Renrui Zhang
Mind-Brush: Integrating Agentic Cognitive Search and Reasoning into Image Generation
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:While text-to-image generation has achieved unprecedented fidelity, the vast majority of existing models function fundamentally as static text-to-pixel decoders. Consequently, they often fail to grasp implicit user intentions. Although emerging unified understanding-generation models have improved intent comprehension, they still struggle to accomplish tasks involving complex knowledge reasoning within a single model. Moreover, constrained by static internal priors, these models remain unable to adapt to the evolving dynamics of the real world. To bridge these gaps, we introduce Mind-Brush, a unified agentic framework that transforms generation into a dynamic, knowledge-driven workflow. Simulating a human-like 'think-research-create' paradigm, Mind-Brush actively retrieves multimodal evidence to ground out-of-distribution concepts and employs reasoning tools to resolve implicit visual constraints. To rigorously evaluate these capabilities, we propose Mind-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark comprising 500 distinct samples spanning real-time news, emerging concepts, and domains such as mathematical and Geo-Reasoning. Extensive experiments demonstrate that Mind-Brush significantly enhances the capabilities of unified models, realizing a zero-to-one capability leap for the Qwen-Image baseline on Mind-Bench, while achieving superior results on established benchmarks like WISE and RISE.
Automated Safety Benchmarking: A Multi-agent Pipeline for LVLMs
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Large vision-language models (LVLMs) exhibit remarkable capabilities in cross-modal tasks but face significant safety challenges, which undermine their reliability in real-world applications. Efforts have been made to build LVLM safety evaluation benchmarks to uncover their vulnerability. However, existing benchmarks are hindered by their labor-intensive construction process, static complexity, and limited discriminative power. Thus, they may fail to keep pace with rapidly evolving models and emerging risks. To address these limitations, we propose VLSafetyBencher, the first automated system for LVLM safety benchmarking. VLSafetyBencher introduces four collaborative agents: Data Preprocessing, Generation, Augmentation, and Selection agents to construct and select high-quality samples. Experiments validates that VLSafetyBencher can construct high-quality safety benchmarks within one week at a minimal cost. The generated benchmark effectively distinguish safety, with a safety rate disparity of 70% between the most and least safe models.
Visual Generation Unlocks Human-Like Reasoning through Multimodal World Models
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Humans construct internal world models and reason by manipulating the concepts within these models. Recent advances in AI, particularly chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, approximate such human cognitive abilities, where world models are believed to be embedded within large language models. Expert-level performance in formal and abstract domains such as mathematics and programming has been achieved in current systems by relying predominantly on verbal reasoning. However, they still lag far behind humans in domains like physical and spatial intelligence, which require richer representations and prior knowledge. The emergence of unified multimodal models (UMMs) capable of both verbal and visual generation has therefore sparked interest in more human-like reasoning grounded in complementary multimodal pathways, though their benefits remain unclear. From a world-model perspective, this paper presents the first principled study of when and how visual generation benefits reasoning. Our key position is the visual superiority hypothesis: for certain tasks--particularly those grounded in the physical world--visual generation more naturally serves as world models, whereas purely verbal world models encounter bottlenecks arising from representational limitations or insufficient prior knowledge. Theoretically, we formalize internal world modeling as a core component of CoT reasoning and analyze distinctions among different forms of world models. Empirically, we identify tasks that necessitate interleaved visual-verbal CoT reasoning, constructing a new evaluation suite, VisWorld-Eval. Controlled experiments on a state-of-the-art UMM show that interleaved CoT significantly outperforms purely verbal CoT on tasks that favor visual world modeling, but offers no clear advantage otherwise. Together, this work clarifies the potential of multimodal world modeling for more powerful, human-like multimodal AI.
NL2CA: Auto-formalizing Cognitive Decision-Making from Natural Language Using an Unsupervised CriticNL2LTL Framework
Dec 20, 2025



Abstract:Cognitive computing models offer a formal and interpretable way to characterize human's deliberation and decision-making, yet their development remains labor-intensive. In this paper, we propose NL2CA, a novel method for auto-formalizing cognitive decision-making rules from natural language descriptions of human experience. Different from most related work that exploits either pure manual or human guided interactive modeling, our method is fully automated without any human intervention. The approach first translates text into Linear Temporal Logic (LTL) using a fine-tuned large language model (LLM), then refines the logic via an unsupervised Critic Tree, and finally transforms the output into executable production rules compatible with symbolic cognitive frameworks. Based on the resulted rules, a cognitive agent is further constructed and optimized through cognitive reinforcement learning according to the real-world behavioral data. Our method is validated in two domains: (1) NL-to-LTL translation, where our CriticNL2LTL module achieves consistent performance across both expert and large-scale benchmarks without human-in-the-loop feed-backs, and (2) cognitive driving simulation, where agents automatically constructed from human interviews have successfully learned the diverse decision patterns of about 70 trials in different critical scenarios. Experimental results demonstrate that NL2CA enables scalable, interpretable, and human-aligned cognitive modeling from unstructured textual data, offering a novel paradigm to automatically design symbolic cognitive agents.
Are Video Models Ready as Zero-Shot Reasoners? An Empirical Study with the MME-CoF Benchmark
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Recent video generation models can produce high-fidelity, temporally coherent videos, indicating that they may encode substantial world knowledge. Beyond realistic synthesis, they also exhibit emerging behaviors indicative of visual perception, modeling, and manipulation. Yet, an important question still remains: Are video models ready to serve as zero-shot reasoners in challenging visual reasoning scenarios? In this work, we conduct an empirical study to comprehensively investigate this question, focusing on the leading and popular Veo-3. We evaluate its reasoning behavior across 12 dimensions, including spatial, geometric, physical, temporal, and embodied logic, systematically characterizing both its strengths and failure modes. To standardize this study, we curate the evaluation data into MME-CoF, a compact benchmark that enables in-depth and thorough assessment of Chain-of-Frame (CoF) reasoning. Our findings reveal that while current video models demonstrate promising reasoning patterns on short-horizon spatial coherence, fine-grained grounding, and locally consistent dynamics, they remain limited in long-horizon causal reasoning, strict geometric constraints, and abstract logic. Overall, they are not yet reliable as standalone zero-shot reasoners, but exhibit encouraging signs as complementary visual engines alongside dedicated reasoning models. Project page: https://video-cof.github.io
Can World Models Benefit VLMs for World Dynamics?
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Trained on internet-scale video data, generative world models are increasingly recognized as powerful world simulators that can generate consistent and plausible dynamics over structure, motion, and physics. This raises a natural question: with the advent of strong video foundational models, might they supplant conventional vision encoder paradigms for general-purpose multimodal understanding? While recent studies have begun to explore the potential of world models on common vision tasks, these explorations typically lack a systematic investigation of generic, multimodal tasks. In this work, we strive to investigate the capabilities when world model priors are transferred into Vision-Language Models: we re-purpose a video diffusion model as a generative encoder to perform a single denoising step and treat the resulting latents as a set of visual embedding. We empirically investigate this class of models, which we refer to as World-Language Models (WorldLMs), and we find that generative encoders can capture latents useful for downstream understanding that show distinctions from conventional encoders. Naming our best-performing variant Dynamic Vision Aligner (DyVA), we further discover that this method significantly enhances spatial reasoning abilities and enables single-image models to perform multi-frame reasoning. Through the curation of a suite of visual reasoning tasks, we find DyVA to surpass both open-source and proprietary baselines, achieving state-of-the-art or comparable performance. We attribute these gains to WorldLM's inherited motion-consistency internalization from video pre-training. Finally, we systematically explore extensive model designs to highlight promising directions for future work. We hope our study can pave the way for a new family of VLMs that leverage priors from world models and are on a promising path towards generalist vision learners.
MLA: A Multisensory Language-Action Model for Multimodal Understanding and Forecasting in Robotic Manipulation
Sep 30, 2025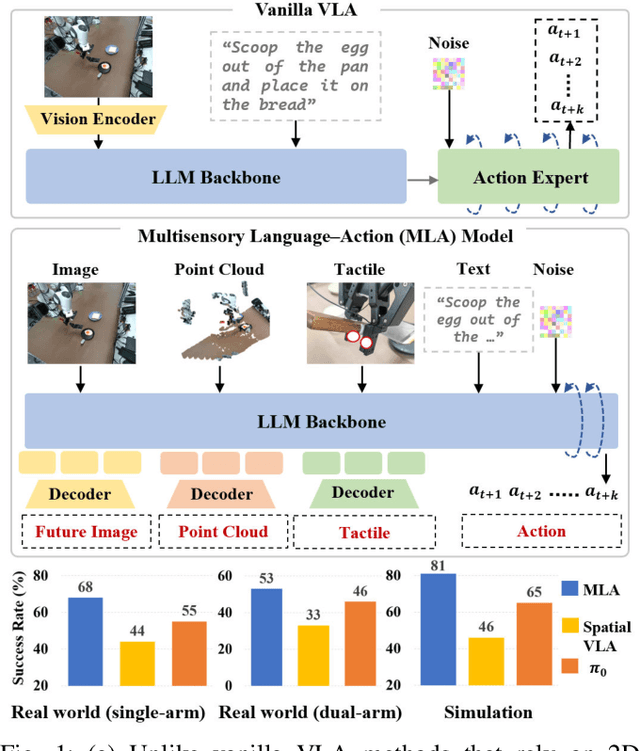
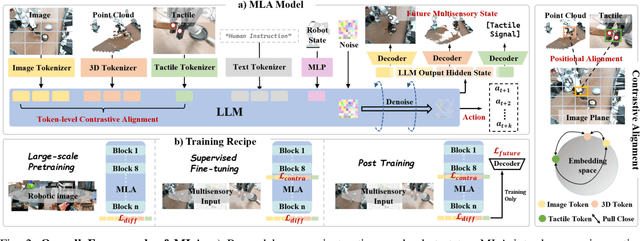
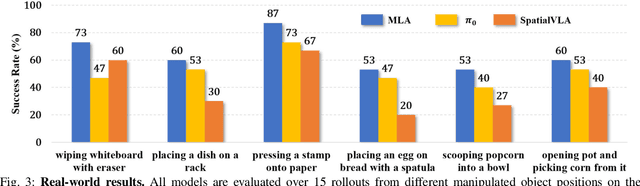

Abstract:Vision-language-action models (VLAs) have shown generalization capabilities in robotic manipulation tasks by inheriting from vision-language models (VLMs) and learning action generation. Most VLA models focus on interpreting vision and language to generate actions, whereas robots must perceive and interact within the spatial-physical world. This gap highlights the need for a comprehensive understanding of robotic-specific multisensory information, which is crucial for achieving complex and contact-rich control. To this end, we introduce a multisensory language-action (MLA) model that collaboratively perceives heterogeneous sensory modalities and predicts future multisensory objectives to facilitate physical world modeling. Specifically, to enhance perceptual representations, we propose an encoder-free multimodal alignment scheme that innovatively repurposes the large language model itself as a perception module, directly interpreting multimodal cues by aligning 2D images, 3D point clouds, and tactile tokens through positional correspondence. To further enhance MLA's understanding of physical dynamics, we design a future multisensory generation post-training strategy that enables MLA to reason about semantic, geometric, and interaction information, providing more robust conditions for action generation. For evaluation, the MLA model outperforms the previous state-of-the-art 2D and 3D VLA methods by 12% and 24% in complex, contact-rich real-world tasks, respectively, while also demonstrating improved generalization to unseen configurations. Project website: https://sites.google.com/view/open-mla
GLEAM: Learning to Match and Explain in Cross-View Geo-Localization
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:Cross-View Geo-Localization (CVGL) focuses on identifying correspondences between images captured from distinct perspectives of the same geographical location. However, existing CVGL approaches are typically restricted to a single view or modality, and their direct visual matching strategy lacks interpretability: they merely predict whether two images correspond, without explaining the rationale behind the match. In this paper, we present GLEAM-C, a foundational CVGL model that unifies multiple views and modalities-including UAV imagery, street maps, panoramic views, and ground photographs-by aligning them exclusively with satellite imagery. Our framework enhances training efficiency through optimized implementation while achieving accuracy comparable to prior modality-specific CVGL models through a two-phase training strategy. Moreover, to address the lack of interpretability in traditional CVGL methods, we leverage the reasoning capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to propose a new task, GLEAM-X, which combines cross-view correspondence prediction with explainable reasoning. To support this task, we construct a bilingual benchmark using GPT-4o and Doubao-1.5-Thinking-Vision-Pro to generate training and testing data. The test set is further refined through detailed human revision, enabling systematic evaluation of explainable cross-view reasoning and advancing transparency and scalability in geo-localization. Together, GLEAM-C and GLEAM-X form a comprehensive CVGL pipeline that integrates multi-modal, multi-view alignment with interpretable correspondence analysis, unifying accurate cross-view matching with explainable reasoning and advancing Geo-Localization by enabling models to better Explain And Match. Code and datasets used in this work will be made publicly accessible at https://github.com/Lucky-Lance/GLEAM.
Quantization Meets dLLMs: A Systematic Study of Post-training Quantization for Diffusion LLMs
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in diffusion large language models (dLLMs) have introduced a promising alternative to autoregressive (AR) LLMs for natural language generation tasks, leveraging full attention and denoising-based decoding strategies. However, the deployment of these models on edge devices remains challenging due to their massive parameter scale and high resource demands. While post-training quantization (PTQ) has emerged as a widely adopted technique for compressing AR LLMs, its applicability to dLLMs remains largely unexplored. In this work, we present the first systematic study on quantizing diffusion-based language models. We begin by identifying the presence of activation outliers, characterized by abnormally large activation values that dominate the dynamic range. These outliers pose a key challenge to low-bit quantization, as they make it difficult to preserve precision for the majority of values. More importantly, we implement state-of-the-art PTQ methods and conduct a comprehensive evaluation across multiple task types and model variants. Our analysis is structured along four key dimensions: bit-width, quantization method, task category, and model type. Through this multi-perspective evaluation, we offer practical insights into the quantization behavior of dLLMs under different configurations. We hope our findings provide a foundation for future research in efficient dLLM deployment. All codes and experimental setups will be released to support the community.
Lumina-mGPT 2.0: Stand-Alone AutoRegressive Image Modeling
Jul 23, 2025



Abstract:We present Lumina-mGPT 2.0, a stand-alone, decoder-only autoregressive model that revisits and revitalizes the autoregressive paradigm for high-quality image generation and beyond. Unlike existing approaches that rely on pretrained components or hybrid architectures, Lumina-mGPT 2.0 is trained entirely from scratch, enabling unrestricted architectural design and licensing freedom. It achieves generation quality on par with state-of-the-art diffusion models such as DALL-E 3 and SANA, while preserving the inherent flexibility and compositionality of autoregressive modeling. Our unified tokenization scheme allows the model to seamlessly handle a wide spectrum of tasks-including subject-driven generation, image editing, controllable synthesis, and dense prediction-within a single generative framework. To further boost usability, we incorporate efficient decoding strategies like inference-time scaling and speculative Jacobi sampling to improve quality and speed, respectively. Extensive evaluations on standard text-to-image benchmarks (e.g., GenEval, DPG) demonstrate that Lumina-mGPT 2.0 not only matches but in some cases surpasses diffusion-based models. Moreover, we confirm its multi-task capabilities on the Graph200K benchmark, with the native Lumina-mGPT 2.0 performing exceptionally well. These results position Lumina-mGPT 2.0 as a strong, flexible foundation model for unified multimodal generation. We have released our training details, code, and models at https://github.com/Alpha-VLLM/Lumina-mGPT-2.0.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge