Dingkun Long
Rethinking Composed Image Retrieval Evaluation: A Fine-Grained Benchmark from Image Editing
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Composed Image Retrieval (CIR) is a pivotal and complex task in multimodal understanding. Current CIR benchmarks typically feature limited query categories and fail to capture the diverse requirements of real-world scenarios. To bridge this evaluation gap, we leverage image editing to achieve precise control over modification types and content, enabling a pipeline for synthesizing queries across a broad spectrum of categories. Using this pipeline, we construct EDIR, a novel fine-grained CIR benchmark. EDIR encompasses 5,000 high-quality queries structured across five main categories and fifteen subcategories. Our comprehensive evaluation of 13 multimodal embedding models reveals a significant capability gap; even state-of-the-art models (e.g., RzenEmbed and GME) struggle to perform consistently across all subcategories, highlighting the rigorous nature of our benchmark. Through comparative analysis, we further uncover inherent limitations in existing benchmarks, such as modality biases and insufficient categorical coverage. Furthermore, an in-domain training experiment demonstrates the feasibility of our benchmark. This experiment clarifies the task challenges by distinguishing between categories that are solvable with targeted data and those that expose intrinsic limitations of current model architectures.
Qwen3-VL-Embedding and Qwen3-VL-Reranker: A Unified Framework for State-of-the-Art Multimodal Retrieval and Ranking
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce the Qwen3-VL-Embedding and Qwen3-VL-Reranker model series, the latest extensions of the Qwen family built on the Qwen3-VL foundation model. Together, they provide an end-to-end pipeline for high-precision multimodal search by mapping diverse modalities, including text, images, document images, and video, into a unified representation space. The Qwen3-VL-Embedding model employs a multi-stage training paradigm, progressing from large-scale contrastive pre-training to reranking model distillation, to generate semantically rich high-dimensional vectors. It supports Matryoshka Representation Learning, enabling flexible embedding dimensions, and handles inputs up to 32k tokens. Complementing this, Qwen3-VL-Reranker performs fine-grained relevance estimation for query-document pairs using a cross-encoder architecture with cross-attention mechanisms. Both model series inherit the multilingual capabilities of Qwen3-VL, supporting more than 30 languages, and are released in $\textbf{2B}$ and $\textbf{8B}$ parameter sizes to accommodate diverse deployment requirements. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that the Qwen3-VL-Embedding series achieves state-of-the-art results across diverse multimodal embedding evaluation benchmarks. Specifically, Qwen3-VL-Embedding-8B attains an overall score of $\textbf{77.8}$ on MMEB-V2, ranking first among all models (as of January 8, 2025). This report presents the architecture, training methodology, and practical capabilities of the series, demonstrating their effectiveness on various multimodal retrieval tasks, including image-text retrieval, visual question answering, and video-text matching.
Towards Universal Video Retrieval: Generalizing Video Embedding via Synthesized Multimodal Pyramid Curriculum
Oct 31, 2025Abstract:The prevailing video retrieval paradigm is structurally misaligned, as narrow benchmarks incentivize correspondingly limited data and single-task training. Therefore, universal capability is suppressed due to the absence of a diagnostic evaluation that defines and demands multi-dimensional generalization. To break this cycle, we introduce a framework built on the co-design of evaluation, data, and modeling. First, we establish the Universal Video Retrieval Benchmark (UVRB), a suite of 16 datasets designed not only to measure performance but also to diagnose critical capability gaps across tasks and domains. Second, guided by UVRB's diagnostics, we introduce a scalable synthesis workflow that generates 1.55 million high-quality pairs to populate the semantic space required for universality. Finally, we devise the Modality Pyramid, a curriculum that trains our General Video Embedder (GVE) by explicitly leveraging the latent interconnections within our diverse data. Extensive experiments show GVE achieves state-of-the-art zero-shot generalization on UVRB. In particular, our analysis reveals that popular benchmarks are poor predictors of general ability and that partially relevant retrieval is a dominant but overlooked scenario. Overall, our co-designed framework provides a practical path to escape the limited scope and advance toward truly universal video retrieval.
$\text{E}^2\text{Rank}$: Your Text Embedding can Also be an Effective and Efficient Listwise Reranker
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Text embedding models serve as a fundamental component in real-world search applications. By mapping queries and documents into a shared embedding space, they deliver competitive retrieval performance with high efficiency. However, their ranking fidelity remains limited compared to dedicated rerankers, especially recent LLM-based listwise rerankers, which capture fine-grained query-document and document-document interactions. In this paper, we propose a simple yet effective unified framework $\text{E}^2\text{Rank}$, means Efficient Embedding-based Ranking (also means Embedding-to-Rank), which extends a single text embedding model to perform both high-quality retrieval and listwise reranking through continued training under a listwise ranking objective, thereby achieving strong effectiveness with remarkable efficiency. By applying cosine similarity between the query and document embeddings as a unified ranking function, the listwise ranking prompt, which is constructed from the original query and its candidate documents, serves as an enhanced query enriched with signals from the top-K documents, akin to pseudo-relevance feedback (PRF) in traditional retrieval models. This design preserves the efficiency and representational quality of the base embedding model while significantly improving its reranking performance. Empirically, $\textrm{E}^2\text{Rank}$ achieves state-of-the-art results on the BEIR reranking benchmark and demonstrates competitive performance on the reasoning-intensive BRIGHT benchmark, with very low reranking latency. We also show that the ranking training process improves embedding performance on the MTEB benchmark. Our findings indicate that a single embedding model can effectively unify retrieval and reranking, offering both computational efficiency and competitive ranking accuracy.
Qwen3 Embedding: Advancing Text Embedding and Reranking Through Foundation Models
Jun 05, 2025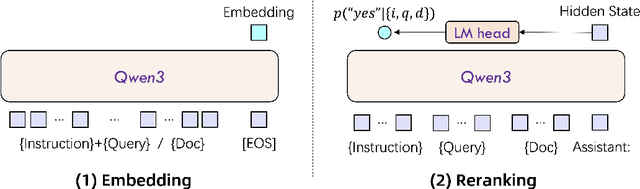
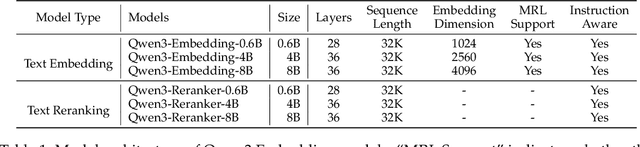
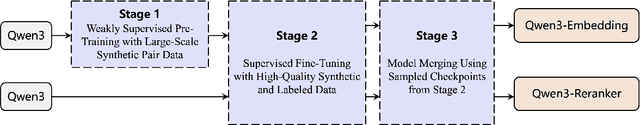
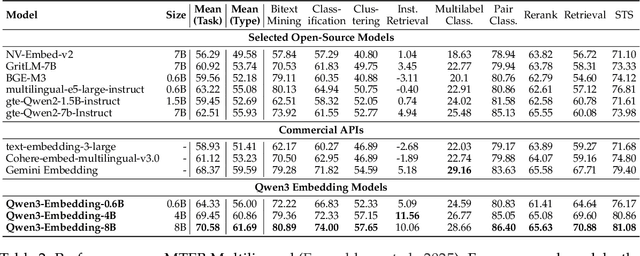
Abstract:In this work, we introduce the Qwen3 Embedding series, a significant advancement over its predecessor, the GTE-Qwen series, in text embedding and reranking capabilities, built upon the Qwen3 foundation models. Leveraging the Qwen3 LLMs' robust capabilities in multilingual text understanding and generation, our innovative multi-stage training pipeline combines large-scale unsupervised pre-training with supervised fine-tuning on high-quality datasets. Effective model merging strategies further ensure the robustness and adaptability of the Qwen3 Embedding series. During the training process, the Qwen3 LLMs serve not only as backbone models but also play a crucial role in synthesizing high-quality, rich, and diverse training data across multiple domains and languages, thus enhancing the training pipeline. The Qwen3 Embedding series offers a spectrum of model sizes (0.6B, 4B, 8B) for both embedding and reranking tasks, addressing diverse deployment scenarios where users can optimize for either efficiency or effectiveness. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that the Qwen3 Embedding series achieves state-of-the-art results across diverse benchmarks. Notably, it excels on the multilingual evaluation benchmark MTEB for text embedding, as well as in various retrieval tasks, including code retrieval, cross-lingual retrieval and multilingual retrieval. To facilitate reproducibility and promote community-driven research and development, the Qwen3 Embedding models are publicly available under the Apache 2.0 license.
Breaking the Modality Barrier: Universal Embedding Learning with Multimodal LLMs
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:The Contrastive Language-Image Pre-training (CLIP) framework has become a widely used approach for multimodal representation learning, particularly in image-text retrieval and clustering. However, its efficacy is constrained by three key limitations: (1) text token truncation, (2) isolated image-text encoding, and (3) deficient compositionality due to bag-of-words behavior. While recent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated significant advances in generalized vision-language understanding, their potential for learning transferable multimodal representations remains underexplored.In this work, we present UniME (Universal Multimodal Embedding), a novel two-stage framework that leverages MLLMs to learn discriminative representations for diverse downstream tasks. In the first stage, we perform textual discriminative knowledge distillation from a powerful LLM-based teacher model to enhance the embedding capability of the MLLM\'s language component. In the second stage, we introduce hard negative enhanced instruction tuning to further advance discriminative representation learning. Specifically, we initially mitigate false negative contamination and then sample multiple hard negatives per instance within each batch, forcing the model to focus on challenging samples. This approach not only improves discriminative power but also enhances instruction-following ability in downstream tasks. We conduct extensive experiments on the MMEB benchmark and multiple retrieval tasks, including short and long caption retrieval and compositional retrieval. Results demonstrate that UniME achieves consistent performance improvement across all tasks, exhibiting superior discriminative and compositional capabilities.
Towards Text-Image Interleaved Retrieval
Feb 18, 2025Abstract:Current multimodal information retrieval studies mainly focus on single-image inputs, which limits real-world applications involving multiple images and text-image interleaved content. In this work, we introduce the text-image interleaved retrieval (TIIR) task, where the query and document are interleaved text-image sequences, and the model is required to understand the semantics from the interleaved context for effective retrieval. We construct a TIIR benchmark based on naturally interleaved wikiHow tutorials, where a specific pipeline is designed to generate interleaved queries. To explore the task, we adapt several off-the-shelf retrievers and build a dense baseline by interleaved multimodal large language model (MLLM). We then propose a novel Matryoshka Multimodal Embedder (MME), which compresses the number of visual tokens at different granularity, to address the challenge of excessive visual tokens in MLLM-based TIIR models. Experiments demonstrate that simple adaption of existing models does not consistently yield effective results. Our MME achieves significant improvements over the baseline by substantially fewer visual tokens. We provide extensive analysis and will release the dataset and code to facilitate future research.
GME: Improving Universal Multimodal Retrieval by Multimodal LLMs
Dec 22, 2024



Abstract:Universal Multimodal Retrieval (UMR) aims to enable search across various modalities using a unified model, where queries and candidates can consist of pure text, images, or a combination of both. Previous work has attempted to adopt multimodal large language models (MLLMs) to realize UMR using only text data. However, our preliminary experiments demonstrate that more diverse multimodal training data can further unlock the potential of MLLMs. Despite its effectiveness, the existing multimodal training data is highly imbalanced in terms of modality, which motivates us to develop a training data synthesis pipeline and construct a large-scale, high-quality fused-modal training dataset. Based on the synthetic training data, we develop the General Multimodal Embedder (GME), an MLLM-based dense retriever designed for UMR. Furthermore, we construct a comprehensive UMR Benchmark (UMRB) to evaluate the effectiveness of our approach. Experimental results show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance among existing UMR methods. Last, we provide in-depth analyses of model scaling, training strategies, and perform ablation studies on both the model and synthetic data.
When Text Embedding Meets Large Language Model: A Comprehensive Survey
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:Text embedding has become a foundational technology in natural language processing (NLP) during the deep learning era, driving advancements across a wide array of downstream tasks. While many natural language understanding challenges can now be modeled using generative paradigms and leverage the robust generative and comprehension capabilities of large language models (LLMs), numerous practical applications, such as semantic matching, clustering, and information retrieval, continue to rely on text embeddings for their efficiency and effectiveness. In this survey, we categorize the interplay between LLMs and text embeddings into three overarching themes: (1) LLM-augmented text embedding, enhancing traditional embedding methods with LLMs; (2) LLMs as text embedders, utilizing their innate capabilities for embedding generation; and (3) Text embedding understanding with LLMs, leveraging LLMs to analyze and interpret embeddings. By organizing these efforts based on interaction patterns rather than specific downstream applications, we offer a novel and systematic overview of contributions from various research and application domains in the era of LLMs. Furthermore, we highlight the unresolved challenges that persisted in the pre-LLM era with pre-trained language models (PLMs) and explore the emerging obstacles brought forth by LLMs. Building on this analysis, we outline prospective directions for the evolution of text embedding, addressing both theoretical and practical opportunities in the rapidly advancing landscape of NLP.
Improving General Text Embedding Model: Tackling Task Conflict and Data Imbalance through Model Merging
Oct 19, 2024

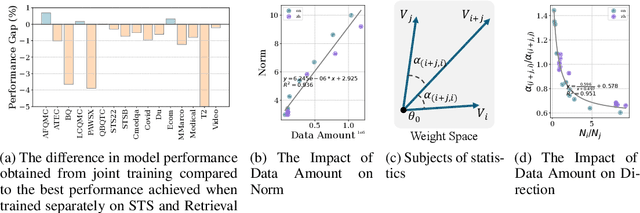

Abstract:Text embeddings are vital for tasks such as text retrieval and semantic textual similarity (STS). Recently, the advent of pretrained language models, along with unified benchmarks like the Massive Text Embedding Benchmark (MTEB), has facilitated the development of versatile general-purpose text embedding models. Advanced embedding models are typically developed using large-scale multi-task data and joint training across multiple tasks. However, our experimental analysis reveals two significant drawbacks of joint training: 1) Task Conflict: Gradients from different tasks interfere with each other, leading to negative transfer. 2) Data Imbalance: Disproportionate data distribution introduces biases that negatively impact performance across tasks. To overcome these challenges, we explore model merging-a technique that combines independently trained models to mitigate gradient conflicts and balance data distribution. We introduce a novel method, Self Positioning, which efficiently searches for optimal model combinations within the interpolation space of task vectors using stochastic gradient descent. Our experiments demonstrate that Self Positioning significantly enhances multi-task performance on the MTEB dataset, achieving an absolute improvement of 0.7 points. It outperforms traditional resampling methods while reducing computational costs. This work offers a robust approach to building generalized text embedding models with superior performance across diverse embedding-related tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge