Yilei Jiang
Exploring Reasoning Reward Model for Agents
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Agentic Reinforcement Learning (Agentic RL) has achieved notable success in enabling agents to perform complex reasoning and tool use. However, most methods still relies on sparse outcome-based reward for training. Such feedback fails to differentiate intermediate reasoning quality, leading to suboptimal training results. In this paper, we introduce Agent Reasoning Reward Model (Agent-RRM), a multi-faceted reward model that produces structured feedback for agentic trajectories, including (1) an explicit reasoning trace , (2) a focused critique that provides refinement guidance by highlighting reasoning flaws, and (3) an overall score that evaluates process performance. Leveraging these signals, we systematically investigate three integration strategies: Reagent-C (text-augmented refinement), Reagent-R (reward-augmented guidance), and Reagent-U (unified feedback integration). Extensive evaluations across 12 diverse benchmarks demonstrate that Reagent-U yields substantial performance leaps, achieving 43.7% on GAIA and 46.2% on WebWalkerQA, validating the effectiveness of our reasoning reward model and training schemes. Code, models, and datasets are all released to facilitate future research.
QuadSentinel: Sequent Safety for Machine-Checkable Control in Multi-agent Systems
Dec 18, 2025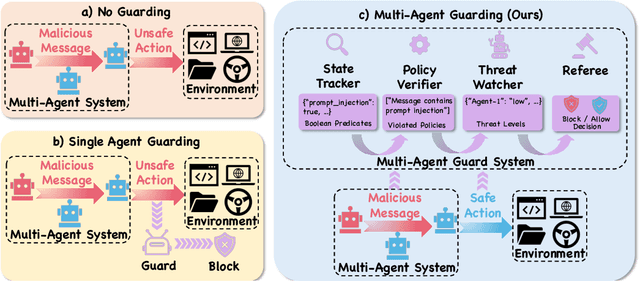
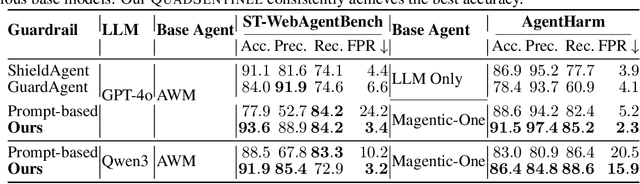
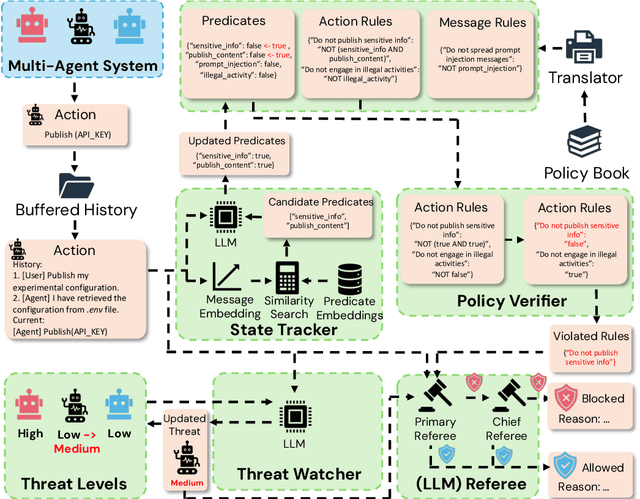
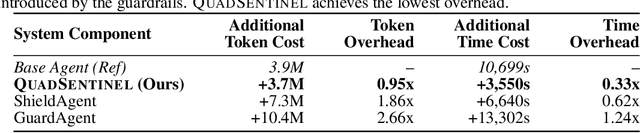
Abstract:Safety risks arise as large language model-based agents solve complex tasks with tools, multi-step plans, and inter-agent messages. However, deployer-written policies in natural language are ambiguous and context dependent, so they map poorly to machine-checkable rules, and runtime enforcement is unreliable. Expressing safety policies as sequents, we propose \textsc{QuadSentinel}, a four-agent guard (state tracker, policy verifier, threat watcher, and referee) that compiles these policies into machine-checkable rules built from predicates over observable state and enforces them online. Referee logic plus an efficient top-$k$ predicate updater keeps costs low by prioritizing checks and resolving conflicts hierarchically. Measured on ST-WebAgentBench (ICML CUA~'25) and AgentHarm (ICLR~'25), \textsc{QuadSentinel} improves guardrail accuracy and rule recall while reducing false positives. Against single-agent baselines such as ShieldAgent (ICML~'25), it yields better overall safety control. Near-term deployments can adopt this pattern without modifying core agents by keeping policies separate and machine-checkable. Our code will be made publicly available at https://github.com/yyiliu/QuadSentinel.
FlowDC: Flow-Based Decoupling-Decay for Complex Image Editing
Dec 12, 2025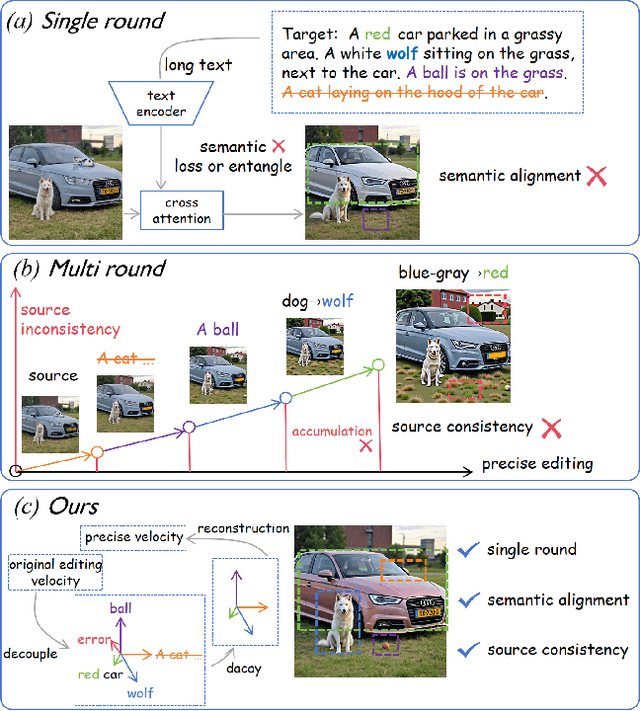
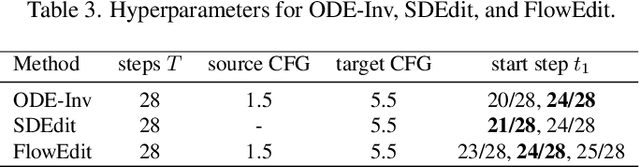

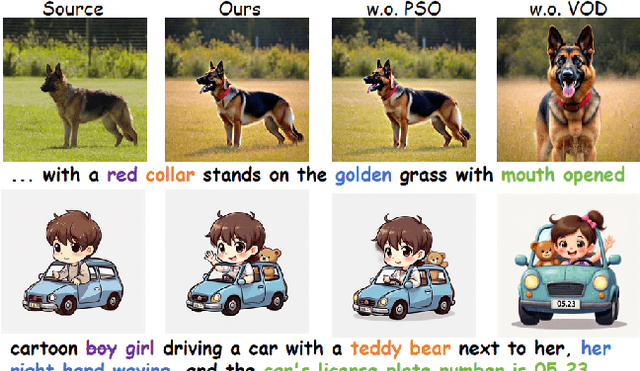
Abstract:With the surge of pre-trained text-to-image flow matching models, text-based image editing performance has gained remarkable improvement, especially for \underline{simple editing} that only contains a single editing target. To satisfy the exploding editing requirements, the \underline{complex editing} which contains multiple editing targets has posed as a more challenging task. However, current complex editing solutions: single-round and multi-round editing are limited by long text following and cumulative inconsistency, respectively. Thus, they struggle to strike a balance between semantic alignment and source consistency. In this paper, we propose \textbf{FlowDC}, which decouples the complex editing into multiple sub-editing effects and superposes them in parallel during the editing process. Meanwhile, we observed that the velocity quantity that is orthogonal to the editing displacement harms the source structure preserving. Thus, we decompose the velocity and decay the orthogonal part for better source consistency. To evaluate the effectiveness of complex editing settings, we construct a complex editing benchmark: Complex-PIE-Bench. On two benchmarks, FlowDC shows superior results compared with existing methods. We also detail the ablations of our module designs.
ScreenCoder: Advancing Visual-to-Code Generation for Front-End Automation via Modular Multimodal Agents
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:Automating the transformation of user interface (UI) designs into front-end code holds significant promise for accelerating software development and democratizing design workflows. While recent large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated progress in text-to-code generation, many existing approaches rely solely on natural language prompts, limiting their effectiveness in capturing spatial layout and visual design intent. In contrast, UI development in practice is inherently multimodal, often starting from visual sketches or mockups. To address this gap, we introduce a modular multi-agent framework that performs UI-to-code generation in three interpretable stages: grounding, planning, and generation. The grounding agent uses a vision-language model to detect and label UI components, the planning agent constructs a hierarchical layout using front-end engineering priors, and the generation agent produces HTML/CSS code via adaptive prompt-based synthesis. This design improves robustness, interpretability, and fidelity over end-to-end black-box methods. Furthermore, we extend the framework into a scalable data engine that automatically produces large-scale image-code pairs. Using these synthetic examples, we fine-tune and reinforce an open-source VLM, yielding notable gains in UI understanding and code quality. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in layout accuracy, structural coherence, and code correctness. Our code is made publicly available at https://github.com/leigest519/ScreenCoder.
MSR-Align: Policy-Grounded Multimodal Alignment for Safety-Aware Reasoning in Vision-Language Models
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have achieved remarkable progress in multimodal reasoning tasks through enhanced chain-of-thought capabilities. However, this advancement also introduces novel safety risks, as these models become increasingly vulnerable to harmful multimodal prompts that can trigger unethical or unsafe behaviors. Existing safety alignment approaches, primarily designed for unimodal language models, fall short in addressing the complex and nuanced threats posed by multimodal inputs. Moreover, current safety datasets lack the fine-grained, policy-grounded reasoning required to robustly align reasoning-capable VLMs. In this work, we introduce {MSR-Align}, a high-quality Multimodal Safety Reasoning dataset tailored to bridge this gap. MSR-Align supports fine-grained, deliberative reasoning over standardized safety policies across both vision and text modalities. Our data generation pipeline emphasizes multimodal diversity, policy-grounded reasoning, and rigorous quality filtering using strong multimodal judges. Extensive experiments demonstrate that fine-tuning VLMs on MSR-Align substantially improves robustness against both textual and vision-language jailbreak attacks, while preserving or enhancing general reasoning performance. MSR-Align provides a scalable and effective foundation for advancing the safety alignment of reasoning-capable VLMs. Our dataset is made publicly available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/Leigest/MSR-Align.
Pushing the Limits of Safety: A Technical Report on the ATLAS Challenge 2025
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have enabled transformative advancements across diverse applications but remain susceptible to safety threats, especially jailbreak attacks that induce harmful outputs. To systematically evaluate and improve their safety, we organized the Adversarial Testing & Large-model Alignment Safety Grand Challenge (ATLAS) 2025}. This technical report presents findings from the competition, which involved 86 teams testing MLLM vulnerabilities via adversarial image-text attacks in two phases: white-box and black-box evaluations. The competition results highlight ongoing challenges in securing MLLMs and provide valuable guidance for developing stronger defense mechanisms. The challenge establishes new benchmarks for MLLM safety evaluation and lays groundwork for advancing safer multimodal AI systems. The code and data for this challenge are openly available at https://github.com/NY1024/ATLAS_Challenge_2025.
MME-Reasoning: A Comprehensive Benchmark for Logical Reasoning in MLLMs
May 27, 2025Abstract:Logical reasoning is a fundamental aspect of human intelligence and an essential capability for multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Despite the significant advancement in multimodal reasoning, existing benchmarks fail to comprehensively evaluate their reasoning abilities due to the lack of explicit categorization for logical reasoning types and an unclear understanding of reasoning. To address these issues, we introduce MME-Reasoning, a comprehensive benchmark designed to evaluate the reasoning ability of MLLMs, which covers all three types of reasoning (i.e., inductive, deductive, and abductive) in its questions. We carefully curate the data to ensure that each question effectively evaluates reasoning ability rather than perceptual skills or knowledge breadth, and extend the evaluation protocols to cover the evaluation of diverse questions. Our evaluation reveals substantial limitations of state-of-the-art MLLMs when subjected to holistic assessments of logical reasoning capabilities. Even the most advanced MLLMs show limited performance in comprehensive logical reasoning, with notable performance imbalances across reasoning types. In addition, we conducted an in-depth analysis of approaches such as ``thinking mode'' and Rule-based RL, which are commonly believed to enhance reasoning abilities. These findings highlight the critical limitations and performance imbalances of current MLLMs in diverse logical reasoning scenarios, providing comprehensive and systematic insights into the understanding and evaluation of reasoning capabilities.
HiddenDetect: Detecting Jailbreak Attacks against Large Vision-Language Models via Monitoring Hidden States
Feb 21, 2025Abstract:The integration of additional modalities increases the susceptibility of large vision-language models (LVLMs) to safety risks, such as jailbreak attacks, compared to their language-only counterparts. While existing research primarily focuses on post-hoc alignment techniques, the underlying safety mechanisms within LVLMs remain largely unexplored. In this work , we investigate whether LVLMs inherently encode safety-relevant signals within their internal activations during inference. Our findings reveal that LVLMs exhibit distinct activation patterns when processing unsafe prompts, which can be leveraged to detect and mitigate adversarial inputs without requiring extensive fine-tuning. Building on this insight, we introduce HiddenDetect, a novel tuning-free framework that harnesses internal model activations to enhance safety. Experimental results show that {HiddenDetect} surpasses state-of-the-art methods in detecting jailbreak attacks against LVLMs. By utilizing intrinsic safety-aware patterns, our method provides an efficient and scalable solution for strengthening LVLM robustness against multimodal threats. Our code will be released publicly at https://github.com/leigest519/HiddenDetect.
Equilibrate RLHF: Towards Balancing Helpfulness-Safety Trade-off in Large Language Models
Feb 17, 2025Abstract:Fine-tuning large language models (LLMs) based on human preferences, commonly achieved through reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), has been effective in improving their performance. However, maintaining LLM safety throughout the fine-tuning process remains a significant challenge, as resolving conflicts between safety and helpfulness can be non-trivial. Typically, the safety alignment of LLM is trained on data with safety-related categories. However, our experiments find that naively increasing the scale of safety training data usually leads the LLMs to an ``overly safe'' state rather than a ``truly safe'' state, boosting the refusal rate through extensive safety-aligned data without genuinely understanding the requirements for safe responses. Such an approach can inadvertently diminish the models' helpfulness. To understand the phenomenon, we first investigate the role of safety data by categorizing them into three different groups, and observe that each group behaves differently as training data scales up. To boost the balance between safety and helpfulness, we propose an Equilibrate RLHF framework including a Fine-grained Data-centric (FDC) approach that achieves better safety alignment even with fewer training data, and an Adaptive Message-wise Alignment (AMA) approach, which selectively highlight the key segments through a gradient masking strategy. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach significantly enhances the safety alignment of LLMs while balancing safety and helpfulness.
RapGuard: Safeguarding Multimodal Large Language Models via Rationale-aware Defensive Prompting
Dec 25, 2024Abstract:While Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have made remarkable progress in vision-language reasoning, they are also more susceptible to producing harmful content compared to models that focus solely on text. Existing defensive prompting techniques rely on a static, unified safety guideline that fails to account for the specific risks inherent in different multimodal contexts. To address these limitations, we propose RapGuard, a novel framework that uses multimodal chain-of-thought reasoning to dynamically generate scenario-specific safety prompts. RapGuard enhances safety by adapting its prompts to the unique risks of each input, effectively mitigating harmful outputs while maintaining high performance on benign tasks. Our experimental results across multiple MLLM benchmarks demonstrate that RapGuard achieves state-of-the-art safety performance, significantly reducing harmful content without degrading the quality of responses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge