Xiaoyu Du
DMAP: Human-Aligned Structural Document Map for Multimodal Document Understanding
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Existing multimodal document question-answering (QA) systems predominantly rely on flat semantic retrieval, representing documents as a set of disconnected text chunks and largely neglecting their intrinsic hierarchical and relational structures. Such flattening disrupts logical and spatial dependencies - such as section organization, figure-text correspondence, and cross-reference relations, that humans naturally exploit for comprehension. To address this limitation, we introduce a document-level structural Document MAP (DMAP), which explicitly encodes both hierarchical organization and inter-element relationships within multimodal documents. Specifically, we design a Structured-Semantic Understanding Agent to construct DMAP by organizing textual content together with figures, tables, charts, etc. into a human-aligned hierarchical schema that captures both semantic and layout dependencies. Building upon this representation, a Reflective Reasoning Agent performs structure-aware and evidence-driven reasoning, dynamically assessing the sufficiency of retrieved context and iteratively refining answers through targeted interactions with DMAP. Extensive experiments on MMDocQA benchmarks demonstrate that DMAP yields document-specific structural representations aligned with human interpretive patterns, substantially enhancing retrieval precision, reasoning consistency, and multimodal comprehension over conventional RAG-based approaches. Code is available at https://github.com/Forlorin/DMAP
Frozen LVLMs for Micro-Video Recommendation: A Systematic Study of Feature Extraction and Fusion
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:Frozen Large Video Language Models (LVLMs) are increasingly employed in micro-video recommendation due to their strong multimodal understanding. However, their integration lacks systematic empirical evaluation: practitioners typically deploy LVLMs as fixed black-box feature extractors without systematically comparing alternative representation strategies. To address this gap, we present the first systematic empirical study along two key design dimensions: (i) integration strategies with ID embeddings, specifically replacement versus fusion, and (ii) feature extraction paradigms, comparing LVLM-generated captions with intermediate decoder hidden states. Extensive experiments on representative LVLMs reveal three key principles: (1) intermediate hidden states consistently outperform caption-based representations, as natural-language summarization inevitably discards fine-grained visual semantics crucial for recommendation; (2) ID embeddings capture irreplaceable collaborative signals, rendering fusion strictly superior to replacement; and (3) the effectiveness of intermediate decoder features varies significantly across layers. Guided by these insights, we propose the Dual Feature Fusion (DFF) Framework, a lightweight and plug-and-play approach that adaptively fuses multi-layer representations from frozen LVLMs with item ID embeddings. DFF achieves state-of-the-art performance on two real-world micro-video recommendation benchmarks, consistently outperforming strong baselines and providing a principled approach to integrating off-the-shelf large vision-language models into micro-video recommender systems.
Jointly Conditioned Diffusion Model for Multi-View Pose-Guided Person Image Synthesis
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Pose-guided human image generation is limited by incomplete textures from single reference views and the absence of explicit cross-view interaction. We present jointly conditioned diffusion model (JCDM), a jointly conditioned diffusion framework that exploits multi-view priors. The appearance prior module (APM) infers a holistic identity preserving prior from incomplete references, and the joint conditional injection (JCI) mechanism fuses multi-view cues and injects shared conditioning into the denoising backbone to align identity, color, and texture across poses. JCDM supports a variable number of reference views and integrates with standard diffusion backbones with minimal and targeted architectural modifications. Experiments demonstrate state of the art fidelity and cross-view consistency.
LeCoT: revisiting network architecture for two-view correspondence pruning
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Two-view correspondence pruning aims to accurately remove incorrect correspondences (outliers) from initial ones and is widely applied to various computer vision tasks. Current popular strategies adopt multilayer perceptron (MLP) as the backbone, supplemented by additional modules to enhance the network ability to handle context information, which is a known limitation of MLPs. In contrast, we introduce a novel perspective for capturing correspondence context information without extra design modules. To this end, we design a two-view correspondence pruning network called LeCoT, which can naturally leverage global context information at different stages. Specifically, the core design of LeCoT is the Spatial-Channel Fusion Transformer block, a newly proposed component that efficiently utilizes both spatial and channel global context information among sparse correspondences. In addition, we integrate the proposed prediction block that utilizes correspondence features from intermediate stages to generate a probability set, which acts as guiding information for subsequent learning phases, allowing the network to more effectively capture robust global context information. Notably, this prediction block progressively refines the probability set, thereby mitigating the issue of information loss that is common in the traditional one. Extensive experiments prove that the proposed LeCoT outperforms state-of-the-art methods in correspondence pruning, relative pose estimation, homography estimation, visual localization, and $3$D~reconstruction tasks. The code is provided in https://github.com/Dailuanyuan2024/LeCoT-Revisiting-Network-Architecture-for-Two-View-Correspondence-Pruning.
IMAGGarment-1: Fine-Grained Garment Generation for Controllable Fashion Design
Apr 17, 2025



Abstract:This paper presents IMAGGarment-1, a fine-grained garment generation (FGG) framework that enables high-fidelity garment synthesis with precise control over silhouette, color, and logo placement. Unlike existing methods that are limited to single-condition inputs, IMAGGarment-1 addresses the challenges of multi-conditional controllability in personalized fashion design and digital apparel applications. Specifically, IMAGGarment-1 employs a two-stage training strategy to separately model global appearance and local details, while enabling unified and controllable generation through end-to-end inference. In the first stage, we propose a global appearance model that jointly encodes silhouette and color using a mixed attention module and a color adapter. In the second stage, we present a local enhancement model with an adaptive appearance-aware module to inject user-defined logos and spatial constraints, enabling accurate placement and visual consistency. To support this task, we release GarmentBench, a large-scale dataset comprising over 180K garment samples paired with multi-level design conditions, including sketches, color references, logo placements, and textual prompts. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms existing baselines, achieving superior structural stability, color fidelity, and local controllability performance. The code and model are available at https://github.com/muzishen/IMAGGarment-1.
Precision Profile Pollution Attack on Sequential Recommenders via Influence Function
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Sequential recommendation approaches have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in modeling user preferences. Nevertheless, they are susceptible to profile pollution attacks (PPA), wherein items are introduced into a user's interaction history deliberately to influence the recommendation list. Since retraining the model for each polluted item is time-consuming, recent PPAs estimate item influence based on gradient directions to identify the most effective attack candidates. However, the actual item representations diverge significantly from the gradients, resulting in disparate outcomes.To tackle this challenge, we introduce an INFluence Function-based Attack approach INFAttack that offers a more accurate estimation of the influence of polluting items. Specifically, we calculate the modifications to the original model using the influence function when generating polluted sequences by introducing specific items. Subsequently, we choose the sequence that has been most significantly influenced to substitute the original sequence, thus promoting the target item. Comprehensive experiments conducted on five real-world datasets illustrate that INFAttack surpasses all baseline methods and consistently delivers stable attack performance for both popular and unpopular items.
Negative Sampling in Recommendation: A Survey and Future Directions
Sep 11, 2024
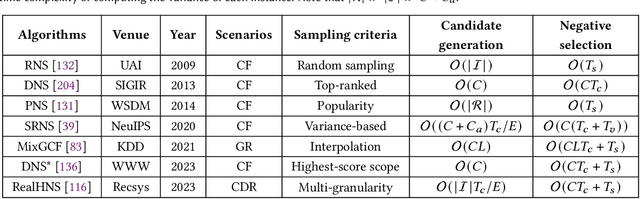

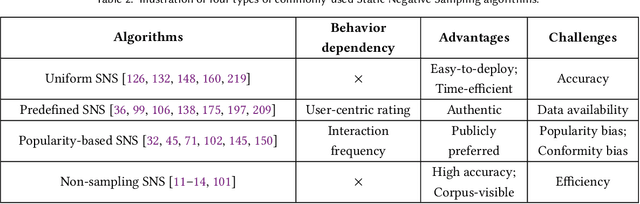
Abstract:Recommender systems aim to capture users' personalized preferences from the cast amount of user behaviors, making them pivotal in the era of information explosion. However, the presence of the dynamic preference, the "information cocoons", and the inherent feedback loops in recommendation make users interact with a limited number of items. Conventional recommendation algorithms typically focus on the positive historical behaviors, while neglecting the essential role of negative feedback in user interest understanding. As a promising but easy-to-ignored area, negative sampling is proficients in revealing the genuine negative aspect inherent in user behaviors, emerging as an inescapable procedure in recommendation. In this survey, we first discuss the role of negative sampling in recommendation and thoroughly analyze challenges that consistently impede its progress. Then, we conduct an extensive literature review on the existing negative sampling strategies in recommendation and classify them into five categories with their discrepant techniques. Finally, we detail the insights of the tailored negative sampling strategies in diverse recommendation scenarios and outline an overview of the prospective research directions toward which the community may engage and benefit.
IMAGDressing-v1: Customizable Virtual Dressing
Jul 17, 2024



Abstract:Latest advances have achieved realistic virtual try-on (VTON) through localized garment inpainting using latent diffusion models, significantly enhancing consumers' online shopping experience. However, existing VTON technologies neglect the need for merchants to showcase garments comprehensively, including flexible control over garments, optional faces, poses, and scenes. To address this issue, we define a virtual dressing (VD) task focused on generating freely editable human images with fixed garments and optional conditions. Meanwhile, we design a comprehensive affinity metric index (CAMI) to evaluate the consistency between generated images and reference garments. Then, we propose IMAGDressing-v1, which incorporates a garment UNet that captures semantic features from CLIP and texture features from VAE. We present a hybrid attention module, including a frozen self-attention and a trainable cross-attention, to integrate garment features from the garment UNet into a frozen denoising UNet, ensuring users can control different scenes through text. IMAGDressing-v1 can be combined with other extension plugins, such as ControlNet and IP-Adapter, to enhance the diversity and controllability of generated images. Furthermore, to address the lack of data, we release the interactive garment pairing (IGPair) dataset, containing over 300,000 pairs of clothing and dressed images, and establish a standard pipeline for data assembly. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our IMAGDressing-v1 achieves state-of-the-art human image synthesis performance under various controlled conditions. The code and model will be available at https://github.com/muzishen/IMAGDressing.
MGNet: Learning Correspondences via Multiple Graphs
Jan 10, 2024Abstract:Learning correspondences aims to find correct correspondences (inliers) from the initial correspondence set with an uneven correspondence distribution and a low inlier rate, which can be regarded as graph data. Recent advances usually use graph neural networks (GNNs) to build a single type of graph or simply stack local graphs into the global one to complete the task. But they ignore the complementary relationship between different types of graphs, which can effectively capture potential relationships among sparse correspondences. To address this problem, we propose MGNet to effectively combine multiple complementary graphs. To obtain information integrating implicit and explicit local graphs, we construct local graphs from implicit and explicit aspects and combine them effectively, which is used to build a global graph. Moreover, we propose Graph~Soft~Degree~Attention (GSDA) to make full use of all sparse correspondence information at once in the global graph, which can capture and amplify discriminative features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MGNet outperforms state-of-the-art methods in different visual tasks. The code is provided in https://github.com/DAILUANYUAN/MGNet-2024AAAI.
MultiCBR: Multi-view Contrastive Learning for Bundle Recommendation
Nov 28, 2023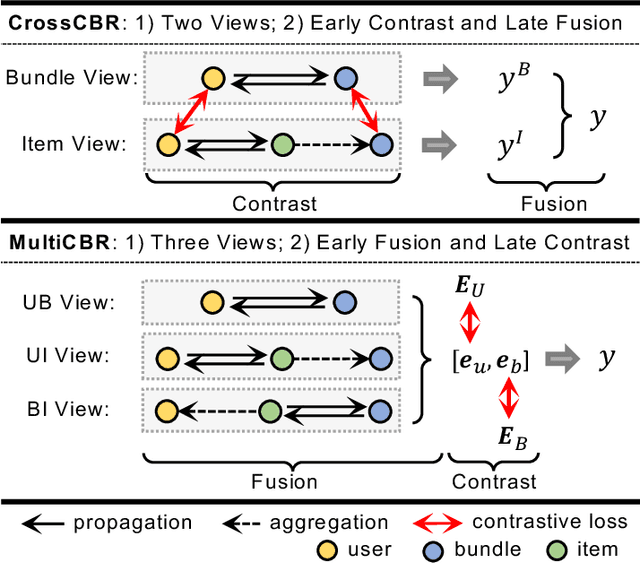
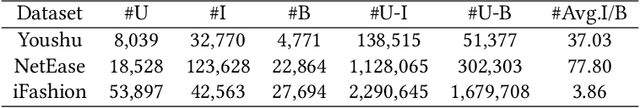
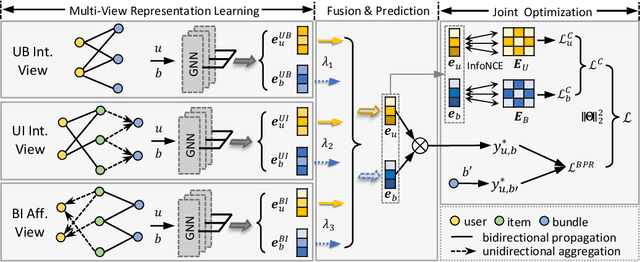
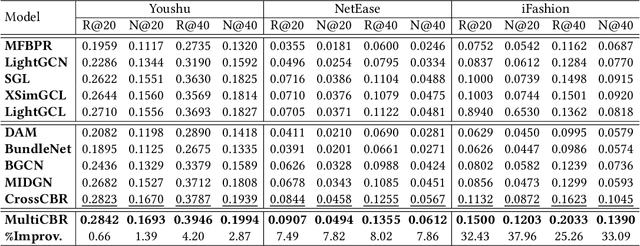
Abstract:Bundle recommendation seeks to recommend a bundle of related items to users to improve both user experience and the profits of platform. Existing bundle recommendation models have progressed from capturing only user-bundle interactions to the modeling of multiple relations among users, bundles and items. CrossCBR, in particular, incorporates cross-view contrastive learning into a two-view preference learning framework, significantly improving SOTA performance. It does, however, have two limitations: 1) the two-view formulation does not fully exploit all the heterogeneous relations among users, bundles and items; and 2) the "early contrast and late fusion" framework is less effective in capturing user preference and difficult to generalize to multiple views. In this paper, we present MultiCBR, a novel Multi-view Contrastive learning framework for Bundle Recommendation. First, we devise a multi-view representation learning framework capable of capturing all the user-bundle, user-item and bundle-item relations, especially better utilizing the bundle-item affiliations to enhance sparse bundles' representations. Second, we innovatively adopt an "early fusion and late contrast" design that first fuses the multi-view representations before performing self-supervised contrastive learning. In comparison to existing approaches, our framework reverses the order of fusion and contrast, introducing the following advantages: 1)our framework is capable of modeling both cross-view and ego-view preferences, allowing us to achieve enhanced user preference modeling; and 2) instead of requiring quadratic number of cross-view contrastive losses, we only require two self-supervised contrastive losses, resulting in minimal extra costs. Experimental results on three public datasets indicate that our method outperforms SOTA methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge