Tianhao Peng
Probing Scientific General Intelligence of LLMs with Scientist-Aligned Workflows
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Despite advances in scientific AI, a coherent framework for Scientific General Intelligence (SGI)-the ability to autonomously conceive, investigate, and reason across scientific domains-remains lacking. We present an operational SGI definition grounded in the Practical Inquiry Model (PIM: Deliberation, Conception, Action, Perception) and operationalize it via four scientist-aligned tasks: deep research, idea generation, dry/wet experiments, and experimental reasoning. SGI-Bench comprises over 1,000 expert-curated, cross-disciplinary samples inspired by Science's 125 Big Questions, enabling systematic evaluation of state-of-the-art LLMs. Results reveal gaps: low exact match (10--20%) in deep research despite step-level alignment; ideas lacking feasibility and detail; high code executability but low execution result accuracy in dry experiments; low sequence fidelity in wet protocols; and persistent multimodal comparative-reasoning challenges. We further introduce Test-Time Reinforcement Learning (TTRL), which optimizes retrieval-augmented novelty rewards at inference, enhancing hypothesis novelty without reference answer. Together, our PIM-grounded definition, workflow-centric benchmark, and empirical insights establish a foundation for AI systems that genuinely participate in scientific discovery.
MVU-Eval: Towards Multi-Video Understanding Evaluation for Multimodal LLMs
Nov 13, 2025
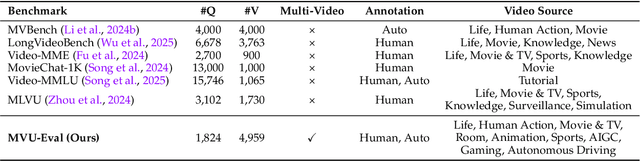
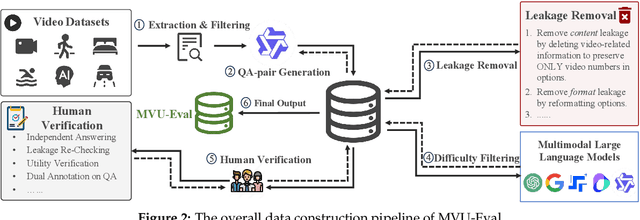
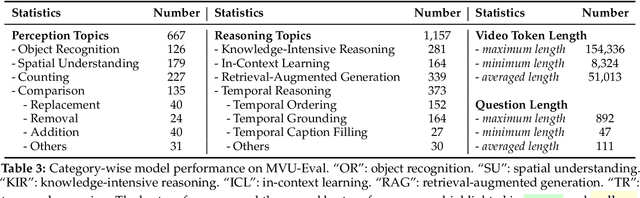
Abstract:The advent of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) has expanded AI capabilities to visual modalities, yet existing evaluation benchmarks remain limited to single-video understanding, overlooking the critical need for multi-video understanding in real-world scenarios (e.g., sports analytics and autonomous driving). To address this significant gap, we introduce MVU-Eval, the first comprehensive benchmark for evaluating Multi-Video Understanding for MLLMs. Specifically, our MVU-Eval mainly assesses eight core competencies through 1,824 meticulously curated question-answer pairs spanning 4,959 videos from diverse domains, addressing both fundamental perception tasks and high-order reasoning tasks. These capabilities are rigorously aligned with real-world applications such as multi-sensor synthesis in autonomous systems and cross-angle sports analytics. Through extensive evaluation of state-of-the-art open-source and closed-source models, we reveal significant performance discrepancies and limitations in current MLLMs' ability to perform understanding across multiple videos. The benchmark will be made publicly available to foster future research.
Agent KB: Leveraging Cross-Domain Experience for Agentic Problem Solving
Jul 08, 2025Abstract:As language agents tackle increasingly complex tasks, they struggle with effective error correction and experience reuse across domains. We introduce Agent KB, a hierarchical experience framework that enables complex agentic problem solving via a novel Reason-Retrieve-Refine pipeline. Agent KB addresses a core limitation: agents traditionally cannot learn from each other's experiences. By capturing both high-level strategies and detailed execution logs, Agent KB creates a shared knowledge base that enables cross-agent knowledge transfer. Evaluated on the GAIA benchmark, Agent KB improves success rates by up to 16.28 percentage points. On the most challenging tasks, Claude-3 improves from 38.46% to 57.69%, while GPT-4 improves from 53.49% to 73.26% on intermediate tasks. On SWE-bench code repair, Agent KB enables Claude-3 to improve from 41.33% to 53.33%. Our results suggest that Agent KB provides a modular, framework-agnostic infrastructure for enabling agents to learn from past experiences and generalize successful strategies to new tasks.
A Survey on Latent Reasoning
Jul 08, 2025


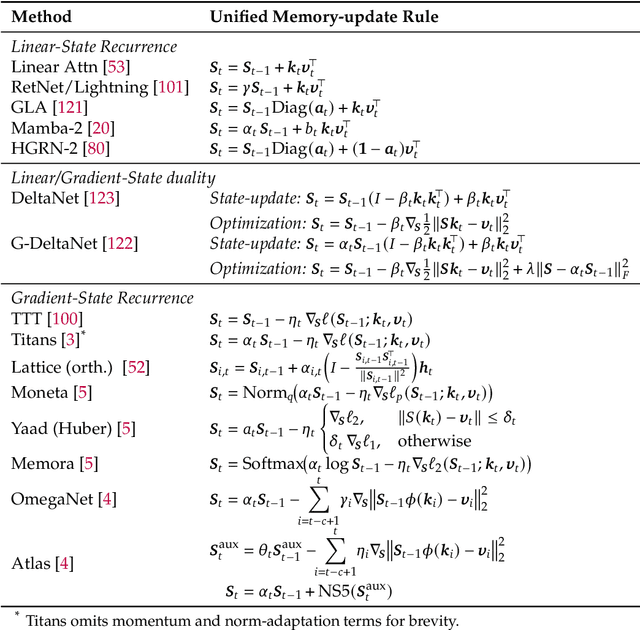
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive reasoning capabilities, especially when guided by explicit chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning that verbalizes intermediate steps. While CoT improves both interpretability and accuracy, its dependence on natural language reasoning limits the model's expressive bandwidth. Latent reasoning tackles this bottleneck by performing multi-step inference entirely in the model's continuous hidden state, eliminating token-level supervision. To advance latent reasoning research, this survey provides a comprehensive overview of the emerging field of latent reasoning. We begin by examining the foundational role of neural network layers as the computational substrate for reasoning, highlighting how hierarchical representations support complex transformations. Next, we explore diverse latent reasoning methodologies, including activation-based recurrence, hidden state propagation, and fine-tuning strategies that compress or internalize explicit reasoning traces. Finally, we discuss advanced paradigms such as infinite-depth latent reasoning via masked diffusion models, which enable globally consistent and reversible reasoning processes. By unifying these perspectives, we aim to clarify the conceptual landscape of latent reasoning and chart future directions for research at the frontier of LLM cognition. An associated GitHub repository collecting the latest papers and repos is available at: https://github.com/multimodal-art-projection/LatentCoT-Horizon/.
Instance Data Condensation for Image Super-Resolution
May 27, 2025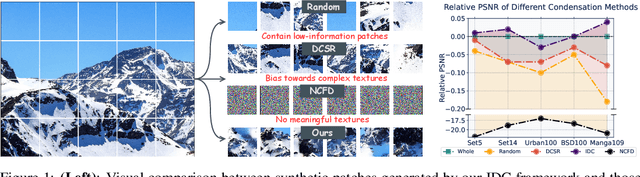
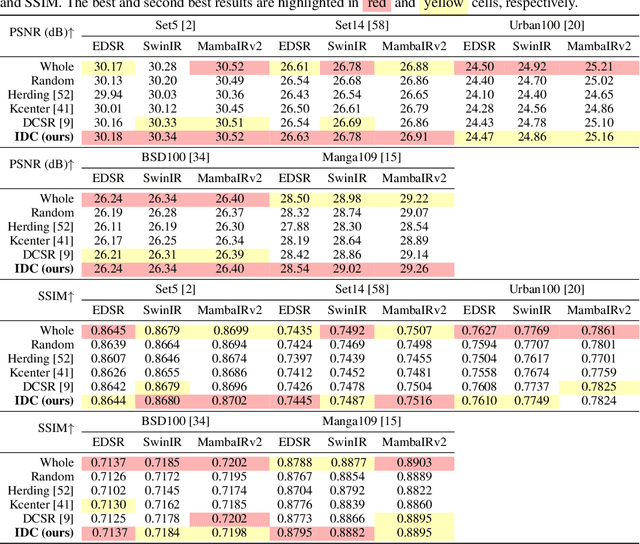
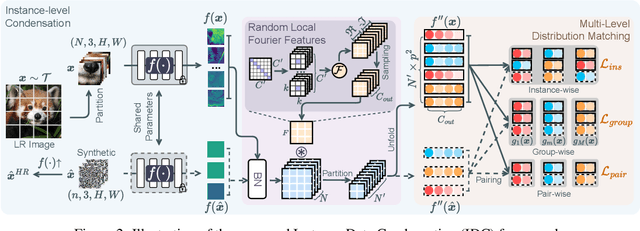
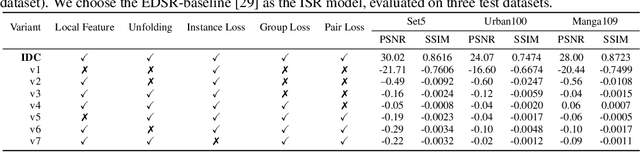
Abstract:Deep learning based image Super-Resolution (ISR) relies on large training datasets to optimize model generalization; this requires substantial computational and storage resources during training. While dataset condensation has shown potential in improving data efficiency and privacy for high-level computer vision tasks, it has not yet been fully exploited for ISR. In this paper, we propose a novel Instance Data Condensation (IDC) framework specifically for ISR, which achieves instance-level data condensation through Random Local Fourier Feature Extraction and Multi-level Feature Distribution Matching. This aims to optimize feature distributions at both global and local levels and obtain high-quality synthesized training content with fine detail. This framework has been utilized to condense the most commonly used training dataset for ISR, DIV2K, with a 10% condensation rate. The resulting synthetic dataset offers comparable or (in certain cases) even better performance compared to the original full dataset and excellent training stability when used to train various popular ISR models. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that a condensed/synthetic dataset (with a 10% data volume) has demonstrated such performance. The source code and the synthetic dataset have been made available at https://github.com/.
GIViC: Generative Implicit Video Compression
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:While video compression based on implicit neural representations (INRs) has recently demonstrated great potential, existing INR-based video codecs still cannot achieve state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance compared to their conventional or autoencoder-based counterparts given the same coding configuration. In this context, we propose a Generative Implicit Video Compression framework, GIViC, aiming at advancing the performance limits of this type of coding methods. GIViC is inspired by the characteristics that INRs share with large language and diffusion models in exploiting long-term dependencies. Through the newly designed implicit diffusion process, GIViC performs diffusive sampling across coarse-to-fine spatiotemporal decompositions, gradually progressing from coarser-grained full-sequence diffusion to finer-grained per-token diffusion. A novel Hierarchical Gated Linear Attention-based transformer (HGLA), is also integrated into the framework, which dual-factorizes global dependency modeling along scale and sequential axes. The proposed GIViC model has been benchmarked against SOTA conventional and neural codecs using a Random Access (RA) configuration (YUV 4:2:0, GOPSize=32), and yields BD-rate savings of 15.94%, 22.46% and 8.52% over VVC VTM, DCVC-FM and NVRC, respectively. As far as we are aware, GIViC is the first INR-based video codec that outperforms VTM based on the RA coding configuration. The source code will be made available.
SOLA-GCL: Subgraph-Oriented Learnable Augmentation Method for Graph Contrastive Learning
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:Graph contrastive learning has emerged as a powerful technique for learning graph representations that are robust and discriminative. However, traditional approaches often neglect the critical role of subgraph structures, particularly the intra-subgraph characteristics and inter-subgraph relationships, which are crucial for generating informative and diverse contrastive pairs. These subgraph features are crucial as they vary significantly across different graph types, such as social networks where they represent communities, and biochemical networks where they symbolize molecular interactions. To address this issue, our work proposes a novel subgraph-oriented learnable augmentation method for graph contrastive learning, termed SOLA-GCL, that centers around subgraphs, taking full advantage of the subgraph information for data augmentation. Specifically, SOLA-GCL initially partitions a graph into multiple densely connected subgraphs based on their intrinsic properties. To preserve and enhance the unique characteristics inherent to subgraphs, a graph view generator optimizes augmentation strategies for each subgraph, thereby generating tailored views for graph contrastive learning. This generator uses a combination of intra-subgraph and inter-subgraph augmentation strategies, including node dropping, feature masking, intra-edge perturbation, inter-edge perturbation, and subgraph swapping. Extensive experiments have been conducted on various graph learning applications, ranging from social networks to molecules, under semi-supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and transfer learning settings to demonstrate the superiority of our proposed approach over the state-of-the-art in GCL.
HIIF: Hierarchical Encoding based Implicit Image Function for Continuous Super-resolution
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in implicit neural representations (INRs) have shown significant promise in modeling visual signals for various low-vision tasks including image super-resolution (ISR). INR-based ISR methods typically learn continuous representations, providing flexibility for generating high-resolution images at any desired scale from their low-resolution counterparts. However, existing INR-based ISR methods utilize multi-layer perceptrons for parameterization in the network; this does not take account of the hierarchical structure existing in local sampling points and hence constrains the representation capability. In this paper, we propose a new \textbf{H}ierarchical encoding based \textbf{I}mplicit \textbf{I}mage \textbf{F}unction for continuous image super-resolution, \textbf{HIIF}, which leverages a novel hierarchical positional encoding that enhances the local implicit representation, enabling it to capture fine details at multiple scales. Our approach also embeds a multi-head linear attention mechanism within the implicit attention network by taking additional non-local information into account. Our experiments show that, when integrated with different backbone encoders, HIIF outperforms the state-of-the-art continuous image super-resolution methods by up to 0.17dB in PSNR. The source code of HIIF will be made publicly available at \url{www.github.com}.
Pre-trained Molecular Language Models with Random Functional Group Masking
Nov 03, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in computational chemistry have leveraged the power of trans-former-based language models, such as MoLFormer, pre-trained using a vast amount of simplified molecular-input line-entry system (SMILES) sequences, to understand and predict molecular properties and activities, a critical step in fields like drug discovery and materials science. To further improve performance, researchers have introduced graph neural networks with graph-based molecular representations, such as GEM, incorporating the topology, geometry, 2D or even 3D structures of molecules into pre-training. While most of molecular graphs in existing studies were automatically converted from SMILES sequences, it is to assume that transformer-based language models might be able to implicitly learn structure-aware representations from SMILES sequences. In this paper, we propose \ours{} -- a SMILES-based \underline{\em M}olecular \underline{\em L}anguage \underline{\em M}odel, which randomly masking SMILES subsequences corresponding to specific molecular \underline{\em F}unctional \underline{\em G}roups to incorporate structure information of atoms during the pre-training phase. This technique aims to compel the model to better infer molecular structures and properties, thus enhancing its predictive capabilities. Extensive experimental evaluations across 11 benchmark classification and regression tasks in the chemical domain demonstrate the robustness and superiority of \ours{}. Our findings reveal that \ours{} outperforms existing pre-training models, either based on SMILES or graphs, in 9 out of the 11 downstream tasks, ranking as a close second in the remaining ones.
RMT-BVQA: Recurrent Memory Transformer-based Blind Video Quality Assessment for Enhanced Video Content
May 15, 2024Abstract:With recent advances in deep learning, numerous algorithms have been developed to enhance video quality, reduce visual artefacts and improve perceptual quality. However, little research has been reported on the quality assessment of enhanced content - the evaluation of enhancement methods is often based on quality metrics that were designed for compression applications. In this paper, we propose a novel blind deep video quality assessment (VQA) method specifically for enhanced video content. It employs a new Recurrent Memory Transformer (RMT) based network architecture to obtain video quality representations, which is optimised through a novel content-quality-aware contrastive learning strategy based on a new database containing 13K training patches with enhanced content. The extracted quality representations are then combined through linear regression to generate video-level quality indices. The proposed method, RMT-BVQA, has been evaluated on the VDPVE (VQA Dataset for Perceptual Video Enhancement) database through a five-fold cross validation. The results show its superior correlation performance when compared to ten existing no-reference quality metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge