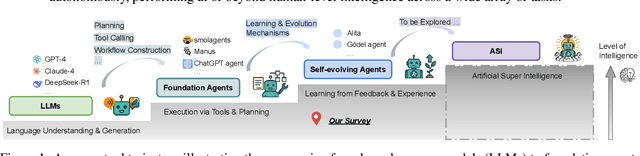
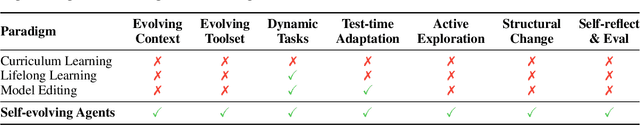
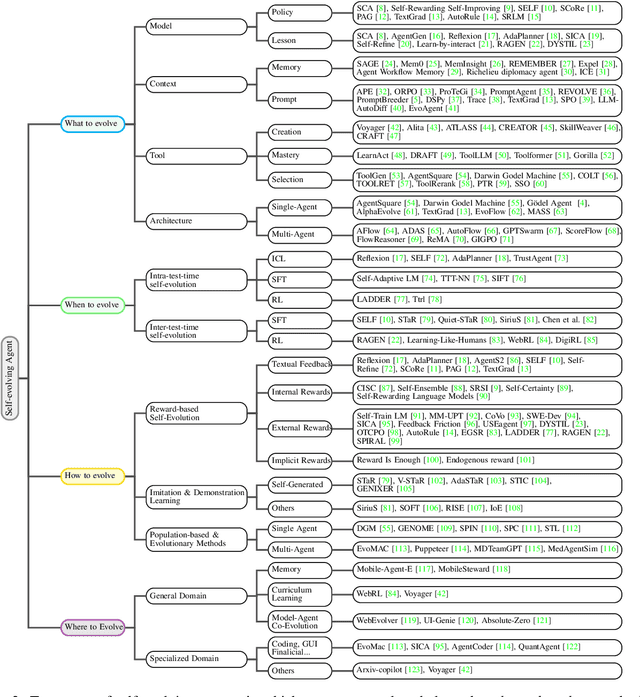
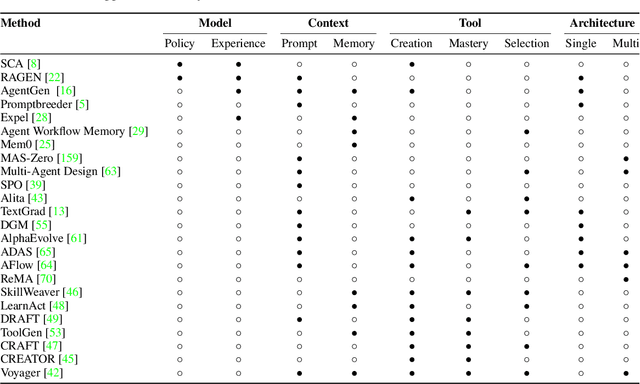
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong capabilities but remain fundamentally static, unable to adapt their internal parameters to novel tasks, evolving knowledge domains, or dynamic interaction contexts. As LLMs are increasingly deployed in open-ended, interactive environments, this static nature has become a critical bottleneck, necessitating agents that can adaptively reason, act, and evolve in real time. This paradigm shift -- from scaling static models to developing self-evolving agents -- has sparked growing interest in architectures and methods enabling continual learning and adaptation from data, interactions, and experiences. This survey provides the first systematic and comprehensive review of self-evolving agents, organized around three foundational dimensions -- what to evolve, when to evolve, and how to evolve. We examine evolutionary mechanisms across agent components (e.g., models, memory, tools, architecture), categorize adaptation methods by stages (e.g., intra-test-time, inter-test-time), and analyze the algorithmic and architectural designs that guide evolutionary adaptation (e.g., scalar rewards, textual feedback, single-agent and multi-agent systems). Additionally, we analyze evaluation metrics and benchmarks tailored for self-evolving agents, highlight applications in domains such as coding, education, and healthcare, and identify critical challenges and research directions in safety, scalability, and co-evolutionary dynamics. By providing a structured framework for understanding and designing self-evolving agents, this survey establishes a roadmap for advancing adaptive agentic systems in both research and real-world deployments, ultimately shedding lights to pave the way for the realization of Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI), where agents evolve autonomously, performing at or beyond human-level intelligence across a wide array of tasks.
Absolute Zero: Reinforced Self-play Reasoning with Zero Data
May 07, 2025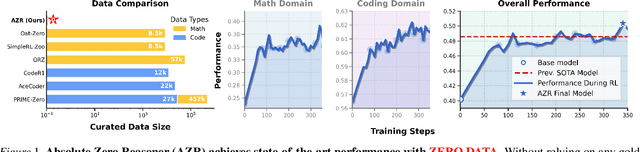
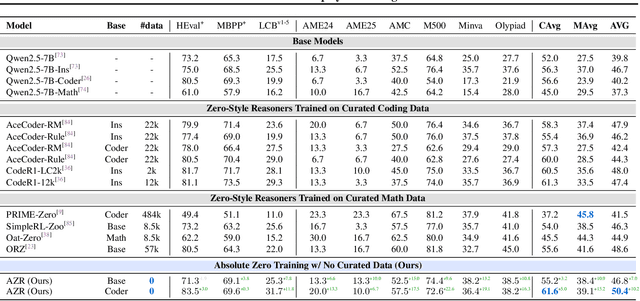
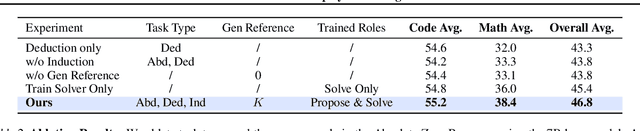
Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has shown promise in enhancing the reasoning capabilities of large language models by learning directly from outcome-based rewards. Recent RLVR works that operate under the zero setting avoid supervision in labeling the reasoning process, but still depend on manually curated collections of questions and answers for training. The scarcity of high-quality, human-produced examples raises concerns about the long-term scalability of relying on human supervision, a challenge already evident in the domain of language model pretraining. Furthermore, in a hypothetical future where AI surpasses human intelligence, tasks provided by humans may offer limited learning potential for a superintelligent system. To address these concerns, we propose a new RLVR paradigm called Absolute Zero, in which a single model learns to propose tasks that maximize its own learning progress and improves reasoning by solving them, without relying on any external data. Under this paradigm, we introduce the Absolute Zero Reasoner (AZR), a system that self-evolves its training curriculum and reasoning ability by using a code executor to both validate proposed code reasoning tasks and verify answers, serving as an unified source of verifiable reward to guide open-ended yet grounded learning. Despite being trained entirely without external data, AZR achieves overall SOTA performance on coding and mathematical reasoning tasks, outperforming existing zero-setting models that rely on tens of thousands of in-domain human-curated examples. Furthermore, we demonstrate that AZR can be effectively applied across different model scales and is compatible with various model classes.
Divide, Optimize, Merge: Fine-Grained LLM Agent Optimization at Scale
May 06, 2025Abstract:LLM-based optimization has shown remarkable potential in enhancing agentic systems. However, the conventional approach of prompting LLM optimizer with the whole training trajectories on training dataset in a single pass becomes untenable as datasets grow, leading to context window overflow and degraded pattern recognition. To address these challenges, we propose Fine-Grained Optimization (FGO), a scalable framework that divides large optimization tasks into manageable subsets, performs targeted optimizations, and systematically combines optimized components through progressive merging. Evaluation across ALFWorld, LogisticsQA, and GAIA benchmarks demonstrate that FGO outperforms existing approaches by 1.6-8.6% while reducing average prompt token consumption by 56.3%. Our framework provides a practical solution for scaling up LLM-based optimization of increasingly sophisticated agent systems. Further analysis demonstrates that FGO achieves the most consistent performance gain in all training dataset sizes, showcasing its scalability and efficiency.
Which Agent Causes Task Failures and When? On Automated Failure Attribution of LLM Multi-Agent Systems
Apr 30, 2025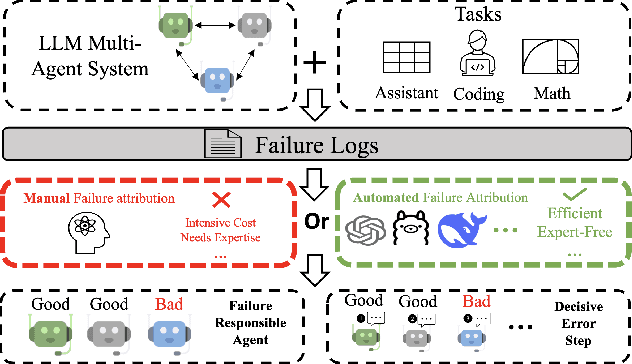
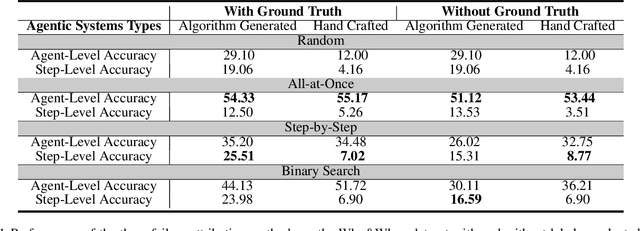
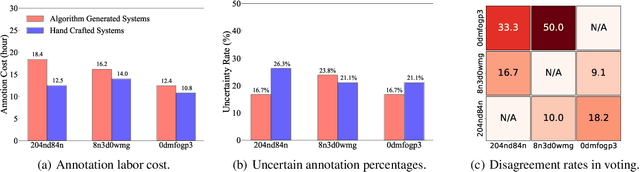

Abstract:Failure attribution in LLM multi-agent systems-identifying the agent and step responsible for task failures-provides crucial clues for systems debugging but remains underexplored and labor-intensive. In this paper, we propose and formulate a new research area: automated failure attribution for LLM multi-agent systems. To support this initiative, we introduce the Who&When dataset, comprising extensive failure logs from 127 LLM multi-agent systems with fine-grained annotations linking failures to specific agents and decisive error steps. Using the Who&When, we develop and evaluate three automated failure attribution methods, summarizing their corresponding pros and cons. The best method achieves 53.5% accuracy in identifying failure-responsible agents but only 14.2% in pinpointing failure steps, with some methods performing below random. Even SOTA reasoning models, such as OpenAI o1 and DeepSeek R1, fail to achieve practical usability. These results highlight the task's complexity and the need for further research in this area. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/mingyin1/Agents_Failure_Attribution
Nemotron-Research-Tool-N1: Tool-Using Language Models with Reinforced Reasoning
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Enabling large language models with external tools has become a pivotal strategy for extending their functionality beyond text generation tasks. Prior work typically enhances tool-use abilities by either applying supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to enforce tool-call correctness or distilling reasoning traces from stronger models for SFT. However, both approaches fall short, either omitting reasoning entirely or producing imitative reasoning that limits generalization. Inspired by the success of DeepSeek-R1 in eliciting reasoning through rule-based reinforcement learning, we develop the Nemotron-Research-Tool-N1 series of tool-using language models using a similar training paradigm. Instead of restrictively supervising intermediate reasoning traces distilled from stronger models, Nemotron-Research-Tool-N1 is optimized with a binary reward that evaluates only the structural validity and functional correctness of tool invocations. This lightweight supervision allows the model to autonomously internalize reasoning strategies, without the need for annotated reasoning trajectories. Experiments on the BFCL and API-Bank benchmarks show that Nemotron-Research-Tool-N1-7B and Nemotron-Research-Tool-N1-14B, built on Qwen-2.5-7B/14B-Instruct, achieve state-of-the-art results, outperforming GPT-4o on both evaluations.
Advances and Challenges in Foundation Agents: From Brain-Inspired Intelligence to Evolutionary, Collaborative, and Safe Systems
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:The advent of large language models (LLMs) has catalyzed a transformative shift in artificial intelligence, paving the way for advanced intelligent agents capable of sophisticated reasoning, robust perception, and versatile action across diverse domains. As these agents increasingly drive AI research and practical applications, their design, evaluation, and continuous improvement present intricate, multifaceted challenges. This survey provides a comprehensive overview, framing intelligent agents within a modular, brain-inspired architecture that integrates principles from cognitive science, neuroscience, and computational research. We structure our exploration into four interconnected parts. First, we delve into the modular foundation of intelligent agents, systematically mapping their cognitive, perceptual, and operational modules onto analogous human brain functionalities, and elucidating core components such as memory, world modeling, reward processing, and emotion-like systems. Second, we discuss self-enhancement and adaptive evolution mechanisms, exploring how agents autonomously refine their capabilities, adapt to dynamic environments, and achieve continual learning through automated optimization paradigms, including emerging AutoML and LLM-driven optimization strategies. Third, we examine collaborative and evolutionary multi-agent systems, investigating the collective intelligence emerging from agent interactions, cooperation, and societal structures, highlighting parallels to human social dynamics. Finally, we address the critical imperative of building safe, secure, and beneficial AI systems, emphasizing intrinsic and extrinsic security threats, ethical alignment, robustness, and practical mitigation strategies necessary for trustworthy real-world deployment.
Memory-Augmented Agent Training for Business Document Understanding
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Traditional enterprises face significant challenges in processing business documents, where tasks like extracting transport references from invoices remain largely manual despite their crucial role in logistics operations. While Large Language Models offer potential automation, their direct application to specialized business domains often yields unsatisfactory results. We introduce Matrix (Memory-Augmented agent Training through Reasoning and Iterative eXploration), a novel paradigm that enables LLM agents to progressively build domain expertise through experience-driven memory refinement and iterative learning. To validate this approach, we collaborate with one of the world's largest logistics companies to create a dataset of Universal Business Language format invoice documents, focusing on the task of transport reference extraction. Experiments demonstrate that Matrix outperforms prompting a single LLM by 30.3%, vanilla LLM agent by 35.2%. We further analyze the metrics of the optimized systems and observe that the agent system requires less API calls, fewer costs and can analyze longer documents on average. Our methods establish a new approach to transform general-purpose LLMs into specialized business tools through systematic memory enhancement in document processing tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge