Chi Wang
EffGen: Enabling Small Language Models as Capable Autonomous Agents
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Most existing language model agentic systems today are built and optimized for large language models (e.g., GPT, Claude, Gemini) via API calls. While powerful, this approach faces several limitations including high token costs and privacy concerns for sensitive applications. We introduce effGen, an open-source agentic framework optimized for small language models (SLMs) that enables effective, efficient, and secure local deployment (pip install effgen). effGen makes four major contributions: (1) Enhanced tool-calling with prompt optimization that compresses contexts by 70-80% while preserving task semantics, (2) Intelligent task decomposition that breaks complex queries into parallel or sequential subtasks based on dependencies, (3) Complexity-based routing using five factors to make smart pre-execution decisions, and (4) Unified memory system combining short-term, long-term, and vector-based storage. Additionally, effGen unifies multiple agent protocols (MCP, A2A, ACP) for cross-protocol communication. Results on 13 benchmarks show effGen outperforms LangChain, AutoGen, and Smolagents with higher success rates, faster execution, and lower memory. Our results reveal that prompt optimization and complexity routing have complementary scaling behavior: optimization benefits SLMs more (11.2% gain at 1.5B vs 2.4% at 32B), while routing benefits large models more (3.6% at 1.5B vs 7.9% at 32B), providing consistent gains across all scales when combined. effGen (https://effgen.org/) is released under the MIT License, ensuring broad accessibility for research and commercial use. Our framework code is publicly available at https://github.com/ctrl-gaurav/effGen.
GeoNorm: Unify Pre-Norm and Post-Norm with Geodesic Optimization
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:The placement of normalization layers, specifically Pre-Norm and Post-Norm, remains an open question in Transformer architecture design. In this work, we rethink these approaches through the lens of manifold optimization, interpreting the outputs of the Feed-Forward Network (FFN) and attention layers as update directions in optimization. Building on this perspective, we introduce GeoNorm, a novel method that replaces standard normalization with geodesic updates on the manifold. Furthermore, analogous to learning rate schedules, we propose a layer-wise update decay for the FFN and attention components. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that GeoNorm consistently outperforms existing normalization methods in Transformer models. Crucially, GeoNorm can be seamlessly integrated into standard Transformer architectures, achieving performance improvements with negligible additional computational cost.
Breaking the Resolution Barrier: Arbitrary-resolution Deep Image Steganography Framework
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Deep image steganography (DIS) has achieved significant results in capacity and invisibility. However, current paradigms enforce the secret image to maintain the same resolution as the cover image during hiding and revealing. This leads to two challenges: secret images with inconsistent resolutions must undergo resampling beforehand which results in detail loss during recovery, and the secret image cannot be recovered to its original resolution when the resolution value is unknown. To address these, we propose ARDIS, the first Arbitrary Resolution DIS framework, which shifts the paradigm from discrete mapping to reference-guided continuous signal reconstruction. Specifically, to minimize the detail loss caused by resolution mismatch, we first design a Frequency Decoupling Architecture in hiding stage. It disentangles the secret into a resolution-aligned global basis and a resolution-agnostic high-frequency latent to hide in a fixed-resolution cover. Second, for recovery, we propose a Latent-Guided Implicit Reconstructor to perform deterministic restoration. The recovered detail latent code modulates a continuous implicit function to accurately query and render high-frequency residuals onto the recovered global basis, ensuring faithful restoration of original details. Furthermore, to achieve blind recovery, we introduce an Implicit Resolution Coding strategy. By transforming discrete resolution values into dense feature maps and hiding them in the redundant space of the feature domain, the reconstructor can correctly decode the secret's resolution directly from the steganographic representation. Experimental results demonstrate that ARDIS significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both invisibility and cross-resolution recovery fidelity.
Agentic Reasoning for Large Language Models
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Reasoning is a fundamental cognitive process underlying inference, problem-solving, and decision-making. While large language models (LLMs) demonstrate strong reasoning capabilities in closed-world settings, they struggle in open-ended and dynamic environments. Agentic reasoning marks a paradigm shift by reframing LLMs as autonomous agents that plan, act, and learn through continual interaction. In this survey, we organize agentic reasoning along three complementary dimensions. First, we characterize environmental dynamics through three layers: foundational agentic reasoning, which establishes core single-agent capabilities including planning, tool use, and search in stable environments; self-evolving agentic reasoning, which studies how agents refine these capabilities through feedback, memory, and adaptation; and collective multi-agent reasoning, which extends intelligence to collaborative settings involving coordination, knowledge sharing, and shared goals. Across these layers, we distinguish in-context reasoning, which scales test-time interaction through structured orchestration, from post-training reasoning, which optimizes behaviors via reinforcement learning and supervised fine-tuning. We further review representative agentic reasoning frameworks across real-world applications and benchmarks, including science, robotics, healthcare, autonomous research, and mathematics. This survey synthesizes agentic reasoning methods into a unified roadmap bridging thought and action, and outlines open challenges and future directions, including personalization, long-horizon interaction, world modeling, scalable multi-agent training, and governance for real-world deployment.
From Spurious to Causal: Low-rank Orthogonal Subspace Intervention for Generalizable Face Forgery Detection
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:The generalization problem remains a critical challenge in face forgery detection. Some researches have discovered that ``a backdoor path" in the representations from forgery-irrelevant information to labels induces biased learning, thereby hindering the generalization. In this paper, these forgery-irrelevant information are collectively termed spurious correlations factors. Previous methods predominantly focused on identifying concrete, specific spurious correlation and designing corresponding solutions to address them. However, spurious correlations arise from unobservable confounding factors, making it impractical to identify and address each one individually. To address this, we propose an intervention paradigm for representation space. Instead of tracking and blocking various instance-level spurious correlation one by one, we uniformly model them as a low-rank subspace and intervene in them. Specifically, we decompose spurious correlation features into a low-rank subspace via orthogonal low-rank projection, subsequently removing this subspace from the original representation and training its orthogonal complement to capture forgery-related features. This low-rank projection removal effectively eliminates spurious correlation factors, ensuring that classification decision is based on authentic forgery cues. With only 0.43M trainable parameters, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance across several benchmarks, demonstrating excellent robustness and generalization.
PACEvolve: Enabling Long-Horizon Progress-Aware Consistent Evolution
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged as powerful operators for evolutionary search, yet the design of efficient search scaffolds remains ad hoc. While promising, current LLM-in-the-loop systems lack a systematic approach to managing the evolutionary process. We identify three distinct failure modes: Context Pollution, where experiment history biases future candidate generation; Mode Collapse, where agents stagnate in local minima due to poor exploration-exploitation balance; and Weak Collaboration, where rigid crossover strategies fail to leverage parallel search trajectories effectively. We introduce Progress-Aware Consistent Evolution (PACEvolve), a framework designed to robustly govern the agent's context and search dynamics, to address these challenges. PACEvolve combines hierarchical context management (HCM) with pruning to address context pollution; momentum-based backtracking (MBB) to escape local minima; and a self-adaptive sampling policy that unifies backtracking and crossover for dynamic search coordination (CE), allowing agents to balance internal refinement with cross-trajectory collaboration. We demonstrate that PACEvolve provides a systematic path to consistent, long-horizon self-improvement, achieving state-of-the-art results on LLM-SR and KernelBench, while discovering solutions surpassing the record on Modded NanoGPT.
FashionMAC: Deformation-Free Fashion Image Generation with Fine-Grained Model Appearance Customization
Nov 18, 2025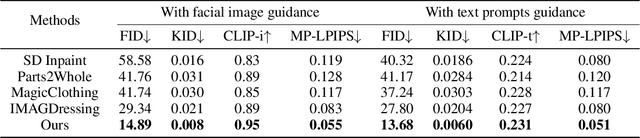
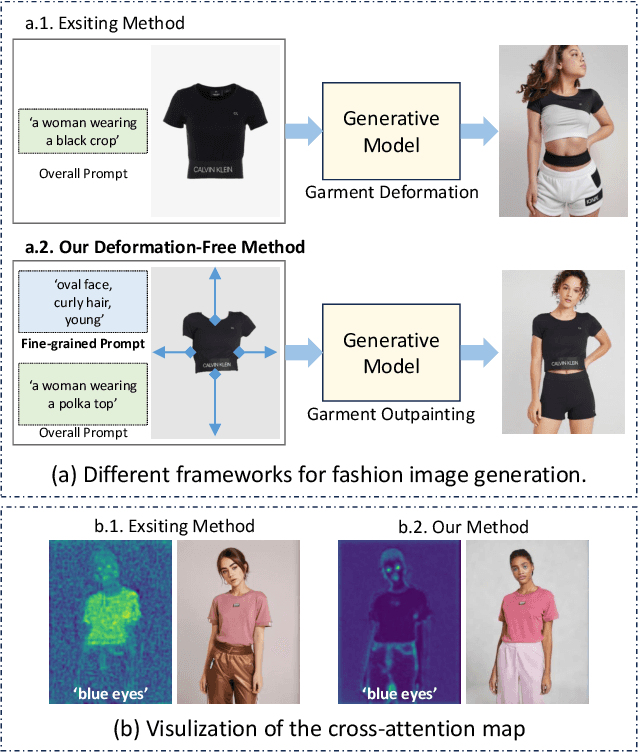
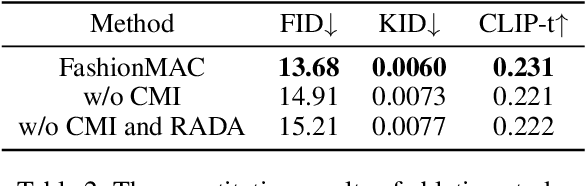
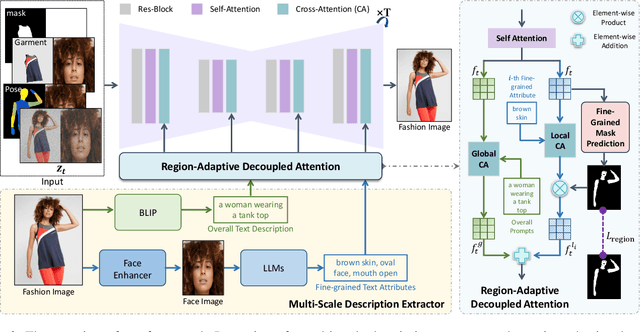
Abstract:Garment-centric fashion image generation aims to synthesize realistic and controllable human models dressing a given garment, which has attracted growing interest due to its practical applications in e-commerce. The key challenges of the task lie in two aspects: (1) faithfully preserving the garment details, and (2) gaining fine-grained controllability over the model's appearance. Existing methods typically require performing garment deformation in the generation process, which often leads to garment texture distortions. Also, they fail to control the fine-grained attributes of the generated models, due to the lack of specifically designed mechanisms. To address these issues, we propose FashionMAC, a novel diffusion-based deformation-free framework that achieves high-quality and controllable fashion showcase image generation. The core idea of our framework is to eliminate the need for performing garment deformation and directly outpaint the garment segmented from a dressed person, which enables faithful preservation of the intricate garment details. Moreover, we propose a novel region-adaptive decoupled attention (RADA) mechanism along with a chained mask injection strategy to achieve fine-grained appearance controllability over the synthesized human models. Specifically, RADA adaptively predicts the generated regions for each fine-grained text attribute and enforces the text attribute to focus on the predicted regions by a chained mask injection strategy, significantly enhancing the visual fidelity and the controllability. Extensive experiments validate the superior performance of our framework compared to existing state-of-the-art methods.
The Denario project: Deep knowledge AI agents for scientific discovery
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:We present Denario, an AI multi-agent system designed to serve as a scientific research assistant. Denario can perform many different tasks, such as generating ideas, checking the literature, developing research plans, writing and executing code, making plots, and drafting and reviewing a scientific paper. The system has a modular architecture, allowing it to handle specific tasks, such as generating an idea, or carrying out end-to-end scientific analysis using Cmbagent as a deep-research backend. In this work, we describe in detail Denario and its modules, and illustrate its capabilities by presenting multiple AI-generated papers generated by it in many different scientific disciplines such as astrophysics, biology, biophysics, biomedical informatics, chemistry, material science, mathematical physics, medicine, neuroscience and planetary science. Denario also excels at combining ideas from different disciplines, and we illustrate this by showing a paper that applies methods from quantum physics and machine learning to astrophysical data. We report the evaluations performed on these papers by domain experts, who provided both numerical scores and review-like feedback. We then highlight the strengths, weaknesses, and limitations of the current system. Finally, we discuss the ethical implications of AI-driven research and reflect on how such technology relates to the philosophy of science. We publicly release the code at https://github.com/AstroPilot-AI/Denario. A Denario demo can also be run directly on the web at https://huggingface.co/spaces/astropilot-ai/Denario, and the full app will be deployed on the cloud.
Prompt-Induced Linguistic Fingerprints for LLM-Generated Fake News Detection
Aug 18, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid development of large language models, the generation of fake news has become increasingly effortless, posing a growing societal threat and underscoring the urgent need for reliable detection methods. Early efforts to identify LLM-generated fake news have predominantly focused on the textual content itself; however, because much of that content may appear coherent and factually consistent, the subtle traces of falsification are often difficult to uncover. Through distributional divergence analysis, we uncover prompt-induced linguistic fingerprints: statistically distinct probability shifts between LLM-generated real and fake news when maliciously prompted. Based on this insight, we propose a novel method named Linguistic Fingerprints Extraction (LIFE). By reconstructing word-level probability distributions, LIFE can find discriminative patterns that facilitate the detection of LLM-generated fake news. To further amplify these fingerprint patterns, we also leverage key-fragment techniques that accentuate subtle linguistic differences, thereby improving detection reliability. Our experiments show that LIFE achieves state-of-the-art performance in LLM-generated fake news and maintains high performance in human-written fake news. The code and data are available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/LIFE-E86A.
Open Source Planning & Control System with Language Agents for Autonomous Scientific Discovery
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:We present a multi-agent system for automation of scientific research tasks, cmbagent. The system is formed by about 30 Large Language Model (LLM) agents and implements a Planning & Control strategy to orchestrate the agentic workflow, with no human-in-the-loop at any point. Each agent specializes in a different task (performing retrieval on scientific papers and codebases, writing code, interpreting results, critiquing the output of other agents) and the system is able to execute code locally. We successfully apply cmbagent to carry out a PhD level cosmology task (the measurement of cosmological parameters using supernova data) and evaluate its performance on two benchmark sets, finding superior performance over state-of-the-art LLMs. The source code is available on GitHub, demonstration videos are also available, and the system is deployed on HuggingFace and will be available on the cloud.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge