Zijun Wang
Compressive Beam-Pattern-Aware Near-field Beam Training via Total Variation Denoising
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Extremely large antenna arrays envisioned for 6G incurs near-field effect, where steering vector depends on angles and range simultaneously. Polar-domain near-field codebooks can focus energy accurately but incur extra two-dimensional sweeping overhead; compressed-sensing (CS) approaches with Gaussian-masked DFT sensing offer a lower-overhead alternative. This letter revisits near-field beam training using conventional DFT codebooks. Unlike far-field responses that concentrate energy on a few isolated DFT beams, near-field responses produce contiguous, plateau-like energy segments with sharp transitions in the DFT beamspace. Pure LASSO denoising, therefore, tends to over-shrink magnitudes and fragment plateaus. We propose a beam-pattern-preserving beam training scheme for multiple-path scenarios that combines LASSO with a lightweight denoising pipeline: LASSO to suppress small-amplitude noise, followed by total variation (TV) to maintain plateau levels and edge sharpness. The two proximal steps require no near-field codebook design. Simulations with Gaussian pilots show consistent NMSE and cosine-similarity gains over least squares and LASSO at the same pilot budget.
Efficient Mixture-of-Agents Serving via Tree-Structured Routing, Adaptive Pruning, and Dependency-Aware Prefill-Decode Overlap
Dec 19, 2025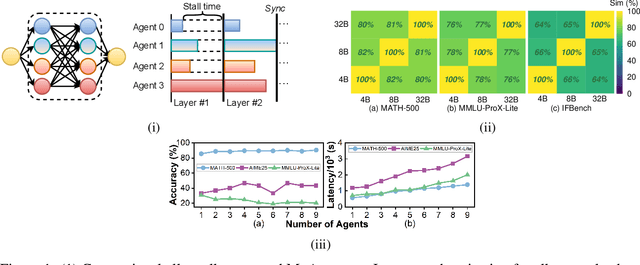
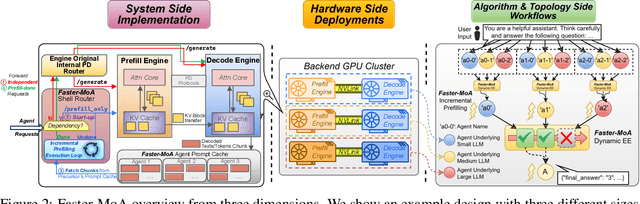
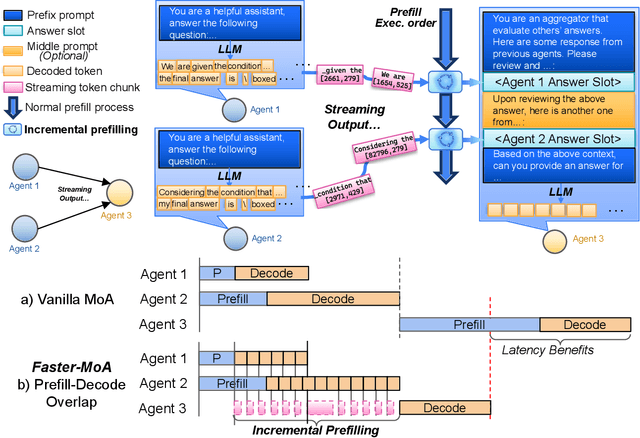
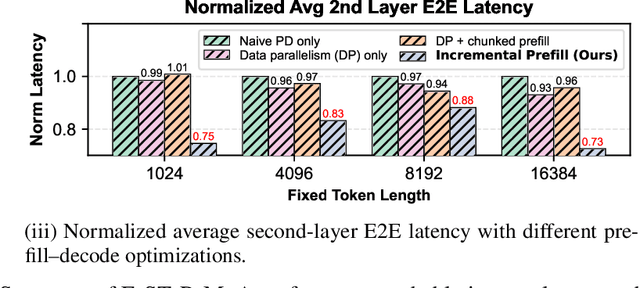
Abstract:Mixture-of-Agents (MoA) inference can suffer from dense inter-agent communication and low hardware utilization, which jointly inflate serving latency. We present a serving design that targets these bottlenecks through an algorithm-system co-design. First, we replace dense agent interaction graphs with a hierarchical tree topology that induces structured sparsity in inter-agent communication. Second, we introduce a runtime adaptive mechanism that selectively terminates or skips downstream agent invocations using semantic agreement and confidence signals from intermediate outputs. Third, we pipeline agent execution by overlapping incremental prefilling with decoding across dependency-related agents, improving utilization and reducing inference latency. Across representative tasks, this approach substantially reduces end-to-end latency (up to 90%) while maintaining comparable accuracy (within $\pm$1%) relative to dense-connectivity MoA baselines, and can improve accuracy in certain settings.
OnePiece: The Great Route to Generative Recommendation -- A Case Study from Tencent Algorithm Competition
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:In past years, the OpenAI's Scaling-Laws shows the amazing intelligence with the next-token prediction paradigm in neural language modeling, which pointing out a free-lunch way to enhance the model performance by scaling the model parameters. In RecSys, the retrieval stage is also follows a 'next-token prediction' paradigm, to recall the hunderds of items from the global item set, thus the generative recommendation usually refers specifically to the retrieval stage (without Tree-based methods). This raises a philosophical question: without a ground-truth next item, does the generative recommendation also holds a potential scaling law? In retrospect, the generative recommendation has two different technique paradigms: (1) ANN-based framework, utilizing the compressed user embedding to retrieve nearest other items in embedding space, e.g, Kuaiformer. (2) Auto-regressive-based framework, employing the beam search to decode the item from whole space, e.g, OneRec. In this paper, we devise a unified encoder-decoder framework to validate their scaling-laws at same time. Our empirical finding is that both of their losses strictly adhere to power-law Scaling Laws ($R^2$>0.9) within our unified architecture.
Cross-Layer Design for Near-Field mmWave Beam Management and Scheduling under Delay-Sensitive Traffic
Nov 16, 2025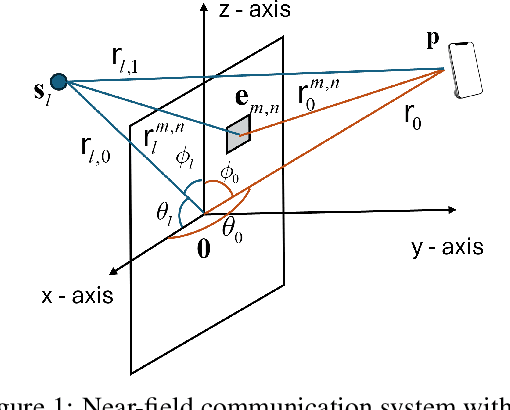

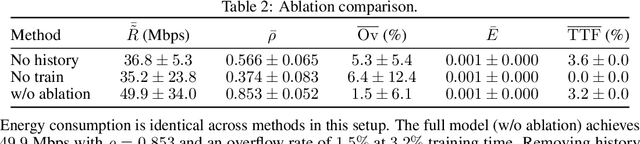
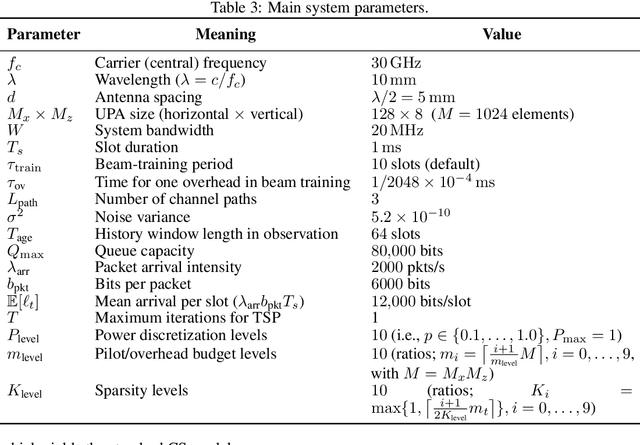
Abstract:Next-generation wireless networks will rely on mmWave/sub-THz spectrum and extremely large antenna arrays (ELAAs). This will push their operation into the near field where far-field beam management degrades and beam training becomes more costly and must be done more frequently. Because ELAA training and data transmission consume energy and training trades off with service time, we pose a cross-layer control problem that couples PHY-layer beam management with MAC-layer service under delay-sensitive traffic. The controller decides when to retrain and how aggressively to train (pilot count and sparsity) while allocating transmit power, explicitly balancing pilot overhead, data-phase rate, and energy to reduce the queueing delay of MAC-layer frames/packets to be transmitted. We model the problem as a partially observable Markov decision process and solve it with deep reinforcement learning. In simulations with a realistic near-field channel and varying mobility and traffic load, the learned policy outperforms strong 5G-NR--style baselines at a comparable energy: it achieves 85.5% higher throughput than DFT sweeping and reduces the overflow rate by 78%. These results indicate a practical path to overhead-aware, traffic-adaptive near-field beam management with implications for emerging low-latency, high-rate next-generation applications such as digital twin, spatial computing, and immersive communication.
Mimicking the Physicist's Eye:A VLM-centric Approach for Physics Formula Discovery
Aug 24, 2025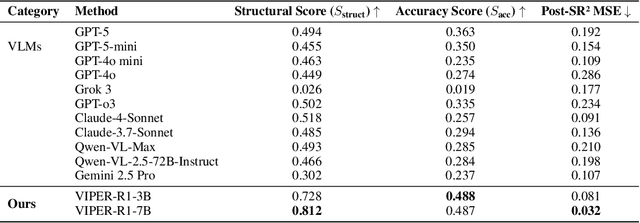
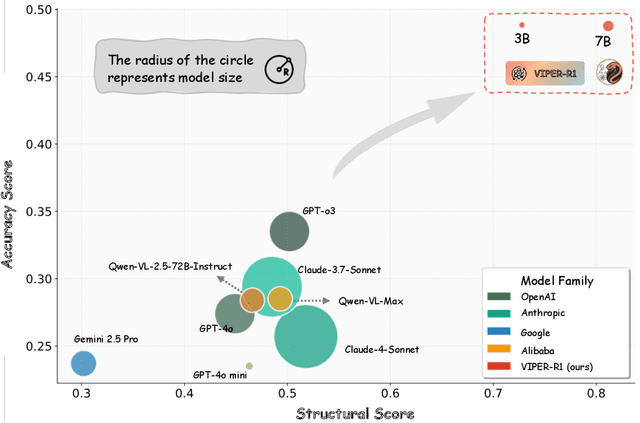
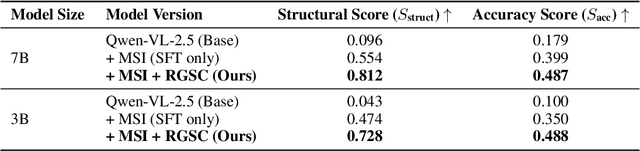
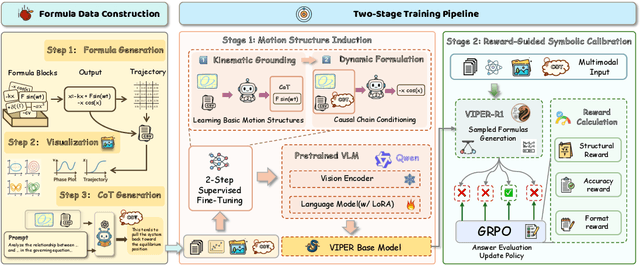
Abstract:Automated discovery of physical laws from observational data in the real world is a grand challenge in AI. Current methods, relying on symbolic regression or LLMs, are limited to uni-modal data and overlook the rich, visual phenomenological representations of motion that are indispensable to physicists. This "sensory deprivation" severely weakens their ability to interpret the inherent spatio-temporal patterns within dynamic phenomena. To address this gap, we propose VIPER-R1, a multimodal model that performs Visual Induction for Physics-based Equation Reasoning to discover fundamental symbolic formulas. It integrates visual perception, trajectory data, and symbolic reasoning to emulate the scientific discovery process. The model is trained via a curriculum of Motion Structure Induction (MSI), using supervised fine-tuning to interpret kinematic phase portraits and to construct hypotheses guided by a Causal Chain of Thought (C-CoT), followed by Reward-Guided Symbolic Calibration (RGSC) to refine the formula structure with reinforcement learning. During inference, the trained VIPER-R1 acts as an agent: it first posits a high-confidence symbolic ansatz, then proactively invokes an external symbolic regression tool to perform Symbolic Residual Realignment (SR^2). This final step, analogous to a physicist's perturbation analysis, reconciles the theoretical model with empirical data. To support this research, we introduce PhysSymbol, a new 5,000-instance multimodal corpus. Experiments show that VIPER-R1 consistently outperforms state-of-the-art VLM baselines in accuracy and interpretability, enabling more precise discovery of physical laws. Project page: https://jiaaqiliu.github.io/VIPER-R1/
Precise Near-Field Beam Training with DFT Codebook based on Amplitude-only Measurement
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:Extremely large antenna arrays (ELAAs) operating in high-frequency bands have spurred the development of near-field communication, driving advancements in beam training and signal processing design. In this work, we present a low-complexity near-field beam training scheme that fully utilizes the conventional discrete Fourier transform (DFT) codebook designed for far-field users. We begin by analyzing the received beam pattern in the near field and derive closed-form expressions for the beam width and central gain. These analytical results enable the definition of an angle-dependent, modified Rayleigh distance, which effectively distinguishes near-field and far-field user regimes. Building on the analysis, we develop a direct and computationally efficient method to estimate user distance, with a complexity of O(1), and further improve its accuracy through a simple refinement. Simulation results demonstrate significant gains in both single- and multi-user settings, with up to 2.38 dB SNR improvement over exhaustive search. To further enhance estimation accuracy, we additionally propose a maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) based refinement method, leveraging the Rician distribution of signal amplitudes and achieving accuracy close to the Cramer--Rao bound (CRB). Simulation shows the single-user and multi-user achievable rates can both approach those obtained with ideal channel state information.
Reinforcing the Diffusion Chain of Lateral Thought with Diffusion Language Models
May 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce the \emph{Diffusion Chain of Lateral Thought (DCoLT)}, a reasoning framework for diffusion language models. DCoLT treats each intermediate step in the reverse diffusion process as a latent "thinking" action and optimizes the entire reasoning trajectory to maximize the reward on the correctness of the final answer with outcome-based Reinforcement Learning (RL). Unlike traditional Chain-of-Thought (CoT) methods that follow a causal, linear thinking process, DCoLT allows bidirectional, non-linear reasoning with no strict rule on grammatical correctness amid its intermediate steps of thought. We implement DCoLT on two representative Diffusion Language Models (DLMs). First, we choose SEDD as a representative continuous-time discrete diffusion model, where its concrete score derives a probabilistic policy to maximize the RL reward over the entire sequence of intermediate diffusion steps. We further consider the discrete-time masked diffusion language model -- LLaDA, and find that the order to predict and unmask tokens plays an essential role to optimize its RL action resulting from the ranking-based Unmasking Policy Module (UPM) defined by the Plackett-Luce model. Experiments on both math and code generation tasks show that using only public data and 16 H800 GPUs, DCoLT-reinforced DLMs outperform other DLMs trained by SFT or RL or even both. Notably, DCoLT-reinforced LLaDA boosts its reasoning accuracy by +9.8%, +5.7%, +11.4%, +19.5% on GSM8K, MATH, MBPP, and HumanEval.
Sparsity-Aware Near-Field Beam Training via Multi-Beam Combination
May 13, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes an adaptive near-field beam training method to enhance performance in multi-user and multipath environments. The approach identifies multiple strongest beams through beam sweeping and linearly combines their received signals - capturing both amplitude and phase - for improved channel estimation. Two codebooks are considered: the conventional DFT codebook and a near-field codebook that samples both angular and distance domains. As the near-field basis functions are generally non-orthogonal and often over-complete, we exploit sparsity in the solution using LASSO-based linear regression, which can also suppress noise. Simulation results show that the near-field codebook reduces feedback overhead by up to 95% compared to the DFT codebook. The proposed LASSO regression method also maintains robustness under varying noise levels, particularly in low SNR regions. Furthermore, an off-grid refinement scheme is introduced to enhance accuracy especially when the codebook sampling is coarse, improving reconstruction accuracy by 69.4%.
STAR-1: Safer Alignment of Reasoning LLMs with 1K Data
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:This paper introduces STAR-1, a high-quality, just-1k-scale safety dataset specifically designed for large reasoning models (LRMs) like DeepSeek-R1. Built on three core principles -- diversity, deliberative reasoning, and rigorous filtering -- STAR-1 aims to address the critical needs for safety alignment in LRMs. Specifically, we begin by integrating existing open-source safety datasets from diverse sources. Then, we curate safety policies to generate policy-grounded deliberative reasoning samples. Lastly, we apply a GPT-4o-based safety scoring system to select training examples aligned with best practices. Experimental results show that fine-tuning LRMs with STAR-1 leads to an average 40% improvement in safety performance across four benchmarks, while only incurring a marginal decrease (e.g., an average of 1.1%) in reasoning ability measured across five reasoning tasks. Extensive ablation studies further validate the importance of our design principles in constructing STAR-1 and analyze its efficacy across both LRMs and traditional LLMs. Our project page is https://ucsc-vlaa.github.io/STAR-1.
Low-Complexity Near-Field Beam Training with DFT Codebook based on Beam Pattern Analysis
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Extremely large antenna arrays (ELAAs) operating in high-frequency bands have spurred the development of near-field communication, driving advancements in beam training and signal processing design. This paper proposed an efficient near-field beam training method using the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) codebook that is conventionally used for far-field users (FUs). We begin by analyzing the received beam pattern and deriving a closed-form expression for its width and central beam gain, which are validated through simulations. Using these derivations, we define a modified Rayleigh distance to distinguish between near-field and far-field users. Building on this, we propose a beam training method capable of simultaneously estimating user angle and distance with a complexity of O(1). Simulation results confirm the effectiveness of our proposed approach, demonstrating its capability for low-complexity near-field beam training while achieving high estimation accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge