Shan Liu
Tracking Drift: Variation-Aware Entropy Scheduling for Non-Stationary Reinforcement Learning
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Real-world reinforcement learning often faces environment drift, but most existing methods rely on static entropy coefficients/target entropy, causing over-exploration during stable periods and under-exploration after drift (thus slow recovery), and leaving unanswered the principled question of how exploration intensity should scale with drift magnitude. We prove that entropy scheduling under non-stationarity can be reduced to a one-dimensional, round-by-round trade-off, faster tracking of the optimal solution after drift vs. avoiding gratuitous randomness when the environment is stable, so exploration strength can be driven by measurable online drift signals. Building on this, we propose AES (Adaptive Entropy Scheduling), which adaptively adjusts the entropy coefficient/temperature online using observable drift proxies during training, requiring almost no structural changes and incurring minimal overhead. Across 4 algorithm variants, 12 tasks, and 4 drift modes, AES significantly reduces the fraction of performance degradation caused by drift and accelerates recovery after abrupt changes.
DALD-PCAC: Density-Adaptive Learning Descriptor for Point Cloud Lossless Attribute Compression
Jan 18, 2026Abstract:Recently, deep learning has significantly advanced the performance of point cloud geometry compression. However, the learning-based lossless attribute compression of point clouds with varying densities is under-explored. In this paper, we develop a learning-based framework, namely DALD-PCAC that leverages Levels of Detail (LoD) to tailor for point cloud lossless attribute compression. We develop a point-wise attention model using a permutation-invariant Transformer to tackle the challenges of sparsity and irregularity of point clouds during context modeling. We also propose a Density-Adaptive Learning Descriptor (DALD) capable of capturing structure and correlations among points across a large range of neighbors. In addition, we develop a prior-guided block partitioning to reduce the attribute variance within blocks and enhance the performance. Experiments on LiDAR and object point clouds show that DALD-PCAC achieves the state-of-the-art performance on most data. Our method boosts the compression performance and is robust to the varying densities of point clouds. Moreover, it guarantees a good trade-off between performance and complexity, exhibiting great potential in real-world applications. The source code is available at https://github.com/zb12138/DALD_PCAC.
SOLID: a Framework of Synergizing Optimization and LLMs for Intelligent Decision-Making
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces SOLID (Synergizing Optimization and Large Language Models for Intelligent Decision-Making), a novel framework that integrates mathematical optimization with the contextual capabilities of large language models (LLMs). SOLID facilitates iterative collaboration between optimization and LLMs agents through dual prices and deviation penalties. This interaction improves the quality of the decisions while maintaining modularity and data privacy. The framework retains theoretical convergence guarantees under convexity assumptions, providing insight into the design of LLMs prompt. To evaluate SOLID, we applied it to a stock portfolio investment case with historical prices and financial news as inputs. Empirical results demonstrate convergence under various scenarios and indicate improved annualized returns compared to a baseline optimizer-only method, validating the synergy of the two agents. SOLID offers a promising framework for advancing automated and intelligent decision-making across diverse domains.
Cross-architecture universal feature coding via distribution alignment
Jun 15, 2025Abstract:Feature coding has become increasingly important in scenarios where semantic representations rather than raw pixels are transmitted and stored. However, most existing methods are architecture-specific, targeting either CNNs or Transformers. This design limits their applicability in real-world scenarios where features from both architectures coexist. To address this gap, we introduce a new research problem: cross-architecture universal feature coding (CAUFC), which seeks to build a unified codec that can effectively compress features from heterogeneous architectures. To tackle this challenge, we propose a two-step distribution alignment method. First, we design the format alignment method that unifies CNN and Transformer features into a consistent 2D token format. Second, we propose the feature value alignment method that harmonizes statistical distributions via truncation and normalization. As a first attempt to study CAUFC, we evaluate our method on the image classification task. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves superior rate-accuracy trade-offs compared to the architecture-specific baseline. This work marks an initial step toward universal feature compression across heterogeneous model architectures.
Instance Data Condensation for Image Super-Resolution
May 27, 2025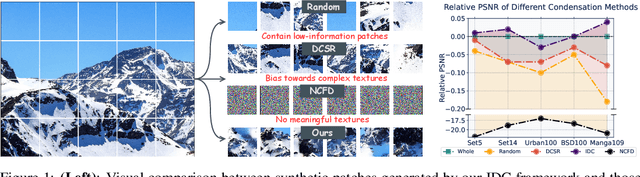
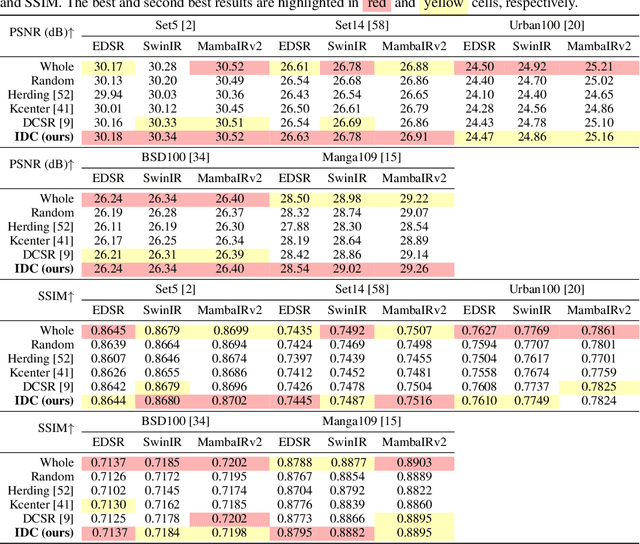
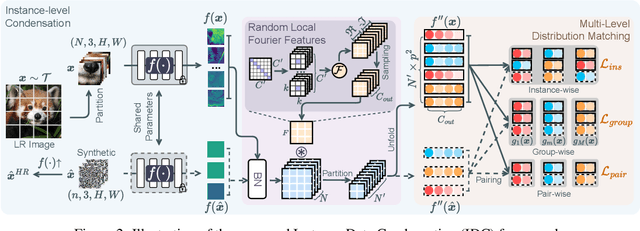
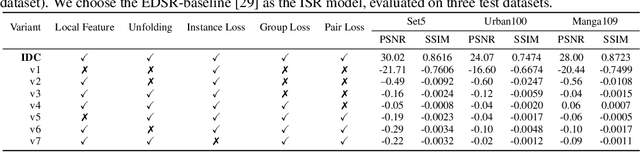
Abstract:Deep learning based image Super-Resolution (ISR) relies on large training datasets to optimize model generalization; this requires substantial computational and storage resources during training. While dataset condensation has shown potential in improving data efficiency and privacy for high-level computer vision tasks, it has not yet been fully exploited for ISR. In this paper, we propose a novel Instance Data Condensation (IDC) framework specifically for ISR, which achieves instance-level data condensation through Random Local Fourier Feature Extraction and Multi-level Feature Distribution Matching. This aims to optimize feature distributions at both global and local levels and obtain high-quality synthesized training content with fine detail. This framework has been utilized to condense the most commonly used training dataset for ISR, DIV2K, with a 10% condensation rate. The resulting synthetic dataset offers comparable or (in certain cases) even better performance compared to the original full dataset and excellent training stability when used to train various popular ISR models. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first time that a condensed/synthetic dataset (with a 10% data volume) has demonstrated such performance. The source code and the synthetic dataset have been made available at https://github.com/.
Distribution Guidance Network for Weakly Supervised Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation
Oct 10, 2024



Abstract:Despite alleviating the dependence on dense annotations inherent to fully supervised methods, weakly supervised point cloud semantic segmentation suffers from inadequate supervision signals. In response to this challenge, we introduce a novel perspective that imparts auxiliary constraints by regulating the feature space under weak supervision. Our initial investigation identifies which distributions accurately characterize the feature space, subsequently leveraging this priori to guide the alignment of the weakly supervised embeddings. Specifically, we analyze the superiority of the mixture of von Mises-Fisher distributions (moVMF) among several common distribution candidates. Accordingly, we develop a Distribution Guidance Network (DGNet), which comprises a weakly supervised learning branch and a distribution alignment branch. Leveraging reliable clustering initialization derived from the weakly supervised learning branch, the distribution alignment branch alternately updates the parameters of the moVMF and the network, ensuring alignment with the moVMF-defined latent space. Extensive experiments validate the rationality and effectiveness of our distribution choice and network design. Consequently, DGNet achieves state-of-the-art performance under multiple datasets and various weakly supervised settings.
AIM 2024 Challenge on Compressed Video Quality Assessment: Methods and Results
Aug 21, 2024
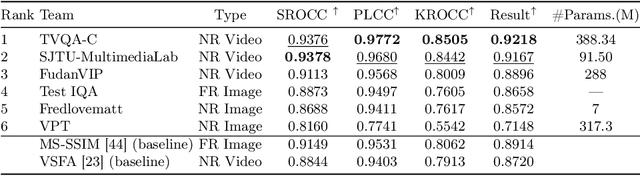
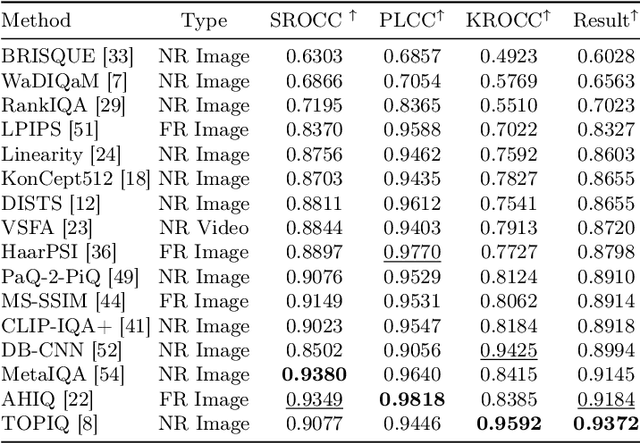
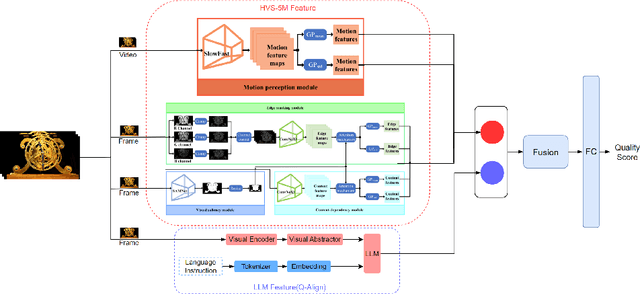
Abstract:Video quality assessment (VQA) is a crucial task in the development of video compression standards, as it directly impacts the viewer experience. This paper presents the results of the Compressed Video Quality Assessment challenge, held in conjunction with the Advances in Image Manipulation (AIM) workshop at ECCV 2024. The challenge aimed to evaluate the performance of VQA methods on a diverse dataset of 459 videos, encoded with 14 codecs of various compression standards (AVC/H.264, HEVC/H.265, AV1, and VVC/H.266) and containing a comprehensive collection of compression artifacts. To measure the methods performance, we employed traditional correlation coefficients between their predictions and subjective scores, which were collected via large-scale crowdsourced pairwise human comparisons. For training purposes, participants were provided with the Compressed Video Quality Assessment Dataset (CVQAD), a previously developed dataset of 1022 videos. Up to 30 participating teams registered for the challenge, while we report the results of 6 teams, which submitted valid final solutions and code for reproducing the results. Moreover, we calculated and present the performance of state-of-the-art VQA methods on the developed dataset, providing a comprehensive benchmark for future research. The dataset, results, and online leaderboard are publicly available at https://challenges.videoprocessing.ai/challenges/compressed-video-quality-assessment.html.
BVI-UGC: A Video Quality Database for User-Generated Content Transcoding
Aug 13, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, user-generated content (UGC) has become one of the major video types consumed via streaming networks. Numerous research contributions have focused on assessing its visual quality through subjective tests and objective modeling. In most cases, objective assessments are based on a no-reference scenario, where the corresponding reference content is assumed not to be available. However, full-reference video quality assessment is also important for UGC in the delivery pipeline, particularly associated with the video transcoding process. In this context, we present a new UGC video quality database, BVI-UGC, for user-generated content transcoding, which contains 60 (non-pristine) reference videos and 1,080 test sequences. In this work, we simulated the creation of non-pristine reference sequences (with a wide range of compression distortions), typical of content uploaded to UGC platforms for transcoding. A comprehensive crowdsourced subjective study was then conducted involving more than 3,500 human participants. Based on this collected subjective data, we benchmarked the performance of 10 full-reference and 11 no-reference quality metrics. Our results demonstrate the poor performance (SROCC values are lower than 0.6) of these metrics in predicting the perceptual quality of UGC in two different scenarios (with or without a reference).
Perception-Guided Quality Metric of 3D Point Clouds Using Hybrid Strategy
Jul 04, 2024Abstract:Full-reference point cloud quality assessment (FR-PCQA) aims to infer the quality of distorted point clouds with available references. Most of the existing FR-PCQA metrics ignore the fact that the human visual system (HVS) dynamically tackles visual information according to different distortion levels (i.e., distortion detection for high-quality samples and appearance perception for low-quality samples) and measure point cloud quality using unified features. To bridge the gap, in this paper, we propose a perception-guided hybrid metric (PHM) that adaptively leverages two visual strategies with respect to distortion degree to predict point cloud quality: to measure visible difference in high-quality samples, PHM takes into account the masking effect and employs texture complexity as an effective compensatory factor for absolute difference; on the other hand, PHM leverages spectral graph theory to evaluate appearance degradation in low-quality samples. Variations in geometric signals on graphs and changes in the spectral graph wavelet coefficients are utilized to characterize geometry and texture appearance degradation, respectively. Finally, the results obtained from the two components are combined in a non-linear method to produce an overall quality score of the tested point cloud. The results of the experiment on five independent databases show that PHM achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance and offers significant performance improvement in multiple distortion environments. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/zhangyujie-1998/PHM.
Video Coding with Cross-Component Sample Offset
Jun 03, 2024



Abstract:Beyond the exploration of traditional spatial, temporal and subjective visual signal redundancy in image and video compression, recent research has focused on leveraging cross-color component redundancy to enhance coding efficiency. Cross-component coding approaches are motivated by the statistical correlations among different color components, such as those in the Y'CbCr color space, where luma (Y) color component typically exhibits finer details than chroma (Cb/Cr) color components. Inspired by previous cross-component coding algorithms, this paper introduces a novel in-loop filtering approach named Cross-Component Sample Offset (CCSO). CCSO utilizes co-located and neighboring luma samples to generate correction signals for both luma and chroma reconstructed samples. It is a multiplication-free, non-linear mapping process implemented using a look-up-table. The input to the mapping is a group of reconstructed luma samples, and the output is an offset value applied on the center luma or co-located chroma sample. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed CCSO can be applied to both image and video coding, resulting in improved coding efficiency and visual quality. The method has been adopted into an experimental next-generation video codec beyond AV1 developed by the Alliance for Open Media (AOMedia), achieving significant objective coding gains up to 3.5\,\% and 1.8\,\% for PSNR and VMAF quality metrics, respectively, under random access configuration. Additionally, CCSO notably improves the subjective visual quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge