Jiankang Deng
UniForce: A Unified Latent Force Model for Robot Manipulation with Diverse Tactile Sensors
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Force sensing is essential for dexterous robot manipulation, but scaling force-aware policy learning is hindered by the heterogeneity of tactile sensors. Differences in sensing principles (e.g., optical vs. magnetic), form factors, and materials typically require sensor-specific data collection, calibration, and model training, thereby limiting generalisability. We propose UniForce, a novel unified tactile representation learning framework that learns a shared latent force space across diverse tactile sensors. UniForce reduces cross-sensor domain shift by jointly modeling inverse dynamics (image-to-force) and forward dynamics (force-to-image), constrained by force equilibrium and image reconstruction losses to produce force-grounded representations. To avoid reliance on expensive external force/torque (F/T) sensors, we exploit static equilibrium and collect force-paired data via direct sensor--object--sensor interactions, enabling cross-sensor alignment with contact force. The resulting universal tactile encoder can be plugged into downstream force-aware robot manipulation tasks with zero-shot transfer, without retraining or finetuning. Extensive experiments on heterogeneous tactile sensors including GelSight, TacTip, and uSkin, demonstrate consistent improvements in force estimation over prior methods, and enable effective cross-sensor coordination in Vision-Tactile-Language-Action (VTLA) models for a robotic wiping task. Code and datasets will be released.
UniMorphGrasp: Diffusion Model with Morphology-Awareness for Cross-Embodiment Dexterous Grasp Generation
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Cross-embodiment dexterous grasping aims to generate stable and diverse grasps for robotic hands with heterogeneous kinematic structures. Existing methods are often tailored to specific hand designs and fail to generalize to unseen hand morphologies outside the training distribution. To address these limitations, we propose \textbf{UniMorphGrasp}, a diffusion-based framework that incorporates hand morphological information into the grasp generation process for unified cross-embodiment grasp synthesis. The proposed approach maps grasps from diverse robotic hands into a unified human-like canonical hand pose representation, providing a common space for learning. Grasp generation is then conditioned on structured representations of hand kinematics, encoded as graphs derived from hand configurations, together with object geometry. In addition, a loss function is introduced that exploits the hierarchical organization of hand kinematics to guide joint-level supervision. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniMorphGrasp achieves state-of-the-art performance on existing dexterous grasp benchmarks and exhibits strong zero-shot generalization to previously unseen hand structures, enabling scalable and practical cross-embodiment grasp deployment.
MaDiS: Taming Masked Diffusion Language Models for Sign Language Generation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Sign language generation (SLG) aims to translate written texts into expressive sign motions, bridging communication barriers for the Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing communities. Recent studies formulate SLG within the language modeling framework using autoregressive language models, which suffer from unidirectional context modeling and slow token-by-token inference. To address these limitations, we present MaDiS, a masked-diffusion-based language model for SLG that captures bidirectional dependencies and supports efficient parallel multi-token generation. We further introduce a tri-level cross-modal pretraining scheme that jointly learns from token-, latent-, and 3D physical-space objectives, leading to richer and more grounded sign representations. To accelerate model convergence in the fine-tuning stage, we design a novel unmasking strategy with temporal checkpoints, reducing the combinatorial complexity of unmasking orders by over $10^{41}$ times. In addition, a mixture-of-parts embedding layer is developed to effectively fuse information stored in different part-wise sign tokens through learnable gates and well-optimized codebooks. Extensive experiments on CSL-Daily, Phoenix-2014T, and How2Sign demonstrate that MaDiS achieves superior performance across multiple metrics, including DTW error and two newly introduced metrics, SiBLEU and SiCLIP, while reducing inference latency by nearly 30%. Code and models will be released on our project page.
Optimizing Multimodal LLMs for Egocentric Video Understanding: A Solution for the HD-EPIC VQA Challenge
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) struggle with complex video QA benchmarks like HD-EPIC VQA due to ambiguous queries/options, poor long-range temporal reasoning, and non-standardized outputs. We propose a framework integrating query/choice pre-processing, domain-specific Qwen2.5-VL fine-tuning, a novel Temporal Chain-of-Thought (T-CoT) prompting for multi-step reasoning, and robust post-processing. This system achieves 41.6% accuracy on HD-EPIC VQA, highlighting the need for holistic pipeline optimization in demanding video understanding. Our code, fine-tuned models are available at https://github.com/YoungSeng/Egocentric-Co-Pilot.
Interact2Ar: Full-Body Human-Human Interaction Generation via Autoregressive Diffusion Models
Dec 22, 2025
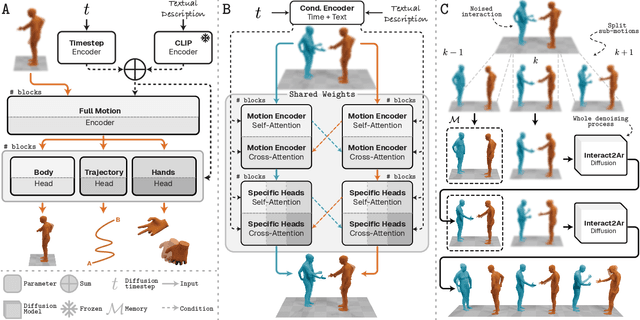
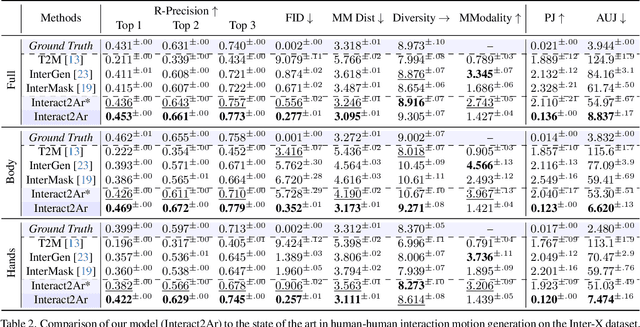
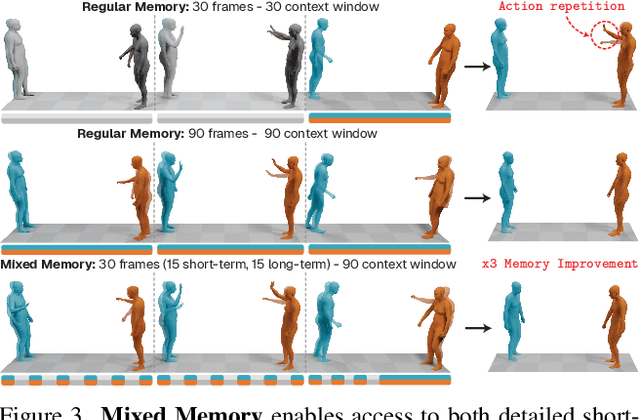
Abstract:Generating realistic human-human interactions is a challenging task that requires not only high-quality individual body and hand motions, but also coherent coordination among all interactants. Due to limitations in available data and increased learning complexity, previous methods tend to ignore hand motions, limiting the realism and expressivity of the interactions. Additionally, current diffusion-based approaches generate entire motion sequences simultaneously, limiting their ability to capture the reactive and adaptive nature of human interactions. To address these limitations, we introduce Interact2Ar, the first end-to-end text-conditioned autoregressive diffusion model for generating full-body, human-human interactions. Interact2Ar incorporates detailed hand kinematics through dedicated parallel branches, enabling high-fidelity full-body generation. Furthermore, we introduce an autoregressive pipeline coupled with a novel memory technique that facilitates adaptation to the inherent variability of human interactions using efficient large context windows. The adaptability of our model enables a series of downstream applications, including temporal motion composition, real-time adaptation to disturbances, and extension beyond dyadic to multi-person scenarios. To validate the generated motions, we introduce a set of robust evaluators and extended metrics designed specifically for assessing full-body interactions. Through quantitative and qualitative experiments, we demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of Interact2Ar.
An Anatomy of Vision-Language-Action Models: From Modules to Milestones and Challenges
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models are driving a revolution in robotics, enabling machines to understand instructions and interact with the physical world. This field is exploding with new models and datasets, making it both exciting and challenging to keep pace with. This survey offers a clear and structured guide to the VLA landscape. We design it to follow the natural learning path of a researcher: we start with the basic Modules of any VLA model, trace the history through key Milestones, and then dive deep into the core Challenges that define recent research frontier. Our main contribution is a detailed breakdown of the five biggest challenges in: (1) Representation, (2) Execution, (3) Generalization, (4) Safety, and (5) Dataset and Evaluation. This structure mirrors the developmental roadmap of a generalist agent: establishing the fundamental perception-action loop, scaling capabilities across diverse embodiments and environments, and finally ensuring trustworthy deployment-all supported by the essential data infrastructure. For each of them, we review existing approaches and highlight future opportunities. We position this paper as both a foundational guide for newcomers and a strategic roadmap for experienced researchers, with the dual aim of accelerating learning and inspiring new ideas in embodied intelligence. A live version of this survey, with continuous updates, is maintained on our \href{https://suyuz1.github.io/VLA-Survey-Anatomy/}{project page}.
SATGround: A Spatially-Aware Approach for Visual Grounding in Remote Sensing
Dec 09, 2025Abstract:Vision-language models (VLMs) are emerging as powerful generalist tools for remote sensing, capable of integrating information across diverse tasks and enabling flexible, instruction-based interactions via a chat interface. In this work, we enhance VLM-based visual grounding in satellite imagery by proposing a novel structured localization mechanism. Our approach involves finetuning a pretrained VLM on a diverse set of instruction-following tasks, while interfacing a dedicated grounding module through specialized control tokens for localization. This method facilitates joint reasoning over both language and spatial information, significantly enhancing the model's ability to precisely localize objects in complex satellite scenes. We evaluate our framework on several remote sensing benchmarks, consistently improving the state-of-the-art, including a 24.8% relative improvement over previous methods on visual grounding. Our results highlight the benefits of integrating structured spatial reasoning into VLMs, paving the way for more reliable real-world satellite data analysis.
Reconstructing 3D Scenes in Native High Dynamic Range
Nov 17, 2025Abstract:High Dynamic Range (HDR) imaging is essential for professional digital media creation, e.g., filmmaking, virtual production, and photorealistic rendering. However, 3D scene reconstruction has primarily focused on Low Dynamic Range (LDR) data, limiting its applicability to professional workflows. Existing approaches that reconstruct HDR scenes from LDR observations rely on multi-exposure fusion or inverse tone-mapping, which increase capture complexity and depend on synthetic supervision. With the recent emergence of cameras that directly capture native HDR data in a single exposure, we present the first method for 3D scene reconstruction that directly models native HDR observations. We propose {\bf Native High dynamic range 3D Gaussian Splatting (NH-3DGS)}, which preserves the full dynamic range throughout the reconstruction pipeline. Our key technical contribution is a novel luminance-chromaticity decomposition of the color representation that enables direct optimization from native HDR camera data. We demonstrate on both synthetic and real multi-view HDR datasets that NH-3DGS significantly outperforms existing methods in reconstruction quality and dynamic range preservation, enabling professional-grade 3D reconstruction directly from native HDR captures. Code and datasets will be made available.
Plug-and-Play Clarifier: A Zero-Shot Multimodal Framework for Egocentric Intent Disambiguation
Nov 12, 2025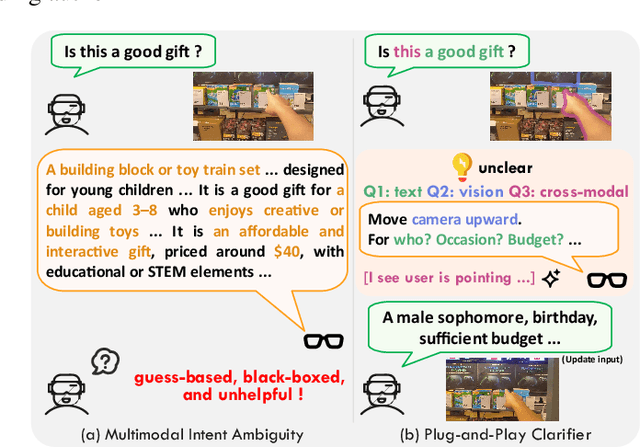
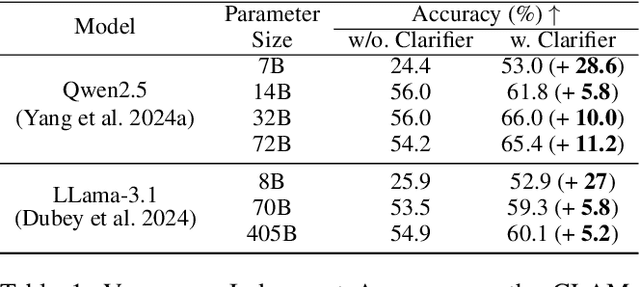
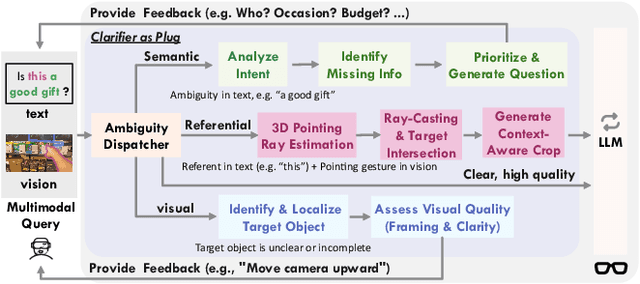
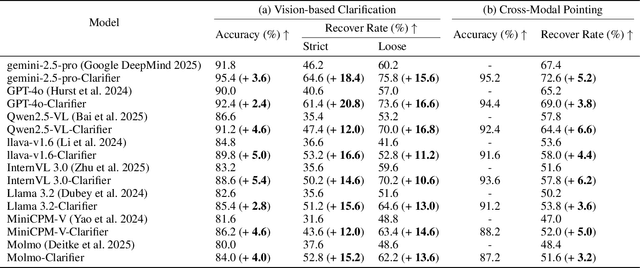
Abstract:The performance of egocentric AI agents is fundamentally limited by multimodal intent ambiguity. This challenge arises from a combination of underspecified language, imperfect visual data, and deictic gestures, which frequently leads to task failure. Existing monolithic Vision-Language Models (VLMs) struggle to resolve these multimodal ambiguous inputs, often failing silently or hallucinating responses. To address these ambiguities, we introduce the Plug-and-Play Clarifier, a zero-shot and modular framework that decomposes the problem into discrete, solvable sub-tasks. Specifically, our framework consists of three synergistic modules: (1) a text clarifier that uses dialogue-driven reasoning to interactively disambiguate linguistic intent, (2) a vision clarifier that delivers real-time guidance feedback, instructing users to adjust their positioning for improved capture quality, and (3) a cross-modal clarifier with grounding mechanism that robustly interprets 3D pointing gestures and identifies the specific objects users are pointing to. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our framework improves the intent clarification performance of small language models (4--8B) by approximately 30%, making them competitive with significantly larger counterparts. We also observe consistent gains when applying our framework to these larger models. Furthermore, our vision clarifier increases corrective guidance accuracy by over 20%, and our cross-modal clarifier improves semantic answer accuracy for referential grounding by 5%. Overall, our method provides a plug-and-play framework that effectively resolves multimodal ambiguity and significantly enhances user experience in egocentric interaction.
RetouchLLM: Training-free White-box Image Retouching
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Image retouching not only enhances visual quality but also serves as a means of expressing personal preferences and emotions. However, existing learning-based approaches require large-scale paired data and operate as black boxes, making the retouching process opaque and limiting their adaptability to handle diverse, user- or image-specific adjustments. In this work, we propose RetouchLLM, a training-free white-box image retouching system, which requires no training data and performs interpretable, code-based retouching directly on high-resolution images. Our framework progressively enhances the image in a manner similar to how humans perform multi-step retouching, allowing exploration of diverse adjustment paths. It comprises of two main modules: a visual critic that identifies differences between the input and reference images, and a code generator that produces executable codes. Experiments demonstrate that our approach generalizes well across diverse retouching styles, while natural language-based user interaction enables interpretable and controllable adjustments tailored to user intent.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge