Xinyu Wei
MICo-150K: A Comprehensive Dataset Advancing Multi-Image Composition
Dec 08, 2025



Abstract:In controllable image generation, synthesizing coherent and consistent images from multiple reference inputs, i.e., Multi-Image Composition (MICo), remains a challenging problem, partly hindered by the lack of high-quality training data. To bridge this gap, we conduct a systematic study of MICo, categorizing it into 7 representative tasks and curate a large-scale collection of high-quality source images and construct diverse MICo prompts. Leveraging powerful proprietary models, we synthesize a rich amount of balanced composite images, followed by human-in-the-loop filtering and refinement, resulting in MICo-150K, a comprehensive dataset for MICo with identity consistency. We further build a Decomposition-and-Recomposition (De&Re) subset, where 11K real-world complex images are decomposed into components and recomposed, enabling both real and synthetic compositions. To enable comprehensive evaluation, we construct MICo-Bench with 100 cases per task and 300 challenging De&Re cases, and further introduce a new metric, Weighted-Ref-VIEScore, specifically tailored for MICo evaluation. Finally, we fine-tune multiple models on MICo-150K and evaluate them on MICo-Bench. The results show that MICo-150K effectively equips models without MICo capability and further enhances those with existing skills. Notably, our baseline model, Qwen-MICo, fine-tuned from Qwen-Image-Edit, matches Qwen-Image-2509 in 3-image composition while supporting arbitrary multi-image inputs beyond the latter's limitation. Our dataset, benchmark, and baseline collectively offer valuable resources for further research on Multi-Image Composition.
Retrieval Feedback Memory Enhancement Large Model Retrieval Generation Method
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities across diverse tasks, yet they face inherent limitations such as constrained parametric knowledge and high retraining costs. Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) augments the generation process by retrieving externally stored knowledge absent from the models internal parameters. However, RAG methods face challenges such as information loss and redundant retrievals during multi-round queries, accompanying the difficulties in precisely characterizing knowledge gaps for complex tasks. To address these problems, we propose Retrieval Feedback and Memory Retrieval Augmented Generation(RFM-RAG), which transforms the stateless retrieval of previous methods into stateful continuous knowledge management by constructing a dynamic evidence pool. Specifically, our method generates refined queries describing the models knowledge gaps using relational triples from questions and evidence from the dynamic evidence pool; Retrieves critical external knowledge to iteratively update this evidence pool; Employs a R-Feedback Model to evaluate evidence completeness until convergence. Compared to traditional RAG methods, our approach enables persistent storage of retrieved passages and effectively distills key information from passages to construct clearly new queries. Experiments on three public QA benchmarks demonstrate that RFM-RAG outperforms previous methods and improves overall system accuracy.
Dynamic Embedding of Hierarchical Visual Features for Efficient Vision-Language Fine-Tuning
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) commonly follow a paradigm that projects visual features and then concatenates them with text tokens to form a unified sequence input for Large Language Models (LLMs). However, this paradigm leads to a significant increase in the length of the input sequence, resulting in substantial computational overhead. Existing methods attempt to fuse visual information into the intermediate layers of LLMs, which alleviate the sequence length issue but often neglect the hierarchical semantic representations within the model and the fine-grained visual information available in the shallower visual encoding layers. To address this limitation, we propose DEHVF, an efficient vision-language fine-tuning method based on dynamic embedding and fusion of hierarchical visual features. Its core lies in leveraging the inherent hierarchical representation characteristics of visual encoders and language models. Through a lightweight hierarchical visual fuser, it dynamically selects and fuses hierarchical features corresponding to semantic granularity based on the internal representations of each layer in LLMs. The fused layer-related visual features are then projected and aligned before being directly embedded into the Feed-Forward Network (FFN) of the corresponding layer in LLMs. This approach not only avoids sequence expansion but also dynamically fuses multi-layer visual information. By fine-tuning only a small number of parameters, DEHVF achieves precise alignment and complementarity of cross-modal information at the same semantic granularity. We conducted experiments across various VL benchmarks, including visual question answering on ScienceQA and image captioning on COCO Captions. The results demonstrate that DEHVF achieves higher accuracy than existing parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) baselines while maintaining efficient training and inference.
CEIDM: A Controlled Entity and Interaction Diffusion Model for Enhanced Text-to-Image Generation
Aug 25, 2025Abstract:In Text-to-Image (T2I) generation, the complexity of entities and their intricate interactions pose a significant challenge for T2I method based on diffusion model: how to effectively control entity and their interactions to produce high-quality images. To address this, we propose CEIDM, a image generation method based on diffusion model with dual controls for entity and interaction. First, we propose an entity interactive relationships mining approach based on Large Language Models (LLMs), extracting reasonable and rich implicit interactive relationships through chain of thought to guide diffusion models to generate high-quality images that are closer to realistic logic and have more reasonable interactive relationships. Furthermore, We propose an interactive action clustering and offset method to cluster and offset the interactive action features contained in each text prompts. By constructing global and local bidirectional offsets, we enhance semantic understanding and detail supplementation of original actions, making the model's understanding of the concept of interactive "actions" more accurate and generating images with more accurate interactive actions. Finally, we design an entity control network which generates masks with entity semantic guidance, then leveraging multi-scale convolutional network to enhance entity feature and dynamic network to fuse feature. It effectively controls entities and significantly improves image quality. Experiments show that the proposed CEIDM method is better than the most representative existing methods in both entity control and their interaction control.
Separation and Collaboration: Two-Level Routing Grouped Mixture-of-Experts for Multi-Domain Continual Learning
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:Multi-Domain Continual Learning (MDCL) acquires knowledge from sequential tasks with shifting class sets and distribution. Despite the Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods can adapt for this dual heterogeneity, they still suffer from catastrophic forgetting and forward forgetting. To address these challenges, we propose a Two-Level Routing Grouped Mixture-of-Experts (TRGE) method. Firstly, TRGE dynamically expands the pre-trained CLIP model, assigning specific expert group for each task to mitigate catastrophic forgetting. With the number of experts continually grows in this process, TRGE maintains the static experts count within the group and introduces the intra-group router to alleviate routing overfitting caused by the increasing routing complexity. Meanwhile, we design an inter-group routing policy based on task identifiers and task prototype distance, which dynamically selects relevant expert groups and combines their outputs to enhance inter-task collaboration. Secondly, to get the correct task identifiers, we leverage Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) which own powerful multimodal comprehension capabilities to generate semantic task descriptions and recognize the correct task identifier. Finally, to mitigate forward forgetting, we dynamically fuse outputs for unseen samples from the frozen CLIP model and TRGE adapter based on training progress, leveraging both pre-trained and learned knowledge. Through extensive experiments across various settings, our method outperforms other advanced methods with fewer trainable parameters.
Perceive Anything: Recognize, Explain, Caption, and Segment Anything in Images and Videos
Jun 05, 2025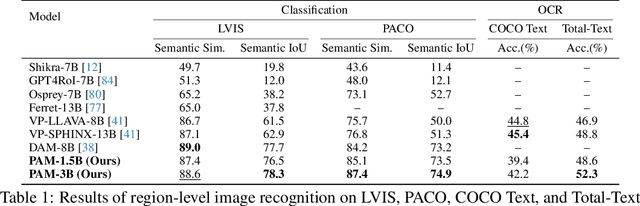
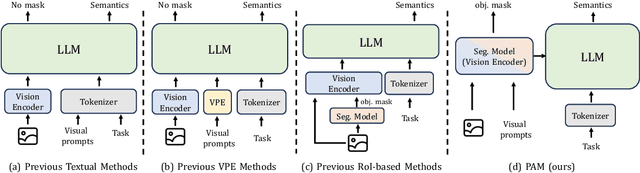
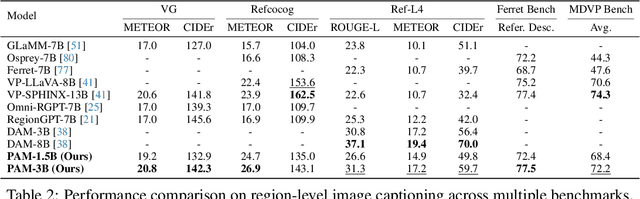
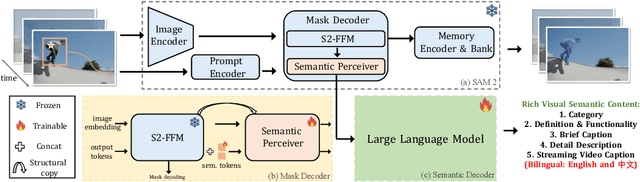
Abstract:We present Perceive Anything Model (PAM), a conceptually straightforward and efficient framework for comprehensive region-level visual understanding in images and videos. Our approach extends the powerful segmentation model SAM 2 by integrating Large Language Models (LLMs), enabling simultaneous object segmentation with the generation of diverse, region-specific semantic outputs, including categories, label definition, functional explanations, and detailed captions. A key component, Semantic Perceiver, is introduced to efficiently transform SAM 2's rich visual features, which inherently carry general vision, localization, and semantic priors into multi-modal tokens for LLM comprehension. To support robust multi-granularity understanding, we also develop a dedicated data refinement and augmentation pipeline, yielding a high-quality dataset of 1.5M image and 0.6M video region-semantic annotations, including novel region-level streaming video caption data. PAM is designed for lightweightness and efficiency, while also demonstrates strong performance across a diverse range of region understanding tasks. It runs 1.2-2.4x faster and consumes less GPU memory than prior approaches, offering a practical solution for real-world applications. We believe that our effective approach will serve as a strong baseline for future research in region-level visual understanding.
Delving into RL for Image Generation with CoT: A Study on DPO vs. GRPO
May 22, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements underscore the significant role of Reinforcement Learning (RL) in enhancing the Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). Two prominent RL algorithms, Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) and Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), are central to these developments, showcasing different pros and cons. Autoregressive image generation, also interpretable as a sequential CoT reasoning process, presents unique challenges distinct from LLM-based CoT reasoning. These encompass ensuring text-image consistency, improving image aesthetic quality, and designing sophisticated reward models, rather than relying on simpler rule-based rewards. While recent efforts have extended RL to this domain, these explorations typically lack an in-depth analysis of the domain-specific challenges and the characteristics of different RL strategies. To bridge this gap, we provide the first comprehensive investigation of the GRPO and DPO algorithms in autoregressive image generation, evaluating their in-domain performance and out-of-domain generalization, while scrutinizing the impact of different reward models on their respective capabilities. Our findings reveal that GRPO and DPO exhibit distinct advantages, and crucially, that reward models possessing stronger intrinsic generalization capabilities potentially enhance the generalization potential of the applied RL algorithms. Furthermore, we systematically explore three prevalent scaling strategies to enhance both their in-domain and out-of-domain proficiency, deriving unique insights into efficiently scaling performance for each paradigm. We hope our study paves a new path for inspiring future work on developing more effective RL algorithms to achieve robust CoT reasoning in the realm of autoregressive image generation. Code is released at https://github.com/ZiyuGuo99/Image-Generation-CoT
Are Large Language Models Good In-context Learners for Financial Sentiment Analysis?
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:Recently, large language models (LLMs) with hundreds of billions of parameters have demonstrated the emergent ability, surpassing traditional methods in various domains even without fine-tuning over domain-specific data. However, when it comes to financial sentiment analysis (FSA)$\unicode{x2013}$a fundamental task in financial AI$\unicode{x2013}$these models often encounter various challenges, such as complex financial terminology, subjective human emotions, and ambiguous inclination expressions. In this paper, we aim to answer the fundamental question: whether LLMs are good in-context learners for FSA? Unveiling this question can yield informative insights on whether LLMs can learn to address the challenges by generalizing in-context demonstrations of financial document-sentiment pairs to the sentiment analysis of new documents, given that finetuning these models on finance-specific data is difficult, if not impossible at all. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first paper exploring in-context learning for FSA that covers most modern LLMs (recently released DeepSeek V3 included) and multiple in-context sample selection methods. Comprehensive experiments validate the in-context learning capability of LLMs for FSA.
MAVIS: Mathematical Visual Instruction Tuning
Jul 11, 2024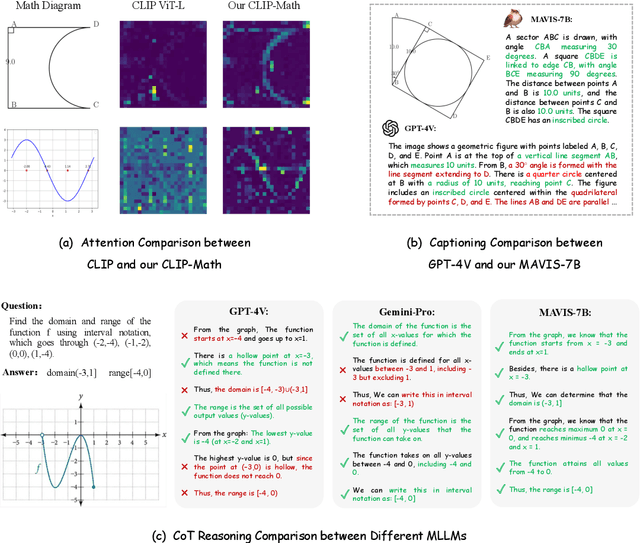
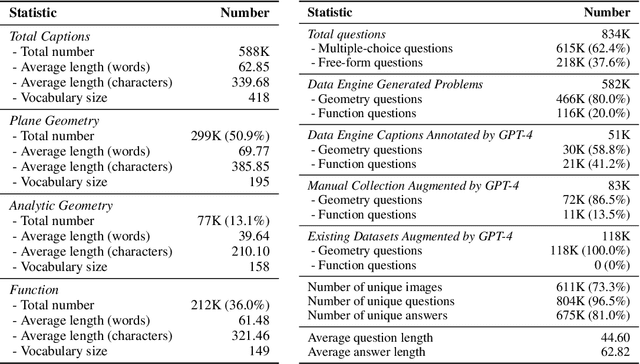
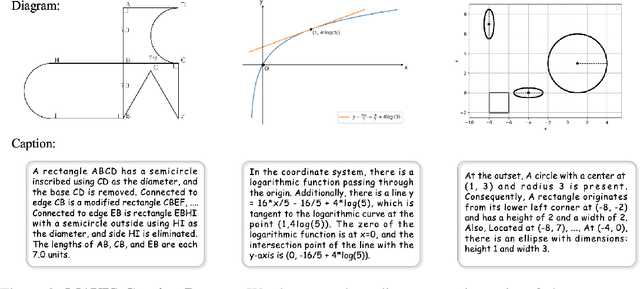
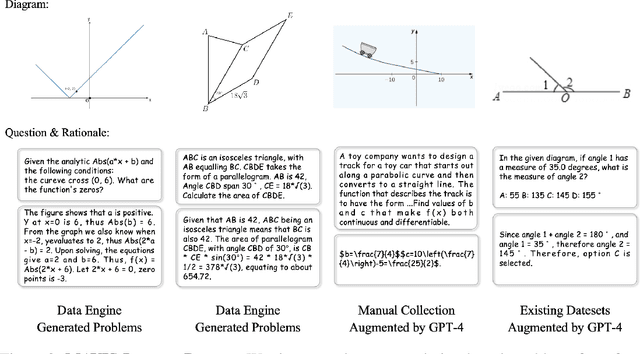
Abstract:Multi-modal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have recently emerged as a significant focus in academia and industry. Despite their proficiency in general multi-modal scenarios, the mathematical problem-solving capabilities in visual contexts remain insufficiently explored. We identify three key areas within MLLMs that need to be improved: visual encoding of math diagrams, diagram-language alignment, and mathematical reasoning skills. This draws forth an urgent demand for large-scale, high-quality data and training pipelines in visual mathematics. In this paper, we propose MAVIS, the first MAthematical VISual instruction tuning paradigm for MLLMs, involving a series of mathematical visual datasets and specialized MLLMs. Targeting the three issues, MAVIS contains three progressive training stages from scratch. First, we curate MAVIS-Caption, consisting of 558K diagram-caption pairs, to fine-tune a math-specific vision encoder (CLIP-Math) through contrastive learning, tailored for improved diagram visual encoding. Second, we utilize MAVIS-Caption to align the CLIP-Math with a large language model (LLM) by a projection layer, enhancing vision-language alignment in mathematical domains. Third, we introduce MAVIS-Instruct, including 900K meticulously collected and annotated visual math problems, which is adopted to finally instruct-tune the MLLM for robust mathematical reasoning skills. In MAVIS-Instruct, we incorporate complete chain-of-thought (CoT) rationales for each problem, and minimize textual redundancy, thereby concentrating the model towards the visual elements. Data and Models are released at https://github.com/ZrrSkywalker/MAVIS
MR-MLLM: Mutual Reinforcement of Multimodal Comprehension and Vision Perception
Jun 22, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in tasks like visual question answering and common sense reasoning, while visual perception models have made significant strides in perception tasks, such as detection and segmentation. However, MLLMs mainly focus on high-level image-text interpretations and struggle with fine-grained visual understanding, and vision perception models usually suffer from open-world distribution shifts due to their limited model capacity. To overcome these challenges, we propose the Mutually Reinforced Multimodal Large Language Model (MR-MLLM), a novel framework that synergistically enhances visual perception and multimodal comprehension. First, a shared query fusion mechanism is proposed to harmonize detailed visual inputs from vision models with the linguistic depth of language models, enhancing multimodal comprehension and vision perception synergistically. Second, we propose the perception-enhanced cross-modal integration method, incorporating novel modalities from vision perception outputs, like object detection bounding boxes, to capture subtle visual elements, thus enriching the understanding of both visual and textual data. In addition, an innovative perception-embedded prompt generation mechanism is proposed to embed perceptual information into the language model's prompts, aligning the responses contextually and perceptually for a more accurate multimodal interpretation. Extensive experiments demonstrate MR-MLLM's superior performance in various multimodal comprehension and vision perception tasks, particularly those requiring corner case vision perception and fine-grained language comprehension.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge