Yiting Lu
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Comp-X: On Defining an Interactive Learned Image Compression Paradigm With Expert-driven LLM Agent
Aug 21, 2025Abstract:We present Comp-X, the first intelligently interactive image compression paradigm empowered by the impressive reasoning capability of large language model (LLM) agent. Notably, commonly used image codecs usually suffer from limited coding modes and rely on manual mode selection by engineers, making them unfriendly for unprofessional users. To overcome this, we advance the evolution of image coding paradigm by introducing three key innovations: (i) multi-functional coding framework, which unifies different coding modes of various objective/requirements, including human-machine perception, variable coding, and spatial bit allocation, into one framework. (ii) interactive coding agent, where we propose an augmented in-context learning method with coding expert feedback to teach the LLM agent how to understand the coding request, mode selection, and the use of the coding tools. (iii) IIC-bench, the first dedicated benchmark comprising diverse user requests and the corresponding annotations from coding experts, which is systematically designed for intelligently interactive image compression evaluation. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our proposed Comp-X can understand the coding requests efficiently and achieve impressive textual interaction capability. Meanwhile, it can maintain comparable compression performance even with a single coding framework, providing a promising avenue for artificial general intelligence (AGI) in image compression.
MME-Reasoning: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Logical Reasoning in MLLMs
May 27, 2025Abstract:Logical reasoning is a fundamental aspect of human intelligence and an essential capability for multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Despite the significant advancement in multimodal reasoning, existing benchmarks fail to comprehensively evaluate their reasoning abilities due to the lack of explicit categorization for logical reasoning types and an unclear understanding of reasoning. To address these issues, we introduce MME-Reasoning, a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the reasoning ability of MLLMs, which covers all three types of reasoning (i.e., inductive, deductive, and abductive) in its questions. We carefully curate the data to ensure that each question effectively evaluates reasoning ability rather than perceptual skills or knowledge breadth, and extend the evaluation protocols to cover the evaluation of diverse questions. Our evaluation reveals substantial limitations of state-of-the-art MLLMs when subjected to holistic assessments of logical reasoning capabilities. Even the most advanced MLLMs show limited performance in comprehensive logical reasoning, with notable performance imbalances across reasoning types. In addition, we conducted an in-depth analysis of approaches such as ``thinking mode'' and Rule-based RL, which are commonly believed to enhance reasoning abilities. These findings highlight the critical limitations and performance imbalances of current MLLMs in diverse logical reasoning scenarios, providing comprehensive and systematic insights into the understanding and evaluation of reasoning capabilities.
NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image Generation Model Quality Assessment
May 22, 2025Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image (T2I) generation model quality assessment, which will be held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement Workshop (NTIRE) at CVPR 2025. The aim of this challenge is to address the fine-grained quality assessment of text-to-image generation models. This challenge evaluates text-to-image models from two aspects: image-text alignment and image structural distortion detection, and is divided into the alignment track and the structural track. The alignment track uses the EvalMuse-40K, which contains around 40K AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) generated by 20 popular generative models. The alignment track has a total of 371 registered participants. A total of 1,883 submissions are received in the development phase, and 507 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 12 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. The structure track uses the EvalMuse-Structure, which contains 10,000 AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) with corresponding structural distortion mask. A total of 211 participants have registered in the structure track. A total of 1155 submissions are received in the development phase, and 487 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 8 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Almost all methods have achieved better results than baseline methods, and the winning methods in both tracks have demonstrated superior prediction performance on T2I model quality assessment.
OmniCaptioner: One Captioner to Rule Them All
Apr 09, 2025Abstract:We propose OmniCaptioner, a versatile visual captioning framework for generating fine-grained textual descriptions across a wide variety of visual domains. Unlike prior methods limited to specific image types (e.g., natural images or geometric visuals), our framework provides a unified solution for captioning natural images, visual text (e.g., posters, UIs, textbooks), and structured visuals (e.g., documents, tables, charts). By converting low-level pixel information into semantically rich textual representations, our framework bridges the gap between visual and textual modalities. Our results highlight three key advantages: (i) Enhanced Visual Reasoning with LLMs, where long-context captions of visual modalities empower LLMs, particularly the DeepSeek-R1 series, to reason effectively in multimodal scenarios; (ii) Improved Image Generation, where detailed captions improve tasks like text-to-image generation and image transformation; and (iii) Efficient Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), which enables faster convergence with less data. We believe the versatility and adaptability of OmniCaptioner can offer a new perspective for bridging the gap between language and visual modalities.
Q-Adapt: Adapting LMM for Visual Quality Assessment with Progressive Instruction Tuning
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Multi-modal Foundation Models (LMM) has paved the way for the possible Explainable Image Quality Assessment (EIQA) with instruction tuning from two perspectives: overall quality explanation, and attribute-wise perception answering. However, existing works usually overlooked the conflicts between these two types of perception explanations during joint instruction tuning, leading to insufficient perception understanding. To mitigate this, we propose a new paradigm for perception-oriented instruction tuning, i.e., Q-Adapt, which aims to eliminate the conflicts and achieve the synergy between these two EIQA tasks when adapting LMM, resulting in enhanced multi-faceted explanations of IQA. Particularly, we propose a progressive instruction tuning strategy by dividing the adaption process of LMM for EIQA into two stages, where the first stage empowers the LMM with universal perception knowledge tailored for two tasks using an efficient transfer learning strategy, i.e., LoRA, and the second stage introduces the instruction-adaptive visual prompt tuning to dynamically adapt visual features for the different instructions from two tasks. In this way, our proposed Q-Adapt can achieve a lightweight visual quality evaluator, demonstrating comparable performance and, in some instances, superior results across perceptual-related benchmarks and commonly-used IQA databases. The source code is publicly available at https://github.com/yeppp27/Q-Adapt.
Lumina-Image 2.0: A Unified and Efficient Image Generative Framework
Mar 27, 2025



Abstract:We introduce Lumina-Image 2.0, an advanced text-to-image generation framework that achieves significant progress compared to previous work, Lumina-Next. Lumina-Image 2.0 is built upon two key principles: (1) Unification - it adopts a unified architecture (Unified Next-DiT) that treats text and image tokens as a joint sequence, enabling natural cross-modal interactions and allowing seamless task expansion. Besides, since high-quality captioners can provide semantically well-aligned text-image training pairs, we introduce a unified captioning system, Unified Captioner (UniCap), specifically designed for T2I generation tasks. UniCap excels at generating comprehensive and accurate captions, accelerating convergence and enhancing prompt adherence. (2) Efficiency - to improve the efficiency of our proposed model, we develop multi-stage progressive training strategies and introduce inference acceleration techniques without compromising image quality. Extensive evaluations on academic benchmarks and public text-to-image arenas show that Lumina-Image 2.0 delivers strong performances even with only 2.6B parameters, highlighting its scalability and design efficiency. We have released our training details, code, and models at https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-Image-2.0.
Hybrid Agents for Image Restoration
Mar 13, 2025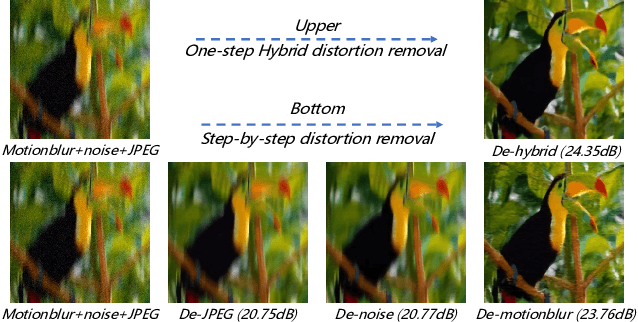
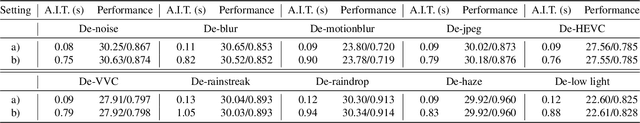
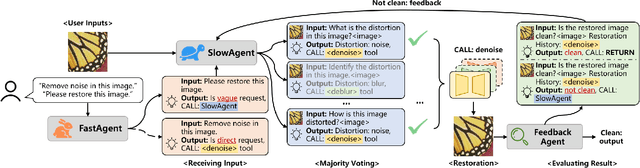

Abstract:Existing Image Restoration (IR) studies typically focus on task-specific or universal modes individually, relying on the mode selection of users and lacking the cooperation between multiple task-specific/universal restoration modes. This leads to insufficient interaction for unprofessional users and limits their restoration capability for complicated real-world applications. In this work, we present HybridAgent, intending to incorporate multiple restoration modes into a unified image restoration model and achieve intelligent and efficient user interaction through our proposed hybrid agents. Concretely, we propose the hybrid rule of fast, slow, and feedback restoration agents. Here, the slow restoration agent optimizes the powerful multimodal large language model (MLLM) with our proposed instruction-tuning dataset to identify degradations within images with ambiguous user prompts and invokes proper restoration tools accordingly. The fast restoration agent is designed based on a lightweight large language model (LLM) via in-context learning to understand the user prompts with simple and clear requirements, which can obviate the unnecessary time/resource costs of MLLM. Moreover, we introduce the mixed distortion removal mode for our HybridAgents, which is crucial but not concerned in previous agent-based works. It can effectively prevent the error propagation of step-by-step image restoration and largely improve the efficiency of the agent system. We validate the effectiveness of HybridAgent with both synthetic and real-world IR tasks.
InternVQA: Advancing Compressed Video Quality Assessment with Distilling Large Foundation Model
Feb 26, 2025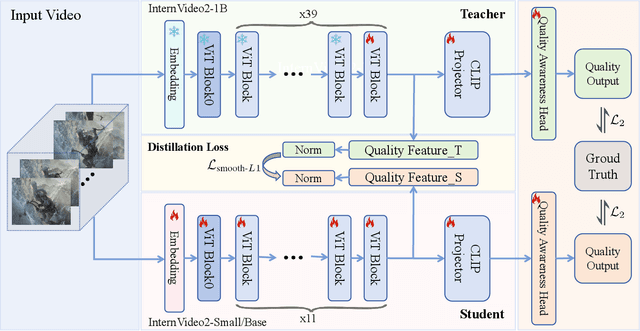
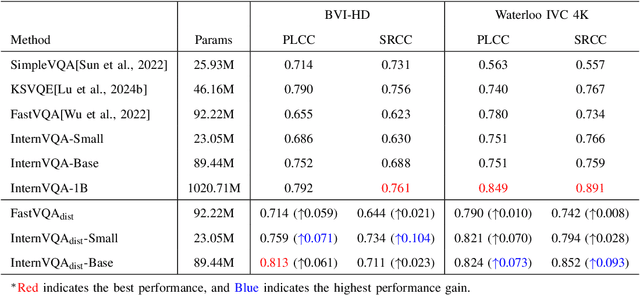
Abstract:Video quality assessment tasks rely heavily on the rich features required for video understanding, such as semantic information, texture, and temporal motion. The existing video foundational model, InternVideo2, has demonstrated strong potential in video understanding tasks due to its large parameter size and large-scale multimodal data pertaining. Building on this, we explored the transferability of InternVideo2 to video quality assessment under compression scenarios. To design a lightweight model suitable for this task, we proposed a distillation method to equip the smaller model with rich compression quality priors. Additionally, we examined the performance of different backbones during the distillation process. The results showed that, compared to other methods, our lightweight model distilled from InternVideo2 achieved excellent performance in compression video quality assessment.
IMAGINE-E: Image Generation Intelligence Evaluation of State-of-the-art Text-to-Image Models
Jan 23, 2025



Abstract:With the rapid development of diffusion models, text-to-image(T2I) models have made significant progress, showcasing impressive abilities in prompt following and image generation. Recently launched models such as FLUX.1 and Ideogram2.0, along with others like Dall-E3 and Stable Diffusion 3, have demonstrated exceptional performance across various complex tasks, raising questions about whether T2I models are moving towards general-purpose applicability. Beyond traditional image generation, these models exhibit capabilities across a range of fields, including controllable generation, image editing, video, audio, 3D, and motion generation, as well as computer vision tasks like semantic segmentation and depth estimation. However, current evaluation frameworks are insufficient to comprehensively assess these models' performance across expanding domains. To thoroughly evaluate these models, we developed the IMAGINE-E and tested six prominent models: FLUX.1, Ideogram2.0, Midjourney, Dall-E3, Stable Diffusion 3, and Jimeng. Our evaluation is divided into five key domains: structured output generation, realism, and physical consistency, specific domain generation, challenging scenario generation, and multi-style creation tasks. This comprehensive assessment highlights each model's strengths and limitations, particularly the outstanding performance of FLUX.1 and Ideogram2.0 in structured and specific domain tasks, underscoring the expanding applications and potential of T2I models as foundational AI tools. This study provides valuable insights into the current state and future trajectory of T2I models as they evolve towards general-purpose usability. Evaluation scripts will be released at https://github.com/jylei16/Imagine-e.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge