Bingchen Zhao
Michael Pokorny
Composable Visual Tokenizers with Generator-Free Diagnostics of Learnability
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:We introduce CompTok, a training framework for learning visual tokenizers whose tokens are enhanced for compositionality. CompTok uses a token-conditioned diffusion decoder. By employing an InfoGAN-style objective, where we train a recognition model to predict the tokens used to condition the diffusion decoder using the decoded images, we enforce the decoder to not ignore any of the tokens. To promote compositional control, besides the original images, CompTok also trains on tokens formed by swapping token subsets between images, enabling more compositional control of the token over the decoder. As the swapped tokens between images do not have ground truth image targets, we apply a manifold constraint via an adversarial flow regularizer to keep unpaired swap generations on the natural-image distribution. The resulting tokenizer not only achieves state-of-the-art performance on image class-conditioned generation, but also demonstrates properties such as swapping tokens between images to achieve high level semantic editing of an image. Additionally, we propose two metrics that measures the landscape of the token space that can be useful to describe not only the compositionality of the tokens, but also how easy to learn the landscape is for a generator to be trained on this space. We show in experiments that CompTok can improve on both of the metrics as well as supporting state-of-the-art generators for class conditioned generation.
GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M: A Million-Scale, GPT-Generated Image Dataset
Jul 28, 2025
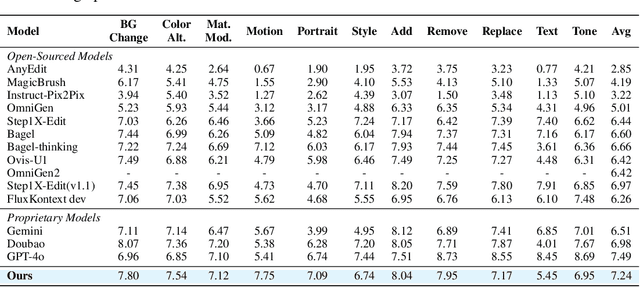
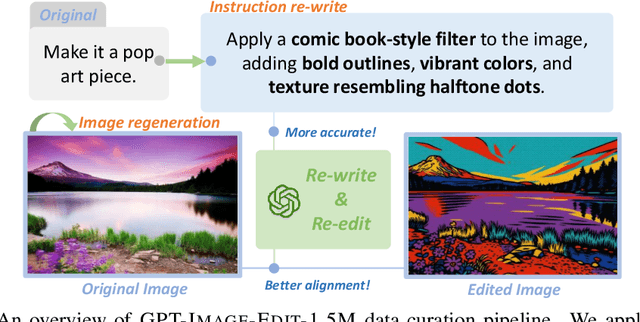
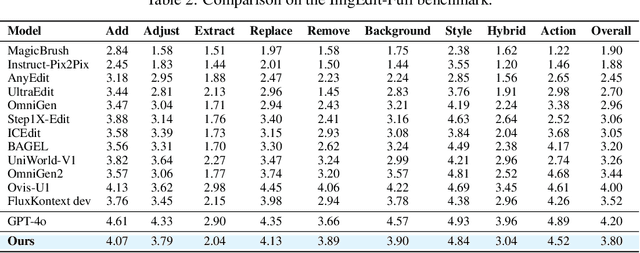
Abstract:Recent advancements in large multimodal models like GPT-4o have set a new standard for high-fidelity, instruction-guided image editing. However, the proprietary nature of these models and their training data creates a significant barrier for open-source research. To bridge this gap, we introduce GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M, a publicly available, large-scale image-editing corpus containing more than 1.5 million high-quality triplets (instruction, source image, edited image). We systematically construct this dataset by leveraging the versatile capabilities of GPT-4o to unify and refine three popular image-editing datasets: OmniEdit, HQ-Edit, and UltraEdit. Specifically, our methodology involves 1) regenerating output images to enhance visual quality and instruction alignment, and 2) selectively rewriting prompts to improve semantic clarity. To validate the efficacy of our dataset, we fine-tune advanced open-source models on GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M. The empirical results are exciting, e.g., the fine-tuned FluxKontext achieves highly competitive performance across a comprehensive suite of benchmarks, including 7.24 on GEdit-EN, 3.80 on ImgEdit-Full, and 8.78 on Complex-Edit, showing stronger instruction following and higher perceptual quality while maintaining identity. These scores markedly exceed all previously published open-source methods and substantially narrow the gap to leading proprietary models. We hope the full release of GPT-IMAGE-EDIT-1.5M can help to catalyze further open research in instruction-guided image editing.
Generalized Category Discovery under the Long-Tailed Distribution
Jun 14, 2025Abstract:This paper addresses the problem of Generalized Category Discovery (GCD) under a long-tailed distribution, which involves discovering novel categories in an unlabelled dataset using knowledge from a set of labelled categories. Existing works assume a uniform distribution for both datasets, but real-world data often exhibits a long-tailed distribution, where a few categories contain most examples, while others have only a few. While the long-tailed distribution is well-studied in supervised and semi-supervised settings, it remains unexplored in the GCD context. We identify two challenges in this setting - balancing classifier learning and estimating category numbers - and propose a framework based on confident sample selection and density-based clustering to tackle them. Our experiments on both long-tailed and conventional GCD datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our method.
Interpretable Text-Guided Image Clustering via Iterative Search
Jun 14, 2025



Abstract:Traditional clustering methods aim to group unlabeled data points based on their similarity to each other. However, clustering, in the absence of additional information, is an ill-posed problem as there may be many different, yet equally valid, ways to partition a dataset. Distinct users may want to use different criteria to form clusters in the same data, e.g. shape v.s. color. Recently introduced text-guided image clustering methods aim to address this ambiguity by allowing users to specify the criteria of interest using natural language instructions. This instruction provides the necessary context and control needed to obtain clusters that are more aligned with the users' intent. We propose a new text-guided clustering approach named ITGC that uses an iterative discovery process, guided by an unsupervised clustering objective, to generate interpretable visual concepts that better capture the criteria expressed in a user's instructions. We report superior performance compared to existing methods across a wide variety of image clustering and fine-grained classification benchmarks.
$\texttt{Complex-Edit}$: CoT-Like Instruction Generation for Complexity-Controllable Image Editing Benchmark
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:We introduce $\texttt{Complex-Edit}$, a comprehensive benchmark designed to systematically evaluate instruction-based image editing models across instructions of varying complexity. To develop this benchmark, we harness GPT-4o to automatically collect a diverse set of editing instructions at scale. Our approach follows a well-structured ``Chain-of-Edit'' pipeline: we first generate individual atomic editing tasks independently and then integrate them to form cohesive, complex instructions. Additionally, we introduce a suite of metrics to assess various aspects of editing performance, along with a VLM-based auto-evaluation pipeline that supports large-scale assessments. Our benchmark yields several notable insights: 1) Open-source models significantly underperform relative to proprietary, closed-source models, with the performance gap widening as instruction complexity increases; 2) Increased instructional complexity primarily impairs the models' ability to retain key elements from the input images and to preserve the overall aesthetic quality; 3) Decomposing a complex instruction into a sequence of atomic steps, executed in a step-by-step manner, substantially degrades performance across multiple metrics; 4) A straightforward Best-of-N selection strategy improves results for both direct editing and the step-by-step sequential approach; and 5) We observe a ``curse of synthetic data'': when synthetic data is involved in model training, the edited images from such models tend to appear increasingly synthetic as the complexity of the editing instructions rises -- a phenomenon that intriguingly also manifests in the latest GPT-4o outputs.
Oasis: One Image is All You Need for Multimodal Instruction Data Synthesis
Mar 13, 2025Abstract:The success of multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) has been largely attributed to the large-scale training data. However, the training data of many MLLMs is unavailable due to privacy concerns. The expensive and labor-intensive process of collecting multi-modal data further exacerbates the problem. Is it possible to synthesize multi-modal training data automatically without compromising diversity and quality? In this paper, we propose a new method, Oasis, to synthesize high-quality multi-modal data with only images. Oasis breaks through traditional methods by prompting only images to the MLLMs, thus extending the data diversity by a large margin. Our method features a delicate quality control method which ensures the data quality. We collected over 500k data and conducted incremental experiments on LLaVA-NeXT. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method can significantly improve the performance of MLLMs. The image-based synthesis also allows us to focus on the specific-domain ability of MLLMs. Code and data will be publicly available.
"Principal Components" Enable A New Language of Images
Mar 11, 2025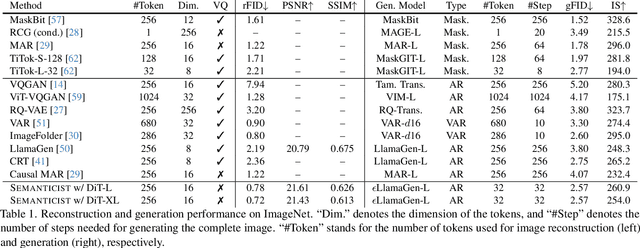
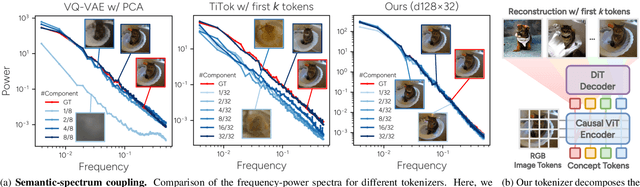
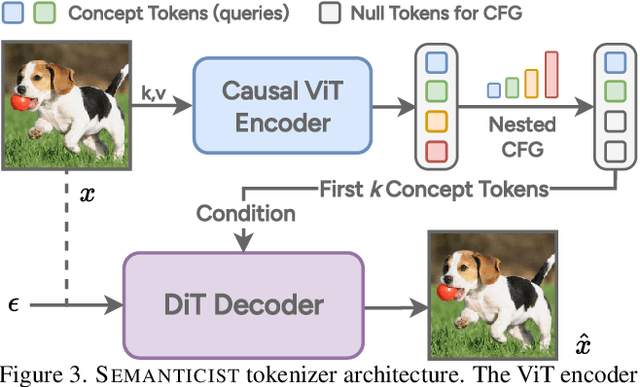
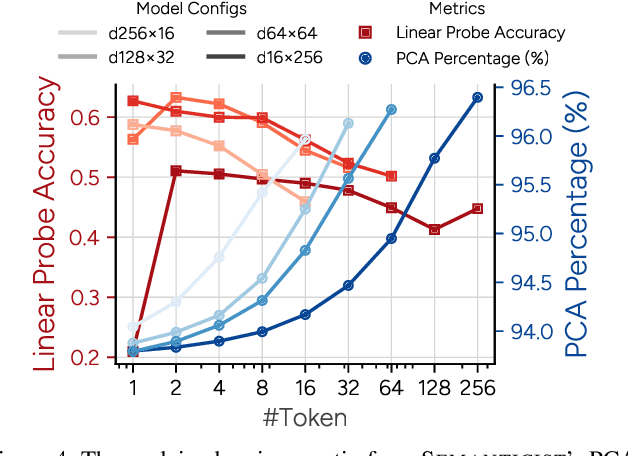
Abstract:We introduce a novel visual tokenization framework that embeds a provable PCA-like structure into the latent token space. While existing visual tokenizers primarily optimize for reconstruction fidelity, they often neglect the structural properties of the latent space -- a critical factor for both interpretability and downstream tasks. Our method generates a 1D causal token sequence for images, where each successive token contributes non-overlapping information with mathematically guaranteed decreasing explained variance, analogous to principal component analysis. This structural constraint ensures the tokenizer extracts the most salient visual features first, with each subsequent token adding diminishing yet complementary information. Additionally, we identified and resolved a semantic-spectrum coupling effect that causes the unwanted entanglement of high-level semantic content and low-level spectral details in the tokens by leveraging a diffusion decoder. Experiments demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art reconstruction performance and enables better interpretability to align with the human vision system. Moreover, auto-regressive models trained on our token sequences achieve performance comparable to current state-of-the-art methods while requiring fewer tokens for training and inference.
A Data-Centric Revisit of Pre-Trained Vision Models for Robot Learning
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Pre-trained vision models (PVMs) are fundamental to modern robotics, yet their optimal configuration remains unclear. Through systematic evaluation, we find that while DINO and iBOT outperform MAE across visuomotor control and perception tasks, they struggle when trained on non-(single-)object-centric (NOC) data--a limitation strongly correlated with their diminished ability to learn object-centric representations. This investigation indicates that the ability to form object-centric representations from the non-object-centric robotics dataset is the key to success for PVMs. Motivated by this discovery, we designed SlotMIM, a method that induces object-centric representations by introducing a semantic bottleneck to reduce the number of prototypes to encourage the emergence of objectness as well as cross-view consistency regularization for encouraging multiview invariance. Our experiments encompass pre-training on object-centric, scene-centric, web-crawled, and ego-centric data. Across all settings, our approach learns transferrable representations and achieves significant improvements over prior work in image recognition, scene understanding, and robot learning evaluations. When scaled up with million-scale datasets, our method also demonstrates superior data efficiency and scalability. Our code and models are publicly available at https://github.com/CVMI-Lab/SlotMIM.
Humanity's Last Exam
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Benchmarks are important tools for tracking the rapid advancements in large language model (LLM) capabilities. However, benchmarks are not keeping pace in difficulty: LLMs now achieve over 90\% accuracy on popular benchmarks like MMLU, limiting informed measurement of state-of-the-art LLM capabilities. In response, we introduce Humanity's Last Exam (HLE), a multi-modal benchmark at the frontier of human knowledge, designed to be the final closed-ended academic benchmark of its kind with broad subject coverage. HLE consists of 3,000 questions across dozens of subjects, including mathematics, humanities, and the natural sciences. HLE is developed globally by subject-matter experts and consists of multiple-choice and short-answer questions suitable for automated grading. Each question has a known solution that is unambiguous and easily verifiable, but cannot be quickly answered via internet retrieval. State-of-the-art LLMs demonstrate low accuracy and calibration on HLE, highlighting a significant gap between current LLM capabilities and the expert human frontier on closed-ended academic questions. To inform research and policymaking upon a clear understanding of model capabilities, we publicly release HLE at https://lastexam.ai.
Libra-Leaderboard: Towards Responsible AI through a Balanced Leaderboard of Safety and Capability
Dec 24, 2024



Abstract:To address this gap, we introduce Libra-Leaderboard, a comprehensive framework designed to rank LLMs through a balanced evaluation of performance and safety. Combining a dynamic leaderboard with an interactive LLM arena, Libra-Leaderboard encourages the joint optimization of capability and safety. Unlike traditional approaches that average performance and safety metrics, Libra-Leaderboard uses a distance-to-optimal-score method to calculate the overall rankings. This approach incentivizes models to achieve a balance rather than excelling in one dimension at the expense of some other ones. In the first release, Libra-Leaderboard evaluates 26 mainstream LLMs from 14 leading organizations, identifying critical safety challenges even in state-of-the-art models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge