Yingying Chen
National Lab of Pattern Recognition, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences
AnomalyMoE: Towards a Language-free Generalist Model for Unified Visual Anomaly Detection
Aug 08, 2025Abstract:Anomaly detection is a critical task across numerous domains and modalities, yet existing methods are often highly specialized, limiting their generalizability. These specialized models, tailored for specific anomaly types like textural defects or logical errors, typically exhibit limited performance when deployed outside their designated contexts. To overcome this limitation, we propose AnomalyMoE, a novel and universal anomaly detection framework based on a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture. Our key insight is to decompose the complex anomaly detection problem into three distinct semantic hierarchies: local structural anomalies, component-level semantic anomalies, and global logical anomalies. AnomalyMoE correspondingly employs three dedicated expert networks at the patch, component, and global levels, and is specialized in reconstructing features and identifying deviations at its designated semantic level. This hierarchical design allows a single model to concurrently understand and detect a wide spectrum of anomalies. Furthermore, we introduce an Expert Information Repulsion (EIR) module to promote expert diversity and an Expert Selection Balancing (ESB) module to ensure the comprehensive utilization of all experts. Experiments on 8 challenging datasets spanning industrial imaging, 3D point clouds, medical imaging, video surveillance, and logical anomaly detection demonstrate that AnomalyMoE establishes new state-of-the-art performance, significantly outperforming specialized methods in their respective domains.
MUG: Pseudo Labeling Augmented Audio-Visual Mamba Network for Audio-Visual Video Parsing
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:The weakly-supervised audio-visual video parsing (AVVP) aims to predict all modality-specific events and locate their temporal boundaries. Despite significant progress, due to the limitations of the weakly-supervised and the deficiencies of the model architecture, existing methods are lacking in simultaneously improving both the segment-level prediction and the event-level prediction. In this work, we propose a audio-visual Mamba network with pseudo labeling aUGmentation (MUG) for emphasising the uniqueness of each segment and excluding the noise interference from the alternate modalities. Specifically, we annotate some of the pseudo-labels based on previous work. Using unimodal pseudo-labels, we perform cross-modal random combinations to generate new data, which can enhance the model's ability to parse various segment-level event combinations. For feature processing and interaction, we employ a audio-visual mamba network. The AV-Mamba enhances the ability to perceive different segments and excludes additional modal noise while sharing similar modal information. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that MUG improves state-of-the-art results on LLP dataset in all metrics (e.g,, gains of 2.1% and 1.2% in terms of visual Segment-level and audio Segment-level metrics). Our code is available at https://github.com/WangLY136/MUG.
MathPhys-Guided Coarse-to-Fine Anomaly Synthesis with SQE-Driven Bi-Level Optimization for Anomaly Detection
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Anomaly detection is a crucial task in computer vision, yet collecting real-world defect images is inherently difficult due to the rarity and unpredictability of anomalies. Consequently, researchers have turned to synthetic methods for training data augmentation. However, existing synthetic strategies (e.g., naive cut-and-paste or inpainting) overlook the underlying physical causes of defects, leading to inconsistent, low-fidelity anomalies that hamper model generalization to real-world complexities. In this thesis, we introduced a novel pipeline that generates synthetic anomalies through Math-Physics model guidance, refines them via a Coarse-to-Fine approach and employs a bi-level optimization strategy with a Synthesis Quality Estimator(SQE). By incorporating physical modeling of cracks, corrosion, and deformation, our method produces realistic defect masks, which are subsequently enhanced in two phases. The first stage (npcF) enforces a PDE-based consistency to achieve a globally coherent anomaly structure, while the second stage (npcF++) further improves local fidelity using wavelet transforms and boundary synergy blocks. Additionally, we leverage SQE-driven weighting, ensuring that high-quality synthetic samples receive greater emphasis during training. To validate our approach, we conducted comprehensive experiments on three widely adopted industrial anomaly detection benchmarks: MVTec AD, VisA, and BTAD. Across these datasets, the proposed pipeline achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) results in both image-AUROC and pixel-AUROC, confirming the effectiveness of our MaPhC2F and BiSQAD.
FLARE: A Framework for Stellar Flare Forecasting using Stellar Physical Properties and Historical Records
Feb 25, 2025
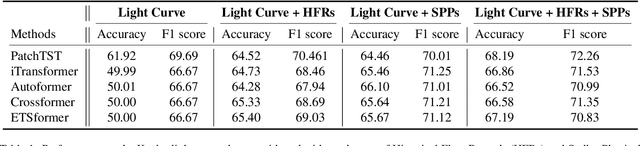
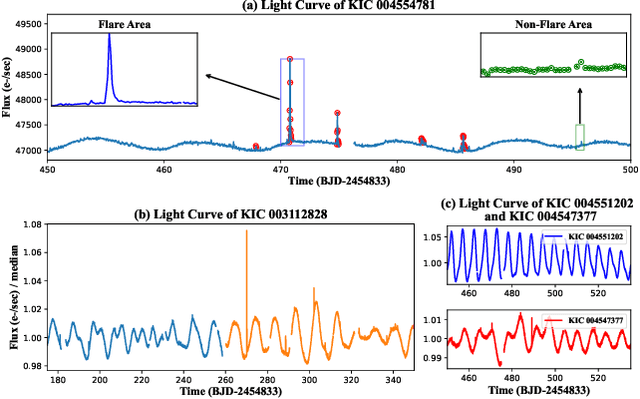
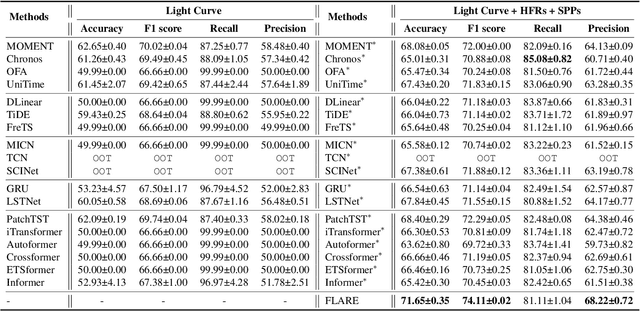
Abstract:Stellar flare events are critical observational samples for astronomical research; however, recorded flare events remain limited. Stellar flare forecasting can provide additional flare event samples to support research efforts. Despite this potential, no specialized models for stellar flare forecasting have been proposed to date. In this paper, we present extensive experimental evidence demonstrating that both stellar physical properties and historical flare records are valuable inputs for flare forecasting tasks. We then introduce FLARE (Forecasting Light-curve-based Astronomical Records via features Ensemble), the first-of-its-kind large model specifically designed for stellar flare forecasting. FLARE integrates stellar physical properties and historical flare records through a novel Soft Prompt Module and Residual Record Fusion Module. Our experiments on the publicly available Kepler light curve dataset demonstrate that FLARE achieves superior performance compared to other methods across all evaluation metrics. Finally, we validate the forecast capability of our model through a comprehensive case study.
FiLo++: Zero-/Few-Shot Anomaly Detection by Fused Fine-Grained Descriptions and Deformable Localization
Jan 17, 2025



Abstract:Anomaly detection methods typically require extensive normal samples from the target class for training, limiting their applicability in scenarios that require rapid adaptation, such as cold start. Zero-shot and few-shot anomaly detection do not require labeled samples from the target class in advance, making them a promising research direction. Existing zero-shot and few-shot approaches often leverage powerful multimodal models to detect and localize anomalies by comparing image-text similarity. However, their handcrafted generic descriptions fail to capture the diverse range of anomalies that may emerge in different objects, and simple patch-level image-text matching often struggles to localize anomalous regions of varying shapes and sizes. To address these issues, this paper proposes the FiLo++ method, which consists of two key components. The first component, Fused Fine-Grained Descriptions (FusDes), utilizes large language models to generate anomaly descriptions for each object category, combines both fixed and learnable prompt templates and applies a runtime prompt filtering method, producing more accurate and task-specific textual descriptions. The second component, Deformable Localization (DefLoc), integrates the vision foundation model Grounding DINO with position-enhanced text descriptions and a Multi-scale Deformable Cross-modal Interaction (MDCI) module, enabling accurate localization of anomalies with various shapes and sizes. In addition, we design a position-enhanced patch matching approach to improve few-shot anomaly detection performance. Experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate that FiLo++ achieves significant performance improvements compared with existing methods. Code will be available at https://github.com/CASIA-IVA-Lab/FiLo.
LINK: Adaptive Modality Interaction for Audio-Visual Video Parsing
Dec 30, 2024



Abstract:Audio-visual video parsing focuses on classifying videos through weak labels while identifying events as either visible, audible, or both, alongside their respective temporal boundaries. Many methods ignore that different modalities often lack alignment, thereby introducing extra noise during modal interaction. In this work, we introduce a Learning Interaction method for Non-aligned Knowledge (LINK), designed to equilibrate the contributions of distinct modalities by dynamically adjusting their input during event prediction. Additionally, we leverage the semantic information of pseudo-labels as a priori knowledge to mitigate noise from other modalities. Our experimental findings demonstrate that our model outperforms existing methods on the LLP dataset.
UniVAD: A Training-free Unified Model for Few-shot Visual Anomaly Detection
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Visual Anomaly Detection (VAD) aims to identify abnormal samples in images that deviate from normal patterns, covering multiple domains, including industrial, logical, and medical fields. Due to the domain gaps between these fields, existing VAD methods are typically tailored to each domain, with specialized detection techniques and model architectures that are difficult to generalize across different domains. Moreover, even within the same domain, current VAD approaches often follow a "one-category-one-model" paradigm, requiring large amounts of normal samples to train class-specific models, resulting in poor generalizability and hindering unified evaluation across domains. To address this issue, we propose a generalized few-shot VAD method, UniVAD, capable of detecting anomalies across various domains, such as industrial, logical, and medical anomalies, with a training-free unified model. UniVAD only needs few normal samples as references during testing to detect anomalies in previously unseen objects, without training on the specific domain. Specifically, UniVAD employs a Contextual Component Clustering ($C^3$) module based on clustering and vision foundation models to segment components within the image accurately, and leverages Component-Aware Patch Matching (CAPM) and Graph-Enhanced Component Modeling (GECM) modules to detect anomalies at different semantic levels, which are aggregated to produce the final detection result. We conduct experiments on nine datasets spanning industrial, logical, and medical fields, and the results demonstrate that UniVAD achieves state-of-the-art performance in few-shot anomaly detection tasks across multiple domains, outperforming domain-specific anomaly detection models. The code will be made publicly available.
Precision Profile Pollution Attack on Sequential Recommenders via Influence Function
Dec 02, 2024



Abstract:Sequential recommendation approaches have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in modeling user preferences. Nevertheless, they are susceptible to profile pollution attacks (PPA), wherein items are introduced into a user's interaction history deliberately to influence the recommendation list. Since retraining the model for each polluted item is time-consuming, recent PPAs estimate item influence based on gradient directions to identify the most effective attack candidates. However, the actual item representations diverge significantly from the gradients, resulting in disparate outcomes.To tackle this challenge, we introduce an INFluence Function-based Attack approach INFAttack that offers a more accurate estimation of the influence of polluting items. Specifically, we calculate the modifications to the original model using the influence function when generating polluted sequences by introducing specific items. Subsequently, we choose the sequence that has been most significantly influenced to substitute the original sequence, thus promoting the target item. Comprehensive experiments conducted on five real-world datasets illustrate that INFAttack surpasses all baseline methods and consistently delivers stable attack performance for both popular and unpopular items.
Friend or Foe? Harnessing Controllable Overfitting for Anomaly Detection
Nov 30, 2024



Abstract:Overfitting has long been stigmatized as detrimental to model performance, especially in the context of anomaly detection. Our work challenges this conventional view by introducing a paradigm shift, recasting overfitting as a controllable and strategic mechanism for enhancing model discrimination capabilities. In this paper, we present Controllable Overfitting-based Anomaly Detection (COAD), a novel framework designed to leverage overfitting for optimized anomaly detection. We propose the Aberrance Retention Quotient (ARQ), a novel metric that systematically quantifies the extent of overfitting, enabling the identification of an optimal "golden overfitting interval." Within this interval, overfitting is leveraged to significantly amplify the model's sensitivity to anomalous patterns, while preserving generalization to normal samples. Additionally, we present the Relative Anomaly Distribution Index (RADI), an innovative metric designed to complement AUROC pixel by providing a more versatile and theoretically robust framework for assessing model performance. RADI leverages ARQ to track and evaluate how overfitting impacts anomaly detection, offering an integrated approach to understanding the relationship between overfitting dynamics and model efficacy. Our theoretical work also rigorously validates the use of Gaussian noise in pseudo anomaly synthesis, providing the foundation for its broader applicability across diverse domains. Empirical evaluations demonstrate that our controllable overfitting method not only achieves State of the Art (SOTA) performance in both one-class and multi-class anomaly detection tasks but also redefines overfitting from a modeling challenge into a powerful tool for optimizing anomaly detection.
FiLo: Zero-Shot Anomaly Detection by Fine-Grained Description and High-Quality Localization
Apr 21, 2024Abstract:Zero-shot anomaly detection (ZSAD) methods entail detecting anomalies directly without access to any known normal or abnormal samples within the target item categories. Existing approaches typically rely on the robust generalization capabilities of multimodal pretrained models, computing similarities between manually crafted textual features representing "normal" or "abnormal" semantics and image features to detect anomalies and localize anomalous patches. However, the generic descriptions of "abnormal" often fail to precisely match diverse types of anomalies across different object categories. Additionally, computing feature similarities for single patches struggles to pinpoint specific locations of anomalies with various sizes and scales. To address these issues, we propose a novel ZSAD method called FiLo, comprising two components: adaptively learned Fine-Grained Description (FG-Des) and position-enhanced High-Quality Localization (HQ-Loc). FG-Des introduces fine-grained anomaly descriptions for each category using Large Language Models (LLMs) and employs adaptively learned textual templates to enhance the accuracy and interpretability of anomaly detection. HQ-Loc, utilizing Grounding DINO for preliminary localization, position-enhanced text prompts, and Multi-scale Multi-shape Cross-modal Interaction (MMCI) module, facilitates more accurate localization of anomalies of different sizes and shapes. Experimental results on datasets like MVTec and VisA demonstrate that FiLo significantly improves the performance of ZSAD in both detection and localization, achieving state-of-the-art performance with an image-level AUC of 83.9% and a pixel-level AUC of 95.9% on the VisA dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge